The problem of infertility remains relevant for many couples. Moreover, in approximately 40% of cases the cause lies in reproductive dysfunction in men. To find out which of the future parents needs the help of specialists, a comprehensive examination of both partners is carried out, including sperm testing. Experts believe that a spermogram analysis should be done even before planning conception, because it is the spermogram that allows one to determine the motility and viability of sperm and their number in the ejaculate, that is, to assess the chances of conception. In addition, the spermogram also determines the volume of seminal fluid, its viscosity, and the presence of foreign cells in it. A normal spermogram indicates a man’s ability to become a father, and identifying abnormalities helps to identify and eliminate the cause of infertility.
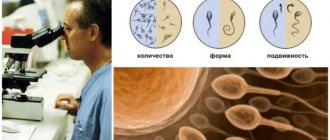
What are the indicators of a spermogram?
Decoding the spermogram includes macroscopic analysis - examination of the appearance of the ejaculate, its volume, consistency, color, smell, pH reaction. Microscopic examination is an assessment of the sperm themselves (their motility, concentration, as well as external structure), blood cells, spermatogenesis cells, etc.
The assessment of sperm, as well as interpretation of the spermogram, is carried out in accordance with the latest WHO guidelines for the examination and processing of human ejaculate, which was published in 2010 (translated into Russian in 2012).
Let us dwell on what are the main indicators of a spermogram, their normal values and deviations when deciphering a spermogram.
How to prepare for spermogram analysis
The main recommended method of obtaining sperm for research is masturbation . When collecting sperm for analysis, it is necessary to collect all the sperm released during ejaculation, including the very first and very last portions, into a sterile plastic container with a wide neck. The reliability of sperm testing directly depends on both the time after which the container with sperm was delivered to the laboratory and the conditions of transportation. It is preferable that the sperm container be delivered to the laboratory within 20 minutes of ejaculation. It is necessary to indicate on the container the exact time when ejaculation occurred. The container with sperm should be protected from temperature changes. During transport, the container with sperm should be placed in the inside breast pocket of the jacket to maintain a temperature close to body temperature. The ideal conditions for collecting sperm for analysis are a separate room next to the laboratory where the research will subsequently be carried out.
It is not recommended to obtain sperm for research through:
- interrupted vaginal intercourse;
- oral intercourse;
- sexual intercourse with a latex condom.
Vaginal secretions, saliva and latex components of the condom can negatively affect the quality of sperm, leading to a distortion of the test result.
Before receiving sperm for testing, you must refrain from ejaculating for 2 days. To obtain an objective and reliable result, it is necessary that sperm examination be performed four times with an interval of 2 weeks. It is permissible to perform sperm examination twice with an interval of 4 weeks. But if the results of at least one of these two studies revealed abnormalities, the sperm test should be repeated at least twice more.
A spermogram consists of several parts, including macro- and microscopic examination of the ejaculate. Currently, WHO criteria are generally accepted for assessing results.
Sperm liquefaction
Immediately after ejaculation, the seminal fluid acquires a gelatinous consistency. This is a completely normal process that characterizes a normal spermogram, and at room temperature it begins to liquefy within a few minutes. A spermogram should normally show a liquefaction time of 15-30 or sometimes 60 minutes. An increase in this time can be observed with chronic inflammatory processes of the gonads (seminal vesicles, prostate) or the presence of enzymatic deficiency. A good spermogram may reveal jelly-like granules (so-called gelatin bodies) that do not liquefy at all; however, they have no clinical significance. In order to most adequately determine the time period of ejaculate liquefaction, a man needs to indicate on the form the exact time of its receipt.
Meaning of the analysis results
Ejaculate volume
Normal: > 1.5 ml.
A decrease in ejaculate volume most often indicates deficiencies in the transportation of the material and therefore does not have much diagnostic value. If all the material obtained is delivered for examination, and a decrease in its volume is detected, this may indicate insufficient function of the sex glands - the prostate gland, seminal vesicles and some others, which in turn may be a manifestation of a reduced level of male sex hormones in the blood. Excess sperm volume is sometimes associated with an inflammatory process of the listed glands, mainly with prostatitis and vesiculitis.
Color
Normal: white, grayish, yellowish.
The appearance of a red or brown tint of ejaculate may be associated with an admixture of blood in the semen, which occurs with injuries to the genital organs, chronic vesiculitis, and calculous form of prostatitis. Yellow semen may be caused by eating food dyes or taking certain medications. In this case, this indicator does not have much diagnostic value.
