Treatment of a disease such as type 1 diabetes involves a number of specific measures aimed at reducing blood glucose levels, which involves not only drug therapy, but also a special diet with an individually selected dietary menu, which will allow a person to feel as comfortable as possible with this incurable condition. diseases.
In this article, we will introduce our readers to how a person diagnosed with diabetes mellitus should eat properly, as well as what diet should be used in the treatment of type 1 diabetes and what should be taken into account.
What is diabetes
Diabetes mellitus has many faces. At its core, diabetes is a whole group of chronic diseases that develop as a result of absolute or partial deficiency of the pancreatic hormone, insulin. The process of glucose absorption by the body is disrupted, causing a persistent increase in blood sugar. With the development of the disease, the imbalance extends to other metabolic processes in the body: water-salt, protein, fat.
Glucose itself is vital for humans. It is a universal source of energy for cells. Carbohydrates, entering the gastrointestinal tract with food, are broken down by enzymes into simple sugars, after which they are absorbed into the blood and supplied to cellular tissue. Thus, glucose plays a vital role in the metabolism and energy supply of the body.
When sugar is not processed properly and accumulates in the blood, the blood vessels are the first to suffer. Excess glucose corrodes the walls of blood vessels, leads to loss of vision, kidney failure, strokes, heart attacks, gangrene of peripheral organs, diabetic coma and can even cause death.
No one is immune from the occurrence and development of diabetes. The disease can develop in a person of any age and gender.
ul
Pregnancy and diabetes
Many people are confused and believe that gestational diabetes and pregnancy diabetes are the same thing. In reality, this is not true at all. Diabetes in pregnant women is when a representative of the fair sex already has an established diagnosis before conceiving a child.
In turn, gestational diabetes is when glucose levels increase during pregnancy. Moreover, before pregnancy there were no problems with sugar.
As medical practice shows, this condition occurs in 2-10% of women during pregnancy. And if it is not controlled, then harmful consequences are revealed not only for the child, but also for the mother.
However, if you look from the other side, this form of pathology is easy to control, and it responds well to treatment through the administration of insulin and special healthy nutrition.
You need to measure your sugar levels in the body several times a day after eating. And also, follow all the doctor’s recommendations, even if your sugar has dropped to the required level and there are no more drops.
A glucose test is recommended between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. It should be noted that testing on an empty stomach is not the best choice, as it may conceal pathology by providing a false positive result. A two-hour glucose tolerance test is your best bet.
The following symptoms of gestational diabetes can be identified:
- Attacks of nausea and vomiting.
- Constant feeling of thirst.
- Frequent and copious urination.
- Extreme fatigue.
- Inflammatory processes in the bladder.
- Blurred vision.
Most often, after the birth of a child, sugar levels in the body return to normal. But there is still a certain probability that type 2 diabetes will develop. Therefore, such women are recommended to follow preventive measures and periodically get tested for glycated hemoglobin.
How does diabetes manifest itself?
The disease, depending on the cause of its occurrence and the severity of its course, manifests itself in different ways, but there are general signs, the appearance of which should alert you.
Thirst and excess urination
A person suffering from diabetes experiences, on the one hand, increased thirst, and on the other, a frequent urge to urinate. It seems that water is not absorbed by the body. High blood glucose levels make you want to drink. Drinking clean water in large volumes can reduce the concentration of glucose in the blood.
The kidneys are responsible for filtering blood and producing urine. High blood glucose levels make it difficult for the kidneys to function. To increase the efficiency of the cleaning process, they need a lot of liquid. The kidneys remove the liquid part of the blood, plasma, which is the reason for the constant fullness of the bladder.
The healers of Ancient Greece knew about this symptom, but since diabetes had not yet been studied at that time, it was believed that the body, due to the disease, loses the ability to retain fluid.
High sugar levels
The achievements of modern science make it possible to easily determine the presence of excess sugar in the blood - including at home. But for the first time, increased glucose levels were discovered in urine: back in the 17th century, scientists discovered that in diabetes mellitus, urine can be sweet.
