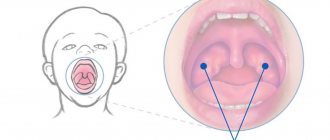
What are the sinuses and the ethmoidal labyrinth?
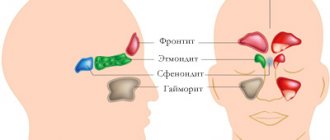
The sinuses are fairly large cavities located in the upper jaw area that lighten the weight of the bone. The area of these sinuses is located directly under the eyes. When examining x-rays, you can see a darkening in this area, indicating the absence of any abnormalities.
Experts today have not been able to establish the significance of the paranasal sinuses in human evolution, but they suggest that the cavities are necessary to increase the volume of the maxillary bone and reduce the overall mass of the skull bones. Air enters the paranasal sinuses through the ethmoid labyrinth, which has the appearance of a bone with many small round holes.
The ethmoid labyrinth is located on the bone of the same name, which is localized in the area of the bridge of the nose and stands slightly higher than the maxillary.
It is worth noting that the bone really has the appearance of a labyrinth with several curls, and there are holes on them.
Both the maxillary sinuses and the ethmoidal labyrinth are paired bones that play a critical role in the breathing cycle, as well as in the formation of the timbre of the human voice.
What is ethmoiditis?
What is it - ethmoiditis (ethmoidal sinusitis)? This is an inflammation of one of the paranasal sinuses, or rather, the cells of the ethmoid bone. It is often a secondary disease that develops against the background of inflammation of the upper respiratory tract. It ranks 5th in terms of the prevalence of diseases that are treated with antibiotics.
The shape of the flow is:
- Acute – a bright and sudden manifestation. More often observed in children and adolescents.
- Chronic – a consequence of anatomical pathology or untreated acute ethmoiditis.
The following types of ethmoiditis are distinguished:
- Together with other departments:
- Maxillary ethmoiditis is inflammation of the ethmoid bone with the maxillary sinuses.
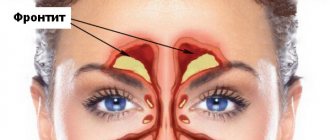
- Frontoethmoiditis is a lesion of the frontal sinus along with the ethmoid bone.
- Rhinoethmoiditis is inflammation of the ethmoid bone together with the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity.
- Sphenoethmoiditis is inflammation of the ethmoidal labyrinth with the sphenoid sinus.
- According to the nature of inflammation:
- Catarrhal.
- Polypous.
- Edema-catarrhal.
- Purulent.
- On the side of inflammation:
- Right-handed.
- Left-handed.
- Bilateral.
go to top
Types of thickening of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinuses, cells of the ethmoidal labyrinth of the nose
Thickening of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinuses and cells of the ethmoidal labyrinth is divided depending on the changes in the tissues, as well as taking into account the course of the pathological process.
Depending on the course, acute, subacute and chronic thickening is distinguished. In the first case, the symptoms are pronounced and appear immediately after exposure to the predisposing factor.
In addition, no more than 3 weeks pass from the onset of the disease to its transition to an advanced stage. In the subacute course, the signs are less pronounced, and the symptoms increase gradually. After approximately 4 weeks, progression of the pathology is observed.
The chronic course of the disease is accompanied by mild symptoms that can persist for 6 weeks or more. In this case, the patient may not suspect the presence of the disease and considers the manifestations to be a signal of a developing cold.