RN
Norm: 7,2 – 8.
Deviation from normal pH may be associated with inflammation of the gonads, primarily with prostatitis or vesiculitis.
Liquefaction time
Normal: up to 60 minutes.
An increase in liquefaction time may be a consequence of long-term chronic inflammation of the gonads - chronic prostatitis or vesiculitis. Less commonly, an increase in liquefaction time is associated with enzyme deficiency in the body. As a result of increased liquefaction time, sperm take longer to gain full motility. This leads to their longer contact with the acidic environment of the vagina, which sharply reduces their chances of penetration into the uterus and fertilization. This spermogram indicator has a direct connection with the likelihood of conception.
Sperm viscosity
The viscosity of sperm is determined by the length of the thread that the sperm forms when flowing from a pipette or a special needle. The length of the thread is measured in centimeters.
Normal: up to 2 cm.
An increase in sperm viscosity is most often associated with chronic inflammation of the gonads - prostatitis and vesiculitis. Increased sperm viscosity leads to difficulty in the movement of sperm into the vagina, to longer contact with the acidic environment of the vagina, which significantly reduces the chances of fertilization. This spermogram indicator is directly related to the likelihood of conception.
Sperm concentration
Normal: more than 15 million in 1 ml of ejaculate.
A decrease in sperm concentration is called oligozoospermia. Most often, oligozoospermia indicates a reduced efficiency of the testicles, which may be associated with a decrease in the level of male sex hormones in the blood, an inflammatory process in the testicles, previous inflammatory or toxic damage to the spermatogenic epithelium of the testicles, the state of the immune system, changes in metabolism and some other factors. The reasons leading to a decrease in sperm concentration have not been fully studied. This spermogram indicator is one of the most important; it is directly related to the possibility of conception naturally.
Some laboratories consider the indicator of polyzoospermia - an increase in sperm concentration of more than 120 million/ml. There is an opinion that polyzoospermia is a precursor to oligozoospermia in a number of patients. It is assumed that patients with polyzoospermia need observation by an andrologist and periodic control spermograms. However, this result does not affect the possibility of fertilization at the moment.
Sperm count
Normal: more than 39 million in ejaculate.
The reasons for a decrease in sperm count are the same as the reasons for a decrease in their concentration.
Sperm motility
Sperm motility is also one of the most important indicators of a spermogram, the result of which directly affects the likelihood of conceiving naturally. Depending on their motility, sperm are divided into 4 groups.
Group A – actively mobile with rectilinear movement. Group B – sedentary with linear movement. Group C – sedentary with oscillatory or rotational movement. Group D – motionless.
Norm: A > 25% or A+B > 32%.
A decrease in sperm motility is called asthenozoospermia. Its causes are very diverse - from various diseases (inflammatory diseases of the gonads, varicocele and others) to various kinds of toxic and thermal effects on the testicles. There is an opinion that a decrease in mobility is caused by a sexually transmitted infection - ureaplasma. However, the ability of ureaplasma to act directly on sperm and reduce their ability to move has not been proven.
Sperm morphology
This indicator reflects the percentage of normal forms of sperm capable of fertilization. This indicator is directly related to the likelihood of conceiving naturally.
Norm: more than 4%.
A decrease in the number of normal forms of sperm is called teratozoospermia. This is often observed with toxic and radiation damage to the scrotal organs, less often with inflammatory or infectious diseases. The morphology of sperm is strongly influenced by the ecology in the region where the man lives.
Live sperm
Percentage of live sperm in the ejaculate. This indicator is directly related to the possibility of conception naturally.
Norm: more than 50%.
A decrease in the number of living sperm is called necrospermia. This occurs primarily with radiation, toxic or thermal damage to testicular tissue, less often with infectious diseases and inflammation of the gonads. There is evidence that sudden necrospermia can be caused by severe stress.
Spermatogenesis cells
These are desquamated cells of the spermatogenic epithelium of the seminiferous tubules of the testicles.
Norm: 2-4 per 100 sperm.
An increase in the number of spermatogenic cells indicates inflammatory, infectious or other damage to the testicular tissue, which indicates a secretory form of male infertility.
Agglutination
Agglutination is the gluing of spermatozoa to each other.
Norm: absent.
