Treatment of hypertrophic rhinitis using traditional recipes
Many people believe that they can cope with the disease on their own and are in no hurry to visit a doctor.
It is worth noting that self-medication is not recommended. Otherwise, improper therapy can lead to dire consequences. You can use folk recipes to combat the disease only after consultation with your doctor. And any alternative medicine methods should be used as an addition to the main therapy prescribed by an otolaryngologist. The most common methods of traditional medicine:
Rinsing the nose with decoctions of medicinal plants
Before you start rinsing your nose with plant decoctions, you need to make sure that they will not cause an allergic reaction. To prepare a decoction, you can use sage, thyme, chamomile or mint. You need to take 2 tbsp. l. dried herbs and 300 ml boiling water. Pour boiling water over the herb and leave for 35 minutes. Then strain through a thin cloth (ordinary gauze will do). Before washing, you need to check the temperature of the broth. It should be a little warm. Only after this can you rinse your nose several times a day.
You can also use regular table salt or natural sea salt in this recipe. You need to take 25 ml of salt and dissolve it in 2 glasses of warm water. Then you can start rinsing your nose.
Cotton swabs with honey
Another effective method is the use of cotton swabs. To do this, you need to take honey and distilled water (component ratio 1:1). Soak cotton swabs in the resulting mixture and then insert into each nostril for about 25 minutes.
Along with the main treatment, it is necessary to adhere to a daily routine, go to bed early and spend more time in the fresh air. You need to eat right, consume a large amount of vegetables and fruits in your daily diet. It is also recommended to exclude fatty, salty and fried foods, and especially fast food. Then curing the disease will be much easier and faster.
Treatment
Treatment of hypertrophic rhinitis will be more effective if several methods are used at once.
Remember! Such an integrated approach increases the chances of a favorable outcome and a reduction in the therapeutic course.
Treatment with drugs
In severe cases and during periods of exacerbation of the disease, potent corticosteroids (Mezaton or Nasonex) are prescribed. They will help relieve swelling and restore breathing.
Further vasoconstrictor drugs are used:
- galazolin;
- xylene;
- Nazivin;
- otrivin;
- rhinazoline.
In case of bacterial infections that increase inflammation, antibiotics may be prescribed.
Additionally, antiseptic nasal solutions are prescribed for rinsing the nose (in case of excessive mucus secretion).
Conservative therapeutic methods
You should know! If the disease can be recognized in the early stages, it is possible to use conservative therapy methods, consisting of the following procedures:
- nasal massage using splenin ointment;
- physiotherapeutic sessions of high-frequency irradiation of the nasal cavities;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- injection of a hydrocortisone suspension into the affected areas of the mucosa;
- cauterization of the affected areas with trichloroacetic or chromic acid and silver nitrate.
Treatment with folk remedies
An additional method of therapy can be the use of traditional medicine:
- Every four hours, four drops of pure agave juice are instilled into each nostril. The procedure is performed daily throughout the course of the main treatment.
- A tablespoon of peppermint is poured into 0.5 liters of cold boiled water. After a day of infusion, the composition is drunk half a glass three times a day and the nasal passages are washed additionally three times a day.
- If it is possible to use an aroma lamp, you can do passive inhalations using tea tree oil. It is enough to do inhalations once a day before going to bed for ten minutes.
- Add a teaspoon of sea salt to half a liter of water and stir until its crystals are completely dissolved. The nasal passages are washed with this product twice a day: in the morning, after waking up, and before bedtime.
Traditional medicine can help alleviate symptoms and speed up the treatment process, but this method cannot be used as the main one due to its low effectiveness.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of “hypertrophic rhinitis” is established only after excluding other possible types of runny nose. To do this, you will need a number of diagnostic examinations, which include:
- a clinician’s examination of the patient’s medical history and life history to identify the causes of the disease and determine the tactics of future therapy;
- a thorough physical examination;
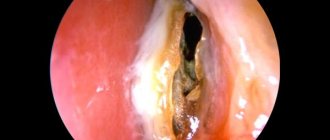
- Rhinoscopy is a procedure for examining the nasal cavity using special instruments. During such an examination, a deviated septum is often detected;
- performing a test using vasoconstrictor nasal drops - this is necessary to differentiate hypertrophic rhinitis from allergic or vasomotor rhinitis.
