If a woman is bothered by frequent urination without pain, the cause of the condition lies either in the characteristics of her body or in the presence of some kind of disease. Hidden infections and hormonal imbalances are important in the regulation of fluid secretion. To deal with this, you need to consult a doctor and together analyze the state of the body, identify accompanying symptoms and, if necessary, prescribe therapy.
Frequent urination, as a normal option
There are no strict rules regarding the number of trips to the toilet per day. It all depends on the physiological characteristics of the body and is directly proportional to the volume of liquid drunk. During the day, the kidneys filter up to two hundred liters of primary urine, but only about one and a half are excreted from the body.
They are formed after concentration due to the reabsorption of water, vitamins, and glucose. During one trip to the restroom, up to 300 ml of liquid is released. The rate of urination ranges from 3 to 9 times a day, but at night you can get up to go to the toilet no more than once. Increased frequency of urination during the day is called polyuria, and at night - nocturia.
Early pregnancy may also be accompanied by an increase in the number of urges. This is completely normal, since the growing uterus puts pressure on the bladder, thereby reducing its useful volume. As the fetus grows, less and less space will remain for other pelvic and abdominal organs, which means urinary episodes will become more frequent.
Also, repeated urges to go to the toilet in a woman can be associated with the following conditions:
- drinking plenty of fluids (workout, diet);
- taking medications;
- use of herbal teas and tinctures, drinks containing caffeine, alcohol;
- pregnancy, menstruation, menopause;
- hypothermia of the lower half of the body, including the bladder;
- prolonged stress.
All these factors can be identified even without visiting a doctor and eliminated.
Normal urination
It is important to understand the fact that there is no exact figure that would characterize the normal, physiological number of urges to urinate.
Urine excretion is individual for each person and depends on lifestyle, gender, weight, age and other factors affecting life activity. In women and girls, the frequency of voiding is approximately 6-9 times a day, while the volume of urine per 1 void on average does not exceed 250-300 ml. But it happens that the state of the body changes for some reason. For example, during hormonal changes or during pregnancy, increased urine production is observed, but this is not a pathology and does not require special treatment.
Causes of frequent urination
In some cases, pollakiuria may be a consequence of some disease. It is difficult to figure this out on your own and identify the cause; a detailed examination is necessary.
Gynecological diseases
There are two main reasons for frequent urination in women without pain:
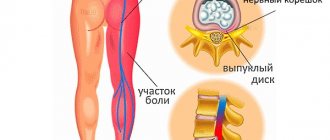
- Uterine fibroids . The tumor grows inside the organ in the form of a node. When it reaches a significant size, it begins to compress neighboring anatomical formations. This leads to a decrease in bladder volume and an increase in the urge to go to the toilet.
- Uterine prolapse . Violation of the elasticity of the ligamentous apparatus leads to a change in the position of all pelvic organs. The consequence of this is frequent urination and incontinence.
An obstetrician-gynecologist will help determine this reason even during a routine examination of a woman.
Kidney and urinary tract diseases
Various pathologies of the urinary system are accompanied by frequent urges to go to the toilet.
These include:
- Cystitis. This is an inflammation of the bladder mucosa. Causes may include prolonged exposure to low temperatures, uncomfortable underwear, and sexually transmitted infections. Cystitis is manifested by repeated urges to go to the toilet, a burning sensation during urination, and a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. In some cases, incontinence and a change in the transparency of the secreted fluid are added.
- Urethritis. Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the urinary canal. It can be mechanical or infectious in nature. Accompanied by pain, itching and burning in the urethra when urine is released.
- Pyelonephritis . Occurs due to bacterial or viral kidney damage. Frequent urge to urinate is a symptom of a chronic form of the disease. In addition, there is fever, lower back pain and cloudiness of the secreted fluid.
- Urolithiasis disease . The sharp edges of the stone, passing along with urine, scratch the ureters and urethra, causing discomfort. A special symptom may be interruption of the stream during the movement of the stone.
- Atony of the bladder. Normally, the organ resembles a dense ball, the walls of which contract, pushing out the contents. But if the muscles are flabby, there is repeated urge to go to the toilet, and very little fluid is released.
- Neurogenic bladder . The disease is characterized by the fact that receptors in the muscles of the bladder react to any increase in pressure, generating the urge to go to the toilet.
