Coxsackie virus is a pathology widespread throughout the world. The disease affects adults and children, men and women, but most often it occurs in children from 3 to 10 years of age. Diagnosing the pathology is difficult, since the disease has many variants of its course.
The situation is aggravated by the fact that in order to determine the disease it is necessary to carry out expensive tests, since even professional doctors cannot always make a correct diagnosis based on external signs. For this reason, it is recommended to closely monitor your health and try to avoid the onset of illness.
What is Coxsackie virus
Coxsackie viruses are infectious pathologies from the herpes virus family. With this disease, bacteria settle and begin to actively multiply in the gastrointestinal tract. Experts have recorded more than 30 forms of the disease.
One of the most common syndromes is “hand-foot-mouth”. The pathology is otherwise called vesicular stomatitis. In this case, Coxsackie infection affects the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
The pathology is transmitted from person to person through close contact with the patient or his personal belongings. The risk group for infection includes children from 3 to 10 years old. Newborn babies who are breastfed are immune to this disease.
Children over 10 years of age, as well as adults, can also become infected with the pathology, but for them it will not occur with pronounced symptoms. Such patients quickly and easily tolerate the disease, and they develop immunity to this form of the disease.
Lists of hotels subject to ban
According to vacationers, the following risk group can be identified in hotels where the infection broke out in 2016-2017.
It is better to go to trusted hotels. Ask your friends, travel agent or read reviews on the Internet
| Cities | Hotels |
| Side | Sunrise Resort Nashira Starlight Resort Starlight Resort |
| Kemer | Limak Limra Grand Haber PGS Rose Residence Amaraprestige |
| Belek | Papillon Belvil Adora Resort Calista Luxury |
| Alanya | Kahya Resort Aqua |
Türkiye is a favorite holiday destination for children and adults. According to medical data and media news, there were no complaints from tourists in 2020. An exacerbation of the virus has currently been recorded in Cyprus in Limassol.
Dr. Maria Agathocleous, head of the pediatrics department at Limassol Central Hospital, told reporters that “there have been several cases of children contracting the Coxsackie virus.” According to her, there are three children in the hospital with this disease.
The hospitable country attracts tourists from all over the world with an affordable, comfortable holiday at sea. Reports about children who suffered infection during the summer season of 2020 made us think - is there Coxsackie virus in Turkey, how safe is this region? State authorities, inviting guests on vacation, notify:
- there is no epidemic in the country;
- the incidence rate over the year has increased insignificantly, infection is not widespread;
- its seasonal increase is possible due to the spread of the virus in a humid environment (swimming pools);
- Following the rules of hygiene will protect you from infection.
It is possible to become infected with the Coxsackie virus in Turkey in the summer in the same way as in other resorts, including the Black Sea coast of Russia. Insurance companies in our country note that there was no mass cancellation of vacation packages in 2020. They were approached by tourists who had suffered a viral infection. Their number from the total number of those who used medical care at the resorts of this country was as a percentage:
- "Rosgosstrakh" - 0.2;
- ERV – 1;
- "Liberty Insurance" - 0.2.
| Resort city | Hotel |
| Side | Sunrise Resort |
| Nashira | |
| Starlight Resort | |
| Seashell Resort Spa | |
| Kemer | Limak Limra |
| Grand Haber | |
| PGS Rose Residence | |
| Amaraprestige | |
| Belek | Papillon Belville |
| Adora Resort | |
| Calista Luxury | |
| Alanya | Kahya Resort Aqua |
Routes of transmission and main causes of the disease
The Coxsackie virus can be infected through poorly washed vegetables, fruits and hands. The pathology is also transmitted through tap water and from person to person, and contact does not necessarily have to be with a patient who has been diagnosed with the disease.
It is enough to communicate with someone who is a carrier to become infected. People often bring pathology from the resorts of Cyprus, Egypt and other hot countries.
Once infected, bacteria begin to multiply in the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, the infection is concentrated in the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx. For these reasons, the infection is transmitted through the fecal-oral route.
The incubation period for the Coxsackie virus ranges from 2 to 10 days. During this time, the infection must completely settle inside the body. After this, the period of acute pathology begins. Symptoms arise - rashes on the epidermis and oral cavity, intestinal disorders, and fever.
If such symptoms appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor, especially in cases where the person has arrived from a resort.
Clinical picture of the disease
Typical signs are:
- symptoms of general intoxication (weakness in the body, fever, muscle pain);
- rash;
- intestinal disorder.
