What does reduced monocytes mean?
The main task of monocytes is to protect the body from parasites, infections, and bacteria. In more detail, monocytes perform the following functions:
- Absorption of extinct tissues.
- Destroying pathogenic bacteria.
- Regulating the body's immune and inflammatory response.
- Restoration of damaged tissues.
- Correction of protein formation.
The norm of monocytes among adult patients is 3-10% of the total level of leukocytes (in children - 2-12%).
When levels decrease below 2-3%, monocytopenia - a reduced content of monocytes in the blood. However, monocytopenia is a rare phenomenon in which the immune system is weakened.
In addition, with the development of pathologies that are associated with monocytopenia, the level of leukocytes in the blood also decreases.
Normal blood levels in adults and children
If we talk about the quantitative content of monocytes in the blood, the norm of this indicator should be in the range of 3–11% (in a child, the number of these cells can fluctuate within 2–12%) of the total number of leukocyte elements in the blood.
Basically, doctors determine the relative quantitative content of these elements (for this, a general blood test is performed), but if serious disorders of the bone marrow are suspected, an analysis is carried out for the absolute content of monocytes, the poor results of which should alert any person.
Women (especially during pregnancy) always have slightly more leukocyte cells in their blood than men, in addition, this indicator may vary depending on age (children may have more).
How to check?
To obtain reliable information on monocyte levels, the patient should prepare for blood sampling as follows:
- The ideal period is the morning hours on an empty stomach. The last meal is 8 hours before the test.
- You should stop taking medications 4 days before blood sampling.
- The day before the procedure, it is necessary to exclude physical and emotional stress.
- Before taking blood directly, you should calm down and sit for a while.
- 3 days before the test, you should exclude fatty, spicy and other unhealthy foods, as well as alcohol, from your diet.
What are monocytes and how are they formed?
Stages of monocyte development
Monocytes are large and quite beautiful cells that have an irregular shape. They are like thunderclouds - plump, grayish, with a well-defined, but loose structure, single core. Sometimes the kernel can take on rather bizarre shapes (walnut, butterfly, mushroom, horseshoe, etc.), but normally it looks like a bean. It is most often located off-center and occupies half or most of the core.
Monocytes are formed in the bone marrow from promonocyte cells. They enter the bloodstream immature, circulate there for 12–32 hours, and then some of them die, and some are released into the tissues. Most often these are lymph nodes, liver, lungs, and spleen. In the tissues they mature completely, increase in size, and sometimes merge with each other, forming giant forms. There they live for up to 30 days. Able to move to the site of inflammation or the introduction of foreign objects. They synthesize and secrete various active substances.
Reasons for the downgrade
The causes of monocytopenia should be divided into physiological and pathological. Thus, a temporary decrease in monocytes is most often associated with the following factors:
- Prolonged fasting.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Constant stress.
- Postoperative period.
Do you want to know about the reasons for the increase in monocytes? Then follow this link.
- Pregnancy.
- Recovery period after illness.
- Chemotherapy for oncology.
- Long-term use of hormonal drugs.
- Poisoning.
- State of shock after injuries, burns, significant blood loss.
Pathological causes of monocytopenia include:
- Infectious diseases, for example, sepsis, typhoid fever, leukemia.
- Anemia.
- Gangrene.
- Pancytopenia (bone marrow damage).
- Hepatitis.
- Oncology.
- Worm infestation (among children).
Causes of the pathological condition
An analysis showing the level of monocytes is an important research method in the diagnosis of various diseases. Rare causes of leukocyte syndrome include:
- the presence of parasitic infections, malaria;
- poisoning with chemical reagents (phosphorus, tetrachloroethane);
- long-term treatment with glucocorticosteroids, consequences of smoking;
- signs of recovery of the hematopoietic system after chemotherapy.
In people from birth to the age of 16 years, the relative indicators of the largest leukocytes fluctuate upward or downward. Absolute values are characterized by a downward trend. In healthy adults, the norm established after 16 years of age should remain unchanged until old age.
With all the variety of pathological causes of monocytosis in adult patients, it often signals the fact of recovery after the acute stage of an infectious disease.
Among the factors that provoke the syndrome, doctors name reduced immunity against the background of viral and colds. In this case, along with monocytes in the blood, platelets also increase.
Immune disorders also provoke rheumatic lesions of the heart and joints, postoperative conditions. For men and women, leukocyte norms are the same, but for children they have their own specifics.
