Pregnancy is an important event in the life of every woman. I want all illnesses and adversities to pass by. But it happens that someone in the family gets chickenpox.
Chickenpox is a childhood disease, but adults can also get chickenpox. The baby will quickly and painlessly overcome the disease, earning immunity for life. But getting chickenpox during pregnancy can have serious consequences. Therefore, you should know for sure whether chickenpox is dangerous for pregnant women or not.
Chickenpox during pregnancy
Chickenpox is an acute infectious disease caused by the third type of herpes virus Herpesviridae - Varicella Zoster. It is characterized by the manifestation of a papulovesicular rash on the body and mucous membranes. The duration of the disease until complete recovery is on average 14 - 19 days.
Chickenpox occurs in 2 - 3 women per year out of 2000 pregnancies. According to medical data, 80 - 90 percent of women suffered from this disease in childhood and have specific immunity, so re-infection is most likely unlikely.
If the expectant mother has not previously suffered from the disease and has not been vaccinated, she runs the risk of getting sick later.
If there is any suspicion of chickenpox, a pregnant woman should consult a doctor - a gynecologist or a general practitioner. Self-medication can lead to negative consequences. Until complete recovery, you should not visit an antenatal clinic to avoid spreading the virus.
Symptoms and possible consequences of chickenpox at different stages of pregnancy
The duration of the incubation period for chickenpox is from 5 to 20 days. A sick person may not be aware that he has chickenpox until the characteristic rash appears. All this time, the infected person is a carrier of the virus. A pregnant woman may not know where the disease overtook her. In order to recognize the disease in time, you need to know its first symptoms.
I trimester
The symptoms of chickenpox during pregnancy are similar to those observed in other people. During pregnancy, some women experience chickenpox symptoms that worsen due to low immunity.
Signs of chickenpox:
- general weakness;
- drowsiness;
- severe headaches;
- low-grade body temperature;
- nausea and stomach pain;
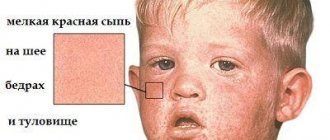
- itching at the site of the rash;
- the appearance of intense rashes;
- within a few hours, the red rash turns into purulent blisters, which after a while burst and become crusty.
If a woman's immunity is severely weakened, complications may arise. Chickenpox makes the body vulnerable to other viruses and infections. Under unfavorable circumstances, the patient may develop bacterial pathologies, pneumonia, and encephalitis. The virus can infect internal organs.
In the 1st trimester, mother's diseases pose the greatest danger to the child. In the first weeks of pregnancy, all the main organs and systems of the baby are formed. Up to 20 weeks, the placenta is not yet able to protect the child from the effects of negative factors. Both the viruses themselves and the drugs used in therapy have a negative effect. Possible consequences of chickenpox for the fetus:
- miscarriage;
- intrauterine infection and death;
- pathologies of development of internal organs;
- improper formation of limbs;
- damage to the central nervous system;
- muscle tissue defects;
- underdevelopment of the visual and auditory organs;
- unformed or scarring of the skin.
The disease very rarely leads to fetal developmental disorders. According to statistics, the probability of pathologies occurring in a child is from 1 to 5%, and the immunity developed by the mother during the illness will protect the baby from the virus during the first months of life.
II trimester
In the 2nd trimester, women tolerate the disease more easily - the symptoms of chickenpox do not appear as intensely. However, severe headaches are typical for pregnant women at any stage. The risk of complications in a child decreases significantly in the middle of the trimester and is less than 2%. After the placenta is fully formed, the disease is not so terrible for the child.
Starting from 18–20 weeks, stronger drugs can be used for treatment. In this regard, it is possible to significantly reduce the manifestations of unpleasant symptoms and treat complicated forms of chickenpox without harm to the baby.
III trimester
In late pregnancy, a woman can easily get chickenpox. However, the baby is at risk if the mother becomes infected in the last weeks before birth. If a woman gets chickenpox shortly before giving birth, the baby is diagnosed with neonatal chickenpox. The disease in newborns is severe.