It is this set of syndromes that determines the clinical picture of infection with the Coxsackie virus.
It all starts as a standard infectious disease. The child develops a high temperature, the baby becomes lethargic and refuses to eat. Older children complain of headaches and body aches.
The next day, more specific symptoms appear - a characteristic rash and vomiting with diarrhea.
The rash consists of bubbles (vesicles) up to 2 - 3 mm in diameter with watery contents. The first place of their appearance is the oral mucosa (inner surface of the cheeks, tonsils, palatine arches).
When infected with the Coxsackie virus, symptoms in children from 2 to 5 years of age manifest themselves most clearly, and treatment has a positive prognosis with timely correct diagnosis. The infection is most severe in people with reduced immunity.
With a sufficient level of the body's defenses, the disease is tolerated easily and without serious consequences. In some cases, complications may develop. Negative consequences of the disease can be represented by damage to the central nervous system, meningitis, pathology of joint tissue, in some cases paralysis, liver pathology and pericarditis.
The course of enteroviral disease caused by the Coxsackie virus in adults and children can be typical or atypical. In the first case, the pathology is characterized by the presence of herpetic sore throat, enteroviral exanthema (“hand-foot-mouth”), epidemic myalgia and/or aseptic meningitis.
On the third day of illness, white papules appear on the skin of the face and body, turning into itchy vesicles, which, after scratching, heal in a couple of days.
Typical shape
For the symptoms manifested by the Coxsackie virus in children, painful sensations in the throat appear, intensifying during swallowing, against a general background of poor appetite, the appearance of fever and signs of poisoning of the body (the appearance of weakness, chills, excessive sweating).
The appearance of an itchy rash in a child is one of the symptoms of Coxsackie
Enterovirus infection, after the incubation period, develops quickly. On the first day, the temperature rises sharply; the indicator on the thermometer scale can reach 38 - 40 degrees. Symptoms of intoxication appear against the background of fever. Usually the temperature lasts three days, after which it becomes normal.
The patient complains of the appearance of an itchy rash, which can be located on the perioral area of the skin, in the chest and back. The rash occurs on the buttocks, arms, and legs (usually the soles of the feet and palms). It is thanks to this arrangement that the syndrome received the second above-mentioned name - “hand-foot-mouth”.
Such a pathology as epidemic myalgia occurs quite rarely. Signs of this form include:
- a sharp increase in temperature;
- the appearance of chills;
- migraine;
- painful sensations in muscles and joints;
- stomach ache.
Serious complications of the disease include meningitis, which can be fatal. The form of aseptic meningitis is characterized by an inflammatory process affecting the meninges. The pathology develops suddenly with fever, severe headaches, and weakness. The patient is bothered by painful sensations in the throat, vomiting (in the absence of nausea).
If the Coxsackie virus is detected in infants, the occurrence of seizures should be monitored. Among the characteristic signs of brain infection are the presence of rigidity of the neck muscles, confusion, and the manifestation of Kernig's sign or Brudzinski's sign.
Atypical form
The atypical (atypical) form is characterized by the absence of signs. However, sometimes the disease develops in the form of enteroviral fever or respiratory pathology. In some cases, the disease occurs in the form of enteroviral encephalitis and meningoencephalitis or pathologies of the heart muscle. For an atypical form of manifestation of the Coxsackie virus, signs of the following diseases are also possible:
- conjunctivitis and uveitis, characterized by increased bleeding;
- spinal or poliomyelitis-like course;
- encephalomyocarditis in infants;
- acute mesadenitis, that is, inflammation of the lymph nodes in the peritoneal area;
- enterovirus infection with damage to the digestive system:
- acute damage to the liver, pancreas and other structures of the digestive tract;
- acute kidney inflammation.
The most common form of atypical course is enteroviral fever. The second name for this pathology is “summer flu.” This name is due to the fact that signs of the disease often appear in the summer, reminiscent of the symptoms of a cold in the warm season. Infection with the “summer flu” occurs during visits to various crowded places, for example, recreation areas, beaches or water parks.
Knowledge of the manifestations of the symptoms of the disease will help you identify the Coxsackie virus yourself, and photos of the main signs of the disease can be seen on our resource. Let us repeat that among the main characteristic features we can highlight:
- increase in temperature (usually up to 39 - 40 degrees);
- the appearance of general weakness;
- migraine;
- muscle pain;
- poor appetite;
- the appearance of vomiting against the background of a feverish state (the coxsackie virus often manifests itself in children, photos are proof of this);
- change in stool.
