3
Author of the article: Marina Dmitrievna
2017.09.15
198
Blood analysis
The period of bearing a child is a serious test for the female body, therefore, during pregnancy, the expectant mother undergoes numerous tests and tests. Once a woman becomes pregnant, it is important to monitor her well-being before giving birth.
Monitoring blood counts is one of the main studies that makes it possible to monitor the health of the woman and the fetus. And if violations are detected, due to the frequency of tests performed, the likelihood of successful treatment is high due to timely diagnosis.
The indicator that doctors pay attention to is blood clotting. The norm in women during pregnancy changes at different stages, which does not always mean pathology, but needs to be monitored.
Coagulability during pregnancy and its features
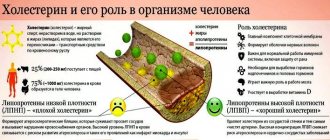
Clotting in medicine is called coagulation. Coagulation is an enzymatic protective reaction of the body, activated to stop bleeding in the event of a violation of the integrity of vascular tissues. Without the help of this protective mechanism, an injury threatens a person with bleeding, even death.
The coagulation mechanism is divided into 2 types:
- Primary hemostasis. Its activation occurs when small-diameter vessels are injured. The formed elements of blood, known as “platelets,” help to bridge the gap in the wall. By sticking together, these cells form a thrombus, which clogs the destroyed part of the epithelium of the vessel. At the same time, rapid contraction of the damaged tissue occurs. The second name of the mechanism is vascular-platelet hemostasis.
- Secondary hemostasis is known as “coagulation”. The process is noticeably more complicated and consists of several stages. Its activator is volumetric damage. During coagulation hemostasis, under the influence of enzymes, fibrin filaments are formed from a substance found in the blood - fibrinogen. The threads form a network that traps formed blood cells, the main part of which are red blood cells, and a blood clot forms.
Stop bleeding
Does hanging clotting affect conception?
Reference! They begin to find out the involvement of thick blood in the problem of childbirth after receiving a diagnosis of “infertility of unknown origin.”
Modern research has established that indeed, impaired hemostasis is a fairly common cause of problems with childbirth. The thickened blood does not reach the thinnest capillaries, and these are the ones that are located in the endometrium, which lines the uterine cavity and is the site of attachment of the embryo after the release of the fertilized egg through the fallopian tubes to the “main site of dislocation.”
As a result of poor blood supply, the endometrium grows slowly, and therefore the fertilized egg cannot attach to it. Thus, the expected pregnancy never occurs, and even if it does, the consequences can be very unfavorable, which we will discuss in more detail in the following sections of the article.
High coagulation rate during pregnancy
To be able to judge the high level of blood clotting during pregnancy, you need to know about the normal rate of the indicator in a woman during this period. Already at the beginning of the second trimester, physiological changes occur in the body of the expectant mother, which results in increased synthesis of substances that regulate the formation of blood clots.
This transformation is aimed at preparing the female body for the upcoming birth. Thanks to the care of nature after childbirth, the vessels located at the placenta separation site are able to tighten, saving the woman from blood loss.
An analysis indicating clotting during pregnancy, which a woman will have to do more than once, makes it possible to notice disruptions in this important process in time. The decoding of the study must be entrusted to a qualified specialist. Fluctuations in the standards of basic coagulation parameters can be found in the table below.
Coagulability is the norm for pregnant women
A blood test indicating high coagulability during pregnancy is a bad sign, signaling the risk of a condition called hypercoagulability.
Signs
Unfortunately, a woman cannot independently establish the connection between her blood condition and a failed pregnancy, since it is almost impossible to determine from external signs that this is the reason. Signs of diseases are detected using special laboratory tests.
Important! To identify blood pathologies that can affect conception, you need to contact a good hematologist and get tested.
You may need:
- general blood test with formula;
- extended coagulogram;
- antibody tests (lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin antibodies, anti-β-glycoprotein antibodies);
- d-dimer assay;
- fibrinogen test.
Reasons for concern are:
- increased hemoglobin level, taking into account that the norm for average women is 120-140 g/l (for smokers and those involved in sports, these figures may be higher);
- increased platelet level (normal 180–320 thousand units/μl);
- elevated fibrinogen levels, as well as d-dimer less than 0.5, which also indicates thick blood.
In any case , you should not make any diagnosis yourself - your condition should be assessed by a competent specialist.
