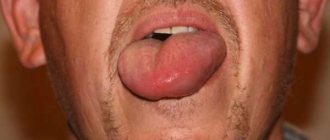
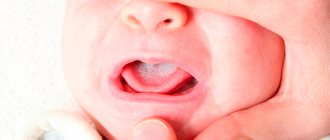
What is ulcerative glossitis
Glossitis, as a rule, becomes a consequence of injury to the mucous membrane of the organ, as a result of which an open wound appears on its surface - a direct path for the penetration of bacteria and infections. This injury can be caused by accidental biting, trauma such as fish bones, exposure to overly spicy or acidic foods, or burns from eating excessively hot foods.
The photo shows ulcerative glossitis
The pathology itself is inflammatory in nature - painful ulcers appear on the surface of the tongue, the tissues of the organ swell, turn red, painful sensations and burning occur, and in the case of the ulcerative form, a dense coating of a grayish tint also forms. The result is unpleasant odor from the mouth, difficulties with eating and speaking.
Plaque research
Plaque, in its intensity, color and thickness, also characterizes the presence of diseases.
A thin, barely visible layer indicates the onset of the disease; its thickening indicates the unhindered development of the disease. If the plaque becomes less intense over time, this indicates an improvement in the condition and a decline in the disease. If the plaque is sticky and difficult to remove from the surface, then there is a reason to take care of examining the patient for gastroenteritis; the presence of a putrid odor promises confirmation of the diagnosis. A thin whitish layer, easily removed, with a metallic taste in the mouth, indicates damage to the stomach and intestines.
A greasy deposit like sludge indicates stagnation of food in the intestines , accumulation of excess mucus, and poor digestion of food. A whitish layer at the base of the tongue indicates enterocolitis, the same at the edges and on the front, not reaching the tip, shows pulmonary problems. If the latter type of deposits turns into a foam-like layer, it means that the patient has chronic bronchitis.
A yellowish coating indicates problems with the gallbladder and ducts, and if it is located in the lower region of the organ, then jaundice begins. If the entire tongue is covered with yellowness, the liver is not working properly, there is excess bile, cholecystitis and problems with the digestive system develop.
The brown color of the layer indicates serious problems with the lungs and stomach , the same sign evenly in the middle part of the tongue, symmetrically with respect to the middle groove, indicates bilateral pneumonia. A black-brown coating, difficult to remove, resembling a chessboard, occurs with pellagra, namely, a deficiency of B vitamins and nicotinic acid. At a late stage of the disease, the organ turns red, and the surface resembles a varnished coating.
Diagnosis of diseases of internal organs by language has been worked out over decades of medical practice. But it is the doctor, seeing the first signs of the disease, who will prescribe an examination and determine the true cause of the appearance of changes on the surface of the tongue. The patient can only raise the alarm on his own; all other actions remain the prerogative of the specialist.
Is the disease contagious?
Regarding the contagiousness of glossitis, it is quite difficult to give a definite answer, since the disease has many different forms, which mainly depend on the root cause of the problem.
“You say that the disease is rarely transmitted, but my son brought this infection from kindergarten! The diagnosis is herpetic glossitis. The tongue was swollen, covered with tiny sores, the child cried in pain. After the examination, the therapist prescribed us tablets and rinses and advised us to buy pharmaceutical chamomile. In principle, I won’t say that the treatment took a very long time, maybe a couple of weeks, but the unpleasant impressions remained. In my family, neither I nor my sisters had this, so I was generally in a panic...”
Lydia D., Nizhny Novgorod, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum
Some forms of the disease can be transmitted by contact
. If the provoking factor is not an infection, then there will be no risk of transmission from the carrier to a healthy person. If the whole point is infection and spread of the fungus, then the disease can be transmitted, but not by airborne droplets, but as a result of direct contact of another person with the affected organ.
Types of ulcers and their clinical manifestations
The appearance of suspicious neoplasms on the surface of an organ is always an alarm bell that cannot be ignored. In this case, the rashes may differ from each other, depending on the disease and the cause of its appearance. Let's consider various clinical manifestations of pathologies of the oral mucosa and find out what they may indicate.
White sores on the surface
If white or yellow ulcers appear on the back of the tongue, gums and inner surface of the cheeks, first of all you need to find out why they appeared. Most often, such a symptom indicates candidiasis (thrush) - it develops as a result of too intense proliferation of yeast fungi in the body.