Endocrine diseases
The reasons for frequent painless urination in women may be imbalances in hormones, which provoke retention or excessive removal of fluid from the body.
The following two pathologies are most common:
- Diabetes . In this case, the tissues do not receive enough insulin or have low receptor sensitivity to it, which leads to an increase in blood sugar levels. Glucose is lost in large quantities by the body through the kidneys, taking water molecules with it. This causes a low concentration of urine with a simultaneous increase in its quantity.
- Diabetes insipidus. Violation of the hypothalamic-pituitary regulation forces the human body to consume and excrete large amounts of fluid every day. In particularly difficult cases, losses reach up to 10 liters of urine per day.
You just pee a lot. Why?
You drink caffeine or water by the liter. Of course, drinking a lot of water (or any other liquid) leads to frequent urination. In addition, drinking eight glasses of water a day is completely optional; No one can figure out where this figure comes from, but it is wiser to quench your thirst as needed and keep your urine pale yellow or clear.
Alcohol and caffeine have diuretic properties, which explains the long lines at bar toilets. Try to reduce their amount, especially before bedtime.
The uterus does not respect the personal space of the bladder. During pregnancy, the body retains extra fluid to support the baby in the belly. As hormone levels and fluid needs change, additional errand trips may be required. Moreover, the growing fetus puts pressure on the bladder and prevents it from filling. As a result, you have to empty it more often, because the kidneys produce a constant volume of fluid.
Taking new medications. Diuretics (diuretics) literally stimulate urine production, as this process lowers blood pressure. (In a sense, you're draining excess fluid from your blood.) What's more, some blood pressure medications, antidepressants, and sedatives can affect your bladder hormones, shifting your bathroom schedule. Be sure to consult your doctor before stopping any drug or changing to a new drug.
Full bladder - and nothing happens
The only thing worse than constantly urinating is not being able to relieve yourself. If you feel like your bladder is full but you can't get a drop out, you may be suffering from urinary retention.
In men, the most common cause of urinary retention is an enlarged prostate. Other possible causes include medications, stroke, multiple sclerosis, and spinal cord injury. The main villains among the drugs are antihistamines, decongestants, tricyclic antidepressants and general anesthetics (if the problem occurs in the immediate hours after surgery).
Urinary retention requires urgent medical attention because stagnant urine can easily become infected. In addition, a distended bladder can lead to pain that is difficult to imagine. Imagine that you want to go to the toilet like crazy, like the last time, but you can’t do anything about it.
Short-term treatment involves inserting a catheter into the urethra to empty the bladder. After this, long-term treatment begins, consisting of taking medications that maintain the urethra in a dilated state.
Urinary incontinence in women after 50 years
The reasons for frequent urination in women during menopause can be natural changes in her body, while the urge is always without pain.
The following factors may be at play:
- Aging of fabrics. With age, the muscles of the bladder lose their elasticity and firmness; they develop areas of atrophy, areas of salt deposition, and areas of ischemia. This changes the function of the organ.
- Erroneous imperative urges . Due to disruptions in the functioning of the nervous system over the years, receptors transmit false signals about the fullness of the bladder, causing another desire to visit the toilet.
- Complicated anamnesis. Infections, diseases of the heart, blood vessels, endocrine glands, a large number of pregnancies and childbirth negatively affect the condition of the bladder, control of the processes of formation and secretion of fluid in general.
- Taking medications . Diuretics, sedatives, and sleeping pills can provoke another trip to the toilet.
It should be borne in mind that many inflammatory processes in elderly women are hidden or asymptomatic, without causing significant inconvenience to patients. This leads to chronicity and worsening of the condition.
Features during pregnancy
In the third trimester, discomfort may occur due to intense pressure of the uterus on the bladder.
Frequent urination is often observed in women carrying a child. In this case, discomfort begins to manifest itself from the beginning of pregnancy and sometimes accompanies until the birth itself. In the first trimester, the disorder is associated with colossal hormonal changes, due to which muscle tone and activity are significantly reduced. This helps to carry the child to term without complications. In the second trimester, the body adapts to the condition and the urge to urinate becomes less pronounced. The last trimester is characterized by active growth of the fetus and an increase in the size of the uterus, which causes increased pressure on the bladder, and the number of urges increases again, and urination at night is bothersome. But this condition does not require treatment; it goes away immediately after childbirth.
Associated symptoms
Painless frequent urination in women may be accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms that are difficult to associate into one nosology.