Increased blood clotting during pregnancy: what is dangerous?
Hypercoagulation threatens the patient:
- Late toxicosis.
- Problems in child development.
- Premature placental abruption.
- Risk of miscarriage.
- Death of a child.
Symptoms of hypercoagulation include increased fatigue, drowsiness and headaches resulting from decreased oxygen supply to the brain. Possible disorders in the functioning of the intestines and other internal organs.
Clotting test: what is it called?
During a woman's pregnancy, doctors constantly conduct blood tests to help monitor the dynamics of the expectant mother's condition. An analysis that informs about the level of coagulation is called a “coagulogram”.
Attention! If the results of the study show that the indicator is higher than normal, the woman is at risk of activation of intravascular coagulation during pregnancy or DIC syndrome, meaning disseminated intravascular coagulation.[/vrach]
Material collection
At risk are women who became pregnant at the age of less than 18 years or after 40, with diabetes mellitus, pathologies of the kidneys and cardiovascular system, and patients who had hypercoagulation before planning pregnancy. It is especially important for them to get tested periodically.
Excessive clotting
Excessively thick blood counts are sometimes recorded during the collection of fluid for testing. In turn, the test conducted can confirm or refute this problem. The danger of increased coagulation during pregnancy is that disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome can be formed.
We are talking about improper blood circulation in the placenta, which leads to a lack of nutrition and oxygen for the fetus. This may be the reason for the formation of abnormal development. Severe cases sometimes result in spontaneous abortion. The risks of developing DIC and blood clotting with increased numbers during pregnancy become higher if certain factors are present.
We are talking about the presence in the woman’s family of vascular problems, varicose veins, thrombosis. It is important to take into account pregnancies that preceded the current one, if there were any, and they proceeded with problems. Sometimes, excessive physical activity before pregnancy can provoke the situation. This is sometimes observed in professional athletes.
Excessive blood thickness during pregnancy is usually treated with diet. We are talking about drinking plenty of water and foods that contain a lot of vitamin C. Don’t forget about light physical exercise. A woman may also be prescribed a special drug course. We are talking about medications that thin the blood.
Treatment of hypercoagulability
If you are diagnosed with high blood viscosity, you will need to use medications called anticoagulants. It depends on the nature of the disease whether anti-inflammatory drugs and antispasmodics will be needed. In case of complications, surgical removal of blood clots is allowed.
Important! The use of medications that have a thinning effect while carrying a child is fraught with consequences such as bleeding. For this reason, taking any drug should be discussed with your doctor.
Changing your usual diet and eating pattern helps to reduce viscosity to some extent. A woman is advised to drink 1.5-2 liters of clean drinking water during the day. The list of liquids includes green or herbal tea, juices from vegetables and fruits (give preference to natural juices).
As for products, eating seaweed and fish, onions and garlic will have a positive effect. Nuts and olive or flaxseed oil are useful for the expectant mother. Remember that the condition of the child depends on the health of the mother.
Doctors' recommendations
It is worth emphasizing right away that if there is a pronounced deviation of the blood clotting indicator in any direction, hospitalization of the woman is indicated. If we are talking about promotion, then while you are in the hospital, an anticoagulant drug will be selected. A slight increase is usually corrected with diet and drinking regimen.
In general, you need to consume about two liters of liquid. It is important to understand that this list also includes a variety of drinks. In the menu, it is important to pay attention to the presence of sufficient quantities of meat and fish, which will provide the body with proteins and fats. Don't forget about fruits and vegetables, which are rich in vitamins and iron. The greatest benefits in a state of increased coagulability will come from nuts, seaweed, bell peppers, garlic and onions.
If you like to cook with oil, give preference to vegetable oils without prior refining. We are talking about flaxseed or olive. You can add sprouted wheat to salads, which can compensate for the lack of vitamins.
If we are talking about a reduced indicator, then it is recommended to abandon hot and spicy dishes. Bad habits such as alcohol or smoking are prohibited. Of course, they are prohibited during pregnancy in principle, but some people neglect this prohibition.
Medicines associated with increasing thrombus-forming function are prescribed if a pregnant woman is sent to a hospital for hospitalization. Reception is carried out under constant monitoring using tests. Sometimes it is necessary to continue it for some time after childbirth.
