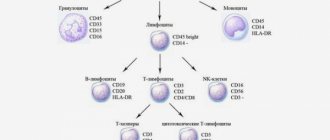
What is a coagulogram and why take it during pregnancy?
Coagulogram is a blood test showing the level of its coagulation in the body (hemostasis). In medicine, a coagulogram analysis is also called a hemostasiogram. The study is complex, as it requires studying the coagulation and anticoagulation systems.
Why is a coagulogram needed? The condition of the circulatory system is an important indicator of health. During gestation, many changes occur and the functions of the circulatory system are no exception. Hemostasis indicators increase as the human and female body adds an additional circle of blood circulation, and it prepares for blood loss during childbirth.
Any changes in coagulogram parameters should alert the expectant mother. If the level of hemostasis is reduced, then placental abruption and severe blood loss are possible. If elevated, there is a risk of thrombosis and fetal hypoxia during pregnancy. Of course, all this is bad for the child.
Insufficient or excessive blood clotting can lead to death
The formation of blood clots threatens blockage of the pulmonary artery vessels and vein thrombosis. A bleeding disorder can lead to spontaneous abortion.
First of all, it would be better to do a coagulogram for women with risk factors for pregnancy failure:
- hereditary poor blood clotting;
- a history of miscarriages and intrauterine fetal death, with gestosis;
- tendency to thromboembolism, heart attack, stroke.
If the indicator is reduced
A reduced level of prothrombin is dangerous because even a minor injury that damages a blood vessel can result in significant blood loss. After all, the formation of a blood clot occurs more slowly than it should.
A decrease in prothrombin levels is provoked by the following reasons:
- Certain liver pathologies, although most of them are accompanied by an increase in protein. The prothrombin content decreases in acute and chronic forms of hepatitis. Liver cirrhosis has a similar effect.
- Insufficient synthesis of vitamin K by the body. This process develops most often due to gastrointestinal ailments and dysbiosis.
- Deficiency of fibrinogen, a protein that is produced in the liver and then converted into fibrin, which is the basis of the clot during blood clotting. Such a deficiency can be either congenital or acquired.
- Taking medications for medicinal purposes that promote blood clotting.
It is possible to bring the prothrombin level back to normal, but anything should be done only after consulting a specialist.
Therapy is aimed at eliminating the ailments that caused the problem. Quite often, the basis of treatment is a special diet.
In some patients, the prothrombin time is reduced - a thrombus (blood clot) forms much faster than required. This is also a dangerous condition that can lead to the development of vascular blockage.
Quite often, a decrease in PT indicates the presence or risk of thrombosis, which is extremely dangerous, as it is often a threat to the patient’s life. A decrease in the indicator is often associated with taking certain groups of hormonal contraceptives. Polycythemia may also be a cause. Pregnant women's blood clots much faster in the third trimester of pregnancy.
DETAILS: Cognac increases or decreases blood pressure
Advanced blood clotting test parameters
The coagulogram can be regular or detailed. In a typical study, 4 main indicators are checked:
With an expanded coagulogram, other indicators are added. They are all interconnected. Minor fluctuations in one indicator may lead to violations of the second.
APTT (what is the norm)
APTT refers to the period required for a blood clot to form. The indicator should fall within the range of 23-35 seconds. During pregnancy, the activated partial thromboplastin time can be reduced to 17 seconds.
If the aPTT is prolonged during pregnancy, there is a risk of hypotonic bleeding, and if it is shortened, there is a risk of developing disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome.
Fibrinogen
This is a globulin group protein involved in blood clotting.
Fibrinogen levels, which are within normal limits, are 2-4 g/l, but its amount increases to 4.8 g/l in the 2nd trimester, and by the time of birth - to 6 g/l.
With a high level of fibrinogen in the blood, there is a possibility of infections and necrotic processes in tissues.
Thrombin time
This is the time during which fibrinogen turns into fibrin, which, in turn, turns into a blood clot, completing the process of stopping bleeding.