Division by gender
In men, the causes of the pathological condition are due to heavy physical and stressful loads, and a high level of mental stress. For women, a slight increase in white blood cells is associated with ovulation, as well as the onset of menstruation, which is explained by hormonal fluctuations.
Due to the restructuring of the female body during pregnancy, the values of all parts of the leukocyte mechanism change. The 1st trimester is characterized by a low threshold of nurse cells. As we move towards the 3rd trimester, the concentration of young macrophages tends to reach a maximum. Among the pediatric category of patients, newborns have the highest percentage of monocytes.
Impact of viral infections
Colonies of immune system defenders are part of the first line of anti-infective defense of the human body. During migration through tissues, young phagocytes are transformed into macrophages, which, during phagocytosis, actively absorb foreign agents, releasing special substances, cytokines and mediators. Therefore, the consequence of viral infections is detected monocytosis.
| Causes of increased leukocyte levels | Types of infectious diseases |
| Acute period of viral infection | In adult patients, influenza and ARVI are among the most common causes of monocytosis. The onset of the syndrome occurs at the onset of the disease, followed by a decrease in the number of “orderlies” together with the extinction of the symptoms of inflammation. |
| Development of infectious mononucleosis | The reason for the appearance of monocytosis is associated with the slow development of viral cells in the body. A sluggish process can last not only months, but can last for years. |
The danger of monocytosis is associated with the onset of immunosuppression associated with hidden changes in the functions of the immune system. If, simultaneously with monocytes, the levels of neutrophils are increased, the process is called neutrophilia, the cause of which is explained by purulent processes. With a concomitant increase in eosinophils, there is reason to suspect allergic diseases and specific types of inflammation.
Bacterial infection
Diagnosis of monocytosis may be a manifestation of chronic pathologies of a bacterial nature, accompanied by tissue proliferation (proliferation) at the final stage of inflammation. The main causes of the pathological condition include:
- tuberculosis, which can affect a number of organs;
- the development of brucellosis, a zoonotic infection prone to chronicity;
- signs of syphilis, systemic venereal pathology.
A similar symptom of an increase in monocytes is associated with bacterial endocarditis in the subacute period, rickettsioses caused by a common pathogen. The pathogenesis of these conditions is similar to viral monocytosis. The reason for the increased volume of white blood cells lies in the ineffective process of phagocytosis, when macrophages that have absorbed bacterial agents are not capable of destroying them. In this case, macrophages become defenders of harmful cells that actively multiply. Cytokines released by macrophages stimulate an increase in nurse cells, which maintains the course of chronic inflammation.
The danger of systemic granulomatosis
The reason for the detection of monocytosis is sometimes associated with low-grade non-infectious inflammation. The result of a chronic process is the launch of an indirect immune response at the cellular level. A dangerous situation leads to the accumulation of lymphocytes together with mast cells in the tissues of various organs, which culminates in the formation of giant cell granulomas.
The reason for the sharp jump in the number of monocytes above 20-40*109 per liter of blood indicates the development of an oncological process in the patient’s body.
In the process of granulomatosis, macrophages provide support for chronic inflammation, which is characteristic of sarcoidosis, Wegener's granulomatosis, which leads to necrotizing vasculitis of the bloodstream.
If the cause of monocytosis is associated with chronic infectious inflammation, the infection affects the nasopharynx, descending into the lungs, spreading through the heart and bone tissues, reaching the pelvic organs. To reduce the number of monocytes, it is necessary to select optimal therapy.
Connective tissue pathologies
The mechanism for the formation of an increased number of large leukocytes in collagenosis is not reliably known. A group of diseases united by a number of similar changes in the structure of connective tissues is characterized by the spread of inflammation to various organs, skin, and musculoskeletal system. Chronicity of the condition in adults is associated with the development of systemic lupus and scleroderma; in children, the cause of monocytosis is polymyositis, which affects the muscles of the limbs with subsequent atrophy of muscle tissue.