Such clinical manifestations are:
- turbidity of urine, the presence of impurities in it;
- discomfort, burning, pain during urination;
- lower back pain;
- bleeding from the genitals not associated with menstruation;
- discomfort during intimate relationships, feeling of a foreign body, etc.
Night urination in a woman can be associated with such not very common infections as tuberculosis, malaria, and pathologies of the cardiovascular system. The kidneys cannot cope with the load and, by increasing the excretion of fluid, they try to maintain the efficiency of their work and the stability of the body.
Additional symptoms in this case may include shortness of breath, swelling, cough, profuse sweating, and increased body temperature.
What to do if you often run to the toilet “smallly”
Doctors recommend that you see a doctor as soon as possible and get tested if you experience frequent urination along with any of these additional symptoms: ✔️ Loss of bladder control; ✔️ Increase in body temperature; ✔ Blood in urine, dark brown color; ✔ Pain when urinating; ✔ Pain in the side, lower abdomen or groin; ✔ Difficulty completely emptying the bladder; ✔️ Any formations or bulges in the pelvic area.
Treating Frequent Urination
If you have an infection and want to pee because of acute cystitis, antibiotics will usually clear it up quickly and effectively. There are also other medications that relax the bladder, which may be helpful in relieving overactive bladder symptoms and reducing episodes of urinary incontinence. In some cases, you can use injections - injections of gel into the urethra when urine leaks from a weak bladder. Nerve stimulation or surgery may also be recommended for some conditions. In any case, abnormalities in urination can be treated only after a comprehensive examination and clarification of the diagnosis.
assignment_ind
Make an appointment with a gynecologist ☏ +7 495 790-0779
Do you often want to pee after sex? Find out how one injection of hyaluronic acid can help girls get rid of this problem.
assignment_ind
Transposition of the urethra for the treatment of cystitis after sex
Diagnostics
The doctor begins getting to know the woman by collecting the necessary information - anamnesis. It includes her family's medical history, lifestyle, number of children, sexual partners, travel abroad, vaccination status and much more. Then there is an examination of the abdomen, palpation and tapping of the anterior abdominal wall.
The second stage is laboratory and instrumental examinations:
- Clinical blood test. The results indicate the presence of inflammation.
- General urine analysis . Detailed the presence of infection specifically in the urinary system. Quantity, density, acidity, color and sediment narrow down your search.
- Biochemical blood test. Allows you to assess kidney function. This is important for determining pyelonephritis and urolithiasis, diabetes mellitus.
- Ultrasound diagnostics of the pelvic organs . Allows you to identify tumors and structural anomalies of the genitourinary system.
- Smear from the vagina and cervical canal . Rules out or confirms the presence of sexually transmitted infections.
Additional studies may be prescribed at the discretion of the specialist, based on the clinical situation.
Pathologies of internal organs and systems
The exact cause of frequent urination should be determined by a doctor, since this symptom may indicate serious, including chronic, pathologies. In this case, nocturia and pollakiuria are secondary symptoms. He appears in the background:
- diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus;
- vascular and heart diseases;
- injuries of the pelvis and internal organs;
- tumors (especially prostate).
Frequent urination is a classic symptom for people with diabetes. In diabetes insipidus, the function of the neurohypophysis, the area of the brain responsible for the release of oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone, is impaired. As a result, kidney function and urine formation are disrupted, and bladder emptying becomes more frequent. The patient drinks much more to restore the lack of fluid. With diabetes, the patient also has a constant desire to drink and defecate. During the release of urine, the patient may experience tingling and a slight burning sensation from the action of sugar.
Diseases of the heart and blood vessels often lead to nocturia. Against the background of such diseases, edema occurs, including hidden edema, which worsens during periods of physical activity. At night, swelling subsides and the body removes excess fluid. Nocturia occurs in both women and men; the patient can visit the restroom 6-8 times per night.
A prostate tumor is the cause of frequent urination in men. In this case, an adenoma is formed, which presses on the urethral canal. The normal process of urination is gradually disrupted, the amount of urine released becomes less and less, and the frequency of urges increases. In this case, the process of emptying is accompanied by pain in the urethra and lower abdomen.
