The last trimester of pregnancy is a constant wait, joyful for some, anxious for others, but mostly both. It’s hard to walk and breathe, you constantly suffer from heartburn, and your legs hurt, but at the same time you clearly feel that inside there is a little man living his own life.
For me, the third trimester was the most exciting of my entire pregnancy. At the 32nd week, it became clear that the baby had not turned over, although this was clear even without an ultrasound - the head protruded so clearly from under my ribs that it was impossible to make a mistake. Breech presentation is not the most terrible diagnosis, but it is also fraught with various complications. Weeks dragged on one after another, but nothing happened, although they continued to assure me that the baby could turn over at any moment, even with the onset of contractions.
How do you know if you have a breech presentation?
Breech presentation is diagnosed from the 30th week. The obstetrician can determine the position of the fetal head from the outside, with his hands. After 34 weeks, the baby takes the position in which he is most likely to approach childbirth. Presentation can be confirmed during examination on the chair. However, this should only be done in an emergency. In the later stages, examination is dangerous. An ultrasound will also help determine the presence of a breech fetus.
Anesthesia. Drugs and procedure
Before the operation, the pregnant woman is given pain relief. When choosing an anesthesia method, they take into account how the caesarean section will take place, the pros and cons for the patient and her child.
The operation is carried out under:
- general anesthesia;
- spinal or regional anesthesia;
- epidural anesthesia.
General anesthesia is used for emergency surgery, the need to remove the uterus, and contraindications for epidural or spinal anesthesia.
Drugs used:
- Sodium thiopental;
- Ketamine;
- Sodium hydroxyutyral;
- Relanium;
- Sedunin
A catheter is inserted into the pregnant woman's vein, through which medication is administered, which puts her into a deep medicated sleep. The pregnant woman is unconscious and has no sensation at all. A tube is inserted into the trachea to supply oxygen and provide artificial ventilation.
The advantages of this anesthesia:
- the expectant mother falls into deep sleep instantly;
- there is no risk of blood pressure drop;
- the muscles are completely relaxed;
- with a long procedure, the exposure time of the medication can be extended;
- the depth of drug supply is controlled;
- The pregnant woman does not follow the caesarean process and does not feel any pain.
Flaws:
- general anesthesia affects the fetus;
- the process of withdrawal from the effects of anesthesia is accompanied by unpleasant sensations: severe weakness in the body, headaches, nausea;
- Due to the insertion of a tracheal tube, a sore, sore throat and cough may occur.
Regional (spinal) or local anesthesia is carried out by injecting into the lumbar region of the spine and administering medication, while only the lower part is anesthetized, the pregnant woman remains fully conscious. This method of pain relief is used during planned surgery.
The process goes as follows:
- the pregnant woman sits down, rests her hands on her knees, arches her back, or lies on her side, tucking her legs bent at the knees towards her stomach, providing maximum access to the spine;
- the doctor gives an anesthetic injection to lose sensitivity in the back muscles;
- An anesthetic is injected into the cerebrospinal fluid with a long needle;
- After the drug enters, the needle is removed.
Pros:
- spinal anesthesia does not affect the child;
- acts almost instantly;
- complete relaxation of the abdominal muscles;
- a small portion of the anesthetic enters the body;
- the woman remains conscious, there are no breathing problems;
- The patient sees the birth of a child.
Minuses:
- a sharp drop in blood pressure is possible;
- the effect of anesthesia is limited to 2 hours, without the possibility of extension;
- after using anesthesia, neurological problems may appear;
The most commonly used in modern obstetrics is epidural anesthesia. It is performed not only during caesarean section, but also to relieve pain during labor.
To carry out anesthesia, the woman provides access to the spine. The injection is placed in the epidural space.
Together with the needle, a catheter is inserted into the hole, through which the anesthetic is supplied. The medicine takes effect within 20 minutes.