Causes of hypertrophic rhinitis
Hypertrophic rhinitis is a disease that has many causative factors that cause it. The main ones are listed below.
1. Acute respiratory diseases (including ARVI). Frequently recurring infectious viral diseases in their acute phase lead to the formation of immune complexes in the blood and the activation of specific antibodies. The main consequence of the increased functioning of the immune system is an increase in the functioning of the nasal secretory apparatus and the production of large amounts of mucus, as well as thickening and proliferation of the mucous membrane. This pathology is caused by frequent exacerbations of acute respiratory diseases, on average five or more per year.
2. Deviation of the nasal septum. This anatomical pathology of the appearance of hypertrophy of the nasal mucosa causes narrowing of the nasal passages and difficulty in the normal outflow of mucus. Impaired capillary circulation and hypoxia of cells of the nasal mucosa include a mechanism for increased cell growth to compensate for these phenomena. Hence – hypertrophic rhinitis.
3. Congenital or acquired anomalies in the development of the nasal passages. The pathogenesis (mechanism of development) of hypertrophic rhinitis in this case is identical to the previous case.
4. Injuries to the nasal bones. As a consequence of traumatic damage to the nasal bones and changes in the size of the nasal passages, a disturbance in the outflow of mucus and congestion may occur. As a consequence of the latter, hypertrophy of the nasal mucosa occurs.
5. Long-term use of vasoconstrictor drugs. Uncontrolled long-term use of nasal sprays or drops with a vasoconstrictor effect can also lead to disruption of the blood supply to the nasal mucosa and its growth through a compensatory mechanism. At the same time, the nasal mucosa thickens, its vessels become fragile, and frequent nosebleeds appear.
6. External irritating factors. Most often these are environmental factors, work in hazardous industries, temperature factors (low or high air temperature), inhalation of dust or gases. All these factors can cause irritation of the nasal mucosa and, as a result, cause inflammation. Chronic exposure and inflammation of the mucous membrane leads to its degeneration and thickening. Inhalation of dust over a long period causes damage to the ciliated epithelium, which leads to the development of metaplasia and a slowdown in the outflow of secretions, as well as the formation of rhinoliths (nasal stones).
7. Cardiovascular pathology. Atherosclerosis of blood vessels (narrowing of their lumen) and hypertension are one of the causes of impaired blood supply to the nasal mucosa, tissue hypoxia and their hyperplastic degeneration.
8. Nasal infections. Polyps, cysts, and adenoids are a reservoir for the proliferation of many types of bacteria and viruses. The latter always cause inflammation of the nasal mucosa, and repeated episodes of inflammation lead to overgrowth of the mucous membrane.
Reasons for the development of pathology
The inside of the nasal cavity is covered with an epithelial layer, which is necessary for cleansing and warming the inhaled air. The disease occurs when this function is disrupted. This happens in the following cases:
- frequent diseases of the ENT organs caused by bacteria or viruses;
- chronic allergic rhinitis;
- curvature of the nasal septum of congenital or acquired etiology (as a result of injuries or surgical interventions);
- frequent and uncontrolled use of vasoconstrictor drugs, which are addictive. Constant forced action on the capillaries of the nasal cavity leads to the fact that the nervous system ceases to recognize commands and expands them, swelling of the mucous membranes occurs, and subsequently hypertrophy;
- some bad habits: smoking or sniffing tobacco or drugs;
- working in polluted and dusty areas or living for long periods in environmentally unfavorable areas.
One of the trigger factors for the development of pathology is a deviated nasal septum.
Also, the reasons for the development of pathology can be:
- diseases of the cardiovascular system, as a result of which the vessels lose their elasticity and are constantly in an expanded state, which leads to hypertrophy of the mucous tissue;
- endocrine diseases that cause hormonal imbalance and the appearance of vasomotor runny nose.
Hypertrophic rhinitis symptoms and treatment
Chronic hypertrophic rhinitis is considered one of the most common problems in modern otolaryngology, since this diagnosis is often made when the patient practically cannot breathe through the nasal cavity. This disease requires more careful diagnosis and treatment in the early stages, so the study of the symptoms of this pathology remains relevant.
Description of chronic hypertrophic rhinitis
Chronic hypertrophic rhinitis is a disease of the nasal cavity, which is characterized by excessive growth of the mucous membrane of the nasal turbinates, which in turn leads to significant difficulty in nasal breathing.