Best materials of the month
- Why you can't go on a diet on your own
- 21 tips on how to avoid buying stale food
- How to keep vegetables and fruits fresh: simple tricks
- How to curb your sweet cravings: 7 unexpected products
- Scientists say youth can be extended
Also, this symptom occurs after injuries and operations on the pelvic and abdominal organs. An increase in the frequency of urges may be painless or accompanied by pain. In such cases, symptoms and treatment are individual. As a rule, attempts are made to eliminate congenital pathologies in infancy. All of the above reasons can occur in adults and children. It is quite difficult to notice such a problem in a child, since they are characterized by frequent urination. However, if redness appears on the genitals, blood or other impurities in the urine, you need to show the child to a pediatric urologist.
Treatment
If repeated trips to the toilet are not normal and cannot be explained by natural causes, the condition requires correction. After determining the etiology, the doctor prescribes the woman drugs and methods that eliminate the pathogenic factor.
It can be:
- Antibiotics. Used to combat infections and helminthic infestations. It is better to take probiotics and antifungal drugs together with them to reduce side effects.
- Means to increase or decrease the acidity of urine . Allows you to dissolve stones and prevent their appearance in the future.
- Diet, reducing the amount of fluid . Limiting foods that have a diuretic effect.
- Hormonal therapy . If the pathology is associated with menopause or caused by endocrine diseases.
Traditional medicine helps reduce discomfort, but for complete therapy and reliable prescriptions it is better to contact a certified specialist.
Rose hips, lingonberry leaves, heather and yarrow help well for the treatment and prevention of urinary tract infections.
A collection of chamomile, poplar buds, horsetail and peppermint is effective. Pour a tablespoon of the mixture into a glass of boiling water and leave for two hours.
To prevent the appearance of sand and stones, you can eat watermelon. It has a pronounced diuretic effect. And drops based on boron uterus help normalize hormone levels.
Major diseases
Frequent urge to go to the toilet can indicate three main classes of diseases:
- diseases of the urinary organs;
- gynecological disorders;
- endocrine problems.
Let's look at each of them. And we will briefly indicate the main ways of treatment.
Diseases of the urinary organs
There are three main misfortunes here:
- Cystitis. I want to go to the toilet very often. You may urinate frequently at night. The act itself is accompanied by cutting pain in the bladder, while it constantly feels as if the bladder has not completely emptied. There may be a few drops of blood in the urine. According to doctors, about 30% of women suffer from this disease at different stages of life. Medical treatment is antibacterial. A special diet without spicy and salty foods is prescribed. Folk remedies are also good - a decoction of kidney tea has an antibacterial effect.
- Pyelonephritis. In fact, this is inflammation of the kidneys. However, this disease directly affects urination - it becomes frequent and slightly painful. If you do not go to the hospital in time, the disease may progress with a deterioration in your general condition: the temperature may rise, vomiting and lower back pain may appear. Treatment is a course of antibiotics that suppress the proliferation of harmful bacteria in the kidneys. To relieve pain, doctors prescribe painkillers and herbal remedies.
- Urolithiasis disease. Due to stagnation of urine and metabolic disorders, stones can form in the bladder. They irritate the mucous membrane, causing a frequent urge to go to the toilet; At the same time, they make urination difficult and painful. Before treatment, the patient undergoes an examination so that doctors can accurately determine the exact size and consistency of the stones, and their chemical composition. After this, medications are prescribed that soften the stones. Surgical interventions are used less frequently.
Here's a good lecture
urologist about diseases of this class.
Gynecological disorders
There are two diseases here:
- Uterine fibroids. It is a benign tumor of muscle tissue. According to some reports, about 70% of women over 50 suffer from this disease. It can occur after medical abortions, other diseases of the genitourinary system, excess body weight and long-term stress. Treatment is usually surgical in combination with conservative treatment.
- Prolapse of the uterus. It is quite rare. Under the influence of gravity, the uterus slowly sinks lower and lower, pressing on the bladder. In the early stages, it causes frequent trips to the toilet without pain. If the disease has been going on for a long time and is constantly progressing, bloody vaginal discharge is possible, and there is a feeling of something foreign in the lower abdomen. The main treatment here is conservative. The doctor’s task is to prevent further prolapse of the uterus until complete prolapse. To do this, special strengthening physical exercises for the abs are prescribed. Sometimes surgery is acceptable. Patients often undergo hormonal therapy.