But even if the urine does not contain sugar, this does not mean that the person is not sick. There is the concept of “diabetes insipidus” - a disease associated with pathology of the kidneys or pituitary gland.
Energy hunger
People with type 2 diabetes often feel weak. With this pathology, glucose loses its ability to be absorbed by cells, and therefore cannot serve as an energy source for the body. As a result, the patient experiences increased fatigue, weakness, and shows low performance.
Physical hunger
Often, due to metabolic disorders in the body, a diabetic patient experiences a constant feeling of hunger. You want to eat so badly that it’s simply impossible to resist. The reasons for this condition are the same inability of cells to absorb and process glucose, which is found in excess in the blood.
Weight loss
Rapid weight loss is usually observed in the case of type 1 diabetes. With increased appetite, the patient may simply look exhausted. The reason lies in metabolic disorders: proteins and fats are broken down super intensively due to the lack of glucose in the metabolic process.
Itchy skin
A sweet environment promotes the active proliferation of fungal colonies. This may be accompanied by a feeling of itching of the skin and mucous membranes.
Diabetic polyneuropathy
Excessive blood sugar negatively affects the nervous system. Neuropathy develops gradually. The first signs can be detected 5 years after the onset of diabetes. Regular surges in blood sugar disrupt metabolic processes and prevent the supply of vitamins, oxygen and microelements to nerve cells. Over the years, the sensitivity of nerve endings decreases more and more. The patient may, unnoticed, become injured. Wound healing in the presence of diabetic neuropathy is a long process.
The patient feels numbness and tingling in the limbs. Over time, muscle weakness develops, then, in the vast majority of cases, diabetic ulcers appear on the legs.
Diabetic foot
The concept of “diabetic foot” unites a group of late complications of diabetes mellitus, including necrotic lesions of the soft tissues, bones and joints of the foot. Amputation is required in 15% of cases.
Diabetic angiopathy
Another complication of diabetes is diabetic angiopathy. With a long course of the disease, excess sugar eats away the walls of blood vessels. Ulceration of the capillaries is called microangiopathy and when the capillaries supplying the retina are damaged, it leads to diabetic retinopathy and vision loss. Damage to large vessels is called macroangiopathy, in most cases the heart and legs are affected.
Diabetic nephropathy
Specific damage to both kidneys at once in patients with diabetes is called diabetic nephropathy, leading to renal failure, disability and premature death.
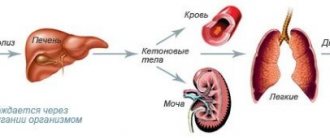
Diabetic ketoacidosis
In cases where cells cannot use glucose as a source of nutrition, the body switches to the breakdown of fats. At the same time, ketone bodies are actively produced, and blood acidity increases. If too many ketones accumulate, the kidneys do not have time to remove waste products from the body. The patient experiences weakness and nausea, and the smell of acetone or overripe apples appears from the mouth. If measures are not taken, the patient falls into a diabetic coma.
ul
Nuances of nutrition for diabetes
For any manifestations of diabetes, you must follow a diet. What can you eat if you have diabetes? For diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2, diet No. 9 is provided. Its main goal is to reduce carbohydrate intake, improve pancreatic function and increase tissue sensitivity to insulin.
The main idea is to reduce the consumption of sugars, baked goods, sweet carbonated drinks and store-bought juices. Priority is given to fresh vegetables, unsweetened fruits, cheeses with fat content up to 30%, skim milk, unsweetened yoghurts.
You need to eat often, but little by little. The daily norm should be divided into 5-6 servings. Breakfast is required. In the morning you need to eat well. To ensure that each meal is balanced, you should visually divide the plate into 2 parts. Half the plate should be occupied by vegetables. The second half should be filled with cereals in combination with fish or meat.
You shouldn't rush while eating. The meal should last at least 15 minutes so that the brain has time to send a signal to the digestive system that it is full. This makes it easier to overcome the increased feeling of hunger.
What to do if you have diabetes?!
