Surely every woman during the period of bearing a baby has heard the following medical terms more than once: increased tone, toned uterus, hypertonicity. Often these words are directed at expectant mothers who are 40 weeks pregnant. The stomach turns to stone - this unpleasant sensation is a symptom that can sometimes lead to premature birth, or may indicate the presence of some pathologies in the body. This problem is quite relevant and requires close attention, let's look at the main reasons for its occurrence and methods of treatment.
View gallery
Fetal development at 40 weeks of gestation
Height: from 48 to 54 cm
Weight: 3000 to 4000 g
The time has come when labor can begin at any moment, although a child born between 38 and 42 weeks of pregnancy is considered completely normal and full-term, i.e. your condition may continue for 1-2 weeks. At this time, many mothers notice that the baby is kicking hard in the stomach - this is a natural process.
In case of post-term pregnancy, the doctor may decide to artificially induce labor. To do this, a pregnant woman is given oxytocin intravenously and waits until her contractions begin. The decision to induce labor is most often made if the cervix is already slightly open and dilated. And the baby is in a head down position. Although you will be examined first to determine the condition of the baby and the placenta, on the basis of which they will decide to continue monitoring and wait for the natural start of the process, induce labor by administering oxytocin, or perform a caesarean section.
Training contractions
Tension of the uterus not associated with the onset of labor is training, or false contractions. These contractions are also well known as Braxton Hicks contractions.
They may appear in the second trimester, from the 16th week. Then the expectant mother gets used to them and knows how to recognize them. But sometimes false contractions begin to actively manifest themselves a few days before birth - at 37–39 obstetric weeks and serve as their harbingers.
False contractions in the second trimester are not significant and do not harm the woman or baby. This is a normal contraction of a muscular organ - the uterus, painless and short-term. In the same way, the uterus contracts outside of pregnancy - for example, during orgasm, but due to its small size and location, a rare woman notices this contraction.
But starting from the 16th week, such contractions are already easily felt by expectant mothers and look like a sudden tension in the abdomen. He becomes stone. This can happen several times during the day.
How to distinguish false contractions from true ones, especially if the obstetric period is 38–39 weeks? How not to miss the onset of labor and not be late for the maternity hospital?
Distinctive features
Is it easy to confuse Braxton Hicks contractions with the onset of labor? No, if you know the features of the first and second processes. False contractions differ from labor contractions in the following ways:
- They are irregular. There is no dependence or pattern between uterine contractions. They can be sporadic throughout the day or quite frequent.
- They are painless. This does not mean that false contractions are weakly felt. A pregnant woman may feel strong pressure in the abdominal area and a distinct contraction of the uterus. These phenomena may be accompanied by a feeling of discomfort, difficulty breathing, but the main sign of labor - pain - will not be present.
- Training contractions do not increase in strength or duration. The first contraction can last a minute, and the second – 10 seconds, after which there will be a break. This is completely normal for Braxton Hicks contractions.
- They weaken or completely stop under the influence of antispasmodics - No-shpa, Papaverine or Viburkol.
Should you be scared if strong irregular contractions suddenly appear at week 39? Should I go to the maternity hospital or can I stay at home? Do I need to take any precautions?
Action tactics
If irregular contractions occur or intensify at 37–39 weeks, these are most likely harbingers of an imminent birth. Perhaps they will come in 1-2 days. It is quite possible to wait for this moment at home, unless the mother has any warning signs or has some diseases that require advance hospitalization.
The need to go to the maternity hospital arises in the following situations:
- If abdominal tension is accompanied not only by a feeling of pressure, but also by pain.
- If contractions last more than two minutes.
- If the contractions have become rhythmic.
- In the case when, along with abdominal tension, bloody discharge from the genital tract appears. And especially if they have been going on for 1-2 days.
- If the expectant mother has somatic diseases - hypertension, heart disease, and other pathologies.
- With an increase in gestosis - the appearance of edema, protein in the urine, and increased blood pressure.
- When complications were noted in previous births, for example, rapid labor, premature placental abruption.
If there are no unpleasant symptoms or complications, then even with an irregular increase in uterine tone, you can continue to enjoy your pregnancy. But do not forget about some precautions.