Upon examination, the doctor may see redness of the mucous tissues of the oropharynx and enlarged lymph nodes. Palpation will reveal changes in the size of the liver. When carrying out therapeutic measures, recovery occurs after 7-10 days.
Do not forget that only a competent specialist can make a correct diagnosis, so do not self-medicate.
An enteroviral disease caused by the Coxsackie virus, which was treated promptly and correctly, rarely causes negative consequences. However, with delayed or incorrect treatment, as well as in the case of reduced immunity, the pathology can be complicated:
- paralysis, paresis;
- inflammation of the meninges;
- meningoencephalitis;
- inflammatory process in the heart muscle;
- pericarditis;
- pathologies of the pancreas, for example, with the subsequent development of diabetes.
Most often, children under 2 years of age, pregnant women, and people with a low level of immunity suffer from this.
The time from infection to the development of the first symptoms ranges from 2 to 10 days. The onset of the disease is usually acute, with a rise in body temperature to 39° C, a sharp deterioration in general health, muscle pain and headache. Typically, such symptoms correspond to viremia - a massive release of viral particles into the systemic bloodstream.
- General intoxication in childhood characterizes almost all infectious diseases. Symptoms indicating the Coxsackie virus develop within a day of the onset of the disease and include:
- The appearance of small painful blisters and ulcers (up to 2 mm in diameter) on the mucous membrane of the mouth, mostly on the inner surface of the cheeks.
- A sore throat with the appearance of blisters on the tonsils is also possible.
- Formation of small vesicles (bubbles with liquid) on the palms, plantar surfaces of the feet, between the toes. Such elements of the rash resemble chickenpox. Then they may appear in small quantities on the skin of the hands (forearms) and buttocks.
- There is no itching on the skin during infection with the Coxsackie virus.
- The temperature persists for several days, then returns to normal (subject to the classic course of the infection).
- Dyspeptic syndrome – development of diarrhea and vomiting. Diarrhea can occur up to 5-10 times a day, the stool is liquid, watery without pathological impurities (blood, mucus or pus).
Tourists visiting Turkey often complain about the viral disease, which most often affects children. Coxsackie virus is the name of a disease that affects the skin and causes severe poisoning of the body.
Here is a message from one social network user: “On the third day of vacation in Turkey, the youngest child caught the Coxsackie virus, although at that time the doctors did not inform us of what exactly was happening. Then the whole family got sick, and now it’s my turn. Symptoms of the disease are a high temperature, 40 degrees, then a rash the size of a pea on the skin, the blisters burst. On top of that there is also diarrhea.”
There are a lot of comments on this message, in which people also report that they suffered from this type of illness in Turkey and managed to bring it to Ukraine. The Minister of Foreign Affairs of Ukraine instructed the Turkish embassy to study data on the epidemic and develop instructions for the behavior of Ukrainian tourists on vacation.
Coxsackie is an enteroviral disease. It actively manifests itself during the hot summer period. The virus is accompanied by diarrhea and disruption of the digestive tract, the appearance of a rash on the skin and high body temperature. Young children are most susceptible to this disease.
The incubation period of the virus ranges from 2 to 10 days. The first signs of infection with the virus are often mistaken for colds. Therefore, if you notice similar symptoms, you should immediately contact a medical facility.
A little later, irrefutable symptoms of a viral disease appear - small blisters appear all over the body. Most often, the focus of the virus is located in the mouth and genitals. Blisters cause discomfort and pain. In addition, severe diarrhea occurs. If you do not pay attention to these signs and do not seek help from a doctor, the consequences can be very serious. This can lead to central nervous system complications, meningitis, paralysis and diabetes.
How do the first signs of the disease appear?
How does the infection progress?