When a cut or injury occurs, blood cells clump together to form a plug
The normal thrombin time (TT) is 11-18 seconds.
Prothrombin (prothrombin index)
The norm of prothrombin during pregnancy is 78-140%, and indicates the activity of the plasma prothrombin complex in comparison with the plasma prothrombin time. An increase in PTI signals the risk of developing placental abruption.
Prothrombin time (PTT)
This is the time during which thrombin is formed from prothrombin, which is involved in the creation of a blood clot that stops bleeding.
The normal prothrombin time for pregnant women is 14-18 seconds.
Antithrombin III
This protein prevents blood clotting. Its values should be in the range of 71-115%.
If antithrombin 3 is reduced during pregnancy, this indicates a risk of thrombosis. Also, deviations from the norm can provoke the development of placental insufficiency and spontaneous abortion.
Platelets
These blood cells are contained in a blood clot that forms in a wound during bleeding. Normal platelet counts are 150-400 thousand/µl.
The test is taken from a vein, it is better to take it in the morning on an empty stomach
A decrease in platelets signals either a decrease in their synthesis or a high level of destruction. A decrease in indicators may indicate malnutrition and the threat of developing disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome.
International normalized ratio (INR)
INR is the calculated coagulogram value, which shows the ratio of a woman’s prothrombin time and the normal average prothrombin time. The international normalized ratio (INR) indicator allows you to monitor the state of the coagulation system if you take blood-thinning drugs (for example, the anticoagulant in the normal course of pregnancy Curantil).
Normal INR levels are 0.8-1.2. During treatment with anticoagulants – no more than 2.5.
Prothrombin in the blood is high
According to the Kwiku method, prothrombin protein is high and exceeds 150.0%.
Reasons for the increase:
- DIC syndrome;
- Fibrin deficiency;
- Genetic predisposition;
- The use of drugs from groups: coagulants, antibacterial agents, heparins, as well as laxatives.
You can reduce the level of prothrombin in the blood with the help of a diet with a maximum content of foods that have a blood-thinning effect:
Oatmeal porridge;- Tomatoes, tomato juice, and beets;
- Consume olive oil;
- Use apple cider vinegar;
- Sour fruits;
- Fish, omega 3 fat.
How to prepare and donate blood for a coagulogram?
It is customary to donate blood for a coagulogram 3 times during pregnancy:
- during registration;
- at 22-24 weeks;
- at 30-36 weeks.
If necessary, unscheduled blood donation is carried out:
- infertility prior to pregnancy;
- previous miscarriage;
- presence of complications;
- phlebeurysm;
- increased bleeding;
- long-term therapy with anticoagulants.
In order for blood clotting indicators to be reliable during pregnancy, you need to know how the test is taken.
- the study is carried out on an empty stomach;
- It is not recommended to eat 8-12 hours before the test, as well as drink coffee, tea, juices;
- You should not eat sweets, even chewing gum. Only clean water without gas is allowed;
- You should not overexert yourself half an hour before the test. A woman should be emotionally calm.
Don't be nervous, relax and drink a glass of water without gases - this will increase the accuracy of the result
Decoding the coagulogram of pregnant women (normal values in the table)
Interpretation of blood results in pregnant women is carried out by a doctor in the antenatal clinic, as they may have errors associated with a lack of vitamins, lack of nutrition, or if you take certain medications. The specialist takes into account all these factors when deciphering the study.
If the coagulogram parameters are normal, a conclusion is made about isocoagulation or something else. If there are deviations, the doctor tells you what treatment during pregnancy and what is possible, what pills to take. See the norms during pregnancy in the table.
Coagulogram during pregnancy: detailed breakdown of indicators:
| Index | Norm |
| Fibrinogen | 1st trimester – 2-4 g/l; |
3 trimester – 6.
2nd trimester – 1000;
3rd trimester – 1500.
