Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) during pregnancy has been a routine procedure for more than 30 years. At different stages of fetal development, this type of diagnosis has one or another meaning.
Ultrasound in the early stages of pregnancy is quite important, as it helps to learn as informatively as possible about the condition and development of the fetus. Many mothers are afraid to conduct an ultrasound examination, considering it dangerous both for themselves and for the developing baby. However, such an opinion is far from the truth. Why? Let's figure it out.
What is ultrasound in early pregnancy
Today this is the only way to accurately diagnose developing gestation. The test strip and blood test only show an increased level of the hormone hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), which can be caused by an ectopic or frozen pregnancy. Ultrasound provides an opportunity to examine in detail what is happening in the uterus. Based on the dimensions of the fertilized egg and embryo, the doctor determines the gestational age with a small error.
If there are no contraindications, the procedure is carried out three times. At an early stage of 10-14 weeks, the woman is prescribed the first ultrasound. The main purpose of screening is to detect defects in the fetus (for example, Down syndrome). In addition, the study is necessary to establish a preliminary date of birth. If pathological phenomena have been discovered that threaten the normal development of the fetus, the woman should see a geneticist. The specialist will offer several options for action. After this, repeated screening may be necessary.
A planned second ultrasound is prescribed at 20-24 weeks, when all the internal organs of the embryo are already formed. They are studied by a specialist during the procedure. The third scheduled screening occurs at 30-34 weeks, during which the condition of the uterus, baby, placenta, and amniotic fluid is assessed. The doctor examines the presentation of the fetus and assesses the readiness of the woman’s body for childbirth.
If there are any complications or doubts about the child’s health, more procedures may be prescribed. The reasons for unscheduled inspections will be:
- aching or nagging pain in the abdomen;
- bloody issues;
- cases of miscarriages in the patient;
- frozen pregnancy, etc.
An ultrasound scan during early pregnancy can be both a joyful event for the expectant mother and a cause for serious concern. Before you worry about your health and the condition of the fetus, make sure that the doctor is highly qualified and experienced and the quality of the equipment he uses. If possible, consult another specialist if pathologies are detected. It is better to perform a repeat ultrasound using the same equipment used for the initial examination. The table shows what can be found out using ultrasound.
| Gestational age | What does screening show? |
| 1-3 weeks after fertilization | It is extremely rare for a study to be conducted this early. An indication may be a suspicion of ectopic pregnancy. In addition, the check is carried out after IVF (artificial insemination). The result helps to establish the presence of pregnancy, its duration, course, and also to identify problems if the delay in menstruation was not caused by conception. |
| 3-4 week | The ultrasound specialist examines the umbilical cord, the anlage of the limbs, and the ears. During this period, the size of the fetus is only 2-4 mm. |
| 10-11 week | Based on the screening results, the doctor evaluates the anatomy of the fetus, checks for abnormalities and threats to pregnancy and the development of the child. For example, if at the 3rd month of pregnancy the nasal bone has not yet formed in the embryo, the specialist assumes the presence of chromosomal abnormalities. At this same stage, the threat of miscarriage can be established. |
| 12-14 week | Deviations from the norm become more noticeable as the baby's body and organs continue to develop. During this period, special attention is paid to studying the thickness of the collar space, the location of the hip bones, the distance between them, the length of the body, and the diameter of the head. The doctor examines in detail the internal organs of the fetus, the outlines of which by this time become clear. The ultrasound specialist evaluates the condition of the placenta and amniotic fluid, uterine tone, and other important aspects. |
| Week 15 | At this stage, women who for some reason could not get to the procedure earlier undergo an ultrasound scan. The fetal heartbeat is listened to and its size is assessed (optimal indicators are 10 cm in height and 70 g in weight). At week 15, the baby’s nervous system and skeleton are already developing. |
Time of first examination
Every expectant mother needs to know when to have the first ultrasound to confirm pregnancy. It is carried out 3-5 weeks after the start of the last menstruation. Today in obstetrics two diagnostic methods are used:
- through the abdominal wall;
- transvaginal using a vaginal sensor onto which a special condom is placed.
It is worth knowing that no matter at what stage you perform your first ultrasound during pregnancy, it is the vaginal examination that increases the reliability and accuracy of the information obtained, since the sensor comes into contact with the internal organs. In this case, there is no need to fill the bladder before diagnosis. Already on the 4-5th day of delay, the fact of classes can be confirmed. It turns out that embryological pregnancy is determined at a period of 2 weeks.