Taking into account changes in tissues, several types of disease can be distinguished:
| Type of pathology | Peculiarities |
| Catarrhal type | This type of hypertrophy is considered the most common and manifests itself in the form of severe tissue swelling and filling with serous exudate. In this case, nasal congestion and other symptoms are observed, which patients confuse with simple rhinitis of colds and allergic origin. |
| Purulent | With purulent inflammation, swelling is less pronounced, but a large amount of purulent masses filling the nasal passages and sinuses leads to nasal congestion. In addition, microorganisms multiplying in purulent masses lead to damage to the mucous membranes. |
| Polyposis | With polypous hypertrophy, compactions form on the mucous membranes, which after some time turn into polyps. These formations are quite dense and disrupt the passage of air masses through the lattice labyrinth. A feature of this type of pathology is the impossibility of treatment without surgery. |
| Purulent-polyposis | The most severe form of the disease, which is accompanied by the appearance of polyps and purulent masses on the mucous membrane of the nasal sinuses and ethmoid labyrinth. In this case, the patient’s condition worsens, since the polyps prevent the flow of air, and the purulent masses provoke a deterioration in the condition of the mucous membrane. |
Additionally, experts distinguish between closed and open forms of pathology. In the first case, hypertrophy is accompanied by inflammation, but the microorganisms do not spread beyond the sinuses and ethmoid labyrinth. In the second case, inflammation and hypertrophy are the result of microorganisms entering from another cavity, for example, the oral cavity.
Diagnostics
An accurate diagnosis is made based on the results:
- examinations by an ENT doctor;
- laboratory tests;
- radiography.
A visit to an otolaryngologist is mandatory to confirm the diagnosis. The specialist conducts a visual examination and rhinoscopy, and studies the patient’s complaints.
External manifestations of ethmoiditis:
- redness and swelling of the eyelids, conjunctiva;
- pain when touching the eyelids;
- cyanosis of the skin in the eye area;
- narrowed palpebral fissure;
- difficulty moving the eyeball.
When the ethmoidal labyrinth is inflamed, the patient experiences sharp pain when pressing on the lacrimal bone and bridge of the nose.
With advanced ethmoiditis, the upper and lower eyelids become inflamed, and small hemorrhages appear on the mucous membrane of the eyes
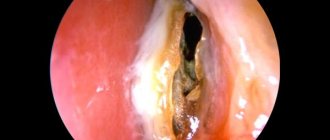
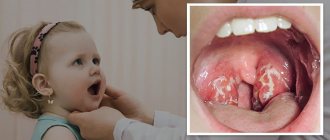
Using anterior and posterior rhinoscopy (examination of the mucous membrane of the nasal passages using an endoscope), the doctor can see the morphological signs of ethmoiditis. This:
- swollen, red mucous membrane of the nasal passages;
- mucous or purulent discharge from the nose;
- accumulation of pus in the upper and middle parts of the nasal passages;
- polypous growths (polypous ethmoiditis);
- narrowing of the nasal passages.
X-ray signs of ethmoiditis:
- darkened cells of the lattice labyrinth;
- decreased density of other sinuses;
- symptoms of periosteum damage (sometimes).
To carry out effective treatment, it is important to differentiate ethmoiditis from other diseases with similar symptoms: dacryocystitis, periostitis of the nasal bones, osteomyelitis of the upper jaw.
Causes of hypertrophy
Thickening of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinuses can develop as a result of many predisposing factors.
The main reasons are as follows:
- Weakening of the immune system.
- Insufficient intake of minerals and vitamins into the body, chronic vitamin deficiency.
- Exposure to the mucous membrane of toxic substances and toxic vapors.
- Chronic diseases of the upper nasal passages with regular exacerbations.
- Long-term smoking.
- Injuries to the nasal septum causing curvature.
- Frequent colds and viral diseases.
- Tendency to allergic manifestations, rhinitis of allergic origin.
- Dry air in the room when the air conditioner or heater is running.
- Environmental factors, such as air pollution.
- Long-term use of hormonal drugs in large dosages.
- Long-term treatment using vasoconstrictor nasal drops.
- Congenital anomalies of the development of the mucous membrane or nasal septum.
- Neurovegetative pathologies in which pathological vasodilation occurs in the absence of other symptoms of thickening of the mucous membranes.
- Pathologies of the teeth of the upper jaw, causing inflammation and thickening of the mucous membranes.
In addition, the pathology is more common in children, which is associated with imperfections of the mucous membrane and frequent colds affecting the nasal passages. Additionally, children are more prone to allergic diseases.