Endocrine disorders
There are two main classes of diseases:
- Diabetes. In this disorder, the body stops producing insulin, an important hormone that breaks down glucose (one of the most basic sources of energy in the body). In the early stages of the disease, frequent urge to go to the toilet is possible. There is weakness and malaise. In some cases - short-term loss of consciousness. A characteristic symptom is bedwetting. The treatment here is complex: insulin injections, a special diet (table number 9) and hypoglycemic drugs are prescribed.
- Diabetes insipidus. An extremely rare disease (occurs in 0.003% of people). Extremely dangerous, but easily diagnosed. A person drinks enough water, but does not get drunk. He is tormented by thirst. The urge to go to the toilet occurs constantly, about 5 liters of urine are released per day. Treatment is hormonal therapy.
Prevention
By following simple recommendations, you can protect yourself from problems with the reproductive and urinary systems.
The following is important:
- daily hygiene;
- examination by a specialized specialist at least once a year;
- stopping alcohol consumption or significantly reducing its amount;
- correction of nutrition and drinking regime;
- selection of clothes in accordance with the weather outside the window, and not the date on the calendar.
A woman should listen sensitively to her body and respond to the slightest oddities. After all, a minor change in daily routine can be a consequence of a hidden disease. If in doubt, it is better to consult a doctor to determine whether the condition is normal or pathological.
Why does frequent urination occur in women?
It is worth talking separately about the characteristics of the female urinary organs. Indeed, due to their anatomical structure, as well as due to the differences in the internal organs that make up the small pelvis, the causes of pathology in men and women differ. But, of course, there are factors that cause frequent urination in women with the same probability as in male patients.
Drinking plenty of fluids or diuretic decoctions will certainly lead to increased urination
First of all, these are infectious diseases that affect all parts of the urinary system and are caused by specific or nonspecific microflora. In second place is urolithiasis, which has characteristic manifestations in both sexes. In addition, there are many physiological or natural reasons that cause frequent urination in women and men. Also, some medications and herbal remedies that have a diuretic effect lead to an increase in urine volume and cause frequent and copious urination.
During pregnancy, when the enlarged uterus compresses and displaces the bladder, its nerve receptors are almost constantly in an excited state. Therefore, if a woman does not have time to reach the toilet, urinary incontinence may occur. But this symptom, like increased urination in a pregnant woman, is also considered physiological.
Frequently running to the toilet during pregnancy is normal
There is also a complex of diseases of internal organs that directly or indirectly affect the process of urination and can change its frequency. This is where some differences already appear in patients of the stronger and weaker sex, associated with anatomical features. First of all, these are gynecological pathologies, as well as hormonal disorders that have appeared in elderly patients due to menopause.
There are many factors that cause increased urination in women.
You can learn more about all the possible causes of this phenomenon, physiological and pathological, from this article.
Tips for women with urinary disorders
Women who suffer from frequent urge to urinate, but the reasons are physiological in nature, need to adhere to several basic rules:
- Limit fluid intake in the evening;
- During urination, you need to tilt your torso slightly forward, this will help to completely empty the bladder;
- Going to the toilet should be done upon immediate request;
- It is necessary to limit the consumption of liquids that have a diuretic effect: coffee, green tea, rosehip decoction;
- Avoid foods that cause thirst: spicy, salty, smoked foods.
Frequent urges that bother you for a long time, even in cases where they are painless, should not be ignored. Therefore, you should not neglect your health; only a timely visit to a doctor will help identify the causes and prescribe the necessary treatment. It is important to remember that a woman’s health is an important component of any nation, and symptoms that appear against the background of any disorders should be dealt with by a doctor.
Treatment of the pathological condition
Treatment of the urinary system
First of all, a therapist and a urologist are involved in determining the causes of impaired urination, and they prescribe appropriate treatment in each individual case.
In case of serious problems with fluid retention, in order to avoid the development of sepsis, intoxication and congestion in the body, a catheter is placed. With its help, excess urine accumulated in the bladder is removed.
If tests reveal the presence of kidney stones, they are crushed and removed, followed by treatment.
Medications are prescribed to relieve spasms and inflammation as needed.
The causes and treatment of the problem under consideration are closely interrelated. To achieve the greatest effect when urination is too slow and intermittent, both conservative techniques and an operative approach can be used. Among non-drug methods, the following are especially popular:
- Therapeutic exercises that strengthen the muscle tissue of the pelvis and perineum.
- When the pressure of the stream weakens due to menopause, hormonal therapy is prescribed.