At the time when you can do your first ultrasound if you are pregnant, the diameter of the ovum is only about 5 mm. To determine the exact date, it is necessary to measure the size of the embryo from the head to the tailbone. The probability of error in this case is no more than three days. If there is no need to confirm the fact of conception, and the absence or presence of uterine pathology has been established in another way, the first planned ultrasound visit is carried out during pregnancy for up to 12 weeks.
We figured out when you can go for the first ultrasound during intrauterine pregnancy, and now let's understand what it shows:
- 7 weeks – embryonic head;
- 8 weeks – fetal limbs;
- 9-11 weeks – limb bones and ossification points;
- 11-14 weeks - presence or absence of the stomach, kidneys, bladder, all fingers of the fetus.
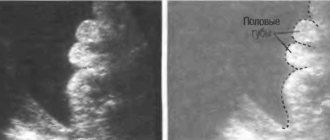
When the first ultrasound examination is performed during pregnancy, the “nuchal translucency space” needs to be measured. The normal size is a maximum of 3 mm. At 3 mm or more, the fetal neck begins to swell, which indicates a chromosomal disorder and the risk of Down's symptom.
It is important to measure the “nuchal space” when carrying twins. The sooner you detect it, the more accurate the result of the examination for the presence of Down syndrome will be, since it is during pregnancy with many children that errors in detecting this symptom are possible.
Even more interesting:
I infected my boyfriend with HPV
The importance and significance of ultrasound diagnostics
As a rule, the first ultrasound examination shortly after a missed period is carried out on the initiative of the woman. However, in some cases it is clinically necessary and is carried out on the direction of a doctor. The main reasons for ultrasound in early pregnancy are:
- artificial insemination (examination takes place 2-3 weeks after pregnancy is confirmed by laboratory tests);
- detection of threatened miscarriage;
- oncological diseases of the uterus;
- the presence of serious chronic diseases, including diabetes mellitus and blood pathologies;
- ectopic or frozen pregnancy.
At risk for improper implantation of the fertilized egg are women who have previously been diagnosed with tubal infertility of any nature, who have a history of abdominal surgery on the pelvic organs, or abortions. In addition, girls with a previously terminated ectopic pregnancy undergo an ultrasound scan, even in cases where both fallopian tubes were preserved. Screening is the only method of visualizing a threatened spontaneous abortion, so it is used for cramping pain in the lower abdomen or lower back, and the appearance of bloody discharge from the vagina.
Sonography is performed at the very beginning of pregnancy and when signs of fetal development are fading. Symptoms indicating such danger are:
- disappearance of toxicosis;
- a sharp drop in hCG and progesterone levels;
- stopping the growth of the uterus;
- lack of heartbeat in an embryo measuring 5 cm or larger;
- discrepancy between the size of the fetus and the expected gestational age.
Ultrasound in the third trimester of pregnancy
In accordance with the standard plan, an ultrasound is performed at 30–32 weeks of pregnancy. Diagnostics is mandatory, since examination during this period allows not only to assess the development of the fetus and its position, but also to determine how the birth process will occur - naturally or through cesarean section.
The main indicators that are determined during ultrasound diagnostics at the third stage:
- Intrauterine position of the fetus. During the examination, the doctor sees how the baby is positioned - with its head or legs relative to the exit from the uterus. For natural delivery, the position of the baby with its head towards the exit is favorable. If the baby is in a reverse or transverse position, the issue of a cesarean section is considered.
- Fetometry indicators. As at the previous stage, an examination with ultrasonic waves is carried out to determine the size of the circumference of the child’s head and abdomen, the length of the arms and legs. The information obtained is used to determine the duration of pregnancy. Since the development of a child in the womb does not occur smoothly, but in jumps, the indicators obtained as a result of the study may have some deviation from the normative data. Also, based on the ultrasound, the child’s body weight is determined.
- Condition of internal organs. During this period, the heart, liver, kidneys and other internal organs are examined to determine the correctness of their structure. If the fetus is in a suitable position during the study, the doctor can determine its sex.
- Assessment of motor activity. If the fetus develops normally, without abnormalities, an ultrasound examination should show fetal activity and movement of its limbs. In this case, the arms and legs should be in a half-bent position, the palms should be clenched into fists. If there is weak muscle tone and relaxation, then most likely the fetus is experiencing a lack of oxygen (hypoxia). It is considered normal if a child makes two or three movements in thirty minutes.