Oncohematology and malignant processes
The cause of a sudden increase in the monocyte count in most cases is recognized as oncohematological pathologies. The outcome of a serious illness, even with timely treatment, is not always favorable. Among blood diseases, monocytosis is caused by two pathologies:
| Name of the disease | Brief information |
| Acute form of leukemia | The monocytic and myelomonocytic varieties of the disease are caused by the identification of monocyte precursors in the structures of the bone marrow and blood. Symptoms of leukemia (anemia, bleeding) lead to an unfavorable prognosis. |
| Myeloma leukemia | Signs of blood cancer, as a result of damage to a special type of leukocytes (plasmocytes), mainly affect older adults (after 60 years). Manifestations of the disease include bone damage and decreased immunity. |
The formation of other types of malignant neoplasms is also based on an increase in the leukocyte count. The dominant causes of monocytosis are the monocytic type of leukemia (monoblastosis) and Hodgkin's syndrome (lymphogranulomatosis) with signs of malignant hyperplasia of lymphoid tissue. The development of lymphopenia due to a decrease in the level of lymphocytes progresses against the background of a combined variation of severe immunodeficiency, which can be hereditary.
Decrease in indicators during pregnancy
A slight decrease in monocytes for pregnant women is a natural state, since the functioning of the immune and endocrine systems of the body changes.
Consequently, the norm of monocytes among pregnant women is 3-6% of the total number of leukocytes. Due to these indicators, many women suffer from frequent colds.
Therefore, every woman must observe a number of preventive measures, namely: sufficient consumption of fruits, vegetables, dairy products, meat; daily walks in the fresh air; sleep - at least 8 hours; reduction of stressful situations.
Important! Monocyte counts stabilize a few weeks after the baby is born.
Types of disease
Monocytosis has 2 types: relative and absolute. Relative monocytosis is determined by the ratio of the number of monocytes to the remaining leukocytes, that is, neutrophils, basophils and eosinophils.
In most cases, the laboratory technician enters the absolute value into the blood test result form. Patients most often see a relative type of pathology in the analysis: monocytic cells in a normal state range from 3 to 7%, relative monocytosis increases from 8% and above.
It has a characteristic feature - the total number of leukocytes remains at a normal level.
If monocytes increase, then leukocytes or granulocytes decrease. But diagnostics does not take this fact into account.
Absolute monocytosis is characterized by a large number of monocytes, while other leukocytes also increase.
Such a change in monocytes requires a complete examination of the person in order to make an accurate diagnosis.
Children and monocyte levels
Monocytopenia among children develops when levels decrease below 2%.
| Age, years | Norm, % |
| Newborns | 3-12 |
| Up to 2 weeks | 5-15 |
| 2 weeks - 1 | 4-10 |
| 1-2 | 3-10 |
| 2-16 | 3-9 |
Most of the pathological and physiological causes of monocytopenia among children coincide with similar indicators among adult patients. The main difference is that in children there are sharp jumps in the level of monocytes due to the active growth and development of the body.
In case of monocytopenia, you need to contact your pediatrician to identify the causes of this deviation. After identifying the pathology, the child is prescribed an individual course of treatment. For example, with the development of helminthic infestation, antibiotics are required.
Norm of monocytes in the blood (table)
Determination of the number of monocytes is carried out using a clinical blood test with a leukocyte formula (includes the absolute and relative number of all types of leukocytes in the plasma).
| Age, years | Absolute indicator, x10⁹/liter | Relative indicator, % |
| To 10 | 0,09-0,8 | 1-6 |
| 10-23 | 0,09-0,8 | 1-7 |
| After 23 | 0,09-0,8 | 1-8 |
Relative monocytosis does not have significant diagnostic value, as it can be caused by a decrease in other parameters of leukocytes (in most cases, neutrophils).
What to do?
The main goal with monocytopenia is to eliminate the causes that led to the appearance of this symptom, since reduced monocytes are not a separate disease.
You can learn more about monocytes from the following video:
The first stage is a visit to the doctor, who prescribes additional examination and ways to eliminate the established pathology. Basically, treatment includes items such as:
- Changing your diet - you should eat more: meat; rose hip; red fish; buckwheat; garlic; spinach; celery; nuts; onion. At the same time, it is worth reducing the consumption of salt, sugar, and carbohydrate products.
- Taking medications – should only be taken with a doctor’s prescription.
- Daily walks in combination with gymnastics (in the absence of contraindications).
- In case of serious deviations, surgical intervention is required.
Important! Self-medication for monocytopenia is unacceptable.
In conclusion, it is worth recalling that the main task of monocytes is the destruction of harmful microorganisms that can harm the body. Therefore, the patient should pay attention to the level of monocytes after blood sampling, because deviations from the norm often lead to the development of serious pathologies, which are discussed in our material.