The problem can be triggered by a sharp decline in immune defense or, for example, taking powerful medications, including antibiotics. With yeast glossitis, rather deep grooves form on the tongue, in which an abundant dense coating begins to accumulate. These symptoms are accompanied by itching and an unpleasant odor. The problem does not pose a serious threat if treatment with antifungal agents is started in time.
This is what leukoplakia of the tongue looks like
Another possible cause of white rashes is leukoplakia. The pathological process is accompanied by excessive growth of soft tissue cells and the appearance of whitish thickenings on the surface of the organ. This diagnosis is often made to heavy smokers, as well as to patients who experience constant trauma to the mucous membrane due to an incorrectly installed filling/crown or due to the crooked position of some teeth.
Reddish translucent bubbles
Almost colorless growths, often filled with blood, usually indicate problems in the digestive system or endocrine glands. Reddish blisters appear on the tip and root area of the tongue, as well as on the inner surface of the cheeks, including with atopic dermatitis.
It could also be due to infection or damage to the mucous membrane. So, for example, a single transparent blister may be the body’s reaction to a thermal burn. Bloody hematomas indicate sudden changes in blood pressure or vascular damage.
The photo shows a blister filled with blood.
Discolored blisters
As mentioned above, colorless neoplasms in the form of blisters most often appear after a burn to the mucous membrane. If small bubbles filled with serous fluid appear on the tongue or other part of the oral mucosa, this may indicate activation of the herpes virus in the body. Sometimes with scarlet fever, light gray rashes appear in the mouth, which gradually become brighter and spread to the throat.
This is what herpes looks like on the tongue
Ulcers on the lateral surfaces
The formation of ulcers is most often a consequence of organ injury. The wound becomes a favorable environment for the proliferation of bacteria, which often leads to the formation of a purulent boil. Sometimes a dark rash appears on the side surfaces, resembling a hematoma in its shape and appearance. This symptom indicates damage to the deeper layers of the epithelium and taste buds.
Ulcerative rashes due to stomatitis
In the first stages of the development of the disease, small rashes appear on the oral mucosa, more like a slight swelling. Gradually more pronounced aphthae appear, when damaged, a white or yellowish membrane with a red rim forms in their place. Such ulcers heal in just a couple of weeks and do not leave scars. Aphthous stomatitis can become chronic. In this case, periods of exacerbation usually bother the patient 1-2 times a year.
The photo shows stomatitis on the tongue
Afty Bednar
Erosive areas appear on the surface of the organ - a similar phenomenon is usually diagnosed in newborns and young children. The cause of canker sores is most often caused by minor injuries received during feeding, due to the habit of sucking the thumb while sleeping or putting foreign objects into the mouth. However, neoplasms, as a rule, are localized on the surface of the hard palate - erosion most often takes on an oval shape. The treatment prognosis is favorable if the problem is recognized in time, the traumatic factor is eliminated and antibacterial therapy is started.
Injuries and mechanical damage
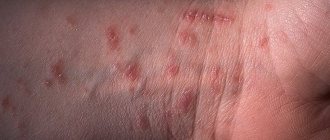
Ulcers and erosions occur as a result of accidental biting, blow, bruise or permanent injury from an incorrectly installed filling or crown, or sharp elements of the braces system. If the integrity of the epithelium is not broken, a dark hematoma will appear on the surface of the mucosa - the result of interstitial hemorrhage. If the mucous membrane is damaged, a painful ulcer will appear at the causative site. The injury usually heals quickly on its own. If the scratch does not go away for a long time, it is better to consult a dentist, since there is a risk of infection of the wound and the development of complications.
Ulcers and erosions can occur as a result of accidental injury
Ulcerative-necrotizing gingivostomatitis
The causative agent of infection is anaerobic microflora, which forms on the palatine tonsils, in carious lesions and periodontal pockets. Therefore, this diagnosis often becomes a complication of sore throat, diseases of the upper respiratory tract, and pathologies of the hematopoietic organs. Ulcerative-necrotizing gingivostomatitis also develops against the background of heavy metal poisoning, infection with Koch's bacillus, the development of syphilis, AIDS and cancer.
The photo shows ulcerative necrotizing gingivostomatitis
After the incubation period, the patient is overcome by weakness, his temperature rises, his gums become covered with ulcers, and the mucosal tissues lose their elasticity and become loose. Often with this form of the disease, the lymph nodes become enlarged and painful.
Signs and methods of treating tongue diseases
The action of external and internal factors individually or in combination causes various pathologies, among which the most common are infectious, congenital and chronic glossitis, leukoplakia, as well as a symptom complex called glossalgia.