- A weak urine stream can be enhanced by electrical stimulation applied to the perineal muscles.
- For disorders provoked by stressful situations or emotional overstrain, psychotherapeutic sessions are used.
Certain pharmaceutical drugs can cause a quick positive effect. In this case, specific drugs are prescribed by the doctor based on the results of the examination. So, if the formation of stones ends with interrupted urination, substances are prescribed that help dissolve them. The type of stones should be taken into account - they can be phosphates, urates or oxalates.
If urine is produced over a long period of time and in too small portions, diuretics may be prescribed. With their help, it will be possible to avoid the accumulation of urine in tissues and organs. In the presence of inflammatory processes that cause dysuria, the use of antifungal, antimicrobial or antiviral drugs is prescribed in accordance with the type of pathogen that provoked the development of the pathology.
If we are talking about how to treat pathology caused by infectious causes, the following drugs should be mentioned:
- Trimethoprim. The product can act on gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms.
- Amoxicillin. A broad-spectrum antimicrobial drug should be prescribed by the attending physician, taking into account side effects and poor combination with other drugs.
- Ciprofloxacin. The main feature is that there is practically no toxic effect on the human body, which allows you not to worry about damage to healthy cells during treatment.
- Fluconazole. It belongs to antifungal drugs and is most often prescribed for thrush accompanied by dysuria.
- Nitrofurantoin. The product has antibacterial properties.
- Acyclovir. Used as an antiviral drug and eliminates herpetic infections.
If the case is complex and the disease is in the final stages of formation, surgical intervention is required. Operations make it possible to remove tumors of various types, correct pathological conditions using plastic surgery, and fix the bladder in case of a disturbed location of the organ.
Let's look at the most effective folk methods for treating this problem.
- Decoction of boron uterus: 10 grams of the dried plant is poured with one glass of boiling water and boiled in a water bath for 10 minutes, then left for 2-3 hours and filtered through a sieve. The decoction should be taken 15 ml 3-4 times a day for 12 weeks. A decoction of boron uterus allows you to normalize hormonal levels during menopause and eliminate the frequent urge to urinate.
- Rosehip root decoction: 40 grams of crushed rosehip root are poured with two glasses of boiling water and boiled for 15 minutes over low heat, then left for 2-3 hours and filtered. Drink 100 ml of medicine before meals 3-4 times a day.
- Infusion of lingonberry leaves: 5 grams of fresh or dried lingonberry leaves are poured with one glass of boiling water, covered with a lid and allowed to brew for 15-20 minutes. Drink the prepared and strained infusion throughout the day, several sips for one month.
- Yarrow infusion: 7-8 grams of the dried plant are poured with boiling water and left for 30-40 minutes, then filtered and drunk 50 ml 3-4 times a day before meals. Important! Medicines prepared from lingonberry leaves, rosehip root and yarrow effectively eliminate inflammation in the bladder and urethra.
- Infusion of corn silks: 10 grams of crushed corn silks must be poured with one glass of boiling water, cover with a lid and leave for 15 minutes. The finished infusion must be filtered through a sieve. I take the medicine 100 ml twice a day for urolithiasis.
Any folk remedy can be used to treat frequent urination only with the permission of the treating doctor.
Be attentive to your health and listen to its signals, one of which is frequent urination, since any pathology of the urinary system can affect a woman’s reproductive function.
How to treat frequent urination?
If frequent urination is not normal and needs correction, then treatment is aimed at eliminating the etiological factor - the disease that caused it.
Antibiotic therapy is most often prescribed to eliminate a bacterial infection or protozoan infestation. Along with taking antibiotics, it is recommended to take antifungal drugs and probiotics. If a woman is susceptible to allergies, the doctor prescribes antihistamines simultaneously with the course of main therapy.
If the problem is related to salts or kidney stones, then the nephrologist prescribes specific drugs to change the acidity of urine. Typically, such preparations contain either salts or are based on plant extracts. Depending on the composition of the stones, the pH of the urine shifts so that the stones dissolve as quickly as possible and pass naturally through the urine.
If frequent urination is associated with a specific diet or water regime, then there is no need to change anything. The only exception is the abuse of alcoholic beverages, which should be avoided.
The urge to urinate that occurs during menopause goes away on its own with proper hormone therapy.
Regular urination associated with pregnancy does not need correction.