The appearance of sperm agglutination may be a manifestation of a disorder of the immune system or autoimmune inflammatory processes. Agglutination can also occur during chronic inflammatory processes in the male gonads. The appearance of agglutination in itself does not reduce the likelihood of conception naturally, but it almost always leads to a decrease in sperm motility.
Aggregation
Aggregation is the accumulation of sperm into large clots.
Norm: absent.
Sperm aggregation can appear with long-term chronic inflammation of the gonads; most often it appears simultaneously with an increase in the liquefaction time and viscosity of the ejaculate. Aggregation itself does not affect the likelihood of conception naturally, but severe aggregation can dramatically impair sperm motility.
Leukocytes
White blood cells must be present in the ejaculate in a certain amount.
Normal: up to 106 in 1 ml (up to 3 - 4 in the field of view).
An increase in the number of leukocytes is a sign of an acute or chronic inflammatory process in the male pelvic organs. This in itself does not affect the likelihood of conceiving naturally, but most often it worsens almost all other spermogram indicators.
Red blood cells
Red blood cells of blood.
Norm: none.
The appearance of red blood cells in the ejaculate may be a sign of injury, tumor diseases of the genital organs, the presence of prostate stones, chronic prostatitis or vesiculitis. The indicator does not affect the possibility of conceiving naturally, but may be a sign of a serious disease of the pelvic organs.
Amyloid bodies
Specific formations that form in the prostate gland.
Normal: present.
The absence of amyloid bodies may be evidence of decreased function of the prostate gland, which most often occurs with long-term chronic inflammation. This indicator does not directly affect the possibility of conceiving naturally.
Lecithin grains
Lecithin grains are produced by the prostate gland.
Normal: present.
The absence of lecithin grains in the ejaculate indicates a decrease in the function of the prostate gland, which is possible with its long-term chronic inflammation. This indicator does not directly affect the likelihood of conceiving naturally.
Viscosity
After liquefaction, the viscosity of the ejaculate is assessed. This parameter is determined by the released drop. In a normal spermogram, they should fall freely. If a drop forms a thread whose length is more than 2 cm, this is a pathology. This may be evidence of the manifestation of inflammatory processes in the male reproductive system. When deciphering a spermogram, it is necessary to take into account that a viscous medium significantly impedes the passage of sperm into the uterus and reduces the fertilizing ability of a man.
Let's talk about physiology
Sperm is a fluid produced by the male gonads. Its release occurs at the climax of sexual intercourse, during orgasm. Sperm, or ejaculate, consists of sperm and seminal fluid.
Sperm are produced in the testicles. This paired sex gland is located in the scrotum. Each testicle contains thousands of seminiferous tubules, and it is here that sperm and male sex hormones are produced.
The prostate gland and the seminal vesicles located next to it are primarily responsible for the production of seminal fluid. Read about how sperm is released in a healthy man in the article at the link.
At the moment of ejaculation, the contents of the testicles enter the lumen of the urethra and mix with the secretions of the prostate and seminal vesicles. The resulting mixture is called sperm.
Male semen begins to be produced during adolescence. Maximum production occurs in mature years; with age, its amount decreases.
Male sperm is a unique liquid in its composition, which is not surprising given the importance of its mission.
Spermogram indicators: agglutination
Agglutination is expressed by the gluing of motile living spermatozoa - flagellum to flagellum, head to head or mixed type. It shouldn't show up well in the spermogram. The presence of agglutination does not in every case directly indicate the presence of immunological infertility; it more likely suggests the presence of antisperm antibodies on sperm. In this case, it is recommended to conduct additional studies for the presence of immunological infertility.
Main risk groups
The following main risk groups can be identified for whom it is recommended to postpone or exclude planning for a child:
- HIV-infected;
- Drug addicted;
- Past illnesses - syphilis, gonorrhea.
When planning a child, before the moment of actual conception, you need to undergo a medical examination and pass the appropriate tests. A gynecologist will recommend visiting the necessary specialists. It is important to remember that many diseases can go unnoticed, but when pregnancy occurs they can lead to difficult childbirth and even miscarriage.
Cells that are different from sperm
In the seminal fluid, in addition to sperm, epidermal cells, blood cells - leukocytes and erythrocytes, and immature sperm are sometimes found. There should be no red blood cells in the seminal fluid. Leukocytes are normally found in the ejaculate in a concentration of no more than 1×106 million/ml (up to two cells). Elevated leukocytes in the spermogram may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process of various origins. In this case, additional diagnostics and consultation with a urologist-andrologist are necessary. Round cells of spermatogenesis are also present in the ejaculate. In a normal spermogram, their number is up to 4 pieces in a standard field of view. A change in this indicator may be evidence of testicular damage and also requires additional diagnostics.