Infectious glossitis
Infectious diseases of the tongue can be recognized by photos and descriptions, but only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
White coating with a cheesy consistency, as in the photo.
Removing plaque is accompanied by pain and bleeding. Children often have fever.
Rashes in the form of small watery blisters, as in the photo.
If they open, erosions appear on the tongue. The rash is painful and accompanied by fever.
The tongue becomes inflamed, red spots appear, in place of which bubbles up to 1 cm in diameter develop, as in the photograph.
When the blisters open, ulcers form.
Catarrhal and ulcerative glossitis
Catarrhal and ulcerative glossitis are also infectious diseases of the tongue, the symptoms and treatment methods of which are similar to the infectious diseases described above.
But the cause most often lies not in infection of the epithelium of the oral cavity itself, but in the complication of general infectious processes (ARVI, influenza) or inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. This diagnosis is often found in smokers and people who abuse alcohol. With the catarrhal form of glossitis, taste perception changes, pain appears, and tingling occurs. Inflammation causes swelling, which leaves teeth marks on the sides of the tongue. A dense layer of white plaque accumulates on the root of the tongue.
If left untreated, catarrhal glossitis turns into an ulcerative form with the formation of bleeding ulcers covered with a layer of dead epithelium and the appearance of an unpleasant odor.
In case of catarrhal and ulcerative forms of glossitis, it is necessary to treat both the general disease, which entails pathological changes in the tongue, and external manifestations (erosions). May be assigned:
- Antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs by mouth.
- Rinsing the mouth with antiseptics and herbal decoctions to eliminate inflammation and heal ulcers that have affected the human tongue. You can use chamomile.
- If plaque accumulates, wipe it off with clean gauze.
Desquamative glossitis
In diseases of the digestive organs and metabolic disorders, diathesis, dysbacteriosis, inflammation of the tongue may be accompanied by a change in the location of the grooves and thickening or desquamation of the papillae.
Subsequently, pink and red spots appear on the surface, clearly delimited by whitish ridges. This set of symptoms is called “geographical tongue.” To eliminate the pathology, it is necessary to treat the disease that led to such changes. Depending on the cause of the pathology, the patient is prescribed different groups of drugs:
- Antiallergic.
- Vitamin.
- Anti-inflammatory.
- Probiotics to eliminate dysbiosis.
For local treatment of a sore tongue, rinsing with antiseptics and lubricating the mucous membrane with a vitamin A preparation are used.
Congenital abnormalities of the tongue
Rhomboid glossitis is caused by congenital features of muscle development.
It appears as a growth on the back of the tongue (near the root) up to 10 mm in length, characterized by a glossy surface of bright red color. Folded glossitis is characterized by congenital uncharacteristic folds on the tongue, although the mucous membrane is of normal color. In the absence of other diseases, this feature does not cause discomfort, but metabolic disorders and vitamin deficiencies can provoke keratinization and cracking of the surface of the folds.
Treatment may include the following:
- If such diseases are complicated by infection or cracking of the tongue, it is necessary to treat the oral cavity with antiseptics.
- For vitamin deficiencies, a special diet and taking vitamins in the form of medications are indicated.
- For rhomboid glossitis, cryotherapy is used. To avoid complications, patients with such problems are not recommended to smoke.
Hairy black tongue
The name of this tongue disease is explained by its photo and description of the symptoms. The tongue does look hairy, but this effect occurs due to the pathological growth of papillae on its back closer to the root. They can reach 2 centimeters in length. Gradually these structures die off and turn black.
The cause of this pathology is metabolic disorders or taking medications harmful to the body. Tobacco smoke and alcohol, which affect the body for many years, can provoke the growth and death of papillae. Doctors admit that the disease may be caused by genetic mutations.
This disease is treated with antiseptic drugs to wash away plaque and keratolytic agents. Papillae that become inflamed and die can be removed using cryodestruction. You need to follow a gentle diet, stop smoking and spicy irritating foods.
Leukoplakia
This tongue disease most often occurs in men in adulthood and is usually associated with metabolic problems or diseases of the digestive system.
Leukoplakia does not cause pain, but the patient may feel discomfort when eating spicy food. Symptoms of this tongue disease can be seen in the photo on the right. The mucous membrane of the organ becomes covered with whitish plaques, which spread to other parts of the oral cavity and may appear in the corners of the mouth. After a few weeks, the affected epithelium thickens. Treatment of the causative disease is necessary. The affected areas of the tongue are cleaned with:
- Laser therapy.