Advantages:
- the pregnant woman remains conscious;
- blood pressure levels decrease slowly;
- the effect of anesthesia can be prolonged;
Flaws:
- it is possible that the drug will act on only one side of the body;
- a good anesthesiologist is needed to carry out the procedure;
- when a large amount of the drug is administered, intoxication occurs;
- drugs for epidural anesthesia affect the child;
- The medicine begins to act after 15-20 minutes.
For epidural and spinal anesthesia use:
- Trimecaine - has an effect after 15 minutes, but is limited to 60 minutes;
- Mepivacaine – active for 1.5 hours;
- Dikain – onset time of exposure is 20 minutes, anesthesia time is up to 3 hours;
- Bupivacaine is the most popular drug, begins to work after 10 minutes, lasts 5 hours.
Contraindications to the use of epidural and regional anesthesia:
- spinal injuries;
- low blood pressure;
- inflammation at the injection site;
- intrauterine fetal hypoxia;
- uterine bleeding due to placental abruption.
What methods exist to “turn” a baby head down?
Birthing with a breech presentation is quite difficult for both mother and baby. There are different techniques that can turn a child: special gymnastics, swimming pool exercises involving “somersaults”. There is also an external rotation according to Arkhangelsky - a set of external techniques in which the fetus can return to the correct position. This method is quite risky and must be performed by highly qualified specialists. At one time, turning along Arkhangelskoye was even prohibited. The method has many contraindications.
Correcting the situation before birth
Diagnosing breech presentation is not a final verdict. At the stage of 32-34 weeks, you can perform special gymnastics that can provoke the fetus to turn over. This is a pelvic tilt performed on an empty stomach, specific exercises performed in a knee-elbow position. In the latter case, the pelvis should be above the level of the head. It is recommended to stay in this position for no more than 20 minutes several times a day.
It is also possible to use gravity. Swimming in the pool helps quite well. Here the pressure decreases, making it much easier for the fetus to turn over on its own.
The effectiveness of the described methods when used regularly varies between 65 – 75%. However, we must not forget that there are contraindications for the above-mentioned gymnastics:
- narrow pelvis;
- risk of premature birth;
- fetal anomaly;
- unsuccessful pregnancy ending in miscarriage in the past;
- too much or too little amniotic fluid;
- pathology of uterine development;
- multiple births;
- placenta previa;
- gestosis;
- a number of concomitant diseases in which such loads are contraindicated.
When can you decide how to give birth?
The decision to manage labor is made at 38 weeks. The choice of tactics is influenced by several factors: the type of presentation, the position of the fetal head (for example, the “bent head” option is preferable), the weight of the fetus, the presence of hypoxia. The woman’s health and the structure of her pelvis are important. Usually, with a breech presentation, a woman is admitted to the maternity hospital at 38 weeks, where she is thoroughly examined. After which a decision is made on the tactics of childbirth. If you are planning a contract birth, you can discuss with your doctor whether hospitalization is really necessary for you.
Useful tips for future parents
No matter how the circumstances develop during embryonic development, a woman and her loved ones should not succumb to unnecessary panic. Increased anxiety and constant discussions of the current situation can only aggravate the situation. A pregnant woman becomes susceptible to any changes, even positive ones.
Having given your consent to surgical delivery, you should take into account all possible risks, since this is still an operation with all the ensuing consequences. In this case, anesthesia cannot be avoided. Coming out of anesthesia always causes stress to the body. Close people should support the woman in labor before and after surgery. It is extremely important to create an atmosphere of mutual understanding and harmony so that a woman can relax and feel protected.
No matter how your pregnancy progresses, the main thing to remember is that you need to trust your doctor, strictly follow all his instructions, and do not hesitate to ask disturbing questions. A qualified specialist will always come to the rescue, helping the pregnant woman to remain calm and avoid complications.
Postoperative sutures will not heal as quickly as we would like. During this period, you should not lift weights or overeat, and the baby should be fed, supported by additional devices or with the help of loved ones.