Children who become infected with the virus shortly before birth or in the first days after it die in 25% of cases. The likelihood of an unfavorable outcome increases if childbirth occurs before the mother begins to develop immunity to the disease (earlier than 6 days before the rash appears). The following complications are possible in infants:
- lesions of the brain and spinal cord;
- pathologies of the respiratory system;
- inflammatory processes in internal organs;
- atrophy of the optic nerves.
If a pregnant woman is suspected of having chickenpox shortly before giving birth, doctors try to maximize the time the baby spends in the womb. 5–6 days after the appearance of the rash, the patient’s body begins to produce antibodies, which are partially transmitted to the child. The later the baby is born after the mother is infected, the easier it will tolerate neonatal chickenpox.
Diagnosis of the disease
The varicella virus manifests itself:
- increased temperature;
- severe itching;
- redness on the skin, which later turns into blisters.
The first signs of a rash appear on the body, and may also appear on the scalp. Spread over the skin occurs quickly, the number of rash elements can reach up to 300 pieces. Each new rash may be accompanied by fever.
Depending on the severity of the disease, skin lesions may appear on the mucous membranes, genitals and eyelids.
If an antique rash, shingles, or re-infection occurs, an accurate diagnosis will require a blood test to detect type 3 herpes.
Repeated infection - reinfection
In this case, the position of the woman does not affect the methods of transmission of infection. This mainly occurs through airborne droplets when the patient sneezes or coughs.
Transmission through skin-to-skin contact is also possible. If the emulsion of the patient's bubbles gets on the skin of a healthy person. Consequently, the infected person's clothing may also be saturated with this liquid.
Contact of a pregnant woman with chickenpox patients guarantees the subsequent development of the disease if the body does not have immunity.
Can a pregnant woman become infected with chickenpox again if she already had it as a child? Theoretically, such a possibility exists: after recovery, the virus does not completely disappear from the body, but continues to exist peacefully in the nerve ganglia. However, in practice this rarely happens.
Re-infection occurs when the mother has a malfunction of the immune system. Reactivation of the virus occurs during HIV infection, cancer, taking immunosuppressive drugs, and after organ transplantation.
During pregnancy, if a woman has already had chickenpox in childhood, contact with Varicella-Zoster Virus makes itself felt with signs of herpes zoster. Under the influence of immunodeficiency, the virus is activated and enters the skin along nerve fibers, causing painful blistering rashes and fever.
Consequences for mother and child in different trimesters. The opinion of doctors and Dr. Komarovsky
Pregnancy is not an aggravating factor in the course of the disease. The difficulty lies in medical therapy; not all medications are safe during pregnancy.
Chickenpox during pregnancy can cause a number of complications for the woman and the unborn child. However, the risk of complications is low, so the disease is not a reason for artificial termination of pregnancy.
Most women undergo home therapy and give birth to healthy children on time.
The fetus can become infected from the mother. Risks depend on the duration of pregnancy and individual facts. There are three fundamental situations that are important to know.
Chickenpox in early pregnancy (1st trimester)
Chickenpox in early pregnancy is the most dangerous. It is in the first 12 weeks from conception that all vital systems are formed, but the placenta remains unformed. During this period, the placenta is not able to fully protect the child from infections. As a result of the disease, the baby may experience serious health complications.
Danger to baby's development
During the gestation period, the health of the expectant mother is especially valuable, because the development of the fetus depends on it.
Various diseases and viruses, including herpes, have a negative impact. Chickenpox and pregnancy in the 1st trimester are practically incompatible with the life of the baby.
In the first weeks, organs and tissues that are not yet protected by the placenta are formed. Therefore, the virus penetrates and infects the fetus.
This threatens:
- miscarriage;
- distorted development of affected organs;
- death of the fetus;
- damage to the central nervous system;
- retarded development of the limbs.