This disease often develops in adulthood and is most common among males. It is in this case that effective Loromax drops of plant origin are suitable.
Initially, the inferior turbinates are involved in the pathological process, then the growth of the mucous membrane spreads to the middle turbinates.
Classification of chronic hypertrophic rhinitis
The classification of hypertrophic rhinitis is based on which elements predominate in the formation of hypertrophy.
There are the following forms of hypertrophic rhinitis:
- Cavernous. This form of hypertrophic rhinitis is considered to be false, since hypertrophy is functional in nature and is a consequence of the individual characteristics of the structure of the nasal cavity, the presence of a large number of choroid plexuses in the nasal cavity. Quite often this form is diffuse and spreads to the entire nasal cavity.
- Fibrous. This form of the disease is characterized by special morphological structural features and is characterized by the proliferation of connective tissue. Symptoms of nasal congestion with this type of disease are increasing. The fibrous form of chronic hypertrophic rhinitis is characterized by slow progression, but irreversible changes. There are diffuse and limited varieties of the fibrous form of this type of runny nose.
- Edema. In the edematous form of chronic hypertrophic rhinitis, the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity swells under certain influence factors, both internal and external. At first, the internal structure of the nasal cavity resembles that of the papilla. Prolonged swelling in the future is a predisposing factor to the formation of polypous growths in the nose.
- Mixed. In most cases, it is difficult to determine the form of a runny nose, since the process is chronic and a gradual transition from one form to another is possible.
Hypertrophic rhinitis photo:
Causes of development of chronic hypertrophic rhinitis
This disease is considered to be polyetiological (has many causes).
The most common causes of this disease are:
- Unfavorable working conditions.
- Bad habits (smoking, inhaling psychotropic substances).
- Foci of infection and chronic diseases of the nose or paranasal sinuses.
- History of chronic allergic rhinitis.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Chronic inflammatory processes in the nasal cavity.
- Poor blood supply to the nose.
- Endocrine disorders in the body.
- Reducing the overall resistance of the body.
- Activation of conditionally pathogenic microflora of the nasal cavity.
In particular cases, the cause of the development of hypertrophy in the nose cannot be determined.
Hypertrophic rhinitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
Symptoms of chronic hypertrophic rhinitis
Treatment methods for chronic hypertrophic rhinitis
Treatment of chronic hypertrophic rhinitis is characterized by the fact that conservative treatment without surgery is not effective, since changes in the nose are morphological in nature.
To do this, procedures are carried out that are prescribed by the doctor:
- UHF;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- Massage with Spenin ointment
- Anticongestants
- Use of Hydrocortisone
Surgical treatment (operation) is resorted to only if a test with vasoconstrictor drugs was not effective, and the diagnosis was finally confirmed.
The gold standard in the treatment of this disease is surgical treatment. This is due to the need for surgical removal of the existing hypertrophied mucous membrane.
Forms
Hypertrophic rhinitis is divided into several main classifications:
cavernous - this form of the disease is considered false, since the proliferation of connective tissue is not organic, but functional in nature. In most cases, it is nothing more than a sign of the individual structure of the nasal cavity;- fibrous - this classification of the disease is distinguished by the fact that the connective tissues have features of the morphological type. It is also characterized by a slow development of symptoms;
- edematous – occurs due to the influence of internal and external factors that provoke the appearance of swelling in the area of the nasal mucous layer;
- mixed - has signs of all types of illness mentioned above.
In addition, there are additionally several types of hypertrophic rhinitis:
- chronic hypertrophic rhinitis - created due to the systematic influence of a certain etiological factor and incorrect therapeutic manipulations;
- vasomotor – a distinctive feature of the ailment is its sudden appearance and disappearance. Does not contribute to tissue deformations, but without treatment it becomes chronic;
- limited – negatively affects a certain area of the nasal cavity;
- diffuse – causes total tissue hyperplasia.
Each of these types has its own negative consequences.
Important! Only timely and qualified treatment of the problem will avoid its transformation into a chronic form.
Treatment
Correct treatment of hypertrophy of the nasal mucous membranes begins with diagnosis. The main thing is to establish the cause of the pathological proliferation of tissues. The following methods are used:
- Adrenaline test;
- Endoscopic examination;
- X-ray and computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses.
Differential diagnosis with vasomotor rhinitis is mandatory.