- Assessment of placenta parameters. At this stage, the placenta undergoes a thorough ultrasound examination, since it is difficult for the organ to meet the needs of the fetus. It is possible to identify signs of oxygen starvation of the fetus.
- Carrying out Doppler sonography. The study is aimed at assessing blood circulation in the fetal vascular system, as well as in the umbilical cord and uterus. This makes it possible to identify the presence of pathology of the placenta, lack of oxygen, determine the sufficiency of the child’s nutrition, and the placement of the umbilical cord. This examination is not prescribed to all pregnant women, but only in cases of extreme necessity.
What kind of ultrasound is done in early pregnancy
Screening methods can be different: the choice depends on the level of the clinic’s material and technical base. The referral for an ultrasound is agreed upon with the obstetrician, who will monitor the woman throughout the entire period of pregnancy. Today, there are 3 main methods of ultrasound examination in early pregnancy:
- Transabdominal . A substance is applied to the skin of the abdomen, thanks to which the internal organs can be examined in detail. This type of ultrasound is performed both in the early stages and immediately before childbirth. Such screening has several advantages: it is carried out quickly, has a low cost, and is completely safe for the fetus and the expectant mother. The disadvantage of transabdominal two-dimensional ultrasound is the need for preliminary preparation (diet, drinking plenty of water and carminatives). In addition, outdated equipment does not always allow us to examine the thickness of the collar space or visualize the nasal bone.
- Transvaginal . The most accurate research method that makes it possible to identify pathologies at the very beginning of embryo development. Screening is carried out using a special vaginal sensor, the results are shown on the monitor. Starting from the 2nd trimester, this type of study is used extremely rarely - in case of certain indications (if there are doubts about the length of the cervix. Transvaginal ultrasound in the early stages of pregnancy helps to diagnose not only uterine, but also ectopic gestation. The method helps to see the first contractions of the embryo's heart Conducting screening does not require special preparation, except for taking Espumisan (a drug against gas formation) - this is an advantage of this method. If there are no pathologies during pregnancy, a transvaginal ultrasound is performed from 11 to 14 weeks.
- 3D and 4D screening . It is carried out in most modern clinics and provides a three-dimensional image. Using such equipment, you can even make a video recording of a child's life in the womb. The image received on the monitor is floral and three-dimensional, so you can examine the baby’s appearance in detail. The advantage of the method is the ability to identify difficult-to-distinguish anomalies and study hard-to-reach structures that are inaccessible with other types of ultrasound. In addition, the gender of the child is more clearly visible in 3D images. The disadvantage of this type of screening is the duration of the procedure (a regular ultrasound takes 15 minutes, but 3D will take twice or three times as long). In addition, there are a number of contraindications for three-dimensional screening related to the timing of pregnancy, the position of the embryo in the womb, etc.
Articles on the topic
- Low blood pressure during early pregnancy - why hypotension occurs and methods of treatment
- Dental treatment during pregnancy - when and how it is safer to do it, contraindications and restrictions
- Polyhydramnios during pregnancy - signs and why it occurs, diagnosis, drug therapy and nutrition
Ultrasound in the second trimester of pregnancy
If, for various reasons, no examination was carried out in the previous trimester, an ultrasound scan is performed at 16, 17, 18 weeks of pregnancy. During this period, sagging membranes can also be detected, hereditary diseases (hemophilia) can be diagnosed, and the sex of the baby can be determined.
In a planned format, an ultrasound is performed at 20–24 weeks of pregnancy to study in detail the anatomical structure of the fetus and identify various pathologies that are diagnosed in the prenatal period. During the examination, the main parameters of the fetus are determined - the volume of the head, abdomen and other indicators. The actual parameters obtained during ultrasound of the fetus during pregnancy are compared with the indicators of the fetometric table and determine how correctly the development of the fetus occurs.
Also, during the ultrasound examination, the doctor determines:
- the presence of defects, developmental delay - if there are certain suspicions, an ultrasound examination is carried out every two to three weeks;
- the length of the nasal bone - this parameter allows you to accurately identify Down syndrome and other chromosomal pathologies in which the bone is absent or its parameters are much less than normal for a fetus of this “age”;
- amniotic fluid volume - determined by calculating a special index;
- placenta parameters - its thickness and other parameters are determined;
- the condition of the cervix - it must remain closed until the very moment of birth; if the cervix opens prematurely, there is a risk of miscarriage, which requires emergency measures, suturing;
- condition and location of the umbilical cord - ultrasound examination shows cases when the umbilical cord is wound around the fetal neck; in the 2nd trimester, this situation is not critical, the fetus is constantly moving and can unwind on its own; The greatest danger from entanglement of the umbilical cord is before delivery.