List of possible pathologies
If the results of a coagulogram during pregnancy are deviated upward or downward, this indicates the development of pathologies:
- diabetes mellitus in pregnancy;
- kidney or liver disease.
The first results are noticeable immediately after sampling. Usually the tests are ready in about a day
If blood clotting is absent, this leads to uterine bleeding and miscarriage. When blood clotting increases, there is a risk of blood clots forming, which cause oxygen deficiency in the fetus, that is, its hypoxia.
Changes in hemostasis values are possible with late toxicosis of pregnant women, which is fraught with serious consequences:
- premature birth;
- intrauterine developmental delay;
- renal and heart failure;
- placental abruption.
When checking the indicators, the doctor looks at the lupus coagulant. During the normal course of pregnancy it should not be present. If it is present, this indicates autoimmune pathologies and the development of diseases such as:
- rheumatoid joint damage (arthritis);
- Libman-Sachs disease (lupus);
- ischemic stroke (cerebrovascular accident);
- spontaneous abortion;
- intrauterine death of a child;
- placental infarction (abrupt cessation of blood supply to the placenta);
- thrombosis of blood vessels.
During pregnancy, the likelihood of developing disseminated intravascular coagulation increases. It is caused by a violation of the blood coagulation system due to the following situations:
- premature placental abruption;
- gestosis;
- entry of amniotic fluid into the woman’s bloodstream;
- placenta previa;
- liver pathologies;
- high blood pressure;
- antiphospholipid syndrome;
- Rhesus conflict;
- infections, hormonal imbalances that threaten pregnancy;
- hemorrhagic shock;
- chronic maternal pathologies (diabetes mellitus, kidney disease, systemic pathologies).
You should not look for transcripts of analyzes on the Internet. Only the attending physician can correctly interpret test results.
If you decipher in time what kind of analysis it is, you can promptly identify the pathology and increase the chances of preventing its further development.
Prothrombin is increased
An increased level of prothrombin in the blood indicates that blood clotting is greater than normal. This means that it becomes too viscous, which impedes blood circulation and leads to blockage of blood vessels.
The following ailments can provoke an increase in prothrombin levels, and therefore blood clotting:
- malignant neoplasms;
- liver pathologies;
- thromboembolism;
- polycythemia;
- progressive angina.
An increase in the amount of protein can also be caused by the following factors:
- an excess of vitamin K in the body, with the help of which prothrombin is produced;
- use of anticoagulants, antibiotics, nicotinic acid, and hormonal contraceptives in therapy. Excessive use of aspirin, anabolic steroids, and laxatives can also affect the increase in prothrombin.
Quite often, the protein content increases during pregnancy. Most often it appears in the last trimester and does not require treatment.
If prothrombin according to Quick is elevated, what could cause this result and what measures should be taken? An increase is indicated by a prothrombin indicator of more than 150%.
The following factors can lead to this:
- Many diseases characterized by a decrease in vitamin K.
- DIC syndrome.
- Diseases that interfere with the normal production of fibrin.
- Heredity and other pathologies that can lead to clotting problems.
- An increase in the indicator can be caused by medications when used for a long time, for example: Aspirin.
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics.
- Heparin.
- Anabolic.
- Laxatives.
- Methotrexate.
- Nicotinic acid.
If a woman is diagnosed with a serious cardiovascular disease, the use of hormonal contraceptive pills should be immediately discontinued. You can replace them with an analogue in the form of suppositories or a vaginal ring.
Causes of deviations in coagulation from the norm
Below is a table of deviations of coagulogram parameters from the norm and possible causes:
| APTT | 17-20 sec. |
| Thrombin time | 18-25 sec. |
| Platelets | 150-400 thousand/µl. |
| D-dimer | 1st trimester – 750 ng/ml; |
| Lupus anticoagulant | |
| Antithrombin III | 74-115% |
| Prothrombin | 78-142% |
| Index | Norm | Deviations | Possible reasons |
| APTT | 15-20 sec. | Increase to 25-39 sec. Or decrease to 10-12 seconds. | vitamin K deficiency; |
· DIC syndrome.