Precautionary measures
If at 38-39 weeks the stomach suddenly turns to stone, as during an orgasm, you need to give it the opportunity to relax. It is advisable at this moment to sit down or lie down, breathe deeply until the muscle tone is completely relieved. Training contractions before childbirth are a great way to practice breathing techniques in advance.
If a woman notices that some actions intensify these contractions, they should be avoided - for example, excessive physical activity. Many expectant mothers in later stages begin to arrange their homes, obeying the instinct of nesting. But this is not a reason to wash floors from morning to evening, move sofas and cabinets or hang curtains. At the moment of muscle contraction, the blood flow in them is disrupted, and, therefore, the supply of oxygen to the tissues deteriorates.
If false contractions suddenly become very frequent, albeit short-lived, it is better to see an obstetrician on the same day so that the baby’s health does not suffer.
Many parents are concerned about the issue of sexual activity at 38–39 weeks. This is especially true with regard to female orgasm, because it is also accompanied by contractions of the uterus.
Signs of post-term pregnancy:
1. More than 42 weeks or 294 days have passed since your last period.
2. A post-term baby has no hair, dry, flaky skin. There is no vernix lubrication, which usually completely or partially covers the newborn’s body. Post-term babies already have long fingernails.
3. When postmaturity most often occurs, there is a risk of fetal hypoxia, since the placenta has already served its term and begins to age quickly, which makes it less able to perform its function of providing the baby with nutrients and oxygen. The amniotic fluid becomes greenish.
You may already have signs of labor. Most likely, the stomach dropped, there were false contractions, sometimes the lower abdomen hurts and pulls, the uterus began to tone more often. In primiparous women and women who have a large difference between their children, a mucus plug comes out before birth, which closes the cervical canal. This usually happens 1-2 days before the start of labor itself. But maybe in a week. In order to determine whether the mucus plug has come out or amniotic fluid has begun to leak, wear cotton pads, not factory ones, so that the doctor can determine the intensity and nature of the discharge, this is very important. Sometimes the amniotic sac ruptures and fluid begins to slowly leak; this can be found out on an ultrasound. You may have to induce contractions as your baby cannot go longer than 12 hours without water. Amniotic fluid is usually clean, transparent, odorless; if the fetus is hypoxic, it may have a green tint.
Possible complications
Despite the fact that at the fortieth week the pregnancy is already coming to an end, there are a number of complications that can be dangerous to the health and even the life of both mother and baby. Suspicion of each of these complications requires prompt consultation with a specialist.
Arrhythmia
Heart rhythm disturbances during pregnancy are almost inevitable due to the heavy load on the woman’s body and the connection of the placenta to the circulatory system. In some women, arrhythmia is asymptomatic and has virtually no effect on the condition of the mother and child, however, there are cases when improper heart function requires medical intervention.
Symptoms of arrhythmia:
- increased or decreased heart rate;
- interruptions in heart function;
- dyspnea;
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- fast fatiguability;
- fainting.
Heart rhythm disturbances can lead to placental insufficiency, oxygen starvation and, as a consequence, delayed fetal development. In severe cases of arrhythmia, pregnancy is terminated at any stage.
Preeclampsia
Toxicosis (or gestosis) is familiar to almost all pregnant women in the first trimester. However, there are frequent cases of late gestosis, which can lead to a number of complications.
Late toxicosis is characterized by edema, increased protein levels in the urine and hypertension (increased blood pressure). And not necessarily all three symptoms at once, sometimes one is enough.
The consequence of gestosis can be placental abruption, premature birth, oxygen deficiency and even fetal death.
Oligohydramnios and polyhydramnios
The amount of amniotic fluid (or amniotic fluid) also affects the condition of the child, in particular, the uninterrupted supply of nutrition and oxygen, and the condition of the mother. As pregnancy progresses, this amount increases and by birth it should be approximately one and a half liters. Lack or excess of amniotic fluid is a serious complication of pregnancy. Oligohydramnios and polyhydramnios can be determined by the size of the abdomen, the height of the uterine fundus and how well the fetus can be felt and how actively it moves. Hospitalization and treatment are prescribed only in critical cases, however, if with polyhydramnios natural childbirth is allowed (though only if the bladder is punctured), then with oligohydramnios they resort to cesarean section.