Features of the study
A comprehensive diagnostic test of sperm is carried out in a medical institution. The delivery of ejaculate occurs only through masturbation with clean hands in a separate room.
What influences the result
The composition of semen includes not only active sperm, but also prostate fluid; their ratio may fluctuate. The quality of the ejaculate, and, accordingly, the result of the spermogram, is influenced by both internal factors (diseases, stress) and external ones. List of the main reasons that can influence the diagnostic result of a spermatogram:
- sexual contact before analysis (three times a day, depending on the type of spermogram);
- ARVI, acute respiratory infections, influenza;
- chronic kidney disease;
- inflammatory process of the genitourinary system (cystitis, prostatitis);
- physical activity before taking the test (a day or less);
- medications;
- taking a hot bath, sauna;
- alcohol, smoking;
- taking antibacterial drugs;
- prostate massage;
- orchitis;
- temperature increase;
- venereal diseases.
Before donating sperm, you must wash your hands with antiseptic soap. If you have eczema, wounds or suppuration on your hands, it is recommended to use sterile gloves.
Why does sperm count decrease?
The content of live sperm in the seminal fluid necessary for fertilization of the egg is 50%.
If this indicator is reduced, then conception is unlikely or impossible. Sperm, the sex cells of a man, are contained in the seminal fluid in two forms: living, active and no longer viable (necrotic). When the number of living sperm decreases, a diagnosis of necrospermia is made.
Necrospermia can be permanent or temporary. With the temporary option, there is a gradual restoration of active sperm and fertilizing ability. This condition occurs after an illness, in diseases of an inflammatory nature. With constant necrospermia, conception is impossible.
Reasons for decreased mobility
In addition to a low number of active sperm, a decrease in the motor function of germ cells may also be observed. Such a violation can be observed when wearing tight underwear, smoking, acute respiratory viral infection or influenza. Dangerous consequences can occur with mumps, or mumps. A common complication after mumps is infertility in men.
If sperm motility is reduced during an attempt at fertilization, a woman may develop an ectopic pregnancy. This occurs if the fertilized egg implants in the wall of the fallopian tube rather than the uterus.
How the analysis is carried out
The analysis is usually carried out in a medical institution, and the patient is provided with a separate room. It is important that the collected biomaterial was obtained as a result of masturbation, and not interrupted sexual intercourse, or from a condom. The amount of semen tested is also important. 3-5 days before the test, you must abstain from sexual intercourse, otherwise the volume of ejaculate obtained will be insufficient. Some research options require a large amount of sperm.
Accuracy of the study
The accuracy of the result depends on the correct biomaterial and the quality of the equipment used to study the properties of seminal fluid. To confirm the result obtained, the analysis is carried out two or three times in a row. If these requirements are met, the reliability of the data obtained is very high.
Sperm concentration, as well as their total number in the ejaculate
These two indicators are not synonymous, but both of them are related to the effectiveness of pregnancy, and also predict the success of conception.
The total number of sperm in the entire seminal fluid usually corresponds to testicular volume and demonstrates the sperm-producing ability of the testes. The fact and possibility of fertilization of the egg, and therefore the occurrence of pregnancy, will depend on the concentration of sperm in the seminal fluid. In a normal spermogram, the minimum sperm content is 39 million/total ejaculate volume, and the lowest concentration is 15 million/ml. A decrease in indicators significantly reduces the possibility of conception.
What affects the accuracy of ejaculate analysis?
Conducted studies show that the results of the analysis vary for the same man and depend on various factors. Prolonged exposure to the sun, taking antiviral drugs, overwork and other conditions can cause temporary oligozoospermia. A small amount of sperm negatively affects the possibility of conception, so the analysis should be repeated after 2 weeks. In the latter case, a normal spermogram is often obtained.
Immunological problems associated with a recent disease can cause sperm to stick together (spermagglutination). This prevents the free movement of germ cells and must be taken into account when deciphering. Like other pathologies, such disorders can be temporary, so testing is carried out three times for high accuracy.
Sperm motility
In the question of what a spermogram should be, one of the most significant parameters is sperm motility. There are 3 categories of mobility: progressively mobile, non-progressively mobile, and immobile.