Unfortunately, intrauterine changes can only be noticed on ultrasound diagnostics in the second trimester. If the examination reveals severe pathologies, then a forced abortion is performed.
If a pregnant woman gets sick in the 2nd trimester, then this will not pose a threat to the baby.
Regardless of the form in which the disease occurs, the baby is reliably protected by the placenta. Its infection is practically excluded.
Chickenpox in pregnant women in the 3rd trimester also poses a high risk of infecting the child. Especially if the mother caught the virus in the last weeks before giving birth.
There is a risk of congenital infection, which can appear either in the womb or at the time of birth. In this case, not only the surface of the body, mucous membranes, but also the internal organs of the nervous system are affected.
Treatment of chickenpox in pregnant women
Gynecologists note that most patients are treated at home. The drugs are selected individually by the attending physician depending on the duration of pregnancy and the severity of the disease.
Treatment of damaged skin with antiseptic agents
Zelenka is often used as an antiseptic. The brilliant green solution is safe at any time.
In moderate and severe forms, use Calamine lotion or Psilo-balm. Both have proven to be highly effective in treating rashes. They have a calming and cooling effect, reduce inflammation and the development of infections. The drugs have contraindications.
Basic drugs for skin treatment
In any case, you should consult your doctor about possible side effects during use.
Immunostimulating drugs
To increase immune resistance, Viferon suppositories are prescribed. According to the instructions, suppositories are allowed to be taken from the 14th week of pregnancy. An analogue of Viferon is Genferon Light suppositories, which are also allowed to be used during pregnancy.
Viferon candles
For moderate or severe
Depending on the severity of the disease, the doctor may prescribe the antiviral drug Acyclovir. It effectively destroys the herpes virus in the body. The use of Acyclovir can reduce rashes and prevent complications.
The medicine proved its high effectiveness in 1977 in scientific experiments. Not recommended for use in the 1st trimester.
In some cases, the immunostimulating drug Immunoglobulin is prescribed. The use of drugs together during pregnancy is possible only if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus.
If the throat is affected by a rash
If you have a sore throat, it is recommended to drink more water without gases. Eat soft, non-spicy foods that do not irritate the throat.
How to protect yourself from chickenpox during pregnancy
If a pregnant woman had smallpox in childhood, she has nothing to worry about. Her body received lifelong immunity to chickenpox. She can communicate with an infected person, even in close quarters. In most cases, the development of recurrent disease does not occur. In a situation where a pregnant woman has not been exposed to the disease, it is necessary to clarify whether chickenpox is dangerous for a pregnant woman during the period of bearing a child.
In order to prevent the disease, it is recommended to resort to preventive measures on the body:
- Stop all communication with young children;
- Do not visit places with many people, especially hospitals;
- It is recommended to limit communication with people who have a rash on the skin or other manifestations of the disease;
- If there are children in the family or close circle who have not yet recovered from the disease, they should be vaccinated against chickenpox.
If an unprotected pregnant woman comes into contact with an infected patient, the following actions should be taken:
- Tell your doctor in more detail about this event;
- Carry out emergency vaccination within the next 96 hours after contact;
- Drugs should be administered intramuscularly and intravenously to block the growth of the virus;
- If the gestational age exceeds 37 weeks, it is recommended to induce labor or perform surgical delivery.
In any case, you should notify your doctor. The main thing is to take all measures that can contribute to the impossibility of contracting a dangerous disease.
Prevention of chickenpox
Effective prevention is vaccination, which must be done 3 months before the planned pregnancy. There are currently two vaccines available for adults: Varilrix or Okavax. Both vaccines are contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation.
The second method of prevention is to avoid places with large concentrations of children.
According to statistics, children are the main carriers; adults rarely get sick. It is necessary to protect yourself from visits to children's approvals.
It is worth noting that a person is contagious with chickenpox before the first symptoms appear on the skin. At this time, he is an active carrier, as he does not limit his movement. The virus can spread several meters from its carrier.