- Radio waves
- Electroexcision method.
- Diathermocoagulation method.
If the doctor suspects the cells have degenerated into malignant ones, surgical treatment will be performed.
Causes and symptoms of pathology
It was already mentioned above that the disease most often develops against the background of damage to the tongue and penetration of infection into the wound. This leads to the appearance of very unpleasant symptoms that prevent a person from living a full life, eating normally and communicating with people. Thus, experts identify several key reasons that can cause the development of ulcerative glossitis:
- organ damage
- thermal injury,
- candidiasis of oral tissues,
- the presence of infectious diseases,
- anemia.
A common cause of pathology is damage to the tongue.
A distinctive feature of this form of pathology is the appearance of numerous painful red ulcers that can appear at the root, side or tip of the tongue, begin to bleed and cause serious discomfort.
On a note! The appearance of white ulcers in the mouth, concentrated mainly under the tongue, usually indicates the development of aphthous stomatitis. Taking into account the color and location of the rashes, a specialist can make a preliminary diagnosis, but to accurately determine the problem, you will most likely need to undergo additional examinations and tests. It is quite difficult to independently diagnose the disease, since many organ pathologies have similar symptoms.
With the ulcerative form of glossitis, a dark gray plaque also appears, and the mouth begins to smell unpleasant. The patient notes a general deterioration in his condition. If these symptoms appear, you should seek medical help as soon as possible, because prolonged ignoring of the signs of the disease can lead to dangerous complications.
Diagnosis of internal diseases by tongue color
Characteristic colors , studied over many years, characterize the beginning pathologies of important organs of the human body:
- Red color signals improper functioning of the heart, lungs and other respiratory organs of the system, diseases of the hematopoietic system, and various infectious diseases.
- Raspberry speaks of severe infectious lesions, poisoning with symptoms of chills, complicated pneumonia.
- Dark red characterizes the same diseases as the red color, but they occur in a more severe form or are advanced. Toxic disorders and severe renal pathology occur.
- Alternating red and white areas on the surface of the tongue indicate scarlet fever, a red lacquered organ indicates the development of pellagra.
- A light bluish tint indicates impaired blood circulation and cardiac or pulmonary failure.
- The coloring of the lower area of the tongue in a bluish color indicates heart failure long before the onset of the disease. This indicator is especially typical for middle-aged people who do not expect such changes in the cardiac system, while older people have the opportunity to seriously take preventive measures.
- Purple color indicates severe disorders of the hematopoietic system and pulmonary diseases.
- Black color suggests cholera infection.
- A pale and bloodless tongue indicates anemia and severe general exhaustion of the body. In this case, tooth marks on the lateral surfaces indicate insufficient absorption through the intestinal walls. If discoloration appears only in certain areas of the tongue, then the disease threatens those organs that correspond to the anatomical distribution of surface zones.
Glossitis in children
The most common form of pathology among children is catarrhal disease, which usually occurs due to biting, injury from a brace system or sharp edges of a filling, or eating hot food. The result is obvious inflammation and severe pain.
The photo shows the desquamative form of glossitis in a child
But children with worms often encounter a desquamative form of the pathology1. At the same time, the child may not have any pain at all, and concerned mothers recognize the disease itself only by suspicious spots that appear on the body of the organ. Among other possible causes of the problem, experts identify pathologies of the endocrine system, atopic dermatitis, infectious diseases, pathologies of the blood and gastrointestinal tract. But candidal glossitis often becomes a consequence of childhood diabetes mellitus, a decrease in the body’s defenses and the use of potent medications, including antibiotics.
Diagnostic features
To determine the form of the pathology and the cause of its development, it is necessary to conduct a differential diagnosis. The specialist must conduct a visual examination of the surface of the tongue, teeth and gums, talk with the patient about recent diseases, injuries and mechanical damage, and allergies. In more severe cases, blood tests may be required - general, cytological, histological or bacteriological. Sometimes microscopy of scrapings and PCR diagnostics are required to identify pathogens.
Tests are required for diagnosis
How is the treatment carried out?
Treatment of ulcerative glossitis in both adults and children should begin with eliminating the root cause of the problem, and this requires a thorough diagnosis. Only after identifying the source of the pathology can the doctor offer effective therapy. As for symptomatic treatment, to relieve acute inflammatory processes, specialists usually prescribe the drugs Hydrocortisone and Prednisopon. At an advanced stage and the presence of keratinized areas, they are removed surgically. Remember: only your doctor can prescribe medications; any attempts at self-medication can result in very unpleasant consequences.