Pathology has four forms of occurrence:
- Flu-like syndrome. Another name is Flu-Like. This pathology has the mildest form. Characteristic symptoms are fever, muscle pain, discomfort in the bones and general malaise. Signs of the disease are observed within three days. Next comes recovery. Influenza-like syndrome rarely causes complications, but only with qualified therapy;
- Intestinal infection. Children under two years of age most often suffer from this form of pathology. With such a disease, it is not necessary that other children will become infected from the child. In a group, this case may be exclusive and no one else may suffer from it. Characteristic symptoms are high fever, discomfort in the bones and general weakness of the body. In the first days of infection, other signs are observed - intestinal upset, nausea accompanied by vomiting. For this reason, the disease is often confused with poisoning. The period of exacerbation is 2-3 days for children of primary school age and a week for newborns. This disease can cause milk intolerance during the first time after recovery. This makes it necessary to give the child medical lactose before breastfeeding or to refuse it;
- Boston Pathology. The disease manifests itself in the same way as rubella, which makes it difficult to diagnose. A child, like an adult infected with the Coxsackie virus, in this case becomes covered with formations of a red hue. Symptoms: high fever, rashes on the epidermis in the form of blisters. The treatment period is 3-5 days. After this, recovery begins. With this form, relapse rarely occurs, and complications are most often not observed;
- Pleurodynia. Another name is Bronholm's disease. Symptoms: high fever, severe pain in the back, abdomen, muscles and chest. Spasms occur at regular intervals – once every 60 minutes. The duration of the attack is from 1 to 20 minutes. They cause spasms in the pleura and peritoneum, which cause pain during friction.
With any form of pathology, the patient needs urgent medical care.
Coxsackie viruses are divided into two large groups
There are two groups of pathology:
- Type A virus: Infection with the Coxsackie virus causes damage to the throat and may cause meningitis.
- Virus type B. Affects the brain, muscles and heart, causing irreversible changes in these internal organs.
Course options: mild, moderate and severe
Pathology has varying degrees of progression. The severity of the disease depends on how much the mucous membranes and internal organs are damaged. The degree is also affected by damage to the body by toxins.
The mild form of the pathology is characterized by a rapid course. Recovery occurs within a few days. In this case, the virus does not affect the patient’s internal organs and brain.
With moderate severity, therapy takes a little more than a week. The pathology has pronounced symptoms. The virus can affect internal organs, but with qualified treatment the problem can be quickly resolved.
The severe form of the disease is characterized by pronounced symptoms and a long course. This causes damage to the brain and internal organs.
Experts also identify the following variants of the pathology:
- smooth – recovery occurs quickly and the disease does not recur;
- wavy - the pathology either fades or flares up with renewed vigor;
- recurrent – after recovery, the disease develops again;
- with complications – the disease is difficult to treat and causes complications.
The virus most often causes a severe form of pathology in adults. To get rid of the disease without serious consequences for the body, it is necessary to begin therapy immediately after infection. Any delay and attempt at self-medication leads to unpredictable and irreversible consequences.
Forms of the disease
There are two forms of pathology:
- Isolated. The disease occurs in one syndrome.
- Combined. In this case, the Coxsackie virus affects several organs and systems at once.
How not to get sick at a resort
The Coxsackie virus was first discovered in the last century in the United States. Since then, outbreaks of the disease have been recorded all over the world, especially often in popular resorts in Turkey, Cyprus, Greece, Spain, Italy and others. Why is this happening?
Now everyone is talking about the coxsackie epidemic in Turkey. Outbreaks of the virus have been recorded in different hotels in Antalya, Alanya, Side, Kemer and Belek. Why does it happen that the virus often lies in wait for tourists at resorts? It turns out that everything is simple.
Causes of epidemics at resorts:
- People are relaxed and don't care about washing their hands.
- The all-inclusive system allows you to have a snack during the day while on site. Of course, almost no one runs to the toilet to wash their hands before helping themselves to a flatbread or an apple.
- A huge number of children are in children's mini-clubs, essentially resort kindergartens, which are an ideal environment for the transmission of various types of viruses. For some reason, this doesn’t surprise us at home, but on vacation we are perceived with surprise.
- A large number of people use a communal swimming pool, in which the water filtration and disinfection system during the peak season may simply not cope with the function of water purification. As a result, we may end up with a reservoir of infection.
Based on this, we will compile a list of recommendations on how to avoid becoming infected with the coxsackie virus while on vacation in Turkey in 2020 and 2020:
- Remember to wash your hands or at least wipe them with damp antibacterial wipes before eating.
- Do not send your child to the mini club.
- Don't swim in the pool, spend time at sea.
- Have breakfast, lunch and dinner outdoors rather than indoors in the main restaurant.
- If possible, choose a bungalow room category rather than a room in the main building. This will minimize your presence in the building with other people (use of common corridors and elevators). Usually, when staying in a bungalow, the room is entered directly from the street.