You can catch the chickenpox virus anywhere: in a store, shopping center, elevator and other places. Currently, the most reliable method is vaccination.
Breastfeeding with chickenpox
Clinical manifestations of chickenpox during pregnancy
From the moment of contact with someone who has chickenpox until the first symptoms appear (incubation period), about two weeks (5–21 days) pass.
The disease is characterized by a staged development of skin rashes
Symptoms of pathology are divided into two groups:
- intoxication;
- damage to the skin and mucous membranes.
Signs of intoxication syndrome:
- a sharp increase in body temperature (more than 38 ° C);
- severe weakness;
- drowsiness;
- loss of appetite;
- nausea, sometimes vomiting;
- bowel disorder.
The longer the pregnancy, the more severe the signs of infection.
Simultaneously with the rise in temperature (less often, during the first day), the first elements of a rash appear on the scalp and torso. Chickenpox is characterized by stages of development of changes on the skin.
Chickenpox rash stages:
| Rash element | Characteristic |
| Spot | Round, painless, non-indense redness of the skin caused by local dilatation of capillaries |
| Papule | A bump that rises above the surface of the skin. Cause – serous swelling of the skin |
| Vesicle | A superficial cavity element that rises above the surface of the skin and contains serous fluid inside. The vesicle is single-chambered, the cover is thin. Appears as dew drops on the skin surrounded by a rim of redness |
| Pustule | The same vesicle, only the liquid inside is cloudy, and the tire is more compacted |
| Crust | A dense brown mass that forms from a secreted vesicle or pustule and covers the healing site |
On the body, chickenpox rash can leave areas of depigmentation that quickly disappear. Single atrophic scars (pockmarks) are possible on the face.
Chickenpox is characterized by a wavy rash. Over the course of 6 days, new elements of the rash appear. In severe cases, rashes are found on the palms, heels, conjunctiva, external genitalia, and mucous membranes of the mouth and throat. All stages of the rash will be present on one area of the skin - false polymorphism. This whole process is accompanied by intense itching.
Answers to the most common questions
What is the likelihood of infection from contact with someone with chickenpox?
The chance of infection through close contact is 99 percent. If you have previously had chickenpox, the risk of infection is minimal.
When can you plan a pregnancy after chickenpox?
Pregnancy after chickenpox is possible after complete recovery. Otherwise, the fetus risks becoming infected from the mother. Doctors recommend waiting 2-3 months for the body to recover.
What to do if you get chickenpox during pregnancy before 12 weeks
It is necessary to contact a general practitioner at your place of residence and inform your gynecologist. If you have chickenpox and are under 12 weeks pregnant, it can be dangerous for the fetus. In the 2nd trimester, it is recommended to do an ultrasound to check for possible complications.
Is chickenpox dangerous during pregnancy?
Chickenpox can be treated. Each case is individual. According to medical statistics, complications in mother and fetus are rare.
Is chickenpox dangerous during pregnancy?
Chickenpox is caused by herpes virus type 3. The virus spreads quickly through contact with a sick person. The probability of infection reaches 99.9%. However, if a child gets sick, he develops lifelong immunity. A woman who has had chickenpox as a child has virtually no risk of contracting it during pregnancy.
Immunity to chickenpox also protects the baby during the first 12 months of life if the mother breastfeeds. However, if she has not had chickenpox, the baby may become infected with the virus upon first contact with the patient.
Chickenpox has specific clinical course in childhood and adulthood. Children easily tolerate the disease, and they have virtually no complications. In adults, the disease takes on a severe form - the symptoms are more intense, and the recovery process is long. In adult patients, chickenpox can cause various complications.
Chickenpox is most dangerous for a pregnant woman. The risk of complications due to weakened immunity increases. The treatment process is also complicated, since during pregnancy the list of approved drugs is narrowed.
However, with timely and correct treatment, the disease does not lead to serious consequences. Most patients undergo therapy at home and safely give birth to healthy babies on time.
Is it possible to treat chickenpox with folk remedies?