How they do it
In the first weeks of gestation, ultrasound examination is performed in two ways - transvaginally and transabdominally. The combination of these procedures helps to examine the entire uterus along with the cervix, even in case of non-standard position of the organ and the presence of factors complicating visualization. Preparation for a transabdominal ultrasound involves an increased drinking regime before the procedure (it begins 2-3 hours before it). This is necessary to accumulate a large amount of urine in the bladder, which will help straighten the uterine flexures and improve visualization.
Sonography is performed with the patient lying on her back. When using a vaginal sensor, a disposable condom is put on it and carefully inserted into the vagina with the patient's legs bent. When examining through the abdominal wall, a special gel is applied to the suprapubic abdomen and iliac region. The information received from the sensor is shown on the monitor. The doctor takes measurements of various structures using a special program, after which the specialist analyzes the data, signs the conclusion, and attaches key images to it.
Is ultrasound examination dangerous for a pregnant woman and fetus?
Data provided in the World Health Organization report suggests that ultrasound waves are safe for diagnosis and do not have a harmful effect on the health of a pregnant woman. Such conclusions were made based on the results of scientific research conducted over several years by specialists from famous world clinics.
Ultrasound has been found to have no harmful effects on the fetus. Studies have shown that ordinary doses of acoustic radiation do not have a harmful effect on individual cellular structures and on the embryo as a whole.
Ultrasound waves cause slight mechanical movement of tissue, but modern diagnostic equipment is designed in such a way that this effect is minimized.
In some cases, women are worried that after an ultrasound the baby is too active. This reaction is most often caused by touching the sensor to the stomach and the emotional state of the expectant mother. Hypertonicity occurs as a reaction to a full bladder.
A standard ultrasound examination requires 15 – 30 minutes to obtain a 3D image of the child, the procedure will take three times longer. Despite this, even 3D ultrasound is considered safe for mother and baby. 3D diagnostics allows you to examine the baby’s appearance in detail, identify cleft lips or the presence of “extra” fingers on the limbs. But you should not often resort to this procedure unless absolutely necessary.
Expectant parents sometimes want to conduct 4D diagnostics, which can result in an entire movie. But at the same time, the expectant mother and baby are exposed to acoustic radiation for a long time. If such a record is of no medical value, then it is advisable not to resort to such a study or to conduct it in a single case.
The use of modern ultrasound equipment makes it possible to accurately determine the condition of the uterus and other organs and how the fetus is developing. In the normal course of pregnancy and observation by a doctor from an early stage, the ultrasound procedure is prescribed three times. If an urgent need arises, additional research is carried out.
Ultrasound diagnostics is carried out on a voluntary basis, its results can promptly reveal dangerous conditions and abnormalities in the development of the fetus. Therefore, you should not neglect modern diagnostics, especially if there are certain indications for its implementation.
What indicators are assessed?
Expectant mothers need to know several basic concepts used by ultrasound doctors and gynecologists. They often use the term “obstetric gestational age,” which refers to the period of fetal development (it is calculated in weeks and days). In addition, the term “embryonic term” is widely used, which is calculated from the date of conception and is approximately 2 weeks shorter than the obstetric term. To estimate the gestational age, only the first calculation method is applicable.
Modern ultrasound machines calculate the gestational age automatically, based on basic parameters entered before the procedure. Ultrasound examination at an early stage is carried out for:
- determining the stage of fetal development;
- detection of a “frozen” pregnancy;
- identifying various disorders or intrauterine anomalies.
At the stage of primary screening (11-13 weeks), the doctor examines the uterine walls, the organ itself and its appendages, in addition, such indicators of embryo growth as:
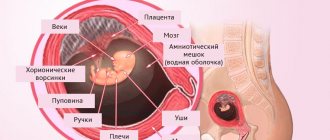
- chorion (outer lining of the placenta);
- yolk sac (extraembryonic, semicircular formation between the amnion and chorion).