It is mandatory to donate blood to check the coagulating function of girls who have given birth before the agreed date, miscarriage and stillbirth, unsuccessful attempts at IVF, or have been diagnosed with infertility.
In addition, total control over this blood indicator is carried out in patients under 18 years of age and after forty. If hypertension or other pathologies of the heart and blood vessels are present. Women with obesity and kidney disease must undergo such an analysis. The category of dangerous situations includes diabetes mellitus, negative living conditions, systemic illnesses and genetic predisposition.
Hello! I'm 26 weeks pregnant. At 18 weeks she was in the hospital. An examination (coagulogram) showed high blood clotting. D-dimer -1.5. They prescribed chimes 0.75 mg 3 times a day, but it didn’t help. Now, against the background of chimes, Fraxiparin was added, 3 ml by injection subcutaneously into the abdomen. Please tell me how serious this disease is, how to treat it and how it can affect the child. Thank you.
Hello! The dose of fraxiparine is monitored based on the duration of bleeding and can be increased until the coagulation system indicators become normal for your stage of pregnancy. Fraxiparine can be injected throughout pregnancy to prevent thrombosis, and then the pregnancy should proceed well and end in a normal birth. It is better to have 2 liters of single-group plasma in stock; it can be stored in the refrigerator for a long time. In case of bleeding or thrombosis during childbirth, transfuse single-group plasma. E.I.
Consequences when planning a child
Attention! Blood clots can lead to various complications when trying to get pregnant.
The first and main problem associated with thick blood is that the long-awaited pregnancy does not occur, despite the fact that the couple is sexually active without using contraception.
The second problem is the increased likelihood of ectopic pregnancy (a fertilized egg, moving slowly through the fallopian tubes due to poor blood supply to the reproductive zone, attaches prematurely, without reaching the uterine cavity). In this case, if special stimulation does not produce an effect, surgical intervention is often necessary.
The third difficulty is associated with the risks of miscarriage and the birth of a healthy child.
Possible:
- constant miscarriages at any stage of pregnancy;
- placental abruption;
- freezing of the fetus at the stage of intrauterine development, that is, frozen pregnancy;
- birth of a premature baby;
- anatomical defects in a newborn;
- delayed psychophysical development in a child.
And finally, thick blood can lead to disability of a pregnant woman, serious illnesses of the mother and child, and even (in case of untimely treatment) have fatal consequences.
Causes
The main causes of poor blood clotting:
- Lack of vitamin K leads to disruption of the synthesis of prothrombin, the precursor of thrombin. Vitamin B12 deficiency reduces fibrinogen levels in the blood. Similar deviations are observed in diseases of the liver and pancreas, especially with excessive alcohol consumption, and with chronic inflammation of the small intestine. The production of essential vitamins can be disrupted in a pregnant woman with the development of toxicosis, and the last trimester is considered the most dangerous.
- Uncontrolled use of certain groups of drugs. Of these, the most frequently used are: analgesics containing aspirin, a blood thinner and its derivatives; some anti-inflammatory and temperature-lowering agents; antibiotics; hormonal contraceptives and anabolics. Systematic self-medication leads to changes in blood coagulogram. People undergoing a course of treatment with fibrinolytics, such as heparin, troxevasin, are at risk. In particular, such prescriptions are made for diseases of the veins of the lower extremities.
- Impaired fibrinogen synthesis, which is usually a hereditary pathology.
- The development of malignant diseases, especially oncology of the hematopoietic organs, has a negative impact.
- Harmful natural and industrial factors that suppress hematopoiesis in general.
- Prolonged profuse bleeding.
Coagulation systems
A pathological condition such as poor blood clotting in men, women and children is often encountered. What is it and why is it dangerous?
There are three functioning blood coagulation systems in humans. They maintain the necessary balance in the body:
- hemostasis, responsible for the timely and effective formation of blood clots and the prevention of blood loss;
- anticoagulation, which counteracts blood clotting and protects the body from diseases such as stroke, vein thrombosis, and myocardial infarction.
- hemocoagulation prevents bleeding from small vessels - capillaries; it is more difficult to cope with venous bleeding, since the resulting blood clots are washed away by the blood flow. Localizes minor inflammatory processes by creating tiny blood clots around the source of inflammation, preventing the spread of infection through the bloodstream.
Currently, the process of human blood clotting is well studied, and this pathology can have several names depending on the deficiency of which component was the cause.