Chickenpox responds well to treatment using unconventional methods, but folk remedies can only be used with the permission of the attending physician.
A few simple recipes:
- If you get chickenpox in the summer, eat half a glass of fresh strawberries every time after a meal. Berries eliminate heat and cleanse the blood of toxic substances.
- For severe itching, add 100 g of soda and potassium permanganate to the bath on the tip of a knife. Such water procedures will help dry out the rash and prevent the spread of infection. The water should be a little cool, the duration of the procedure should be no more than a quarter of an hour.
- In the absence of allergies, eat 15 g of a mixture of equal amounts of honey and lemon juice three times a day, the product strengthens the body's protective functions.
To speed up the process of restoration of the epidermis, lubricate areas where the crusts have already fallen off with a solution of vitamin E.
Symptoms
Chickenpox during pregnancy has pronounced symptoms that are difficult to confuse with other diseases:
- Intoxication of the body.
- General malaise.
- High body temperature.
- Weakness is observed in pregnant women with chickenpox.
- A red rash that develops into blisters of fluid.
- Unbearable itching.
The rash continues for at least 5 days. The signs of the disease in adults and children are the same, but children often tolerate it much easier due to less severe symptoms.
The incubation period for chickenpox in pregnant women, like other adults, is 10-21 days. The mechanism of infection of cells occurs through airborne droplets, for example, during a conversation, if an infected person sneezes or coughs and saliva gets on a healthy person.
Chickenpox during pregnancy is not uncommon, because during this period the mother’s body is very weakened, immunity is reduced, and it’s easy to catch various kinds of diseases.
After chickenpox enters the body during pregnancy, the virus is mainly located on the mucous membrane, in the nasopharynx, oral cavity, etc.
Prevention
All women planning a pregnancy who do not remember or are not sure that they had chickenpox in childhood should have their blood tested for the presence of immunoglobulins (IgG) to Varicella Zoster. In case of a negative result, it is recommended to get vaccinated against chickenpox six months before the planned conception.
During pregnancy, the administration of live vaccines (which is the chickenpox vaccine) is contraindicated.
To avoid becoming infected, pregnant women must follow safety rules: avoid contact with presumably sick people, limit visits to children's groups.
General symptoms
Symptoms significantly depend on both the age and the individual characteristics of the sick woman. If a pregnant woman gets chickenpox, the following symptoms begin to appear:
- the stomach often starts to hurt;
- body temperature rises;
- there is general malaise;
- after 2 days, a rash begins to appear in the form of red blisters filled with cloudy liquid;
- rashes appear sporadically;
- episodes repeat every 3–5 days.
The symptoms of chickenpox in pregnant women are similar to the symptoms of chickenpox in children, only the number of rashes is much greater. The disease is accompanied by severe intoxication. The rash begins to develop later than with chickenpox in children. Blisters always appear with purulent contents.
Why is chickenpox dangerous for pregnant women?
When carrying a child, the infection threatens complications for the mother and fetus. In this regard, at the first symptoms of the virus during pregnancy, you should contact a specialist. This will prevent negative outcomes that can cause miscarriage, fetal pathologies and other complications.
Pregnancy and chickenpox are quite common; depending on how far along the woman is, the problems may differ slightly:
- If infected in the early period of pregnancy, the complications will be much more serious, they threaten deformities and pathologies of the fetus.
- The second trimester is a position in which the baby is already protected by the placenta, so the effect of chickenpox on pregnancy and the baby is reduced.
- Infection in recent months does not threaten the mother and fetus, but even in this case, consultation and monitoring by a doctor is necessary. It is dangerous only in the last days before childbirth; there is a risk of infection of the newborn and the formation of a congenital form of chickenpox.
Despite the fact that chicken pox and pregnancy are a high risk of negative consequences for the newborn baby and mother, abortion is extremely rarely resorted to. In case of infection, you must seek help from a qualified doctor, he will prescribe effective treatment.