· heart attack.
Prothrombin according to Quick
Quick analysis is done for additional examination of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as the liver.
Quick analysis is performed in the following cases:
- When clotting is impaired.
- There are ailments associated with the liver.
- There is a process of increased thrombus formation.
- With a disease such as blood cancer.
- In cases associated with vitamin K deficiency.
What limits of indicators are acceptable:
- Up to 6 years – 80–100.
- From 6 to 12 - 79–102.
- From 12 to 18 - 78–110.
- From 18 to 25 - 82–115.
- From 25 to 45 - 78–135.
- From 45 to 65 - 78–142.
The norm for women and the norm for men, regardless of age, are identical.
Prothrombin time is an indicator that reflects the seconds during which plasma coagulates after adding the desired mixture to it.
- In children, especially newborns, this figure is 14–18 seconds.
- For adults, the normal figure is 10–15. The optimal value of prothrombin time ranges from 9–12 seconds.
The test allows you to identify the activity of factors in the prothrombin complex of the patient’s blood when compared with the known PTT of “normal” plasma. This method is undoubtedly more informative compared to calculating the PTI. Prothrombin according to Quick determines FII in a patient, based on a calibration graph (the dependence of PTT on the total, total, activity of all participants in the reaction - factors of the prothrombin complex of diluted “healthy” plasma).
Normal prothrombin values according to Quick vary within a wider range than PTI, and normally range from 75 to 140%. In women, the upper limits of normal are usually lower. The results of the analysis may depend on the age of the patient, the treatment he is taking (anticoagulants), and the sensitivity of the reacting substances.
Prothrombin according to Quick, first of all, decreases during treatment with indirect anticoagulants (INR increases in this case), therefore, when monitoring anticoagulant therapy, this fact should be kept in mind first of all and, taking it into account, the patient’s blood is analyzed in one way and in one CDL.
Prothrombin values according to Quick and PTI (prothrombin index) often give the same results in the normal range. As for the zone of low values, here the results vary noticeably, for example, you can get the following test answers: PTI - about 60%, and prothrombin according to Quick - 30%)
Changes in coagulogram parameters by trimester
Normal hemostasis is the key to successful pregnancy and easy childbirth. Therefore, special attention is paid to the quality of blood clotting. During this period, the amount of blood in a woman’s body increases, and any clotting failures are fraught with complications.
If you are taking any medications, tell your doctor about it.
A planned coagulogram is performed for pregnant women every trimester. If the doctor has doubts about the health of the expectant mother, blood should be donated more often. As pregnancy progresses, the normal coagulogram parameters change, which is why the study is carried out at least 3 times during pregnancy. Changes in parameters in a pregnant woman’s body are normal. This is how he prepares for the large blood loss that is inevitable during childbirth. It is important that hemostasis at this stage is high, and any bleeding stops quickly so that it does not threaten the mother and child.
- In the early stages, platelets fibrinogen in the blood of a pregnant woman increase. Shorter clotting periods appear;
- during pregnancy, fibrinogen is increased, and in the third trimester it increases to a level of 6 g/ml;
- D-dimer also increases. If in a healthy woman the level does not exceed 250 ng/ml, then by the 3rd trimester of pregnancy it reaches 1500 ng/ml;
- One coagulogram indicator that should not change throughout 9 months is the prothrombin index. Its increase indicates a developing process of detachment and a serious danger for the child.
About the author : Borovikova Olga
gynecologist, ultrasound doctor, geneticist
Graduated from the Kuban State Medical University, internship in the specialty “Genetics”.
Thrombin time is one component of a clinical blood test that is required to evaluate a bleeding or thrombotic disorder. A significant percentage of people with reduced or dysfunctional fibrinogen may have no symptoms. It may then be diagnosed if an abnormality is detected during testing or if there is prolonged bleeding after a surgical procedure or injury.