Hypertonicity of the uterus
As already written above, periodic abdominal tension without water breaking or ichor secretion (training contractions) means that the body is preparing for childbirth. However, if the tension does not go away for a long time, you should urgently consult a doctor.
Umbilical cord entanglement
The umbilical cord is a “communication channel” between mother and child; it supplies nutrients and oxygen to the fetus. Umbilical cord entanglement is one of the most common complications during pregnancy.
Depending on how many times the umbilical cord wraps around the baby’s neck, a distinction is made between single, double or triple wrapping. The first type is practically not dangerous, is not a pathology or an indicator for the use of cesarean section, but the other two can lead to serious consequences:
- absolute hypoxia or suffocation;
- developmental delay;
- placental abruption due to too much tension on the umbilical cord.
In case of repeated entanglement of the umbilical cord, natural childbirth is contraindicated.
The belly becomes hard during pregnancy: associated risk factors
Doctors include genetic predisposition, pathological processes during pregnancy and diseases of internal organs as the main risk factors for the development of hypertension. Endocrine diseases, frequent colds, diseases of the thyroid gland and reproductive system can provoke this unpleasant phenomenon. In addition, working with harmful chemicals, daily schedules and business trips also negatively affect the health of the expectant mother.
The age of the woman giving birth is of no small importance. It is known that women who give birth for the first time after 35 years are much more likely to experience hypertension. To avoid negative consequences, you need to surround yourself with kind and positive people, give up alcohol and smoking, and also sleep more and spend time outdoors.
Possible discomfort and troubles
Throughout pregnancy, a woman faces some discomfort, and for some reasons, at the end of expecting a baby, this discomfort intensifies. Here are the possible troubles that await the expectant mother at the end of the third trimester.
Discomfort associated with prolapse of the uterine fundus
At the fortieth week of pregnancy, as a rule, the fundus of the uterus drops significantly, and the stomach also visually drops. In this regard, the expectant mother often experiences discomfort: the uterus puts pressure on the pelvic bones, bladder and intestines. As a result, hemorrhoids (blood and pain during bowel movements), urinary incontinence, stomach upset and, as a result, constipation or loose stools are possible.
Due to the rapid increase in weight and a shift in the center of gravity, the back can become very painful and even sciatica may appear. To alleviate the condition of the expectant mother, experts recommend wearing a bandage that will support the stomach and properly distribute the load on the back and legs.
Thanks to the bandage you can reduce back pain
Varicose veins also often occur, as the fetus makes it difficult for the blood to flow freely in the legs. In this case, in the maternity hospital, the woman in labor is asked to tightly bandage her legs or wear compression stockings.
Stretch marks, chloasma, dental condition
However, it is not only the position of the uterus and additional weight that cause discomfort. Due to a significantly enlarged belly, the skin becomes very tight and itchy, and stretch marks appear. Moisturizing creams, special oils and light massage will help you cope with these troubles.
Stretch marks appear due to the relatively rapid enlargement of the abdomen and skin tension
Experience shows that preventing stretch marks is much more effective. It is better to moisturize the skin of the abdomen, legs and chest in advance, even in the first weeks of pregnancy. It is impossible to treat stretch marks that have already appeared with cream or oil; it is only possible to minimize the discomfort.
However, it is not only the skin on the abdomen that suffers. Pigmented spots (chloasma) may appear on the face, neck or chest area. This occurs mainly due to hormonal changes in the body, but improper skin care before pregnancy (abuse of solarium or use of low-quality cosmetics) can aggravate the situation. Most often, age spots disappear after pregnancy without any intervention.
The location of age spots on the face is individual
Due to hormonal changes, it is also necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the oral cavity. Plus, the amount of calcium in a pregnant woman’s body is significantly reduced, and this has a detrimental effect on the condition of the teeth.