Women who have experienced a caesarean section in their lives are afraid to plan a new pregnancy. Of course, there are a number of objective reasons for refusal, but you should trust an experienced doctor who will assess the condition of the woman’s body and draw a final conclusion.
After a cesarean section, stitches remain on the walls of the uterus and abdominal cavity, which can diverge during a second pregnancy. If a woman is prone to obesity and also has a number of health problems, for example, diabetes, hypertension, intestinal diseases, it is advisable to exclude subsequent conception. Most likely, after a cesarean section, the doctor will advise such women to refuse a new pregnancy.
An hour before the operation, premedication is given - an injection that reduces anxiety and facilitates the administration of anesthesia. In private clinics, the caesarean section procedure is treated with special attention. In the operating room, relaxation music is often played, and if necessary, the medical staff places additional bolsters on the woman in labor to facilitate her position on the operating table.
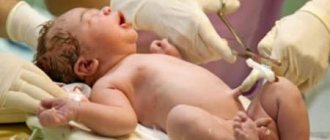
If everything goes correctly, the operation takes 40-50 minutes. The postoperative suture is made “cosmetic”, capable of dissolving after six months. The baby comes out of the uterus 5-7 minutes from the start of the operation, and the rest of the time the doctors care for the young mother.
All medications that are prescribed to a woman after surgery are compatible with lactation, so there is nothing left to do but follow the doctor’s recommendations without unnecessary worries.
| C-section |
| Childbirth via caesarean section |
| Fast recovery after caesarean section |
We also recommend:
— Questions about caesarean section or let’s talk heart to heart
— Indications for caesarean section: a verdict without appeal or just a recommendation?
How does natural childbirth work?
As you know, with a cephalic presentation, the head, as it were, “expands” the path for the birth of the entire child. During a breech birth, the baby's pelvis is born first. And then, during the birth of the body and head, the umbilical cord is compressed by the head. Because of this feature, it is necessary for the child to be born quite quickly, but alas, this is not always possible, and for the baby, quickly passing through the pelvic area is fraught with complications. In addition, there are also nuances in the form of raising the arms, straightening the head, and so on. However, it is possible to give birth on your own with a breech presentation. It is not considered an absolute indication for cesarean section.
Natural childbirth with a breech presentation should proceed without problems at every stage. Any anomaly automatically means that the birth will end with a caesarean section. Acute fetal hypoxia, which began during childbirth, requires emergency cesarean section.
Why me? Possible causes of presentation
This question worries every mother whose baby is settled in her stomach “not as it should be.” There are several possible reasons.
- Pathological hypertonicity of the lower segment of the uterus and decreased tone of its upper sections. The fetal head is pushed away from the entrance to the pelvis and takes a position in the upper part of the uterus. This happens after inflammatory processes, repeated curettage, multiple pregnancies, complicated childbirth, and a scar on the uterus after a cesarean section.
- Features of fetal behavior and development, for example, increased mobility due to polyhydramnios, small head size, prematurity.
- Structural features and anomalies of the uterus and pelvis: bicornuate, saddle-shaped uterus, the presence of septa or fibroids in the uterus, anatomical narrowing or abnormal shape of the pelvis.
- Limitation of fetal mobility: entanglement in the umbilical cord, oligohydramnios, etc.
Usually the position of the baby in the uterus is fixed by the 32nd–34th week of pregnancy. All these reasons only increase the risk that by this time the child will remain in the wrong position, but they cannot be considered a “final verdict.”
When is the best time to have a caesarean section?
The operation must be performed under the following conditions: the most unfortunate variant of breech presentation is the foot one, the fetus weighs more than 3600 g, the head is straightened, the fetus suffers, and the woman feels unwell. If you have these signs, you should agree to surgery without hesitation.
Caesarean section for breech presentation is scheduled, provided that there were no problems during pregnancy. If the condition of the mother and baby does not cause concern, hospitalization before childbirth is not necessary. You can come to the maternity hospital already with contractions.