Drug therapy
Treatment in the early stages is carried out using conservative methods, but in advanced cases the only option is surgical intervention:
- In the initial stages, washing with saline or soda solutions may be sufficient;
- If inflammation affects only mucosal tissues, hydrocortisone may be administered;
- Using the drug "Splenin" in the form of injections or ointments - it has a powerful anti-inflammatory effect;
- Cauterization with trichloroacetic acid with preliminary anesthesia with a 1% solution of cocaine or dicaine. This method is used in most cases when treating children, because it does not cause negative emotions;
- If the previous methods are ineffective, they resort to galvanocaustics - cauterization of the mucous membrane using a blunt or needle tip. Currently, the method is rarely used;
- More modern methods are ultrasonic disintegration and laser destruction;
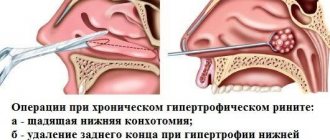
- Surgical methods are lower conchotomy and osteoconchotomy.
Surgical treatment of hypertrophic rhinitis
Folk remedies
Any type of chronic runny nose can lead to hypertrophic rhinitis. Therefore, you can treat a runny nose in its mildest form using folk remedies. However, at the same time, observe the measure and the basic rule of ancient healers “do no harm”:
- The main way to keep the mucous membrane in working condition is daily rinsing, preferably with a solution of sea salt (0.5 tsp per glass of boiled water) or with ready-made pharmaceutical products. The solution should be warm, and it is advisable to start washing after studying the technique;
- Peppermint infusion (1 tablespoon per 500 ml of boiling water) is an excellent anti-inflammatory agent, suitable for both drinking and rinsing. Infusions of other herbal remedies are also suitable - licorice, wild rosemary, viburnum bark;
- Make a snuff mixture: 10 g of deciduous cap, 10 g of hoofed grass root, 1 g of rue herb. All components are crushed and snorted several times a day;
- Take mumiyo (0.2-0.3 g) dissolved in milk or a mixture of cow fat and honey (1:20), and also lubricate the nasal turbinates with the product. Oral administration is carried out on an empty stomach and before bedtime. The course of treatment is 20-25 days, after a 10-day break, if necessary, the course is repeated;
- To relieve swelling, dilute honey in half with boiled water, moisten tampons and insert into the nasal passages for 0.5 hours before bedtime. The course of treatment is 10 days;
- Make inhalations with essential oils: 3 drops of tea tree and mint oil per 0.5 liters of boiling water. Inhalations are carried out for 15 minutes. once a day for 10 days;
- Brew 1 tbsp. l. crushed plantain leaves 200 ml boiling water, infuse, filter, add 1 tsp. alcohol tincture of propolis, instill 5 drops into each nostril twice a day for 2 weeks;
- Instill fresh Kalanchoe juice 3-4 drops every 4 hours or lubricate the nasal passages several times a day;
- The juices of the following herbs are instilled 3-4 times a day: calendula - 3 drops, blood-red geranium leaves - 2 drops, coltsfoot - 2-3 drops, St. John's wort infusion - 3-4 drops.
Treatment
How to treat hypertrophic rhinitis? Conservative therapy is effective only in the initial stages of the disease. During this period, vasoconstrictor and anti-inflammatory drops are used, ultraviolet irradiation of the nasal cavity, exposure to high-frequency radiation, and nasal massage using 20% splenin ointment are prescribed. In case of diffuse proliferation of tissues of the mucous layer of the nasal cavity and the ineffectiveness of conservative therapy, the only treatment method is surgery.
Surgical intervention is a mechanical, laser, thermal effect on the affected part of the nasal concha in order to restore nasal breathing, sense of smell and prevent further pathological growth of the mucous membrane.
The following types of operations are performed:
- Conchotomy (submucosal, total, partial) – excision of a section of the mucous layer of the lower and middle parts of the nasal concha. If the periosteum and bone tissue are involved in the pathological process, partial or complete removal of the inner lining of the nasal cavity along with bone elements is performed (osteoconchotomy).
- Cryodestruction is the effect on hypertrophied areas with a special applicator cooled with liquid nitrogen.
- Laser vasotomy – coagulation of vessels located under the mucous layer of the nasal cavity. Used for mild illness.