For what purpose is the level of monocytes determined?
Dietary supplements
Monocytes are one of the important components, the main components of which give the doctor a general idea of the patient's health status. Both an increase and decrease in monocytes, which can be observed in children and adults, indicates the development of some kind of internal disorder. Monocytes are examined especially carefully when examining pregnant women, because during pregnancy the immune system directs all its forces to preserving the health of the fetus, so a variety of bacteria enter the woman’s body, with which all types of lymphocytes wage a continuous struggle.
pregnancy and childbirth (as for pregnancy, in the first trimester in women a sharp decrease in the amount of all formed blood elements is detected in the blood, including those included in the leukocyte formula, and during childbirth the body is depleted); exhaustion of the body (special attention is required pay attention to reducing monocytes in the blood of children, because if their number falls against the background of exhaustion of the body, then the work of all internal organs and systems is disrupted);
If it is discovered that monocytes are low in the blood of one of the children, then such a child is prescribed additional tests for the presence of infection in the body, as well as disorders of the immune or hematopoietic system.
There are quite a lot of diseases in which monocytes in the blood are increased, because the increase in the number of these cells occurs against the background of infectious or viral agents entering the human body (parents are recommended to pay special attention to the child, since during the growth of the body the immune system works weakly, so vital activity nothing interferes with pathogenic agents).
The main reasons for the development of this condition include:. If, after receiving the analysis, it is discovered that monocytes are elevated in an adult, then you must immediately consult a doctor to conduct additional tests (in fact, in the case of the development of the same condition in children, you must do the same)
It is worth saying that it is pointless to treat conditions in which a change in the number of leukocyte elements in the blood occurs in the body of children or adults. First, the doctor determines the cause of the development of this disease, and then prescribes the necessary pharmaceuticals for its treatment.
If, after receiving the analysis, it is discovered that monocytes are elevated in an adult, then you must immediately consult a doctor to conduct additional tests (in fact, in the case of the development of the same condition in children, you must do the same). It is worth saying that it is pointless to treat conditions in which a change in the number of leukocyte elements in the blood occurs in the body of children or adults. First, the doctor determines the cause of the development of this disease, and then prescribes the necessary pharmaceuticals for its treatment.
If a blood test shows that monocytes in the blood are elevated, then it is worth finding out the reasons. An increase in the content of these cells occurs in quite rare cases and may indicate quite serious diseases.
If for certain reasons monocytes are elevated, their powerful protective function is noticeably weakened, leading to unwanted diseases. It is very important to understand the main aspects of this problem, including its causes and issues of treatment and prevention.
Patients who are encountering the problem for the first time are interested in if there are elevated monocytes in the blood, what does this mean. To answer this question, we must first consider what they are. In modern science, monocytes are one of the special types of white blood cells.
Their main task is to protect the body by eliminating damaged or dead cells, including cancer cells, with the help of other leukocytes. They take the form of a single large nuclease.
Individually, each monocyte is a leukocyte that has the property of changing its appearance depending on the requests of the immune mechanism. These microscopic compounds are formed in the bone marrow.
From there they are transported into the blood and in its composition are carried to other organs, including the liver, lungs, spleen, etc. Having reached the required degree of maturity, they are transformed into macrophages - large white blood cells with one nucleus.
It is the mature macrophages that fight all kinds of infections and “trash” clogging the body, breaking it down and neutralizing it. They also perform an equally important signaling function, warning our body about the ingress of harmful substances. The third most important function of monocytes is direct participation in the formation of organs.
Norm and content
According to the latest scientific data from domestic and foreign scientists, monocytes make up from 1% to 10% of all leukocytes in human blood. At the same time, doctors have developed a special scale for their number, giving a gradation of monocytes.
If their proportion does not exceed 4%, they speak of low monocytes; with a range from 4% to 10%, we are talking about their normal number. When this proportion falls in the range from 11% to 15%, the body is dealing with elevated, and when the ratio is above 15%, it is dealing with high monocytes.
For women, the normal rate is from 3% to 11%, and before the onset of critical illness - from 3% to 9%. When a girl reaches the age of 16, the level rises to 11%.
The term “monocytosis” is used for an increased number of monocytes. Its cause in adults, as a rule, is a weakened human immune system or severe psychological shock, which often always provokes some kind of disease.