Progressively motile sperm are sperm that move actively, in a circle of large radius or linearly, regardless of speed. In the previous spermogram indicator of this Guide, among this group of cells, fast and slow cells are distinguished by speed, which means progressively motile sperm; according to the new classification, it is the sum of sperm of types A and B. Their minimum number is 32 percent.
Non-progressively motile – in this case, sperm movements with the absence of any progression: moving in a circle of small diameter, the flagellum moves the head with some problems, or there is only a beating of the flagellum. The total number of motile sperm must be at least 40 percent.
Immotile – sperm that do not show any movement.
A decrease in the percentage of progressively motile sperm has a very negative effect on the possibility of pregnancy. Therefore, this factor requires additional research.
What terms are used to describe sperm disorders?
There are various terms to describe sperm disorders.
Normospermia - all characteristics of the ejaculate are normal, normal sperm. Normozoospermia - all characteristics associated with sperm fertility are normal, but deviations that do not affect infertility are acceptable (increased content of round cells, abnormal pH, abnormal viscosity or non-liquefaction of the ejaculate). Oligospermia - insufficient ejaculate volume (less than 2 ml). Oligozoospermia - insufficient sperm count (concentration less than 20 million/ml). Asthenozoospermia is insufficient sperm motility (A<25% or A+B<50%). Akinozoospermia is complete immobility of sperm. Teratozoospermia - increased content of abnormal sperm (more than 50% when examining native ejaculate or more than 85% when examining a stained semen smear). Necrozoospermia is the absence of living sperm. Leukocytospermia - increased leukocyte content (more than 1 million/ml). Hemospermia is the presence of red blood cells in the ejaculate. Azoospermia is the absence of sperm in the ejaculate.
Every single characteristic of sperm changes greatly over time. If the sperm volume during analysis was 3 ml, then at the next ejaculation it may have completely different values, and it will also have different values after a month, especially after six months. The same principle applies to other parameters. That is why in reproductive medicine it is generally accepted that for analysis it is necessary to examine sperm twice with an interval of at least two weeks, and in case of significant differences in parameters - three times.
Of course, spermogram results are individual for each person. Do not try to diagnose yourself based on the results of a spermogram; only a doctor can comprehensively evaluate the data of a sperm analysis and draw the correct conclusion about the state of your health.
Spermogram morphology
The next important indicator is the morphology of the spermogram. When studying the morphology of the spermogram (external structure) of sperm, a colored fixed preparation is prepared. The assessment is carried out at a thousand times magnification under a microscope.
With a good spermogram, a normal sperm consists of a neck, head, and tail (flagellum). The head should be oval in shape with smooth, clear contours and of normal size. The head secretes an acrosome—enzymes that are necessary for fertilization of the egg, as well as genetic material. In a normal spermogram, the acrosome should occupy at least 40-70 percent of the total volume of the head. The sperm neck should be thin and clearly defined. Its axis in a good spermogram should completely coincide with the central axis of the head. In a normal spermogram, the flagellum should be clear, even, thinner than the neck, its length is approximately ten times the length of the head. In this case, deviations from these criteria classify the spermatozoon as an abnormal type (cervical anomaly, head anomaly, tail anomaly).
Only a morphologically normal sperm is capable of high-quality fertilization of an egg, leading to the conception and birth of a completely healthy child. With a normal spermogram, the minimum proportion of normal male germ cells is 4 percent. The range of normal percentages in fertile as well as infertile patients is 0-30 percent and few semen samples contain more than 25 percent normal sperm.
Of course, spermogram indicators are very variable and depend on many external as well as internal factors. For this reason, it is recommended to carry out a second or even a third re-analysis of the ejaculate if a borderline or pathological condition is detected. In conclusion, it should be noted that there are simply no minimum values at which pregnancy is likely to occur. In addition, it is impossible to make a diagnosis using only one transcript of the spermogram; additional examinations are required.
Decoding the results of indicators according to the table
Trying to decipher the analysis result yourself is not recommended, since the data obtained, which can be checked against the table, must be compared with each other and carefully studied. You need to know the features, possible deviations, causes, and be able to analyze all this for diagnostic purposes.