At the same stage, a detailed study of the collar zone of the embryo is carried out - the area between the tissues and skin in the neck area. The thickness of the collar zone is designated by the abbreviation TVP, which normally should not exceed 2.7 mm. Standard indicators are shown in the table:
| Gestation period | Collar thickness (mm) | ||||||||
| According to N.A. Altynik, M.V. Medvedev | According to E.A. Shevchenko | According to E.S. Nekrasova | |||||||
| 5 | 50 | 95 | 5 | 50 | 95 | 5 | 50 | 95 | |
| 11 weeks – 11 weeks and 6 days | 0,8 | 1,6 | 2,4 | 0,5 | 1,4 | 2,2 | 0,9 | 1,3 | 2,1 |
| 12 weeks – 12 weeks and 6 days | 0,7 | 1,6 | 2,5 | 0,6 | 1,5 | 2,5 | 1,0 | 1,6 | 2,4 |
| 13 weeks – 13 weeks and 6 days | 0,7 | 1,7 | 2,7 | 0,7 | 1,6 | 2,4 | 1,2 | 1,8 | 2,5 |
There is a descriptive statistics term called percentile. Its average value is indicated in the “50” column, and the maximum and minimum acceptable values are entered in the “95” and “5” columns. Another parameter that is still being studied is the nasal bone. At 11-13 weeks, it should also be visualized during an ultrasound examination. At this stage, the coccygeal-parietal size of the embryo is measured. For a child in early development (11-13 weeks), 45-80 mm is considered the norm. The table below shows normal indicators by stage of pregnancy.
| Gestation period (n. – weeks, d. – days) | CTE in cm | Gestation period | CTE in cm |
| 6 n. 2 days | 0,55 | 10 n. 2 days | 3,32 |
| 6 n. 3 days | 0,61 | 10 n. 3 days | 3,46 |
| 6 n. 4 days | 0,68 | 10 n. 4 days | 3,6 |
| 6 n. 5 days | 0,75 | 10 n. 5 days | 3,74 |
| 6 n. 6 d. | 0,81 | 10 n. 6 d. | 3,89 |
| 7 n. | 0,89 | 11 n. | 4,04 |
| 7 n. 1 day | 0,96 | 11 n. 1 day | 4,19 |
| 7 n. 2 days | 1,04 | 11 n. 2 days | 4,35 |
| 7 n. 3 days | 1,12 | 11 n. 3 days | 4,51 |
| 7 n. 4 days | 1,2 | 11 n. 4 days | 4,67 |
| 7 n. 5 days | 1,29 | 11 n. 5 days | 4,83 |
| 7 n. 6 d. | 1,38 | 11 n. 6 d. | 5 |
| 8 n. | 1,47 | 12 n. | 5,17 |
| 8 n. 1 day | 1,57 | 12 n. 1 day | 5, 34 |
| 8 n. 2 days | 1,66 | 12 n. 2 days | 5,52 |
| 8 n. 3 days | 1,76 | 12 n. 3 days | 5,70 |
| 8 n. 4 days | 1,87 | 12 n. 4 days | 5,88 |
| 8 n. 5 days | 1,97 | 12 n. 5 days | 6,06 |
| 8 n. 6 d. | 2,08 | 12 n. 6 d. | 6,25 |
| 9 n. | 2,19 | 13 n. | 6,43 |
| 9 n. 1 day | 2,31 | 13 n. 1 day | 6,63 |
| 9 n. 2 days | 2,42 | 13 n. 2 days | 6,82 |
| 9 n. 3 days | 2,54 | 13 n. 3 days | 7,02 |
| 9 n. 4 days | 2,67 | 13 n. 4 days | 7,22 |
| 9 n. 5 days | 2,79 | 13 n. 5 days | 7,42 |
| 9 n. 6 d. | 2,92 | 13 n. 6 d. | 7,63 |
| 10 n. | 3,05 | 14 n. | 7,83 |
| 10 n. 1 day | 3,18 |
In addition to CTE, the doctor assesses the biparietal and fronto-occipital size of the fetus. The first indicator is the distance between the temples, the second represents the distance from the occipital to the frontal bone.