Possible complications
The Coxsackie virus, like any bacterial infection, can cause complications. Since it has several forms of flow, various organs and systems can be affected.
Brain swelling may occur due to the Coxsackie virus. This is the main danger of infection. If such a situation occurs, the person requires immediate resuscitation measures. Untimely assistance can result in death.
The Coxsackie virus also has the following consequences:
- During infection, additional infections may join the virus. As a result, bronchitis, sinusitis, meningitis, pneumonia and other similar pathologies occur;
- Dehydration. Most often observed in children. This condition occurs due to intestinal disorders, as well as in the absence of a drinking regime;
- The risk of diabetes increases. The infection provokes the development of type 1 pathology;
- False croup. This makes breathing difficult and swelling of the larynx occurs. This can cause suffocation and death;
- The central nervous system is damaged. This leads to paralysis, epileptic seizures and other similar problems;
- Pulmonary edema. Occurs against the background of the development of pneumonia;
- Atopic dermatitis. An intestinal infection can trigger exanthema with the Coxsackie virus;
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular system. In particular, heart failure and other similar diseases appear;
- Infertility. Occurs in young men during puberty due to damage to the testicles;
- Liver pathologies;
- Complications on the eyes. Vision deteriorates to the point of complete blindness.
With the Coxsackie virus, hair also suffers and nails peel off, but only in severe cases of the pathology.
Symptoms and photos
Characteristic symptoms of the Coxsackie virus:
- an increase in body temperature, and it rises sharply and does not fall below 380 for several days;
- general weakness of the body even without excessive physical activity;
- a sore throat;
- white plaque in the mouth;
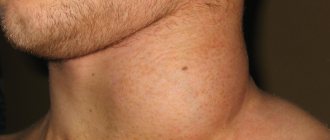
- lack of appetite;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the neck.
What the Coxsackie virus looks like is shown in the photo below.
There are several clinical forms of pathology. The classification is based on the predominance of the syndrome:
- Pharyngitis. When such an enteroviral disease occurs, rashes and white plaque appear in the oral cavity and tonsils;
- Exanthema. The pathology is characterized by the appearance of rashes on the epidermis;
- Myalgia. Symptoms – the appearance of pain in the muscles;
- Fever. With this form of infection, body temperature rises. There are no symptoms of colds. The child may also complain of weakness;
- Diseases of the nervous system. Brain damage occurs, severe headaches appear and intoxication of the body occurs. Sometimes paralysis develops.
If symptoms of infection are detected, you should immediately consult a doctor to prescribe treatment. Any delay can lead to complications and even death.
Coxsackievirus in children
Children are most often infected with the Coxsackie virus. The main danger of this pathology is that it can be confused with chickenpox or allergies due to the similarity of symptoms.
Particularly often, confusion occurs if the virus appears in infants, since it is difficult to identify additional symptoms due to the fact that the child is not yet able to complain of feeling unwell.
If the disease is incorrectly diagnosed, the doctor will prescribe the wrong treatment. Because of this, the virus will progress in the body, causing complications. For this reason, it is important to correctly diagnose the pathology.
What the Coxsackie virus looks like in children is shown in the photo below.
Symptoms of the virus in children
Signs of Coxsackie virus in children:
- increase in body temperature from 380 and above;
- nausea accompanied by vomiting;
- pain in the head area;
- chills;
- weakness and fatigue even in the absence of physical activity;
- rhinitis;
- a sore throat;
- muscle pain;
- tachycardia;
- swelling of the larynx;
- lack of appetite.
If infection occurs, the child should be shown to a doctor immediately, without waiting for the disease to develop.
Infection prevention measures
The head of Rospotrebnadzor Anna Popova said that the situation with the Coxsackie virus in our country is under control. According to her, in the first half of the year only eight cases of infection were recorded in the Russian Federation.
Coxsackievirus is an enterovirus transmitted by airborne droplets. When infected, people develop a temperature of up to 40 degrees and the body becomes covered in a rash.
In order to avoid becoming infected with the Coxsackie virus in Turkey and other countries, it is necessary to find out the epidemiological situation in the region before purchasing a ticket. Parents should know how to protect themselves from infection. Prevention includes the following measures:
- be sure to wash your hands with soap after visiting public places, the toilet, and before eating;
- Pour boiling water over fruits and vegetables before eating;
- give children water only after boiling;
- do not eat at dubious food outlets.