Why these reasons lead to diseases is obvious: they destroy the protective mechanism that every minute guards health and reliably blocks or destroys substances that are dangerous to it.
In addition, many specific diseases can lead to an increase in monocytes, that is, undesirable consequences for humans, ranging from all kinds of disorders, inflammations, tumors and ending with various kinds of infections (for example, pneumonia), fungal diseases.
Doctors also list a number of specific diseases leading to elevated monocytes: sarcoidosis, granulomatous disease, Cushing and Langerhans syndromes, tuberculosis, syphilis, rheumatism and others. Often an increase occurs after operations. In children, the main factors are often the presence of viral diseases, vaccination, previous injuries, and hereditary diseases.
Symptoms of deviation
The main symptoms of deviation of the number of monocytes from the norm, experts include manifestations of weakness, increased fatigue and high temperature, which manifest themselves differently depending on the causes of the disease.
This is especially true for fatigue, when a person, for various reasons, does not fully restore the strength of an exhausted body. When several significant causes are combined simultaneously, an absolute content of elevated monocytes is observed.
Because their immune systems are not strong enough, children tend to experience more severe symptoms.
As in many other cases of complex diseases, elevated monocytes are determined by a general blood test, which is carried out according to a procedure perfected over many years in almost all medical institutions and centers, and, if the patient wishes, at home.
Laboratory tests are performed when a patient shows signs of an infectious or other disorder. Based on the data obtained, specialists accurately determine the percentage of monocytes in the blood.
Sometimes the doctor also prescribes additional tests to clarify the diagnosis.
The key to treatment is to make it clear what influenced the increased level of monocytes in the blood and what is the main reason for the increase. When the doctor, using the results of a blood test and other laboratory tests, makes a final diagnosis, the treatment program will consist of eliminating the underlying cause.
If the analysis reveals an excess of monocytes, it is necessary to determine exactly what caused them.
In some cases, one should not be afraid of monocytosis, since in such situations it is possible and even predictable and therefore does not pose a serious threat.
However, such cases are rather an exception to the rule, so they should not be underestimated. The true reasons for the fact that monocytes are increased are, naturally, determined by a professional doctor, but not by the person himself.
In the same way, instructions on nutrition and other aspects of life of a person, adult or child, who has an increase in monocytes, should only be given by an experienced physician.
The most frequently used recommendations include advice to streamline your lifestyle, especially nutrition: systematically use some nutritional supplements and foods that have been proven to normalize the content of monocytes in the blood.
The list of foods that contain high levels of antioxidants that are extremely necessary for the body usually includes:
- onion;
- cherries;
- spinach;
- turmeric;
- garlic;
- black cumin;
- beans;
- grapes, etc.
Nutritionists also recommend using various supplements containing, for example, fish oil (cod liver).
They also advise eliminating sugar and other foods containing it from your diet, namely candy, other sweets and carbonated drinks. On the other hand, it is advisable to eat more fish, or constantly take a valuable Omega-3 nutritional supplement.
Finally, a firm rule should be to avoid drinking alcohol, which is one of the worst enemies of human health.
What to do if a pathology occurs?
An increase in the level of monocytes is in any case a mandatory reason to seek the help of a specialist - a doctor to further clarify the causes of this condition. Even a slight increase in the level of phagocytes should cause caution.
First of all, you will need to retake a general blood test again in order to detect an increase in other indicators or only a narrow increase in monocytes. And if a repeated increase is detected, it is imperative to further examine them and find out the root cause of monocytosis.
Having figured out what this means, you should find out what to do with monocytosis in an adult. Tactics depend on the circumstances of detection of pathology.
If an increase in the blood of monocytes in a man or woman was discovered by chance during preventive screening, it is advisable to repeat the analysis. For comparison, it is better to choose another laboratory. If there are a lot of monocytes in the blood, this means that it is necessary to trace the process over time. If the result is confirmed, it becomes necessary to conduct a more in-depth examination to establish the exact cause of the deviation.
An increase in monocytes in the blood in adults is often detected when there is an already diagnosed cause. Such a study is carried out to monitor the dynamics of the underlying disease. This means that even if the elevated level of monocytes in the blood test decreases to normal numbers, it is necessary to strictly follow the doctor’s instructions and continue to treat the specific pathology.