Decreased prothrombin
If the prothrombin index is low, this may indicate excessive activity of the prothrombin protein. A decrease may be observed in pregnant women, those suffering from polycythemia (this is increased blood viscosity), and patients with venous thrombosis.
A decrease in the indicator may indicate the following diseases:
- Gastrointestinal diseases.
- Dysbacteriosis.
- Prothrombin deficiency.
- Hypovitaminosis.
- Oncological diseases.
- Allergic reaction.
Typically, specialists prescribe their patients the use of medications such as heparin and warfarin.
In conjunction with drug treatment, you need to monitor your diet. Here is a list of foods that are not recommended for consumption if prothrombin levels are low:
- Animal fats.
- Buckwheat porridge.
- Beets, red cabbage, red pepper.
- Bakery products.
- Pickling and smoking.
- Greenery.
- Legumes.
Failures in prothrombin levels can lead to bleeding. They can be prevented if you include the right foods in your diet as preventive measures:
- Fish and fish oil.
- Onion and garlic.
- Citrus fruits, especially lemon.
- Ginger root.
- Green tea and cocoa.
- Oatmeal.
- Cranberries, raspberries or figs.
What is thrombin time
When an injury occurs and bleeding begins, the body forms a blood clot at the site of injury to stop blood loss. Small fragments of cells called platelets stick together, accumulate and become activated at the site of injury. At the same time, the coagulation cascade begins and proteins called coagulation factors, including fibrinogen, are activated. Fibrinogen is then converted into insoluble strands that are stitched together to form a fibrin network that adheres to the site of injury. Along with platelet adhesion, this creates a stable clot and prevents additional blood loss by remaining in place until the injury heals.
To form a clot, a sufficient number of functioning platelets and coagulation factors is necessary. If there are dysfunctional factors or platelets, or too few of them, it can lead to bleeding episodes or abnormal blood clotting.
Thrombin time in a blood test evaluates the part of the hemostatic process in which soluble fibrinogen is converted into fibrin threads. This means that it measures the rate of fibrin clot formation after adding a standard amount of thrombin to the plasma. It is influenced by the level or function of fibrinogen and the presence of inhibitors such as heparin, fibrinogen degradation products. By adding thrombin to the test sample, it bypasses other clotting factors and focuses on fibrinogen function.
Blood clotting tests are based on something that happens artificially in a laboratory setting. The test alone has insufficient diagnostic value and must be interpreted in the context of additional coagulation tests.
Methodology for studying prothrombin time
To determine the prothrombin time, fresh plasma from the patient being studied is used. The blood is collected in a tube containing sodium citrate to bind blood calcium. Next, the sample is mixed, centrifuged, and an excess amount of calcium is added at a temperature of 37C to restore the blood’s ability to clot. After this, tissue coagulation factor (better known as factor III) is added and the time of blood clot formation is noted.
It should be taken into account that in some pathologies the prothrombin time may be increased or decreased.
Prothrombin time is increased with:
1. Congenital deficiency of certain blood coagulation factors such as II (prothrombin), V (Proaccelerin), VII (Proconvertin), X (Stewart-Prower factor).
2. Acquired deficiency of blood coagulation factors resulting from diseases (chronic liver and kidney diseases, amyloidosis, autoimmune diseases).
3. Disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome (DIC syndrome), which develops in blood diseases, including cancer.
4. The use of indirect anticoagulants (warfarin) in the main therapy.
5. Developmental hypovitaminosis K (for diseases of the pancreas and gall bladder, dysbacteriosis, malassorption syndrome).
6. An increase in the level of antithrombin in the blood.
The use of certain drugs also leads to an increase in prothrombin time (some antibiotics, steroid hormones, laxatives, acetylsalicylic acid in doses exceeding therapeutic ones).