- Ultrasonic disintegration of the nasal passages - sclerosis of the blood vessels of the nasal cavity under the influence of ultrasound.
Surgical treatment of hypertrophic rhinitis.
The indication for surgical intervention for hypertrophic rhinitis is the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment. The type of surgical intervention is determined by the doctor, taking into account the clinical picture and severity of the disease. The result of successful treatment is the restoration of free nasal breathing, the disappearance of other complaints, and an improvement in the patient’s quality of life. There are several types of operations:
- Submucosal disintegration (destruction) of the inferior turbinates using ultrasound.
- Lateroconchopexy is a displacement of the concha to widen the nasal passages.
- Submucosal vasotomy is the destruction of areas of the choroid plexus feeding the inferior turbinates.
- Lower conchotomy (removal of the posterior section) using a gentle technique, accompanied by preservation of the anterior turbinates.
- Endoscopic osteoconchotomy under microscopic control.
- The shape of the nasal septum is also corrected if it is deviated.
If, in the chronic form of the disease, irreversible changes in the structures of the nose are observed, surgical intervention is indicated. Depending on the area and degree of damage, the following methods are used:
- osteoconchotomy (removal of the bony edge of the inferior concha). The operation is performed under local or general anesthesia in a hospital setting in the absence of acute tissue inflammation;
- conchotomy (partial resection of the nasal mucosa and its turbinates). During the operation, the doctor eliminates hypertrophied tissue and removes polyps. Often, thickening of the epithelium leads to a deviated nasal septum, which can also be corrected;
- galvanocaustics. During the operation, the mucous membranes are cauterized, as a result of which the epithelium is reduced in volume and swelling is eliminated, which allows for improved nasal breathing.
Disease prevention
Untreated colds often lead to structural changes in the mucous membrane and other deeper tissues of the nasopharynx. Therefore, to prevent such an unpleasant disease from appearing, it is worthwhile to promptly and effectively treat all nasal diseases with medication after examination by a doctor.
Read Symptoms and various methods of treating rhinitis
Patients should be careful to harden themselves, walk more often and not be afraid of sunbathing. In hazardous work where there is a lot of gas and dust, protective respirators and masks must be used. At the first signs of an allergic effect, you should avoid contact with the irritant and take antihistamines. It is important to treat all ENT diseases: sinusitis, enlarged and inflamed adenoids, sinusitis, inflammation of the tonsils.
Treatment
The process of curing this disease largely depends on its stage. In fact, getting rid of it completely is quite difficult, since it often becomes chronic due to incorrect therapy.
Medication
This option is only suitable for mild to moderate stages, as long as the mucosal epithelium has not undergone radial deformations. In this case, the following treatment methods can be applied to the patient:
- Injection of Splenin ointment into the mucosal epithelium. It is an active biological agent that does not contain a protein component. It has highly effective antihistamine, decongestant and restorative effects. Its main goal is to launch the restoration process in the mucosal area.
- Carrying out injections based on Hydrocortisone into the nasal mucous tissue. The manipulation is also called “nasal blockade”, the effect of which is aimed at returning normal breathing by removing excess swelling.
- Instillation of anticongestant drugs into the nasal cavity. These include: Ephedrine, Naphazoline, Xylometazoline, Phenylephrine, etc. Their effect is aimed primarily at stimulating adrenergic receptors in the nasal mucosa. Once the drops have reached their destination, they help reduce epithelial swelling and inflammation.
Treatment with medications will not bring the desired result if the disease is protracted, or if it has caused radical changes in the deep parts of the nasal membranes.
It is highly desirable that procedures be implemented in conjunction with UHF.
Physiotherapy
The following manipulations are quite effective in the fight against hypertrophic rhinitis:
- UHF. It is an ultra-high-frequency therapy that affects the tissue surface of the nose through the use of an electric field. Thanks to the energy of high-frequency waves, the tissue of the nasal passages is treated. It also has a beneficial effect on the condition of the ciliary epithelium and glandular tissue, the efficiency of cellular metabolism increases, the degree of inflammation decreases, capillary tone is normalized, local immunity increases, and complete regeneration of destroyed tissues occurs.
- UV irradiation of nasal conchas. Through the use of ultraviolet radiation, a specialist is able to stop the process of reproduction of bacterial flora in the nasal cavity (during the addition of an additional infection), improve tissue trophism, and also improve the degree of resistance of the epithelium to hostile agents.