In table No. 1 you can view the normal limits of sperm parameters:
Table No. 1
| Time for liquefaction | 10-60 min. |
| Semen volume | 2 - 6 ml |
| Acidity level | 7,2 — 8 |
| Color | Milky, yellow, white-gray |
| Sperm count | 40 - 500 million |
| Leukocytes | 1 million/1 ml |
| Red blood cells | Not found |
| Slime | Not found |
In table No. 2, the limits of the norm for sperm assessment:
Table No. 2
| And weakly mobile per 1 ml of ejaculate | Not less than 25% |
| In weakly mobile ejaculate per 1 ml | Not less than 50% |
| From weakly mobile per 1 ml of ejaculate | No more than 50% |
| D immobilized for 1 ml of ejaculate | Less than 10% |
| Sperm aggregation | Not detected |
| MAP test | Not higher than 50% |
| Concentration in 1 ml of ejaculate | 20 to 120 million in 1 ml |
If DNA fragmentation is high, additionally prescribe:
Protamine-histone
Study of sperm nucleoproteins
Price: 2600 rub.
The ratio of the content of protamines and histones in spermatozoa is studied. If the balance is disturbed, this causes an increase in the sperm fragmentation index.
ROS test
Study of reactive oxygen species in native ejaculate
Price: 1500 rub.
If semen contains excessive amounts of free radicals (reactive oxygen species), they are likely to damage the integrity of sperm DNA and cause fragmentation. Learn more about the sperm oxidative stress (ROS) test
Spermogram deviations from the norm and IVF
Almost 50% of men have certain deviations from normal spermogram parameters. For some of them, it is enough to establish a daily routine and rest, rationalize nutrition, give up bad habits - this improves the quality of sperm and increases fertility (the ability to fertilize).
But in some cases, only IVF will help to conceive a child, the procedure of which includes a selection of active and without pathological deviations from the morphology of sperm.
If the spermogram results are pathological (presence of azoospermia, teratospermia, necrospermia, asthenozoospermia, etc.), the IVF procedure is extended, one of the stages of which is ICSI.
ICSI is an assistive technology and consists of several stages:
- obtaining viable sperm from the testicle using microsurgical operation;
- sperm cultivation;
- choosing the best and most active sperm;
- introduction of sperm into the egg using intracytoplasmic injection;
- freezing remaining viable sperm for future use.
In addition to abnormal sperm analysis, ICSI is performed in the presence of antisperm antibodies in both women and men.
Methods to improve sperm quality
In addition to eliminating inflammatory and endocrine diseases, the treatment of which is prescribed by a doctor (antibiotics and hormones), to improve sperm quality, you must follow simple rules:
Temperature
The testicles are the only organ that is located outside the abdominal cavity. Consequently, heating the testicles contributes to the deterioration of sperm quality: sperm activity decreases and pathological morphological forms appear.
Accordingly, you should refuse to take frequent hot baths/showers, visit the bathhouse and sauna less often, and give up the pleasure of soaking in a jacuzzi.
In addition, clothing (underwear and trousers) should be loose and not put pressure on the testicles or overheat them. It is recommended to avoid tight-fitting panties and tight jeans.
Avoid stress
Stressful situations “hit” not only the nerves, but also the sperm. If possible, conflicts, overwork, and nervous tension should be avoided.
Sex life
The rhythm of sexual life plays an equally important role in the quality of sperm. Too infrequent sexual intercourse leads to a decrease in sperm motility, and, on the contrary, frequent intimate contacts make the sperm “liquid,” that is, the sperm content in it is significantly reduced.
The optimal rhythm of sexual life is 4-6 times a week.
Deviations from the norm
- oligozoospermia – low sperm concentration;
- asthenozoospermia – low sperm motility;
- teratozoospermia – reduced number of morphologically normal forms;
- azoospermia – there are no sperm in the ejaculate;
- aspermia – no ejaculate;
- oligospermia – sperm count less than 2 ml;
- leukospermia – increased number of leukocytes;
- akinospermia – all sperm are immobile;
- cryptospermia is a very low sperm count, which is determined only after centrifugation of the ejaculate.
For repeated miscarriages or delays in fetal development
DNA fragmentation
in sperm
Price: 8500 rub.
The connection between successful pregnancies and DNA damage transmitted by men was established not so long ago. And this discovery created a real breakthrough in the field of infertility treatment for couples who have no problems conceiving, but have problems with pregnancy. The analysis allows you to determine the number of sperm with damaged DNA. It is fertilization with such sperm that can cause miscarriage or arrest in fetal development. Read more about sperm DNA fragmentation