Edema
Finally, another danger to the health of the expectant mother and baby is edema. They occur due to stagnation of fluid in the body, since the kidneys may no longer cope with the load. Edema appears in the vast majority of women at the end of pregnancy: legs, arms or fingers increase in size, weight gain is more than 300 grams more than normal; if you press on the skin, a white mark will remain. If these symptoms are detected, it is necessary to reduce salt intake, limit water consumption and, of course, consult a gynecologist.
If a white dent remains on the skin from finger pressure, it means there is swelling of the limb
Why the stomach turns to stone: reasons for structural changes
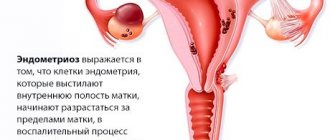
The reasons sometimes lie in the condition of the uterine walls:
- endometriosis – proliferation of endometrial tissue;
- fibroid is a benign tumor;
- inflammation of the appendages and uterus, suffered before conception or detected during pregnancy;
- genital infantilism – underdevelopment of the genital organs (small size of the uterus);
- overstretching of muscle fibers due to multiple births or high water intake;
- disturbances in the functional activity of the central nervous system, the reason for this is severe stress, chronic fatigue, hard work, infectious diseases.
Deviations from the norm
If 40 obstetric weeks (280 days) have already passed and labor does not begin, you should immediately visit your gynecologist.
During the examination, the doctor will assess the degree of risk of such a situation in relation to the baby and the level of preparedness of the body for childbirth.
If there are no precursors of labor, and the body, according to doctors, is ready for childbirth, then doctors stimulate the onset of labor.
Indications for stimulation:
- Postmaturity (pregnancy beyond 41 weeks).
- Absence of contractions during the first day after the rupture of amniotic fluid.
- Polyhydramnios.
- Diabetes.
- Preeclampsia (preeclampsia with symptoms of cerebrovascular accident). This disease often causes headaches and nausea.
Important! If labor does not occur, you can speed up its appearance in the following ways:
- Detachment of the amniotic membrane.
- Administration of prostaglandins. These are substances that cause the cervix to dilate.
- Use of Oxytocin. This is a drug that stimulates uterine contractions.
Other methods of stimulation:
- Sex. During intimate life, the uterus contracts.
- Castor oil. Taken orally. The oil stimulates the intestines, which leads to contractions of the uterus.
It is not difficult to induce labor on your own, but it is extremely undesirable. This should be done by qualified doctors based on the condition of the pregnant woman.
Before birth, a CTG of the fetus (cardiotocography) is required. This procedure records uterine contractions and fetal heartbeat.
Harbingers of childbirth
If a woman is in her second or third pregnancy, labor may begin 1–2 weeks earlier.
Multiparous women are already familiar with the warning signs of labor, so they won’t come as a surprise to them.
Note! For first-time mothers, the harbingers of labor can be very frightening, because they are similar to the symptoms of many diseases. Therefore, women should learn in advance about the signs of the onset of labor, so that during their onset they do not worry and properly prepare for childbirth.
Table: harbingers of childbirth
| Precursor | Description |
| Abdominal prolapse | A downward shift of the abdomen indicates the body is preparing for the upcoming birth. At this time, the cervix shortens and gradually dilates |
| Altered gait | In the last week of the process of bearing a child, after the abdomen subsides, the woman begins to move with a “goose gait”. This gait is a consequence of the fetus exerting pressure on the pelvic bones, which actively expand in preparation for childbirth. |
| Frequent urination and constipation | Appear due to pressure of the uterus on the bladder |
| Diarrhea | The onset of mild diarrhea indicates that labor will occur within 2–4 days |
| Changes in vaginal discharge | The last month of pregnancy causes hormonal changes that affect vaginal discharge. They become more liquid and abundant |
| Removal of the mucus plug | This sign cannot be called a reliable symptom of imminent labor. If the plug comes out, it means that the body has completed preparations for childbirth. But there is one peculiarity. Many women, after the plug came out, carried the baby for another 1-2 weeks, and some already gave birth a day later, so it is impossible to judge by this sign. The plug resembles an accumulation of mucus, sometimes with bloody streaks. After the plug comes out, you may experience pink or brown vaginal discharge |
| Pregnant weight loss | A week before giving birth, a woman loses excess fluid due to hormonal changes. |
| Uterine tone | Increased uterine tone at 40 weeks does not threaten the baby’s life. The uterus becomes toned thanks to training contractions |
| Rush or leakage of amniotic fluid | This is a direct sign of the imminent onset of labor. |
Immediately before giving birth, there is a strong pull in the lower back, the stomach becomes stiff and the lower abdomen hurts.