Since the virus spreads quickly in pool water, children should not swim there. If there is a threat of infection, it is better to refrain from visiting water parks and places with large crowds of people. Measures to prevent Coxsackie infection include the need to:
- each person should use their own towel and utensils;
- avoid swimming in dirty waters;
- after visiting the pool, take a hot shower;
- isolate the sick person from other family members;
- increase immunity;
- If signs of illness appear, seek medical help.
Even before going on vacation, make sure to purchase medical insurance for all vacationing family members.
If during your vacation you find yourself in a situation like vacationers in Turkey, the main thing is not to panic. There are prevention methods that work. They are suitable for both adults and children:
- wash your hands often with soap or treat them with special antiseptic solutions;
- avoid crowded places;
- drink only tested water from safe sources;
- do not buy ready-made food in markets and untrusted places;
- wash all vegetables and fruits you eat with soap;
- try not to swim in public pools;
- when swimming in open water, try to avoid getting water into your mouth, as this is the most likely possibility of infection;
- rinse your mouth and nose with Chlorhexidine solution after visiting crowded places.
At the first sign of discomfort at the source of infection, consult a doctor.
If someone close to you gets sick, allocate (if possible) a separate room. He should also have separate hygiene items and utensils.
The Coxsackie virus is very contagious in children. It is not easy to avoid infection with it. But this infection has not reached epidemic proportions.
Under no circumstances should you give in to panic. Follow the rules of personal hygiene, try to be in crowded places as little as possible, and the chance of getting sick will decrease tenfold.
Although the Coxsackie virus is extremely contagious - upon contact with a patient, infection occurs with almost 100% probability - preventive measures are aimed at preventing the widespread spread of infection. Prevention includes:
- Isolate the patient for 1-2 weeks. Until the symptoms of the disease completely disappear.
- If you are in hotspots of infection (for example, at a resort in Turkey), avoid visiting swimming pools and public events. Such restrictions especially apply to children.
- Twice wet cleaning daily in the room where the patient is located, and regular ventilation.
- Administration of immunoglobulin to young children and pregnant women who have been at the site of infection.
- Boiling water, thoroughly washing the fruit and then pouring boiling water over it.
- Compliance with temperature conditions and shelf life of dairy products.
- Disinfection of cutlery, toys, boiling of sick person’s underwear and bed linen. Separate dishes and towels are provided for the patient.
- Frequent hand washing, treatment with alcohol-containing antiseptics.
You should not treat summer infections irresponsibly; they often lead to serious complications. Most patients infected with the Coxsackie virus do not require hospitalization, have no negative consequences, and recover within 10-14 days.
The most severe disease occurs in children under 2 years of age and people with immunodeficiency. Babies are at high risk of developing dehydration, especially with vomiting and diarrhea. Timely diagnosis of viral infection and medical care in the development of critical conditions are also important. In severe cases of the disease, laboratory confirmation of the presence of the Coxsackie virus is necessary, but not all clinics perform such an analysis.
Tags: virus child
There is no vaccine for the Coxsackie virus, so all prevention comes down to observing basic sanitary standards.
- Each time before eating, you should wash your hands thoroughly with soap.
- All purchased fruits, vegetables, and berries should also be washed with soap and water before consumption.
- You should eat in well-tested, reliable places or cook your own food.
- If possible, it is recommended to avoid crowded places and groups of children.
Coxsackievirus in adults
In adults, the disease is very rare, but the possibility of infection exists. The infection can be identified by the following symptoms:
- redness of some areas of the epidermis;
- pink rash on the skin;
- fever that is short-lived;
- rhinitis and cough;
- lack of appetite;
- problems with stool.
Pathology also requires timely qualified treatment. Only this will help avoid the development of complications and relapse of the disease.
How to treat
Your doctor will tell you how to treat the pathology and how to treat it. If the infection has not affected the internal organs and systems, then therapy is carried out in the same way as for any cold pathology.
A comprehensive treatment for the Coxsackie virus is prescribed, which is based on the use of antipyretics, analgesics and antiseptics.
The doctor will also prescribe antihistamines if symptoms of an allergic reaction are detected. Complete therapy is impossible without antibiotics and immunomodulatory agents.
If Coxsackievirus occurs, treatment of skin rashes is not prescribed. The doctor prescribes only medications for internal use. They also help get rid of the external manifestations of pathology.