Prothrombin time is reduced with:
1. Polycythemia.
2. Pregnancy in the last trimester.
3. Thrombosis of deep veins of the lower extremities.
4. Use of acetylsalicylic acid in small doses.
5. Taking oral contraceptives.
The norm and reasons for deviation from it: table
TV test results are measured in seconds. Normal values for men and women range from 11 to 18 seconds. This means that after adding chemicals, the blood requires this range of time to clot. The exact standards for normal values may vary depending on what reference values the laboratory uses. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor if there are any abnormalities.
Remember that abnormalities do not diagnose any specific disease. This only gives an idea of the time it takes for the blood to clot. Multiple diseases and conditions can lead to abnormal results.
Thrombin time testing is considered one of the important methods prescribed several times during pregnancy.
Indicators reflecting the rate of transformation of fibrinogen into fibrin make it possible to prevent a number of complications during pregnancy and childbirth. Therefore, it is worth considering the main indications for such an analysis and the features of its implementation.
What factors can affect the accuracy of the result?
The prothrombin time test may become unreliable not only because the person was taking anticoagulants, but also due to poor nutrition, taking medications, and dietary supplements.
What prolongs the clotting process
- products - alcoholic drinks, excessively fatty foods, beans, soybeans, green vegetables;
- medicines - from the groups of antibiotics, anabolic steroids, heparins;
- high dose aspirin, diuretics, reserpine, laxatives and other drugs.
- foods with high concentrations of vitamin K;
- medications - Vikasol, vitamin C, antihistamines, corticosteroids, barbiturates, drugs with a high caffeine content, xanthines, contraceptives (oral), many others.
- In addition, the value of prothrombin time is affected by dehydration of the body, which appears as a result of excessive vomiting, diarrhea and other factors.
Deviation from the norm or unreliable data in diseases can be obtained if the patient consumed before the analysis:
- a lot of alcohol;
- green vegetables, especially broccoli, spinach, lettuce;
- fish with a high fat content;
- green tea;
- liver.
Blood thinning products
Changes in indicators are also caused by medications:
- antibiotics;
- hormonal drugs;
- anabolics;
- anticonvulsants;
- diuretics;
- contraceptives in tablets;
- aspirin, paracetamol, indomethacin;
- heparin.
Smoking, vomiting, fever or diarrhea may affect the results.
In some cases, the result of the study may be inaccurate. The following factors can increase blood clotting time:
- Consumption of alcoholic beverages, excessively fatty foods, legumes and some vegetables.
- Therapy using drugs. These include some antibiotics, anticoagulants, anabolic steroids, heparin, diuretics, and laxatives.
The following factors can make the time period shorter:
- Eating foods high in vitamin K.
- Dehydration after prolonged diarrhea or vomiting.
- The use of antihistamines, contraceptives, caffeine-containing products.
In order to increase the accuracy of the study, a few days before blood sampling, the patient should stop drinking green tea, products containing soy, pork and beef liver, greens, any types of cabbage and legumes, and alcoholic beverages.
Indications for analysis
A pregnant woman needs to maintain normal blood clotting rates during all trimesters.
But this analysis becomes especially important:
- if the doctor detects signs of fibrinogen defect or deficiency;
- when the woman was prescribed heparin therapy;
- with identified DIC syndrome;
- for liver diseases;
- in the presence of substances indicating fibrinogen degradation;
- after diagnosing spontaneous abortion for a period of up to 22 weeks, two or more times.
During normal functioning of the human body, thrombin time is in the range of 15-18 seconds. When carrying a child, these parameters are slightly different. But if significant deviations from this condition are observed, timely medical attention is required.
Features of human hemostasis
Blood is considered a unique organ that is constantly in a liquid state. At the same time, the body's systems are organized in such a way as to ensure the constancy of the composition and physical parameters of the contents of the vessels.
Thus, the hemostasis system is considered a natural defense against blood loss when capillaries or large vessels are damaged. Thrombosis plays an important role in this process.
If during an injury the tightness of the vessel wall is broken, the concentration of thromboplastin in the blood increases, which triggers coagulation.
