The chemical table of elements is replete with useful substances for the development of the human body, but calcium occupies a special place in it. This unique “building” material is necessary for the skeletal system, since it takes part in physiological and biochemical processes inside cells. Calcium stabilizes the functioning of the heart, immune system and nervous system, strengthens blood vessels and has a beneficial effect on metabolic processes.
The amount of this macroelement in the body is 1.5-2% of human weight. About 99% is present in bones, teeth, hair and nails and only 1% in muscles and intercellular fluid. With calcium deficiency, a whole range of disturbances in the functioning of various systems appears. That is why it is important to consume foods containing calcium, the table of which will be given below.
Classification
A microelement such as calcium enters the human body with food. However, for the full functioning of all body systems, the calcium content in the food taken may not be enough. In this case, you should take medications containing this substance.
Calcium preparations contain its salts, which, when they enter the gastrointestinal tract, are absorbed, and the mineral circulates in the blood in its finished form.
Most often, calcium carbonate is used to treat mineral deficiency, as well as to treat ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract. Less commonly, preparations contain other salts.
All products can be divided into those that contain only calcium, as well as combination preparations. The first include:
- Vitacalcin.
- Calcium carbonate.
- Scoralite.
- Additive calcium.
Combination tablets contain additional components for the treatment of specific nosological conditions. For the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis, calcium and vitamin D preparations are used, which helps in the absorption of the mineral:
- Calcium D3 Classic.
- Calcium D3 Nycomed.
- Complements calcium D3.
- Natekal D3.
There are more rare combinations, for example, calcium + vitamin C, calcium + vitamin C + vitamin D, multivitamins containing a large number of different substances.
A large number of dietary supplements contain the microelement in question. However, these drugs have not been sufficiently certified to be considered medicinal products.
Products for better absorption
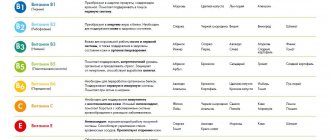
It is not enough to know where calcium is most present in food. It is necessary to properly combine it with food enriched with vitamin D, phosphorus and magnesium. This will help the body fight viruses and colds. Vitamin D controls the amount of phosphorus and calcium in the blood and speeds up the recovery process for bone fractures. A sufficient amount of vitamin D is present in fatty fish and dairy products and is synthesized by the body under the influence of ultraviolet radiation.
The body also needs to receive other foods that improve its condition - vegetables, meat and beans. They contain vitamins E, A, C, B and saturate the organs with calcium.
The simultaneous intake of magnesium allows you to balance Ca. As it decreases, calcium is absorbed more slowly. Magnesium is present in sufficient quantities in bran and wholemeal bread and nuts.
Important! There are foods that help remove calcium from the body - caffeine, sugar, excess salt, nicotine and fat. Those who decide to eat healthy need to exclude them from the diet or leave a minimum amount.
What prevents absorption?
The key reasons for problematic learning are:
- Failure to comply with the drinking regime (you should drink more than 6 glasses of water per day, you can add a little lemon juice).
- Lack of macro- and microelements.
- Constant consumption of foods after heat treatment.
Factors causing element deficiency:
- stress;
- gastrointestinal diseases, endocrine disruptions, renal failure, diabetes;
- excess proteins and fats, sugar and salt in the diet;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- frequent consumption of chlorinated water;
- starvation;
- prolonged use of hormonal, laxatives, anticonvulsants.
Mechanism of action
Calcium preparations have a fairly wide range of therapeutic effects, which means that their mechanism of action is quite complex. Here are just a few examples of the effects of drugs:
- Calcium salts, entering the stomach, neutralize the acidity of gastric juice by affecting hydrochloric acid. Unfortunately, after the cessation of the drug's effect, an increase in secretion is observed, so the drugs are used for the symptomatic elimination of a hyperacid state with a subsequent transition to antisecretory drugs.
- By reducing the acidity of gastric juice, the drugs prevent the formation of ulcers of the gastric mucosa; this is typical for non-atrophic gastritis, which sooner or later leads to the formation of a defect in the mucosa due to the aggression of hydrochloric acid.
- Calcium supplements normalize the acid-base state of the body, as well as electrolyte balance. A normal ratio of calcium, sodium, magnesium and potassium ions is necessary for the functioning of nerve and muscle cells.
- One of the main properties of a microelement is its participation in the construction of bone tissue. Bone consists of mineral and protein parts. For osteoporosis or osteomalacia, the drug restores bone density and its functional properties.
Taking together the information listed above, we can highlight the following effects of calcium supplements:
- Antacid – neutralization of hydrochloric acid of the stomach.