To restore organ tissue, doctors usually prescribe rinse solutions with an antiseptic effect. These include “Furacilin” and “Chlorhexidine”. But to cope with pain, doctors usually prescribe drugs that have both anesthetic and antiseptic properties - Ledocaine and Kamistad. When answering the question of how to treat other forms of glossitis of the tongue, it is important to note that therapy is selected taking into account the type of pathology and the individual characteristics of the clinical picture.
Desquamative form of pathology
This form is widely known as “geographic language”. On the back of the organ, irregularly shaped light spots appear framed by a whitish coating. From the outside, the drawing somewhat resembles a map of the world, which is why the disease received its name among the common people. Most often, this type of glossitis becomes a consequence of pathological processes in internal organs and systems.
This is what geographic language looks like
Treatment is primarily aimed at achieving stable remission without exacerbations, since the desquamative type of the disease itself most often has a chronic form. Regular treatment of the organ and tissues of the oral cavity is required using anti-inflammatory gels and solutions, such as Chlorophyllipt or Karotolin. If the patient complains of severe pain, novocaine blockades and phonophoresis (ultrasound exposure simultaneously with drug therapy) are prescribed. The patient will also have to follow a special diet and take B vitamins.
Folded tongue
Quite deep and noticeable longitudinal and transverse grooves are formed on the back of the organ. Most often this is a congenital phenomenon, but there are cases when the pathology becomes a consequence of injuries, burns and infections. Symptomatic treatment of the folded form of glossitis is prescribed in the presence of severe discomfort, burning sensation, pain and breathing problems. In this case, antiseptic rinse solutions are prescribed, for example, Chlorhexidine, as well as anti-allergenic drugs if acute symptoms were provoked by an allergic reaction. During therapy you will have to give up salty and spicy foods.
This pathology is treated when causing inconvenience
Catarrhal type of disease
The development of the pathological process is accompanied by the formation of swelling, redness of individual parts of the organ, and the appearance of a dense white coating over the entire surface of the back. The cause of the problem may be a thermal or chemical burn or mechanical injury. As part of therapy, rinses with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory solutions are prescribed, nutrition is adjusted and vitamin complexes are prescribed.
Some problems can be solved by rinsing
Candidal glossitis
The distinctive symptoms of this pathology are a thick cheesy plaque and bad breath. In this case, patients usually do not experience significant discomfort or pain. Candidiasis infection, caused by too intense proliferation of yeast-like fungi Candida, can be triggered by an imbalance of microflora in the oral cavity after long-term drug therapy, taking antibiotics or insufficient hygiene.
Therapy in this case is aimed at restoring the balance of microflora. To do this, a complete sanitation of the oral cavity is carried out, antifungal drugs are prescribed, such as Nystatin or Fluconazole, and vitamin complexes are recommended to strengthen the immune system.
Diamond shape
The epithelial layer noticeably thickens and becomes thicker, taking on the shape of a diamond or rectangle, and a characteristic plaque appears. This type of illness usually indicates a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract. Since most often this is only a symptom and not an independent disease, treatment should be aimed at eradicating the source of the problem, and rinsing with antiseptics and anti-inflammatory solutions is usually prescribed to relieve symptoms. If the patient complains of pain, painkillers are prescribed.
Purulent-phlegmous type of pathology
The lesion spreads to the deeper layers of the epithelium and may affect adjacent areas of the oral cavity. This is one of the most severe forms, during the development of which the patient’s temperature rises and all signs of intoxication of the body are noted. In such a situation, antibiotics are usually prescribed: Doxycycline, Ceftriaxone, Rocephin and others. In particularly severe clinical cases, surgical removal of the purulent neoplasm is performed, followed by monitoring the patient’s condition during the rehabilitation period.
Gunter's glossitis
This form develops against the background of serious pathological conditions associated with the functioning of the hematopoietic system. The disease is considered a frequent companion to anemia. In this case, the surface of the organ becomes unnaturally smooth and acquires an overly bright red or crimson color. It is necessary to treat first of all the anemia or pathology that has become the root cause of such symptoms. Vitamin B12 is often prescribed as part of therapy.