As a result, proteins are activated, creating a dense blood clot in the area of damage. Moreover, prothrombin, turning into thrombin, activates fibrinogen. It, in turn, is transformed into fibrin, which retains platelets in the damaged area.
The opposite process is fibrolysis. It leads to the resorption of already unnecessary blood clots. By maintaining a balance between the different properties of the blood, optimal functioning of the entire system is ensured.
A violation of thrombin time can be detected using a coagulogram. This study allows you to isolate the various components of blood and determine their compliance with regulatory criteria.
Thrombin time during pregnancy
How is a coagulogram performed?
Coagulation testing requires taking a sample from a vein. To ensure accurate data, it is important to ensure proper preparation for analysis. So, the sample must be taken in the morning on an empty stomach. About 8-12 hours should pass since the last meal.
Before going to the clinic, you need to give up tonic drinks: coffee, tea and energy drinks. Drinking alcohol, regardless of strength, is strictly prohibited.
If your health condition requires regular use of medications, you should notify the specialist in advance. Especially if the medicine affects the blood clotting factor.
During the procedure, it is recommended to calm down and relax your muscles as much as possible. A little cold water taken immediately before blood sampling will help alleviate the condition.
The samples taken are examined, resulting in results that can only be interpreted by specially trained people.
Features of studying hemostasiogram
First, specialists assess fibrinogen levels. In the normal state, its amount is 2-4 g/l. Deviations are often provoked by an inflammatory process or tissue necrosis. During pregnancy, the concentration of fibrinogen can increase to 6 due to the expansion of the circulatory system.
This test involves measuring activated partial platelet time, which is normally 24-35 seconds. As fibrinogen increases, the speed of the process increases, which reduces the time period to 20 seconds or less.
Doctors may be concerned about the discovery of a lupus anticoagulant, which should not be in the body of a pregnant woman. Their appearance may be a sign of autoimmune disorders or manifestations of pathologies in fetal development.
An important criterion for the state of the blood is the number of platelets. Their concentration is usually in the range of 150-400 thousand/µl.
Pregnancy can lead to a decrease in the indicator to 130. But a more significant decline is often caused by problems with the formation of new bodies, or with their increased consumption.
The first problem can be solved by changing the power system. The second sign is considered the main symptom of DIC syndrome. At the same time, the values of prothrobin, antithrobin III and D-dimer are calculated.
Prothrombin time, INR and prothrombin index - what is it?
Naturally, the rate of blood clotting when the outer layers of the vascular wall are damaged is not an absolute indicator. By the way, the normal PT should be from 11 to 16 seconds, and in order to obtain accurate data on the functioning of the body, additional tests are necessary.
Modern medicine uses the international normalized ratio, or INR. In such a study, the patient’s prothrombin time is compared with the same indicator of plasma normalized according to international standards. The formula looks something like this: patient PT/normalized plasma PT (the result is raised to the power of the so-called international thromboplastin sensitivity index).
The prothrombin index also determines the ratio of the control plasma PT to the patient plasma PT, but as a percentage. By the way, normally the index should be 95 – 100%.
Prothrombin time according to Quick is by far the most accurate test. This test compares the patient's prothrombin complex activity with that of control plasma.
The prothrombin index (PTI) is the ratio between the clotting time of “healthy” plasma (control) and the clotting time of the blood of a sick person. The result is calculated as a percentage (PTT of normal plasma: PTT of patient plasma x 100%), the norm is from 90 to 105%. The inverse ratio (clotting time of the patient’s blood: clotting time of “healthy” plasma), expressed as a percentage, is called the prothrombin ratio (PR).
A low prothrombin index and prolonged PTT result in many pathological conditions:
- Congenital deficiency of certain blood clotting factors (II, V, VII, X);
- Damage to hepatocytes during a chronic pathological process localized in the liver parenchyma;
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome;
- Hemorrhagic syndrome caused by low plasma fibrinogen content (fibrinogenopenia);
- Impaired fibrinogen polymerization (dysfibrinogenemia);
- Vitamin K deficiency;
- Carrying out anticoagulant therapy;
- The use of clotting factor inhibitors, such as heparin, which inhibits the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin.