- Antiulcer – prevention of the formation of defects in the gastrointestinal mucosa.
- Normalization of mineral metabolism.
- Replenishment of microelement deficiency in the body and in bone tissue in particular.
Having highlighted the main features of the mechanism of action of these drugs, we can suggest indications for their use.
Compatibility of calcium with other elements
The mineral reacts with various substances, which significantly affects the course of calcium metabolism. You already know about the influence of the main ally of the nutrient vitamin D, let’s look at some other substances.
B vitamins combine well with macronutrients. Without calcium, it is impossible to absorb cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12). Pyridoxine (vitamin B6) maintains the necessary concentration of the mineral in the blood, slowing down the process of its elimination. The high chemical activity of the nutrient blocks the absorption of manganese, iron and zinc. At least 4-6 hours should pass between taking medications containing these chemical elements. If the magnesium content in a food or drug is half the calcium concentration, they are perfectly absorbed together. With a larger amount of magnesium, the absorption of the mineral worsens.
Calcium is one of the most important chemical elements for the healthy functioning of the human body. To avoid the development of serious pathologies, you should ensure your daily intake of the mineral through a balanced diet or medications.
Share on social media networks:
Indications
You cannot use tablets uncontrollably. Excess minerals in the body cause complications, which will be discussed below. The presence of side effects forces the use of the substance according to indications. These include the following conditions:
- Increased acidity of the stomach due to excess hydrochloric acid. It is observed in acute and chronic gastritis, duodenitis, peptic ulcers, erosions of the gastrointestinal mucosa, reflux gastritis.
- Symptomatic elimination of hyperacidity after consuming alcohol, nicotine, coffee, certain groups of medications, and errors in diet.
- Osteomalacia is a decrease in bone mineral density that does not lead to functional impairment. It precedes the onset of osteoporosis and is detected using densitometry.
- Osteoporosis is a clinically significant disease associated with a significant decrease in bone mineral density.
- Postmenopause, occurring with symptoms of osteoporosis. Calcium treatment is supplemented with vitamin D.
- Rickets is a disease of the child’s body that is associated with impaired bone growth due to a deficiency of microelements.
- Caries in children and adults. Tablets are used for prevention and treatment.
- Tetany is a syndrome that denotes a pathological process in muscle tissue, which leads to its hypertonicity. Associated with micronutrient deficiency.
- Hypocalcemia is a decrease in mineral in the body due to impaired absorption, insufficient intake, use of corticosteroids, and kidney diseases.
There are quite a few indications for taking tablets, but most often they are used for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis.
Calcium and vitamin D
The body needs vitamin D to absorb calcium-containing foods in the small intestine.
Vitamin D prevents the development of osteoporosis, rickets, periodontal disease, rheumatism, and is necessary for blood clotting, tissue growth, smooth functioning of the heart, and the health of the nervous system.
Up to 90% of vitamin D is synthesized by the skin under the influence of the sun. Natural synthesis is hampered by fear of sunbathing and intensive use of sunscreens. Sunbathing is necessary, but only in places with clean air, when the concentration of ultraviolet radiation is maximum - in the morning or evening.
Eliminating vitamin D deficiency with food and synthetic vitamins requires the body to do some work. Therefore, it is difficult to assert the usefulness of this approach. Moreover, sometimes taking foods artificially fortified with vitamin D provokes the deposition of calcium salts.
Vitamin D is rich in fish oil, cod or halibut liver, Atlantic herring, mackerel, tuna, mackerel, raw egg yolk, cheese, cottage cheese, butter, as well as pork, beef, fish or poultry liver.
Contraindications
Tablets containing a microelement have restrictions on their use. The drugs are contraindicated in the following pathologies:
- Hypercalcemia is an increased content of a mineral in the body.
- Allergic reactions to the components of the drug.
- Hypersecretion of the parathyroid glands.
- Metastases of tumor diseases in bone tissue.
- Urolithiasis localized in the kidneys.
- Chronic kidney diseases occurring with organ failure.
- Multiple myeloma is a tumor of red bone marrow cells.
- Phenylketonuria is a hereditary metabolic disease.
These diseases limit the use of tablets. If there are simultaneously indications for its use, alternative options for strengthening bone tissue should be considered.
Calcium and phosphorus
To absorb calcium, you need foods containing phosphorus. Phosphorus reserves are concentrated in the teeth. Sufficient synthesis of vitamin D maintains an optimal ratio of these elements in the blood.
A modern resident receives enough phosphorus. It contains fish, meat, cheese, egg yolk, lentils, peas, beans, pears, millet, nuts, bread.