Recommendations for expectant mothers
There is very little time left until your baby is born. Try to treat yourself carefully during this period, listening to your feelings. And at the same time, you should not allow anxious thoughts to arise. There is no need to constantly be in tension while waiting for birth. Don't worry, your baby will be born. Well, if there is a delay in labor, talk to your gynecologist about this topic. Think about how you will get to the maternity hospital. Of course, it will be more comfortable to get there accompanied by people close to you. Don't worry about your upcoming birth or how to make labor painless. The level of knowledge of the medical staff, as well as the provision of the maternity hospital with the necessary equipment, will ensure a successful birth.
Fortieth week of pregnancy
Does labor always begin at 40 weeks of pregnancy?
The larger the belly becomes, the more the expectant mother wants to see her baby. Most women believe that they will go into labor immediately after the 40th week of pregnancy. This isn't always the case, pregnancy can last anywhere from 38 to 42 weeks, so don't panic if you're 41 weeks pregnant and have no contractions, or if contractions start 7-10 days before your expected due date. As a rule, a woman’s body perfectly senses when it’s time to give birth.
How is the baby doing?
Depending on the individual developmental characteristics, the weight of the child at the 40th week of pregnancy reaches 2500-4000 g, height 48-54 cm. He is already ready to breathe independently and feed on breast milk. There is no need to worry if, on the eve of birth, the baby has become less active and moves much less energetically in the stomach. This is due to the fact that at 40 or 41 weeks of pregnancy, his stomach is already quite cramped and uncomfortable to move. You have to sleep more and accumulate strength for the upcoming important test: your own birth.
Mom needs to rest too
The expectant mother needs to follow his example and rest as much as possible. Another hormonal change occurs in the body. There is no longer a need to maintain the pregnancy, so estrogens, necessary for the development of contractions, begin to be intensively produced. Many women at 40-41 weeks of pregnancy feel an increased need for rest. You shouldn’t fight with yourself and try to redo all the household chores - both mother and baby will benefit from getting a lot of sleep, enjoying peace and idleness.
What is better to refuse
At 40-41 weeks of pregnancy, you should not go on trips, not only distant ones, but also to the other end of the city or out of town to the country. Even for a walk in the nearest public garden, it is better to go out with your husband, mother or friend. Childbirth can begin at any moment; the signs indicating its proximity are not always clearly expressed. You should also not organize crowded receptions at home or go to a concert, theater or nightclub; it is better to arrange your life during this period so that it is convenient to lie down, eat and go to the toilet at any time. It is equally important to avoid people and situations that may be unpleasant for the expectant mother; her body is already under significant stress:
When is it time to go to the hospital?
In the fortieth week of pregnancy, labor can begin at any time. Therefore, it is very important not only to prepare a bag for the maternity hospital, but also to closely monitor the condition of the expectant mother so as not to miss the warning signs of childbirth.
It is important that in primiparous and multiparous women these precursors may be slightly different.
Precursors of labor in first-time mothers
The first noticeable sign of the imminent birth of a baby is a drooping of the abdomen. In addition, it becomes much easier for a pregnant woman to breathe, since the fetus no longer puts pressure on the diaphragm, and the baby’s head drops into the pelvis. For the same reason, the frequency of trips to the toilet increases.
In the photo on the left the stomach has not yet dropped, but in the photo on the right it has dropped significantly
Another sign is a significant increase in discharge. These may be supplemented by the detached mucus plug, which was mentioned earlier.
Training contractions also appear - periodic irregular contractions of the uterus. What distinguishes them from real contractions is the lack of rhythm.
Finally, an indisputable signal for the onset of labor is the breaking of water. After this, you need to urgently go to the maternity hospital.
Precursors of labor in multiparous women
Signs of the imminent birth of a child in multiparous or large mothers most often appear much later than in women with their first pregnancy. In this case, you should go to the maternity hospital already at the first regular contractions, since childbirth will go much faster . However, for women after a cesarean section, the precursors of labor will be the same as for first-time mothers.