Only a doctor can determine the need for such manipulations, taking into account the degree of neglect of the disease and damage to the nasal cavity.
ethnoscience
In no case should traditional medicine recipes be used as an independent treatment option - exclusively in the form of complex therapy, which involves the following manipulations:
- inhalations with the addition of mint, lemon, orange, lavender, tea tree oil, etc.;
- nasal drops prepared from woodlice or St. John's wort;
- decoctions based on mint, chamomile, plantain, motherwort, etc.
It is also very effective to rinse the nasal cavity with saline solution, then insert cotton swabs soaked in honey or water for half an hour.
If you have an individual intolerance to bee products, you should avoid honey.
Signs and possible complications of chronic hypertrophic rhinitis in children
Children are more sensitive to infections, since the body is just developing, so hypertrophic chronic rhinitis will have more pronounced symptoms, which can affect the child’s health in the future.
Let us highlight several signs characteristic of children:
- The child breathes through his mouth, breathing is difficult.
- Headache.
- Gets tired quickly.
- Hearing loss.
- Lack of smell.
- Nasal voice.
- Decline in school performance.
- Poor concentration.
What are the possible complications for a child with this disease:
- Significant impact on the child’s psychomotor development and educational success.
- It provokes frequent otitis media, sinusitis, bronchial asthma, and pneumonia.
To avoid the transition of rhinitis to chronic hypertrophic, it is necessary to adhere to the doctor’s recommendations in therapy and promptly treat infectious diseases in children
It is important to carry out hardening procedures, maintain optimal room temperature, carry out preventive fortification, and walk in the fresh air more often
Chronic rhinitis
Chronic rhinitis is a consequence of a protracted acute process or develops as an independent disease due to prolonged exposure to microparticles from the human environment: in the workshops of enterprises, in industrial production, etc. Allergic and drug-induced chronic rhinitis are distinguished separately.
Chronic catarrhal rhinitis.
It is characterized by congestive long-term hyperemia of the mucous membranes and enlargement of the nasal turbinates. The main symptoms are mucous or purulent mucous discharge, impaired sense of smell, impaired nasal breathing, which worsens in the cold. In a lying position, nasal congestion is observed on the side on which the person lies. The reason for this is the filling of the cavernous cavities of the nasal concha with blood, the blood supply to the dilated vessels of the mucous membrane.
Chronic hypertrophic rhinitis.
This form is characterized by overgrowth (hyperplasia) of the mucous membrane, often of the inferior turbinate. Rarely, the middle and/or superior turbinate is involved. The dominant symptom is severely impaired nasal breathing, which does not improve even after taking vasoconstrictors. Accompanied by varying degrees of discharge from the nose, mucous or mucous mixed with pus. The sense of smell and taste may decrease or completely disappear, and a nasal tone may appear in the voice. If hyperplasia of the anterior sections of the turbinates has developed, the patient may experience conjunctivitis and constant lacrimation.
You can distinguish hypertrophic rhinitis from catarrhal rhinitis using a simple test. The mucous membrane of the nasal cavity and, especially, the turbinates is lubricated with a cotton swab moistened with 0.1% adrenaline. If there is an almost complete or significant decrease in the volume of the mucous membrane, it is worth talking about the catarrhal form of chronic rhinitis. If no visible changes are noted, hypertrophic rhinitis is diagnosed.
Symptoms
Hypertrophic rhinitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Difficulty in nasal breathing. Patients complain of a feeling of constant nasal congestion. More rarely, patients compare the feeling of stuffiness with the presence of a foreign body in the nose.
- Headache.
- Periodic insomnia.
- Decreased sense of smell. The function of the sense of smell is significantly reduced (up to complete anosmia) if the mucous membrane in the upper parts of the nasal cavity is hypertrophied. In the initial stages, hypoosmia is observed.
- Closed nasality. This symptom is caused by the presence of a mechanical obstruction to normal air flow. This leads to changes in the patient's voice.
- Bleeding. This symptom develops due to constant injury to the nasal mucosa. Patients often try to clear the nasal passages, and since they are narrowed due to hypertrophy, this leads to damage to the superficial vessels and the development of bleeding.
Hypertrophic chronic rhinitis will have symptoms similar to those of an allergic or infectious form of the disease, but will also have its own characteristics.