Excess phosphorus disrupts hormonal control. Until the level of phosphorus in the blood returns to normal, the kidneys excrete calcium in the urine. Until this point, the body uses up calcium reserves from bone tissue.
The daily adult norm of phosphorus is 1.6 g.
Phosphorus and calcium contain products: green peas, beans, celery, fresh cucumbers, radishes, cabbage of any variety, low-fat cheeses, apples, Hercules.
Side effects
Medicines containing trace elements, like any other drug, can cause unwanted side effects. To prevent them, it is necessary to use medications when indicated, in the required dosage and after consulting a doctor.
Possible side effects:
- Allergies of varying severity.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Abdominal pain.
- Flatulence and stool disorders.
- Constipation.
- Increased production of hydrochloric acid after using an antacid.
- Hypercalcemia.
The last side effect is the result of an overdose of the described drugs. It is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Migraine, weakness.
- Loss of appetite.
- Dyspeptic disorders.
- Abdominal pain of varying degrees of intensity.
- Thirst and increased urine output.
- Pain in muscles and joints.
- Cardiac arrhythmias.
- Kidney failure.
To eliminate hypercalcemia, activated charcoal and gastric lavage are prescribed. Compensate for the functions of affected organs and systems.
Prevention of hypocalcemia
Prevention of this pathological condition for healthy people who do not suffer from diseases leading to calcium deficiency consists of a number of basic things that everyone can do.
- Daily consumption of foods containing a sufficient amount of macronutrients that can satisfy the daily requirement for it;
- Consumption of foods rich in vitamin D, which ensures the transformation of Ca in the body and its better absorption (fermented milk, vegetable oils, eggs, seafood, fish liver, fish oil, oatmeal, greens);
- Preventive intake of vitamin D for children in the autumn-winter period (on the recommendation of a doctor);
- Sufficient exposure to sunlight during safe hours, excluding the period from 12 to 15.00, which ensures the synthesis of vitamin D in the human body;
- Periodic use of balanced vitamin-mineral complexes, but on the recommendation of a doctor and observing physiological dosages. Drug prevention of hypocalcemia is especially important for pregnant, lactating and elderly women;
- Compliance with proper physical activity, feasible sports.
How to use?
To use the pills safely and effectively, you must take the medications correctly. Regardless of whether it is a combination drug or a single drug, it is used as follows:
- Take 1 tablet orally with half a glass of water.
- The substance is better absorbed when taken with food.
- The drugs need to be taken 2-3 times a day, depending on the dose required by the patient.
- With long-term use, monitor the level of calcium in the urine.
The use of antacid medications is somewhat different. They should be used during heartburn or abdominal pain. After relieving the hyperacid condition, the need to use antisecretory drugs should be considered. To reduce the production of hydrochloric acid, you can take H2-histamine blockers or proton pump inhibitors.
Table of calcium content in food groups
| Products | Calcium content (mg per 100 g of product) | % of the average daily value |
Milk, egg | ||
| Powdered milk | 1000 | 100 |
| Cow's milk 2.5% - 3.5% | 120 | 12 |
| Kefir | 120 | 12 |
| Egg | 110 | 11 |
| Sour cream 10% | 80 | 8 |
| Soy milk | 80 | 8 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||
| Parmesan cheese | 1200 | 120 |
| Russian cheese | 900 | 90 |
| Latvian cheese | 800 | 80 |
| Hard cheeses | 800 — 1200 | 80-120 |
| Cheese "Roquefort" | 750 | 75 |
| Goat cheese | 500 | 50 |
| Low-fat cottage cheese | 100 | 10 |
Legumes | ||
| Soybeans | 200 | 20 |
| Beans | 190 | 19 |
| Beans | 100 | 10 |
| Peas | 50 | 5 |
Nuts, seeds | ||
| Poppy | 1600 | 160 |
| Sesame | 1400 | 140 |
| Almond | 250 | 25 |
| Hazel | 225 | 22,5 |
| Pistachios | 130 | 13 |
| Sunflower seeds | 100 | 10 |
| Walnuts | 90 | 9 |
| Peanut | 60 | |
Fish, seafood | ||