Advice for a woman in labor
Despite the fact that childbirth is an uncontrollable process, the expectant mother should do everything possible to minimize pain and the risk of injury to the child.
- Even before labor begins, learn to breathe correctly. Inhale through your nose for three counts, then exhale through your mouth. This will help you calm down, relax and significantly reduce pain.
- Take a position that is comfortable for you. If at some point you want to walk around and move your hips a little, don’t be shy. Jumping on a fitball also helps.
- Try not to strain your muscles, but in the intervals between contractions, relax as much as possible and give your body a rest.
- Follow the instructions of the obstetricians strictly. If doctors tell you to push, try to do it with your diaphragm without straining other muscles.
- And finally, as difficult as it may be, try not to yell. Screaming not only takes away strength, but also stops the normal supply of oxygen to the child.
Experience shows that it is better to rehearse childbirth in advance and think through various behavioral tactics. Of course, things will most likely not go according to plan, but preparation will help avoid unnecessary panic.
Child development
At the end of the 9th month of pregnancy, the baby is already fully formed. Its weight is approximately 3500 g, and its height ranges from 48 to 55 cm.
Features of baby development in the womb in the last week:
- The baby can distinguish sounds and distinguishes the mother's voice well.
- The baby can distinguish between volumes.
- The baby's sucking reflex has fully developed.
- Dentin formation occurs in the baby's teeth.
All the baby’s organs are fully formed and functioning. The only exceptions are the lungs. They will begin to work with the baby's first breath.
At the 40th week of pregnancy, the baby changes its position in the womb and turns head down.
Size, weight and developmental characteristics of the child
The child is ready to be born, his organs are formed. He continues to gain weight, accumulating subcutaneous fat. The minimum weight of a full-term baby is 2700 grams, but more often this figure is closer to three kg. Height - from 50 centimeters. Because of these dimensions, it is very difficult for the baby to move in the womb, so his movements are minimal. The gynecologist can determine all these indicators using ultrasound.
At this stage, the baby looks the way his mother sees him
Another indicator that doctors record on ultrasound at the end of the third trimester is head circumference. Normally it is 32–38 centimeters. By comparing this indicator with the width of the expectant mother’s hips, the specialist can determine the tactics for managing childbirth.
Diagnosis of hypertension
If the stomach becomes stone during pregnancy, this indicates an approaching birth (in the early stages - a spontaneous miscarriage), as mentioned above. Palpation will help to accurately determine this phenomenon. The gynecologist examines the abdominal wall and determines increased tone. On examination, the uterus is hard, compacted and tense. Even by running your hand over a woman’s abdomen, you can assess the condition of the uterus and the position of the embryo. If the doctor confirms the diagnosis, the woman is immediately sent to the hospital and the cause of this symptom is determined.
Also, with the help of ultrasound, you can understand why the lower abdomen becomes stiff in late pregnancy, and determine the thickening of the myometrium of the uterine layer. The third diagnostic method is called tonusometry: a special sensor is applied to the woman’s stomach, which determines hypertonicity.
About uterine tone
Let's talk a little about the uterine muscle fibers, which by nature contract or become toned. Normally, during pregnancy, these muscle fibers are in a relaxed state, then the doctor speaks of normotonus. The muscular layer of the uterus is responsible for the state of rest, which responds to various external and internal changes (irritants).
Some women often experience discomfort in the abdominal area during pregnancy, especially if the pregnancy is 40 weeks. The abdomen becomes hard in later stages for several reasons, one of which is training contractions. The uterus begins to actively contract and causes similar phenomena. Usually there is no bloody discharge (bleeding is typical during real contractions).
But it’s better not to risk it and call an ambulance, since the term is very long, and a woman can give birth right at home. A doctor can determine hypertonicity using an ultrasound. You can independently recognize the presence of tone by the following clinical symptoms: periodic cramping, nagging pain appears in the lumbar and abdominal area, and the abdomen often becomes stiff. To avoid this phenomenon, you should avoid physical overexertion, be less nervous and get more rest.