The following specialists treat diseases that cause monocytosis:
- infectious disease specialist;
- rheumatologist;
- phthisiatrician;
- gastroenterologist;
- dermatologist.
In their practice, a pulmonologist and an allergist encounter this problem when treating severe pneumonia. Specialists such as an immunologist and hematologist are most directly related to the problem of high levels of monocytes in an adult.
First of all, when diagnosing this abnormality in a blood test, you should contact a therapist at the clinic.
- Functions of monocytes
- Causes of monocytosis
- Comprehensive diagnostics
Functions of monocytes
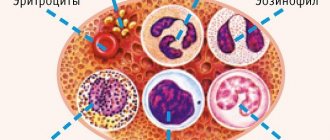
Monocytes are the constituent elements of “white” blood, but without granules in their structure, as a result of which these cells are sometimes called agranulocytes.
These blood particles perform several unique functions to ensure the body's immune response to invading dangerous elements.
Mature histiocidal monocytes:
- protect humans by phagocytosis, capturing and deactivating foreign particles, which can be toxins, viruses, bacteria;
- create a barrier between healthy and infected tissues;
- contribute to the activation of interferon production;
- eliminate dead leukocytes from the source of inflammation;
- fight the occurrence of cancer;
- agranulocyte prevents thrombus formation.
If other blood elements, when faced with dangerous aliens, die almost immediately, then monocytes are ready to fight them repeatedly and even transmit information about foreign particles to future generations.
Monocyte cells are formed in the bone marrow and, entering the bloodstream, spend some time in the circulatory system, after which they penetrate the body tissues in order to accumulate energy and nutrient media.
Energized and nourished cells are considered mature and ready to perform the above functions.
The number of monocytes in the blood is diagnosed during a general blood test: for this purpose, the patient’s individual leukocyte formula is indicated in the laboratory.
The normal content of monocytic cells for adults is considered to be from 3 to 11% in relation to other leukocytes (relative indicator).
For women during pregnancy, other relative indicators of the number of monocytic cells are considered normal: during the first trimester, cells should not exceed 3.9%, the second - 4%, the third - 4.5%.
Monocytes: features of production and structure
The ancestor of monocytic bodies are monoblasts. Before becoming mature cells, they must go through several stages of development. Promyelocytes are formed from the monoblast, then promonocytes, and only after this stage monocytes mature. They form in small quantities in the lymph nodes and connective tissues of some organs.
Mature forms are distinguished by their cytoplasm, which contains various enzymes and biological substances. These include lipase, carbohydrase, protease, lactoferrin, etc.
Monocytes cannot be produced in significantly increased numbers like other types of white blood cells. Strengthening their products is possible only 2-3 times, no more. Phagocytic mononuclear cells, which have already moved from the bloodstream into the tissues of the body, are replaced only by newly arrived forms.
As soon as the bodies enter the peripheral bloodstream, they migrate through the vessels within three days. Then they stop in the tissues, where they fully mature. Thus, histiocytes and macrophages are formed.
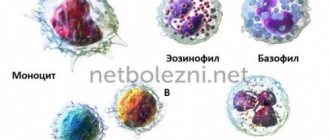
Agranulocytic or non-granular leukocytes perform various functions. They were even combined into the MFS group to make it more convenient to classify activities. The mononuclear phagocytic system includes the following cells:
- Monocytes , which are found in the peripheral bloodstream .
Immature leukocyte bodies cannot perform the main work of phagocytes. They simply circulate in the blood to move to the tissues where they will undergo the final stage of maturation.
- Macrophages, mature monocytic bodies.
They belong to the dominant elements of the MFS and are distinguished by their heterogeneity. They are tissue-specific and tissue-specific. The first type is mobile histiocytes, which cope well with phagocytosis. They synthesize a large amount of proteins, lysozyme, and produce hydrolase.
Tissue-specific macrophages, in turn, are divided into several types:
- Immobile - concentrated in the liver, have the ability to absorb macromolecules and destroy them;
- Epithelial - localized in granulomatous inflammatory zones (tuberculosis, brucellosis, silicosis);
- Alveolar – in contact with allergic particles;
- Intraepidermal - engaged in the processing of antigens, presenting foreign bodies;
- Giant cells - arise from the fusion of epitolyod species.
The bulk of macrophages are located in the liver/spleen. Also present in large quantities in the lungs.