Causes
Chronic ethmoiditis usually occurs against the background of:
- untreated acute inflammation;
- weakened immune system;
- frequent colds and infections of the ENT organs.
The main causes of acute ethmoiditis include:
- penetration of infection from the primary focus;
- complication caused by a viral infection;
- complication after inflammation of the nasal passages or sinuses (rhinitis, sinusitis, sinusitis).
In newborns, acute ethmoiditis can occur against the background of umbilical, skin or intrauterine sepsis.
Infectious diseases of a viral and bacterial nature are a common cause of ethmoiditis in school-age children and adolescents. Ethmoiditis is often complicated by scarlet fever, much less often by measles, influenza, and other infections.
Acute ethmoiditis in children often develops after scarlet fever, the causative agent of which is group A hemolytic streptococcus
In adults, the main cause of the disease is sinusitis, frontal sinusitis or rhinitis. The causative agents are streptococci and staphylococci, hemophilus influenzae. And when ethmoiditis is combined with sinusitis or frontal sinusitis, bacteriological analysis often reveals a microbial association - the presence of several types of bacteria.
Symptoms
In the initial stages of the disease, the patient only talks about nasal congestion. This manifestation significantly worsens the patient’s quality of life, as he loses his sense of smell and appetite. After some time, headaches and dizziness appear, associated with insufficient oxygen supply to the vessels of the brain.
As the pathology progresses, the patient's lack of smell leads to a deterioration in the functioning of taste buds. The patient refuses food because it does not bring him pleasure. With a long course of the disease, the patient loses body weight, the skin becomes pale, and sweating increases.
Another manifestation is the release of a large amount of mucus. Its consistency and color varies depending on the degree of neglect of the condition and possible complications.
After clearing the nasal sinuses of mucus, the patient does not feel relief; he has to constantly use vasoconstrictor drops, which only temporarily improve the condition. In many patients with such disorders, the timbre of the voice changes, there is congestion in the ears, noise or ringing, which intensifies when water gets in.
Allergic reactions often worsen in patients due to the development of hypertrophy. Headaches intensify and accompany the person constantly. Possible deterioration of vision and pain in the eyeballs, especially when bending.
Additionally, patients' body temperature rises. Pain appears in the joints and muscles. The latter manifestations are a sign of exacerbation of the disease or the addition of complications.
With the disappearance of acute symptoms of the pathology, the patient’s condition improves somewhat, but nasal congestion, as well as the lack of smell, persists. The body temperature does not rise, but headaches and dizziness appear periodically.
Symptoms of catarrhal ethmoiditis
The complexity of the catarrhal form of ethmoiditis is considered to be the vagueness of symptoms. Signs of damage to the membranes of the ethmoid labyrinth are similar to the picture of a classic runny nose. Let us indicate the main symptoms of catarrhal ethmoiditis:
- increased lacrimation;
- attacks of nausea;
- loss of smell;
- nasal discharge (initially serous, then purulent);
- dizziness;
- subfebrile temperature (the readings on the thermometer increased in the evening, returned to normal after sleep). The temperature is within 37 - 38.5 degrees;
- general weakness;
- redness of the eyelids;
- redness of the eye vessels (they fill with blood and may themselves become damaged);
- the bridge of the nose swells.
A doctor can recognize the catarrhal form of ethmoiditis by the patient’s complaints of pain in the area of the bridge of the nose (root of the nose). If the inflammatory process spreads to the posterior areas of the cells, the pain syndrome is recorded in the internal areas of the eye sockets.
Sick people (adults, children) experience difficulty breathing through the nose. Their health may sharply deteriorate, they are worried about insurmountable weakness and headaches.
With bilateral ethmoiditis, inflammation covers the entire cellular surface of the ethmoid bone, covering the frontal sinuses. Bilateral ethmoiditis can develop in any form. To make an accurate diagnosis, radiography and CT are required.