Important! If you are worried about whether chickenpox is dangerous for pregnant women who suffered from this disease in childhood, then discard all worries, there is no reason for them. Acquired immunity after an infection completely protects both the woman and the fetus.
In order to understand whether chickenpox is dangerous during pregnancy, you should consult your doctor. As already described above, a lot depends on the period of the disease; from 14 to 36 weeks this infection is completely safe for the child. At other times, this virus can threaten the baby, and this is a real reason for concern and consultation with several specialists.
Possible complications
What are the risks of chickenpox during pregnancy, possible pathologies:
- Cataract.
- Underdevelopment of the eyeballs.
- Violation of the development of internal organs.
- Fetal asymmetry, atrophy of the arms or legs, the presence of an extra phalanx.
- Absence or severe defects of the skin.
- Delayed psychological and physical development.
It is important to understand that these complications occur in isolated cases and you should not immediately take it personally. Modern diagnostic equipment can determine a lot in the early stages of formation.
How does chickenpox affect pregnancy, extremely rare consequences:
- Miscarriage.
- Fading pregnancy.
- Stillborn fetus.
You should not decide on your own whether chickenpox is dangerous for pregnant women; your experiences can negatively affect the child, not the chickenpox virus. Yes, of course, various pathologies can develop, but in any case, you need consultation with several specialists to make the right decision.
Features of the disease
Chickenpox is a highly contagious airborne infectious disease characterized by the appearance of small blistering rashes on the skin. It is usually accompanied by fever, as well as deterioration in general condition. The causative agent is one of the types of herpes viruses - Varicella Zoster. In addition to chickenpox, it also causes herpes zoster.
The incubation period is 7-21 days. The virus enters the pregnant woman’s body through the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose. It is carried throughout the body by blood, penetrates the mucous membranes and skin, where it begins to multiply.
A person with chickenpox becomes contagious 2 days before the blistering rash appears, and remains contagious for 7-10 days.
Often in adults, between the incubation and febrile periods, there is also a prodromal period, when the symptoms of the disease themselves have not yet appeared, but signs of ill health have already appeared, such as headaches, lower back pain, and sometimes fever.
Chickenpox in pregnant women - features of the disease
After conception, a natural weakening of the immune system occurs, so the body protects the fetus from rejection. Against the background of weakening protective functions, all infectious diseases in expectant mothers are severe.
Stages of disease development:
- In the first days, you are worried about fatigue, weakness, headache, irritability, and your appetite worsens or completely disappears.
- After about 3 days, the temperature rises to 38 degrees or more, and general health rapidly deteriorates.
- By the end of the first week, characteristic rashes appear - small blisters with clear liquid inside. The rash first affects the face and genitals, gradually spreading throughout the body, accompanied by itching and sometimes severe swelling of the tissues.
- The blisters burst, become covered with crusts, and until complete healing there are many pimples on the body at different stages of development.
If you become infected with chickenpox again during pregnancy, the disease will be a little easier, but the likelihood of serious consequences for you and your baby remains.
Management of late pregnancy with chickenpox
To prevent the mother from infecting the fetus with chickenpox, on the eve of childbirth (if the rash appears 1–2 weeks before the expected date of birth), the woman is hospitalized in the infectious diseases department of the maternity hospital.
If rashes are present on the external genitalia, a planned cesarean section is recommended.
They try to delay the birth as much as possible so that the antibodies have time to pass from mother to child. Immediately after birth, the baby is given a specific immunoglobulin.
If the child does not have signs of intrauterine infection with chickenpox, he is isolated from the mother for the period while there is a risk of infection. Mom remains contagious for up to 5 days from the moment of the last addition. Breastfeeding occurs with expressed milk.
What is chickenpox?
This is an acute viral infection, the causative agent of which is the herpes virus of the 3rd type. Infection occurs in two ways: through the liquid that fills the blisters, or by airborne droplets.
The opinion that if a person has chickenpox at an early age, then he develops lifelong immunity to it is erroneous. The virus mutates and acquires new properties, which means there is always a chance of catching it again.