| Dried fish with bones | 3000 | 300 |
| Atlantic sardine (canned) | 380 | 38 |
| Crabs | 100 | 10 |
| Shrimps | 90 | 9 |
| Anchovies | 82 | 8,2 |
| Oysters | 82 | 8,2 |
| Carp | 50 | 5 |
| Cod | 25 | 2,5 |
| Pike | 20 | 2 |
| Trout | 19 | 1,9 |
| Salmon | 10 | 1 |
Meat and meat products | ||
| Chick | 28 | 2,8 |
| Veal | 26 | 2,6 |
| Chicken | 10 | 1 |
| Beef liver | 10 | 1 |
| Rabbit meat | 9 | 0,9 |
| Beef | 5 | 0,5 |
| Pork | 5 | 0,5 |
| Mutton | 3 | 0,3 |
| Sausage | 22 | 2,2 |
| Sausages | 12 | 1,2 |
| Ham | 11 | 1,1 |
Cereals | ||
| Grain bread | 55 | 5,5 |
| White bread | 52 | 5,2 |
| Cereals | 50 | 5 |
| Rice | 33 | 3,3 |
| Rye bread | 30 | 3 |
| Bran bread | 23 | 2,3 |
| Buckwheat | 21 | 2,1 |
| Semolina | 18 | 1,8 |
| Pearl barley | 15 | 1,5 |
Vegetables | ||
| Basil | 370 | 37 |
| Parsley | 245 | 24 |
| Celery | 240 | 24 |
| Savoy cabbage | 212 | 21,2 |
| White cabbage | 210 | 21 |
| Watercress | 180 | 18 |
| Shiite bow | 130 | 13 |
| Dill | 126 | 12,6 |
| Broccoli | 105 | 10,5 |
| Green olives (canned) | 96 | 9,6 |
| Green onion | 86 | 8,6 |
| Leaf lettuce | 37 | 3,7 |
| Carrot | 35 | 3,5 |
| Radish | 35 | 3,5 |
| cucumbers | 15 | 1,5 |
| Tomatoes | 14 | 1,4 |
| Potato | 6 | 0,6 |
Fruits (dried fruits), berries | ||
| Dried apricots | 180 | 18 |
| Dried figs | 54 | 5,4 |
| Raisin | 50 | 5 |
| Oranges | 42 | 4,2 |
| Raspberries | 40 | 4 |
| Kiwi | 38 | 3,8 |
| Tangerines | 33 | 3,3 |
| Currant | 30 | 3 |
| Strawberries | 26 | 2,6 |
| Dates | 21 | 2,1 |
| Grape | 18 | 1,8 |
| Pineapples | 16 | 1,6 |
| Apricots | 16 | 1,6 |
| Watermelon | 10 | 1 |
| Pears | 10 | 1 |
| Bananas | 9 | 0,9 |
| Peaches | 8 | 0,8 |
| Apples | 7 | 0,7 |
| Melons | 6 | 0,6 |
Confectionery | ||
| Milk chocolate | 200 | 20 |
| Milk ice cream | 130 | 1,3 |
| Dark chocolate | 60 | 0,6 |
| Fruit ice cream | 15 | 1,5 |
| Shortbread cookies | 6 | 0,6 |
| Natural honey | 4 | 0,4 |
Alternative to tablets
Since calcium supplements have a number of side effects, it is sometimes recommended to replace them with natural sources of the microelement.
Normally, we get the mineral from food. Even when treating severe osteoporosis, it is reasonable to use the right diet in combination with vitamin D; this combination will help completely eliminate the symptoms of pathology.
If you take about 2 grams of a trace element per day, you can avoid most side effects and eliminate deficiency phenomena. At the same time, much attention is paid to dairy products. They contain the most calcium.
With a nutritious diet with plenty of dairy products, you can avoid the phenomena of osteomalacia and osteoporosis and normalize the mineral balance in the body.
It can be useful:
- Instructions for use of Indomethacin ointment
- Alflutop's analogs
- Gout: ointments for treating leg pain
- What injections are prescribed for osteochondrosis?
- Instructions for use of Voltaren Emulgel
How to provide the body with the necessary amount of calcium
A healthy person gets calcium from food. If a person eats correctly, then such an amount of calcium comes from food that will allow all organs to function without disruption. But this only happens if the acid-base balance in the body is not disturbed. If an acidic environment predominates in the body, then salts will begin to be deposited in the joints, and stones will form in the kidneys. Prerequisites for cardiovascular and immune diseases will appear. That is, if the acid-base balance is disturbed, a person can get sick.
How to protect the body from such diseases?
This is where calcium comes to the rescue - the only chemical element that can neutralize acid. And if there is no acidic environment, then there will be no disease.
The need for calcium depends on the age of the person. It varies at different periods of a person’s life. A child from birth to 6 years of age needs up to 1500 mg of calcium per day. The second such period of increased calcium intake lasts from adolescence and ends around the age of 20 years. Pregnant and breastfeeding women also need increased calcium intake. In old age, calcium is naturally washed out of the bones. This can lead to a disease called osteoporosis.