Dangerous symptoms that should not be ignored:
The mechanism of changes in the structure of the mucosa
Thickening of the mucous membrane develops gradually, especially in patients whose immunity is not weakened. When the maxillary sinuses are affected, the damage begins with the development of swelling of the mucous membrane, as well as blocking of the ducts through which mucus is excreted.
Thickening of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinuses
These secretions cannot be removed through the ducts, so the swelling intensifies, which worsens the patient’s condition. Pressure increases in the sinuses, which leads to the formation of cysts and polyps. If, before the development of edema, pathogenic microorganisms enter the sinus cavity, pus is formed when the ducts are blocked and the mucous membranes swell.
This development mechanism is observed in most cases. When the pathological process is mild, there are no microorganisms in the cavity, which reduces the likelihood of complications.
Prevention
After suffering from an acute form of sinusitis, incl. and ethmoiditis, with timely diagnosis and quality treatment, the signs of the disease disappear without a trace, and a person with strong immunity may no longer encounter the pathology.
Chronic lesions of the ethmoid labyrinth require preventive measures. They are as follows:
- it is necessary to promptly and fully treat viral diseases;
- support the body (especially in the autumn-winter period) by taking immunomodulators and vitamin complex preparations;
- avoid hypothermia;
- do not forget about hardening, it is necessary to accustom children to hardening procedures from birth;
- eat well and practice a healthy lifestyle.
Medical statistics claim that among adult patients, the disease occurs more often in smokers. In addition, in people who cannot overcome the craving for smoking, chronicity of the pathological process occurs even after proper therapy.
Complications without treatment
Quite often, patients develop complications because they do not see a doctor when the first symptoms of the disease appear.
The most common ones are:
- Transition of the disease to the chronic stage with regular relapses.
- Irreversible changes in the mucous membrane, which can only be eliminated through surgery.
- Displacement of the nasal septum, interfering with the patient's breathing.
- Neurological disorders of the brain associated with lack of sleep, headaches and other manifestations.
- Decreased performance.
- Penetration of infection into the patient’s blood.
In addition, the general condition of the patient is disturbed, which affects the functioning of all organs and systems.
Possible complications
As with other forms of inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, ethmoiditis can lead to complications such as:
- Loss of smell - anosmia.
- Eye infections (diseases), including blindness.
- Bone infections – osteitis, osteomyelitis.
- Cyst formation.
- Sepsis (blood poisoning).
- Increased risk of asthma.
- Brain (membranes) – meningitis, encephalitis, etc.
- Heart diseases – pericarditis, endocarditis, etc.
Although many of the risks mentioned are rare, it is important to get timely treatment in any case. Even with the acute form of ethmoiditis, it is important to treat inflammation at an early stage, and not lead to a chronic course.
Establishing diagnosis
Several examination methods are used to make a correct diagnosis. The initial stage is a general examination and interview of the patient, listening to complaints and identifying the conditions for the appearance of symptoms of the disease. After this, the doctor prescribes a general and biochemical blood test.
These studies are mandatory because they help identify common signs of inflammation. After this, the patient is sent for fluoroscopy of the maxillary sinuses. In the image, the specialist can see deviations from the bones, especially the nasal septum.
The next stage of the examination is rhinoscopy. This method is a study of the nasal passages with a special device. At the same time, the doctor notes the degree of damage to the mucous membranes and detects possible complications.
If necessary, magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed, which allows you to see polyps and other neoplasms, as well as complications. Based on diagnostic data, treatment is prescribed.
Treatment of chronic ethmoidal sinusitis
The doctor’s task is to conduct a thorough physical diagnosis and effective X-ray examination (including CT, MRI) and laboratory tests for this disease. This will help differentiate ethmoiditis from osteomyelitis of the jaw, periostitis of the nasal bones and inflammation of the lacrimal sac. An endoscopic examination is carried out to determine the source of purulent masses (posterior or anterior cells of the ethmoid bone), detect polypous growths and assess the condition of the mucosa.