The photo shows Gunter's glossitis
"Hairy" tongue
Due to the thickening and keratinization of the filiform papillae covering the back of the tongue, the surface of the organ acquires a dark brown or even black color, its texture becomes rough, visually reminiscent of hard stubble. This type of pathology has been studied much less than others. Until now, experts cannot establish the exact prerequisites for its formation. Possible causes include genetic predisposition, infections, taking powerful medications and bad habits.
This pathology is eliminated surgically
To eliminate the defect, it is usually necessary to surgically remove the hypertrophied filiform papillae, after which antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity and anti-inflammatory therapy are prescribed.
Desquamative (geographic) glossitis
Desquamative glossitis is popularly called “geographical” tongue, which is associated with the appearance of a specific pattern on it, similar to a map. The basis of the disease is the rejection of epithelial cells of the tongue, their keratinization, as well as dystrophy of the papillae.
The affected tissues stand out clearly against the background of healthy epithelium; they look like bright red spots with a whitish border. Glossitis develops quite quickly; uneven spots appear on the tongue, which differ in size and complexity of damage to the filiform papillae.
This deviation is also characterized by inconsistent localization of the lesion. Red spots change, quickly appear and disappear, moving to another part of the tongue.
The disease is more often diagnosed in children, and the reasons for this are related to malnutrition or congenital anomalies. Some children are already born with a “geographical” tongue, which is why this disease is considered to be congenital.
Advice! Glossitis of a desquamative nature is diagnosed more often in young girls and women. Men suffer from this disease relatively rarely.
Folk remedies - treatment at home
Traditional medicine is relevant only as an auxiliary therapy; with their help, you can quickly get rid of annoying symptoms and return to normal life. However, even in this case, you should not use certain home recipes on your own - first, consult your doctor and get his consent.
Chamomile decoction helps well in treatment
So, in order to speed up tissue restoration, it is recommended to make applications with rosehip oil and ointments with vitamin A - “Actovegin” or, for example, “Vinizol”. A chamomile decoction for rinsing or a light solution of hydrogen peroxide will help relieve severe inflammation. Tea tree oil has excellent wound healing properties.
Preventing tongue ulcers
No one is immune from microtraumas to the mucous membrane and the appearance of minor wounds on its surface. However, provided you have good health, good immunity and good hygiene, such a minor nuisance is unlikely to lead to serious problems. To protect yourself from diseases of the teeth and soft tissues of the oral cavity, it is enough to maintain hygiene, regularly brush your teeth, visit the dentist for preventive maintenance and professional dentistry. hygiene at least once every six months.
Preventive examinations at the dentist will help to recognize pathology in time
It is also advisable to monitor the health of the body as a whole, give up cigarettes and alcohol, diversify your diet with healthy foods, take vitamins from time to time to strengthen the immune system, and try to lead an active lifestyle.
How to treat desquamative tongue?
Desquamative glossitis is treated with local and general remedies. Drugs that enhance immunity, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and antihistamines are required. The doctor gives the patient recommendations on proper nutrition and eliminating bad habits. The following drugs and procedures are used in the treatment of glossitis:
- electrophoresis, ultraphonophoresis;
- antiseptic rinses with solutions of soda, potassium permanganate;
- painkillers;
- sanitation of the oral cavity;
- strengthening the immune system.
“Geographical” tongue does not pose a risk to human health, but requires constant maintenance of oral hygiene and strengthening of the defense mechanism. Eliminating the traumatic factor, taking vitamins, and proper nutrition will help maintain the tongue in normal condition.
Which doctor treats glossitis and when should you contact him?
When suspicious ulcers are discovered on the tongue, many begin to ask a completely logical question regarding which doctor to turn to for help. In such a situation, you can, of course, immediately make an appointment with a dentist, but it is not a fact that the pathology was caused by a dental problem, and this specialist will be able to provide the necessary assistance. It is better to first consult with your attending physician - after a visual examination, he can send the patient for additional examination, the necessary tests, or immediately refer him to a highly specialized doctor: a gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, immunologist, or again to a dentist.
The formation of strange suspicious spots, plaque and ulcers on the surface of the main speaking organ, the occurrence of obvious pain, burning and tingling sensations - all these are signs of tongue pathology. If we are talking about glossitis, then it can be an independent disease, since it is a secondary sign of disturbances in the functioning of internal organs and systems. In any case, the problem requires an immediate solution, so in such a situation the only correct instruction for action is to urgently consult a doctor.
- Kharitonova, M. P. Burning tongue syndrome (Etiology, clinical picture, differential diagnosis, treatment), 2000.