A high prothrombin index (shortened PTT) is observed in the following cases:
- Formation of blood clots in blood vessels blocking blood flow as a result of various pathological conditions of the hemostasis system (thrombosis);
- Consumption coagulopathies (DIC syndrome);
- Excessive activation of the anticoagulant system, excessive formation of plasmin (hyperfibrinolysis), which leads first to bleeding, and then (with depletion of plasminogen) to thrombosis;
- Liver diseases;
- Increased activity of factor VII (traumatic tissue damage, necrosis);
- Activation of protective mechanisms in women during childbirth.
Thus, prolongation of PTT will reduce the prothrombin index and indicate possible hypocoagulation (low blood coagulability, tendency to bleeding). And, conversely, a reduction in clotting time (PTT) increases the values of the prothrombin index and indicates the presence of signs of hypercoagulation, that is, increased blood clotting (risk of developing thromboembolic conditions).
Causes and consequences of impaired coagulation parameters during pregnancy
During pregnancy, it is necessary to evaluate the state of the circulatory system more often, since in this condition the following are considered common phenomena:
- changes in hormonal levels;
- expansion of the circulatory system;
- launching preparatory processes for blood loss during childbirth.
If the health of the expectant mother and fetus does not cause concern, then the test is prescribed once per trimester. An unscheduled study is required for symptoms of gestosis in the form of hypertension, swelling of the extremities, and protein in the urine.
Signs of uterine hypertonicity will be a reason to further evaluate the blood condition. You should be more attentive to the condition of a pregnant woman whose close relatives suffer from the consequences of a heart attack, stroke, varicose veins and other pathologies of the circulatory system.
If you miss the fact of a clotting disorder, it can contribute to the formation of DIC syndrome. It is characterized by a slight increase in fibrinogen levels in the first weeks after conception with a decrease in the concentration of the substance in subsequent periods.
Such a violation can cause severe blood loss during childbirth, which will endanger the life of the mother.
The cause of the pathology may be related to:
- bleeding accompanying premature placental abruption;
- amniotic fluid embolism;
- endometritis.
Elevated levels of fibrinogen can lead to antiphospholipid syndrome, which is associated with increased blood clot formation. If you ignore the pathology, the chances of bearing a child are reduced to a minimum.
What to do with an increased prothrombin level
How to reduce prothrombin level? This category of people must adhere to a certain diet and lifestyle.
You need to eat as many foods as possible that help thin the blood. It is important to understand that there are a number of foods that can cause blood to thicken.
List of necessary ingredients to lower prothrombin levels:
- Everyone knows oatmeal. Oatmeal not only helps stabilize digestion, but also prevents blood thickening. Ideally, you should consume this dish as breakfast. If desired, you can supplement the porridge with fresh berries.
- Tomato juice, especially when made from fresh vegetables yourself. Many people make the grave mistake of adding salt to juice.
- Beetroot is an ideal vegetable that helps reduce prothrombin levels.
- What is a diet without ginger? It can be added to tea. Ginger root thins the blood and prevents the formation of blood clots.
- Flaxseed oil, olive oil.
- Fish fat. Currently, it can be purchased in pharmacies in capsule form. This is an excellent odorless and tasteless option.
- It is recommended to use apple cider vinegar during cooking.
- A pineapple. It is enough to eat just a little to trigger beneficial processes in the body.
What rules should you follow during the diet:
- Give preference to vegetables, fruits and fresh berries.
- Meat may be present on the table, but in minimal doses.
- Meat can be replaced with fish.
- Limit your consumption of baked goods.
- It is best to cook in a double boiler.
- You need to eat more often, but in doses.
- Be sure to drink regularly.
What not to eat or drink:
- Smoked meats.
- Fatty, rich soups.
- Canned food.
- Alcoholic drinks.