The treatment course begins immediately after confirmation of the diagnosis. Treatment of acute and chronic ethmoid sinusitis follows the same principle. To reduce swelling of the mucous membrane, restore the outflow of secretions and normalize air exchange in the cells of the ethmoid labyrinth, vasoconstrictor drops (Xylometazoline or Oxymetazoline), combination drugs (Phenylephrine, Rinofluimucil, Polymyxin), antihistamines (Erius, Cetrin, etc.) are used.
If the examination reveals a bacterial environment, the doctor will select an antibiotic based on the sensitivity of the pathogen. This can be a tablet drug or an injectable drug that will be administered in a hospital setting. Broad-spectrum antibiotics (Cefix, Augmentin, etc.) may also be indicated. Solutions of antibacterial agents are also prescribed for rinsing the paranasal sinuses.
To eliminate pain, relieve inflammation and reduce temperature, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs based on ibuprofen or paracetamol are needed.
The treatment regimen includes immunomodulatory drugs and vitamin-mineral complexes.
A positive treatment result will be consolidated by physiotherapeutic procedures - UHF, phonophoresis, electrophoresis, therapeutic laser, etc.
If conservative treatment does not give the expected result, it is possible to avoid the development of complications and get rid of the pathology only through surgical intervention.
Conservative treatment
Thickening of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinuses in catarrhal and purulent forms is treated using conservative methods. Medicines, physiotherapy and other methods to alleviate the condition are used.
Drainage of secretions
In case of acute development of pathology, it is necessary to use a special small bulb, which can be purchased at a pharmacy. It helps remove liquid mucus and make breathing easier. The procedure must be carried out with caution 2 to 4 times a day.
Additionally, it is recommended to use vasoconstrictor drops, for example, Naphthyzin, Rhinorus or Xylometazoline. They have a pronounced effect and make breathing easier within 4-5 minutes. Drops can be administered no more than 3 times a day, the maximum course duration is 10 days.
Antibiotics
For purulent inflammation, antibacterial drugs are a mandatory element of therapy. Experts prescribe medications from different groups, which are selected individually for each patient.
The most effective medications:
- Augmentin – an effective remedy from the penicillin group, helps to quickly destroy bacteria and prevent complications. It is prescribed for any form of pathology when body temperature rises and concomitant disorders appear. The patient receives 2 intravenous injections per day. For 1 time, take 1 bottle of the drug and add 10 ml of sodium chloride. Treatment lasts at least 10 days. The drug is not used during pregnancy, intolerance to its components and severe liver damage.
- Ceftriaxone is used quite often for hypertrophy with signs of suppuration. It is highly effective and helps to quickly eliminate common symptoms. The patient receives 2 to 4 g of medication intravenously or intramuscularly per day, depending on the severity of the condition. Treatment lasts from 7 to 14 days. The drug is contraindicated in patients with severe liver and kidney damage, as well as those with allergies to its components.
- Azitral is one of the most effective antibiotics that helps destroy pathogenic microorganisms in a short period. Prescribed for severe hypertrophy with signs of suppuration and the formation of polyps. Not used if the components are intolerant. The daily dosage for a patient ranges from 1-2 g, depending on the severity of symptoms. The course lasts no more than 10 days, most often 1 week is enough. Tablets are taken orally 2-4 per day.
- Clarithromycin is an effective medication that is used for severe purulent hypertrophy. The medicine is taken 1 tablet 2-3 times a day, depending on the severity of the disease. The course lasts up to 10 days. The drug is contraindicated in patients with allergies to its composition, as well as end-stage renal failure.
There are other medications; the selection of the drug is carried out taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient and the degree of neglect of the condition.
Natural drops
Thickening of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinuses of the catarrhal type responds well to treatment with drops based on natural ingredients.
- The most popular medicine is Pinosol. This medicine contains eucalyptus essential oil, due to which the therapeutic effect is achieved. Prescribed for any pathologies of the nasal sinuses, accompanied by congestion and secretion of mucus in large quantities. It is necessary to instill drops 2-3 times per day, repeat for 1-2 weeks. The only contraindication is an allergy to the composition of the medicine.