Diagnostics
Only a doctor can determine that the fetus is positioned with its buttocks or legs down. The following methods help diagnose TP:
- Obstetric examination (external). An incorrect position is judged by the definition of a large soft part closer to the pelvis, while the head is felt in the uterus (round, mobile, quite hard). A heartbeat can be heard in the area of the expectant mother's navel (sometimes above it).
- Vaginal examination. If the baby is positioned with the buttocks down, then the soft part is determined below. It is quite voluminous. In the foot/mixed position, the bottom of the foot can be distinguished.
- Ultrasound. The diagnostic method allows not only to accurately see the position chosen by the baby, but also to assess the degree of extension of the head. This indicator must be taken into account when choosing a method of delivery, because excessive extension can lead to a number of injuries when the baby passes through the birth canal.
If the pelvic position is identified before the 28th week, then it does not cause concern: the baby can turn closer to the date of birth. All doctors do is monitor the fetus over time. If the revolution does not happen, then from the 30th week the doctor determines tactics aimed at changing the situation. Most often, special gymnastics are prescribed to correct the position of the fetus. It can be done only according to indications and after consultation with a gynecologist. Gymnastics is really effective, but it has a number of contraindications. For example, it cannot be done if the fetus has anomalies, the mother has a narrow pelvis, or abnormalities in the development of the uterus are recorded. Also, gymnastics can be dangerous with placental presentation and multiple births.
If the study shows that the position of the fetus has not changed by the 32nd week, then the doctor begins to discuss birth options with the patient. The final decision is made based on monitoring the pregnant woman, test results, medical history and risk assessment. Most often, a planned CS is performed.
Indications for a planned CS
Modern methods of monitoring pregnancy make it possible to plan delivery by CS in advance in the following cases:
- narrow pelvis, that is, a reduced size of at least one of its dimensions by 1.5-2 cm or more;
- Incorrect location of the placenta when it blocks the baby’s exit path (its presentation);
- fibroids in the cervical area, which can also interfere with passage through the birth canal;
- other neoplasms in the pelvis that will become obstacles to the birth of the baby;
- a scar on an organ formed as a result of operations or injuries;
- diseases of the heart, kidneys, dilation of the veins of the cervix, vagina, which during natural childbirth pose a danger to the life of the mother;
- high myopia (myopia), threat of retinal detachment;
- difficult pregnancy, in which natural childbirth can provoke preeclampsia, eclampsia;
- damage to the pelvis and spine, which can cause a woman’s bones to separate during normal delivery;
- incorrect position of the fetus when it is with its head up or across the uterus;
- multiple pregnancy, including those accompanied by breech presentation;
- genital herpes, transmitted to the baby as it passes through the birth canal;
- entanglement of the fetus with the umbilical cord;
- The baby's head is too large compared to the size of the mother's pelvis.
How many operations can you do?
The answer to this question may surprise you. But a woman can have a caesarean section as many times as needed.
Each subsequent operation is carried out on the previous scar. After removing the baby from the uterus, surgeons excise the old scar and apply new stitches. For this reason, each subsequent scar is slightly thinner than the previous one, which means that each subsequent pregnancy is a riskier business than the previous one.
In the USSR, it was not recommended to become pregnant again after a caesarean section. Doctors dissuaded women from such a decision not because they did not know how to perform repeated operations on an old scar, but because the technology and suture material were different, the scars turned out rough and the risk of their divergence during a second pregnancy was high.
By the end of the last century, doctors indicated to women who had a chance to give birth through surgery that they could have another child, but not earlier than after 3 years. In the 2000s, three operations were secretly allowed. Until recently, this number was considered the only possible, extreme one.
Before the third cesarean section and today, doctors suggest that women consider the possibility of surgical sterilization in order to even theoretically exclude the possibility of another pregnancy. Many agree. But those who do not sign such consent sometimes come for a fourth child.