The symptoms will be as follows:
- Mucous discharge from the nose. However, they are colorless and odorless, but may have purulent impurities.
- The nose is stuffy, breathing is difficult. In this case, vasoconstrictor drops do not help.
- Headache.
- Nervous excitability.
- Sleep problems.
- Chronic fatigue.
- Odor recognition gradually deteriorates.
- Heaviness in the head.
- The man speaks through his nose.
- Watery eyes, redness and swelling of the eyelids.
- Conjunctivitis.
The manifestations of chronic hypertrophic rhinitis are in some ways similar to vasomotor rhinitis. Adults complain of periodic difficulty breathing, which becomes constant over time, and the patient is forced to breathe through the mouth. Such complaints occur at any time of the year and have no seasonality. Deterioration of hearing and nasal voice are associated with disturbances in the aerodynamics of inhalation and exhalation. Often the disease exists for a long time, patients do not pay attention to it at first.
In the early period of the onset of the disease, scanty and viscous nasal discharge appears, which is difficult to remove. Hypertrophied epithelium is unable to create a physiological secretion, so its composition undergoes changes. A feeling of congestion and difficulty breathing appears with a long course of the disease.
Treatment of chronic rhinitis
Surgical treatment of chronic hypertrophic rhinitis
Chronic rhinitis: how to treat
General signs of chronic hypertrophic rhinitis include headache, general weakness, fatigue during the period of exacerbation of symptoms. Patients often wake up during sleep due to breathing problems, and hearing deterioration is observed. Rhinitis can be accompanied by hypertrophied tonsillitis due to stagnation in the lymphatic vessels and microcirculation disorders in the arterioles and veins. Children experience snoring during sleep, deterioration in school performance, and poor results in physical fitness.
Any runny nose for a long time should raise suspicion in the patient, especially if it does not respond to treatment. However, the onset of hypertrophy can be recognized by several characteristic symptoms:
- Nasal congestion. It becomes constant, interfering with nasal breathing and forcing you to breathe through the mouth. Even the use of drugs for the common cold only provides relief for a short time;
- The nature of the discharge. When they are abundant and transparent, this rather indicates the allergic nature of the runny nose. However, thick, sometimes purulent or even brown discharge is a serious reason to visit an otolaryngologist;
- Headache. When a headache begins to ache against the background of congestion and a constant runny nose, this indicates the seriousness of the problem and the need to begin treatment;
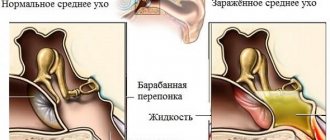
- Hearing loss. If, due to the presence of a prolonged runny nose, hearing problems begin, then it is quite possible that the process begins to spread to adjacent areas;
- Changing the timbre of the voice. It also indicates the progression of inflammation. Often the patient himself is not able to appreciate this change, but loved ones should be attentive and draw the patient’s attention to the symptom.
What are the symptoms and treatment of hypertrophic rhinitis? The main symptoms of hypertrophic rhinitis can be different. And very often they can be confused with symptoms of other diseases of the nasal cavity.
The main signs of hypertrophic rhinitis are:
- The main symptom of this disease is difficulty breathing. The patient has constant congestion in the nasal sinuses. Sometimes some patients compare the sensations during illness with the presence of a foreign body in the nose;
- Severe headache is also noted;
- Due to the fact that hypertrophy contributes to difficulty breathing, the patient may experience insomnia;
- Smell disorders. If the mucous membrane in the upper parts of the nasal cavity is hypertrophied, then there may be complete immunity to various odors;
- Nasality in the voice;
- Having a runny nose;
- Nosebleeds. Bleeding from the nose often occurs due to the fact that the mucous membrane is constantly injured. Also, quite often patients try to clear their sinuses on their own, which leads to bleeding.
The symptoms of the disease are very similar to those of other forms of the common cold. Among them:
- constant nasal congestion, difficulty breathing;
- opaque nasal discharge, possible clots of pus;
- headache;
- hyposmia or anosmia (decreased or disappeared sense of smell);
- hearing loss;
- change in voice timbre, nasality.
If this set of symptoms appears, you should immediately consult a doctor. They do not always indicate hypertrophic rhinitis; sinusitis with sinusitis may well give a similar picture. But any of these diseases requires immediate treatment in order to minimize the risk of severe complications and prevent radical surgery.