- Sinuforte is a product of plant origin, which is available in the form of a lyophilisate for preparing a solution. After receiving the drops, they must be injected into the nasal passages 3 times a day. Treatment lasts up to 2 weeks. The medication helps relieve swelling, is used for catarrhal hypertrophy, dilutes mucus and removes it from the sinuses. You should not use the medication in case of polypous form of pathology, under the age of 12 years, as well as uncontrolled arterial hypertension.
- Aqua Maris - natural drops based on sea water. They are used only in the initial stages of catarrhal hypertrophy in the absence of complications. They help remove mucus from the sinuses, while slightly drying out the mucous membranes, but do not provoke vasoconstriction. The drug is absolutely safe for adults and children; it is not used if the main component of the composition is intolerant. It is worth using drops 3-4 times a day, injecting them into the nasal passages. Course duration is up to 2 weeks.
Physiotherapy
Therapy using physiotherapy is used only in the absence of acute symptoms of inflammation, complications, and the patient’s body temperature is normal. In the case of a purulent type of pathology, such treatment is strictly contraindicated; it is not used when polyps appear in combination with purulent inflammation.
Warming up is the most popular method. The procedure is carried out on an outpatient basis and lasts up to 20 minutes. During the manipulation, special cannulas are inserted into the patient's nasal sinuses, through which heat enters the sinuses. The course consists of 10-15 sessions, helps to significantly improve the patient’s condition, warming stimulates the restoration of the mucous membrane.
UHF therapy is considered a good way to accelerate the recovery of mucous membranes. At the same time, ultra-high frequency waves act on the tissue, which leads to rapid regeneration. The procedure lasts 15-20 minutes and is carried out 3-4 times a week. The course consists of 12-15 sessions.
It is important to remember that in the acute stage any procedures are contraindicated. But in the absence of acute symptoms, they help enhance the effectiveness of medications.
Treatment
Treatment of acute ethmoiditis
Conservative therapy is the main treatment for acute ethmoiditis . In the acute period, the following are prescribed:
- Intranasal vasoconstrictors (sprays or drops) – up to 5 days,
- Mucolytic agents - to soften the contents of the ethmoid sinus,
- Systemic antibacterial drugs - taking antibiotics. Injectable forms may be recommended.
Additionally, nasal sprays with anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory effects are recommended.
Surgical correction of the nasal cavity is recommended after the acute period of ethmoiditis has stopped.
Treatment of chronic ethmoiditis
If chronic ethmoiditis occurs, surgical treatment . It is primarily necessary to remove the contents of the sinus, as well as to correct the anatomical structures of the nasal cavity that provoke this condition.
The most effective method of this type of treatment is endoscopic sinus surgery or ethmoidotomy. This method not only reduces the risk of postoperative complications, but also significantly reduces the recovery period and the patient’s hospital stay.
Sign up for a consultation
Surgical treatment methods
For polypous and polypous-purulent forms of hypertrophy, conservative methods are almost never used, but the operation brings good results.
Most often, 2 methods are used:
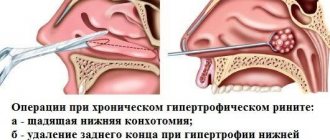
- Galvanocaustics is an operation performed using a special electrode. In this case, local anesthesia is used. The essence of the operation is to cauterize the area of thickening. In this case, scarring of the cauterized area occurs and nasal breathing is completely restored. The rehabilitation period lasts no more than 3 weeks.
- Conchotomy is a method of surgical intervention that uses a wire loop and general anesthesia. The essence of the method is to remove hypertrophied lesions and polyps, followed by cauterization of the tissue. The recovery period is approximately 4 weeks, and nasal breathing is completely restored.
Both methods are effective; the choice is made depending on the degree of neglect of the condition and the individual characteristics of the patient.