| Gestation period (weeks) | Biparental size (mm) | Fronto-occipital size (mm) | ||||
| 10 | 50 | 95 | 10 | 50 | 95 | |
| 11 | 13 | 17 | 21 | — | — | — |
| 12 | 18 | 21 | 24 | — | — | — |
| 13 | 20 | 24 | 28 | — | — | — |
| 14 | 23 | 27 | 31 | — | — | — |
| 15 | 23 | 31 | 31 | — | — | — |
| 16 | 31 | 34 | 37 | 41 | 45 | 49 |
The average value is indicated in the “50” column, the maximum and minimum in the “95” and “5” columns. Separately, the doctor examines the size of the fertilized egg. The average values of the latter are:
| Date of last menstruation (weeks) | Conception time (weeks) | Inner diameter (mm) | Area (sq. mm) | Volume (mm cubed) |
| 5 | 3 | 18 | 245 | 2187 |
| 6 | 4 | 22 | 363 | 3993 |
| 7 | 5 | 24 | 432 | 6912 |
| 8 | 6 | 30 | 675 | 13490 |
| 9 | 7 | 33 | 972 | 16380 |
| 10 | 8 | 39 | 1210 | 31870 |
| 11 | 9 | 47 | 1728 | 55290 |
| 12 | 10 | 56 | 2350 | 87808 |
| 13 | 11 | 65 | 3072 | 131070 |
In addition, the heart rate must be examined. The norm can be determined by the average values indicated in the table:
| Gestation week | Heart rate (beats per minute) |
| 10 | 161-179 |
| 11 | 153-177 |
| 12 | 150-174 |
| 13 | 147-171 |
| 14 | 146-168 |
Signs of multiple pregnancy
As a rule, an ultrasound to determine pregnancy does not show the presence of twins in the uterus; this becomes noticeable only at 8-12 weeks of intrauterine development. Embryos can be located in different parts of the uterine space - this depends on the area of egg implantation. The heartbeat of twins is detected later than in gestations with one embryo. You can hear your heart beat, but determining how many hearts are beating is a difficult task. As a rule, the second or third heart can be differentiated only by week 20.
Unscheduled ultrasounds
In our country, according to standards, it is recommended to do three screenings throughout the entire pregnancy. Additionally, a woman usually goes for an ultrasound at the first suspicion of an interesting situation. But there are situations in which a visit to an ultrasound diagnostic doctor may be unscheduled:
- Intrauterine growth retardation
- Bleeding at any time
- Previously identified fetal pathology
- Low location of the placenta - ultrasound control in later stages
- Discrepancy between the size of the uterus and gestational age
- Absence of movements and other signs of fetal life
Is ultrasound harmful?
Carrying out an ultrasound examination does not have negative consequences for the fetus, both in the short and long term. At the same time, despite development in an aquatic environment, the child can feel directed acoustic vibrations, but they are not capable of causing harm to the fetus: ultrasonic waves do not have a destructive effect on the tissues, genetic material or cellular structures of the embryo. They do not cause destruction of intermolecular bonds and do not affect proliferation processes (tissue growth through cell division).
The harm of ultrasound during early pregnancy is a myth, since this examination method cannot disrupt the development of the child and does not in any way affect the functioning of his vestibular apparatus. In addition, in the early stages the baby does not yet have an auditory system. In the first half of pregnancy, the embryo only develops the inner and middle ear, and the active development of the auditory system occurs from the 7th month. Air cavities filled with a jelly-like substance provide additional protection to the fetus from external acoustic influences.
Why and when is ultrasound performed during pregnancy?
Diagnostics using ultrasound equipment is an accessible, harmless and informative method of studying the condition of the expectant mother and child. The first ultrasound during pregnancy allows you to confirm the presence of this condition in a woman. The procedure is subsequently carried out to solve the following problems:
- monitoring the dynamics of fetal growth and development;
- analyzing the condition of the fetus, identifying various abnormalities;
- determining the size and weight of the fetus;
- determining the amount of amniotic fluid;
- studying blood circulation in the uterus, blood vessels, placenta;
- identifying the condition of the ovaries and other organs.
Ultrasound is performed during pregnancy using the transabdominal method or using a transvaginal sensor, which is a more highly accurate examination method.
International standards provide for examinations using ultrasound equipment during the following stages of pregnancy:
- in the period from the 11th to the 13th week;
- during the period 20 to 24 weeks;
- during the period 30 to 32 weeks.
If the need arises, there is a risk of complications, pain or other alarming symptoms, the leading doctor gives the woman a referral for additional ultrasound examination. The most optimal is to perform an ultrasound at the 12th week of pregnancy, as well as at the twenty-second and thirty-second weeks.