If you are lucky with the doctor, he will always find the right words to encourage the woman. If you are unlucky (and this happens, according to reviews, often), even after the second caesarean section the woman will be actively dissuaded from giving birth at the antenatal clinic.
Observing a pregnant woman after 2, 3, 4 previous operations on the uterus is a big risk. If something happens to her, the doctor will be personally responsible. That is why women begin to hear horror stories about a thin scar and the unsightly prospects of a rupture. Uterine ruptures are rare. And abortions due to fear of rupture, unfortunately, are common.
Progress of the operation
First, drugs for general or regional anesthesia are administered, the skin and uterus are cut, the baby and placenta are removed, the tissue is sutured, and the patient is transferred to the recovery room.
What kind of anesthesia will it be?
The vast majority of women (about 90%) use spinal or epidural anesthesia. It is carried out in this way: a solution of the drug is injected between the lumbar vertebrae with a thin spinal needle or a set (needle + catheter) for epidural anesthesia.
There is a complete loss of sensitivity from the lower back to the feet, which allows you to perform all the necessary manipulations without pain and discomfort. The woman in labor is conscious all the time, she is separated from the surgical field by a screen, but can maintain contact with the surgeon. After the baby is born, you can immediately put it to the breast.
If such regional anesthesia is contraindicated, or there is a need for a long operation, then general anesthesia is prescribed. The drugs are first injected into a vein, then, after the onset of drug-induced sleep, a tube is installed into the trachea through which the gas mixture is supplied. With the help of these medications, complete relaxation of the muscular system and loss of consciousness occurs.
How is a second planned caesarean section performed?
The second cesarean section differs from the first in that the incision is made close to an existing scar.
All other stages of the operation are similar:
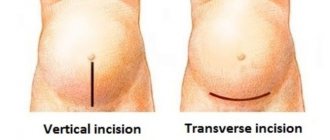
- The incision in the skin of the subcutaneous layer (for most women with a planned cesarean section, it is horizontal above the pubis, no more than 10 cm, this protects against hernias and heals faster).
- Dissection of the uterus in the lower part.
- Opening the membranes, removing amniotic fluid.
- Removing the child.
- Crossing the umbilical cord.
- Removal of the placenta.
- Layer-by-layer suturing of tissues.
- Fixing a protective bandage on the skin and placing an ice pack on top.
After the second, and especially the third, caesarean section, the woman is offered tubal ligation surgery. This is a fairly reliable way to prevent unwanted pregnancy in the future, since carrying a fetus with scars on the uterus is very dangerous.
Possible complications and their prevention
With a caesarean section, especially a repeat one, there are risks of complications:
- blood loss exceeding the norm (up to 500-750 ml is allowed) - the uterine cavity, due to the strong relaxation of muscles during anesthesia, can be difficult to contract; to prevent severe anemia, blood or its components are injected, and if the bleeding cannot be stopped, then removal of the uterus is necessary ;
- adhesive disease - any operation in the abdominal cavity during healing causes the formation of adhesions, that is, fibers that connect organs (for example, intestinal loops, bladder with the body of the uterus), which later lead to the appearance of chronic pain in the abdominal area, and if affect the patency of the fallopian tubes, they become the cause of ectopic pregnancy and infertility; treatment – physiotherapy, therapeutic exercises;
- inflammation of the inner layer of the uterus (endometritis) - occurs due to the penetration of bacteria into the uterine cavity; for prevention, antibiotics are mandatory before surgery;
- infection of the suture - accompanied by redness, pain, discharge, fever, to prevent this, the woman is prescribed treatment with antiseptic solutions, and at home must be lubricated with wound-healing ointments (Levomekol, Bepanten plus);
- the formation of a rough scar at the site of skin stitching - Contractubex and Dermatix are used to soften and form a thin seam;
- divergence of the edges of the wound - occurs when there is an understanding of the severity, strong straining during bowel movements, hacking cough in the first days, as well as when an infection is attached; medications are prescribed for treatment; surgical debridement of the wound and re-application of suture material may be necessary.