Surgery is considered the only method that helps eliminate the symptoms of hypertrophy when polyps appear or purulent inflammation occurs. As a rule, manipulation does not provoke complications, provided it is carried out correctly.
Thickening of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract is a common problem among young and mature patients. When the tissues of the maxillary sinuses are damaged, severe symptoms are observed that worsen the patient’s condition. Conservative and surgical methods are used for treatment, which help eliminate manifestations and prevent complications.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Classification of maxillary ethmoiditis
Sinusroethmoiditis differs in the type of course of the disease. They can be acute or chronic. There are also sinusroethmoiditis: exudative and productive. The exudative form of the disease, in turn, is divided into the following types:
- catarrhal;
- serous;
- purulent.
A productive form of sinusitis can be:
- with tissue hyperplasia;
- with the appearance of polyps.
In the nasal cavity there are antrochoanal and ethmoidal polyps. Polypous maxillary ethmoiditis is often accompanied by a disease such as non-allergic asthma. Ethmoiditis is characterized by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the ethmoid bone.
In addition, there are unilateral and bilateral sinusitis.
Causes of the disease
Otolaryngologists note acute and chronic ethmoiditis.
Each of them is characterized by its own manifestations. A chronic disease develops after an untreated acute manifestation of the disease. This type of ethmoiditis affects children and adolescents more. The development of acute ethmoiditis is preceded by an acute respiratory disease with inflammatory processes due to viruses or bacteria entering the body. Otolaryngologists talk about three causes of the disease.
- Spread of the pathogen from the source. This cause of ethmoiditis is especially common in children. Along with the blood flow, pathogenic flora moves in the body. But the movement of infection can also occur through contact or with the flow of human lymph. The primary sites of the disease are the tonsils, lungs, and nose.
- As a complication after infections or viral diseases (measles, flu, scarlet fever, tonsillitis). Acute ethmoiditis develops mainly after suffering from scarlet fever, which is caused by streptococcus. It is characterized by active sedimentation and reproduction in the patient’s tonsils. Becomes the cause of the development of sore throat and croup. If the pathogen enters the blood, the patient is diagnosed with a severe form of scarlet fever - septic. And it moves the pathogen to other organs. Measles and flu do not often cause an acute inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the ethmoid sinus. If it has developed, it is associated with dysfunction of the mucous membranes, which is observed in these diseases.
- If an adult falls ill with acute ethmoiditis, then the disease is associated with damage to other sinuses. So, sinusitis, sinusitis, chronic sinusitis become the cause of the disease. Otolaryngologists call this combined forms of ethmoiditis (sinusroethmoiditis, rhimoethmoiditis). This is due to the direct contact of the ethmoid labyrinth with other sinuses. Ethmoiditis is also noted as a complication of sinusitis.
If the acute stage of ethmoiditis is not treated correctly or the patient comes in in an advanced state, then the disease takes on chronic manifestations. It appears 3 months after the acute stage. In this case, the infection spreads to the mucous membrane and bone tissue. Inflammation affects cells located deeply, while the anterior structures are not affected. The lesion reaches the periosteum, which leads to the development of periostitis.
The occurrence of the disease is facilitated by the weakening immunity of the body in general and the protective forces of the nasal membrane in particular
Treatment of chronic ethmoiditis is difficult. It requires complex prescription of drugs. And the consequences of this disease are complex. Otolaryngologists advise promptly and completely curing emerging ailments and increasing the body’s immune strength.
Features of sinusroethmoiditis in children
One of the main features of the course of this disease in children is that at first the disease practically does not manifest itself. Symptoms characteristic of ethmoiditis can occur only on the 10th - 14th day of the disease. In this regard, a diagnosis may be made late, which entails a risk of complications. After all, it is not always clear whether a child is sick. Children may simply have whims or mood swings.
Inflammatory processes that occur in the ethmoid sinuses can spread to the orbital area. A characteristic symptom is swelling of the eyelids. In more advanced stages, purulent inflammation in the eye sockets is likely, the elimination of which is quite difficult - surgical intervention may be required.
Children with weak immunity are predisposed to the development of sinusitis. The reasons for decreased immunity in childhood can be various inflammatory processes occurring in the body. Severe allergic reactions can also contribute to the development of inflammation in the sinuses. In addition, helminth infestations can contribute to decreased immunity.
What is sinusitis, symptoms and treatment in adults and children
Sinusroethmoiditis is an inflammation of the mucous membranes of the ethmoid and maxillary sinuses; it can occur in acute and chronic forms. The course is quite complicated, since initially one sinus is affected, and then the inflammation spreads to other areas.
If treated incorrectly and untimely, it can cause complications that lead to brain damage and death of the patient.
Peculiarities
The maxillary sinuses are located on both sides of the nasal cavity in the thickness of the upper jaw.
They are characterized by the fact that their openings are quite thin, located slightly above the very bottom of the nasal sinus. The disease is acute, which is due to the complex anatomical structure of the nasal sinuses. The contents inside the sinuses accumulate and are not able to be expelled, which is why complex inflammatory processes occur.
Causes
Sinusroethmoiditis can be caused by:
- prolonged inflammatory process in the sinuses;
- pathologies of the nasopharynx;
- allergy;
- decreased immunity;
- hypothermia;
- incompletely cured respiratory diseases;
- penetration of infection.
Symptoms
Regardless of whether sinusitis is bilateral or unilateral, the symptoms are quite vivid and characteristic, which is why the patient can immediately recognize the presence of inflammation. Sometimes the disease has a chronic course or smoothly flows from rhinitis or sinusitis.
The first signs of the disease:
- severe weakness, fatigue;
- nasal discharge;
- nasal congestion;
- voice change;
- headache;
- intermittent cough;
- temperature increase;
- painful sensations in the nasal cavity.
In addition, there is an additional decrease in the sense of smell, loss of appetite, and tearfulness.
Diagnostics
Initially, you need to take a blood test, since in the presence of sinusitis, an increased number of leukocytes in the blood is observed, which indicates the occurrence of purulent processes in the body.
An increased ESR is considered the most important sign of an inflammatory process.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor may order an x-ray of the sinuses. The x-ray will show the nasal sinuses and their contents. If there is sinusitis in the sinuses, the level of fluid, the localization of the inflammatory process, as well as changes in the bones will be visible.
To determine which pathogenic microorganisms provoked sinusitis, nasal contents are collected. This will allow you to create a treatment plan.
Treatment
To reduce the amount of discharge from the nasal mucosa, vasoconstrictor drugs are prescribed. To quickly eliminate pathogens, antibacterial agents are widely used after identifying the causative agent of sinusitis.
Antiviral, antiallergic, antifungal therapy is carried out. Also, at elevated temperatures, antipyretic drugs are prescribed. To improve the outflow of mucus, nasal rinses are used, which will eliminate pathogens, reduce swelling of the mucous membrane and the amount of mucus released.
If conservative methods of therapy do not bring the required effect, then surgical intervention is performed to prevent complications from occurring. During the operation, the patient is punctured in the nasal sinus, the accumulated mucus and pus are pulled out. This ensures rapid improvement.
The puncture is performed exclusively in a hospital setting. After the puncture, the patient expects a long recovery and periodic rinsing of the nasal sinuses. Sometimes, with extensive inflammation and severe disease, it is necessary to perform several punctures of the nasal sinuses. After a puncture, the patient often expects periodic relapses.
Treatment of the chronic form
Chronic maxillary ethmoiditis is considered a rather complex disease, occurring with a predominance of characteristic infectious and inflammatory changes.
Initially, surgical intervention is performed to eliminate accumulated mucus and pus in the nasal cavity. At the same time, complex therapy is carried out to normalize the patient’s general condition, as well as increase the body’s resistance to pathogens.
Quite often, against the background of existing complications, polypous maxillary ethmoiditis can occur, which requires more thorough treatment, as well as removal of polyps and subsequent restoration of the nasal mucosa.