We recommend reading an exclusive article on how to forget about diabetes forever... Read more >> |
What can you eat if you have diabetes:
- fruits (non-starchy, low glycemic index);
- fresh or cooked vegetables;
- greenery;
- lean meat, fish;
- mushrooms;
- dairy products;
- rice, buckwheat;
- berries;
- natural fruit and vegetable juices, preferably freshly squeezed, diluted with water.
What not to eat if you have diabetes:
- confectionery, sugar, baked goods;
- fatty meats, duck, smoked products;
- sweet cheeses, salty cheeses, heavy cream, ice cream;
- fatty fish, canned food containing oil, salted fish;
- fresh baked goods, white bread;
- semolina and pasta;
- pickled and salted vegetables;
- animal fats;
- sweet compote, dried fruits, carbonated drinks;
- alcohol.
It is necessary to reduce the consumption of potatoes, beets, carrots, peas, bread and sweet fruits.
The norm for bread consumption for diabetes is 150g per day.
The diet for type 2 diabetes involves daily consumption of 1.5 liters of free liquid, no more than 12 g of salt, up to 100 g of protein, about 50 g of animal fats and 30 g of vegetable fats, 300-350 g of carbohydrates.
For type 1 diabetes, drinking tea and coffee with sugar, canned juices and other foods containing large amounts of sugar is strictly prohibited.
In cases of severe diabetes mellitus, it is necessary to learn how to count bread units and consume no more than 8 bread units at one time.
For people with diabetes, a line of diabetic sweets is produced. Fructose is used in their production. However, moderation is necessary when consuming fructose; it is not harmless to the body.
ul
Specific signs in different patients
In addition to the general symptoms, diabetics may exhibit additional symptoms, depending on the age or gender of the patient.
Table No. 1 Special manifestations of type 1 diabetes mellitus
| Patient category | Symptoms | What causes this phenomenon? |
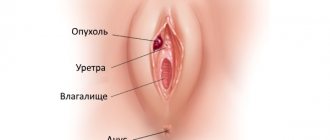
| Women | Unbearable itching in the perineum and genitals | Diabetes symptoms are caused by sugar crystals that appear in the urine. After urination, droplets of urine remain on the skin and mucous membranes and cause an itching sensation. It is recommended to consult a doctor |
| Men | Symptoms affect the genitourinary system: erection is impaired and sexual desire decreases or completely disappears | Often, insulin-dependent diabetes occurs secretly (latently) or the patient does not associate sexual dysfunction with this disease. |
| Newborns and babies of the first year of life | The baby is not gaining weight well, but eats well; constantly wants to drink. The child is worried about thirst, but he cannot talk about it, so he becomes restless and capricious. Diaper rash appears on the skin, and in the genital area the skin becomes inflamed. In girls this manifests itself in the form of vulvitis, in boys - balanoposthitis (inflammation of the foreskin). | Since the common symptoms that are often present are not associated with the development of diabetes mellitus, the disease is detected by chance when it develops into a more serious form and a diabetic coma develops. |
Type 1 diabetes
There are two types of diabetes. Type 1 carbohydrate metabolism disorder develops in girls and young women before and after 30 years of age with a hereditary predisposition to diabetes mellitus. Triggering factors can be stress, viral or bacterial infections.
The consequence of the disease is a process in which the immune system perceives pancreatic cells as foreign and destroys them using its own antibodies. As a result, glandular cells are replaced by connective tissue.
Accordingly, the pancreas in certain areas stops producing the hormone insulin, which is designed to ensure homeostasis of the internal environment of the body by regulating the level of glucose in the blood. The autoimmune process goes unnoticed and can last for months after the girl has suffered a viral infection. The patient’s well-being sharply deteriorates, while the following symptoms of diabetes mellitus in women simultaneously appear:
- Constant thirst as a result of not absorbing glucose. The patient has a sore throat due to dryness, she drinks a lot of water, but cannot get drunk.
- Losing weight, sometimes up to 10 kg within a month, despite excessive appetite. Weight loss is a consequence of metabolic disorders that occur due to hormonal imbalance. The tissues seem to stop noticing and absorbing glucose.
- Metallic taste.
- Frequent urination as a result of drinking large amounts of liquid. A condition with 12 urges per day and a daily urine volume of 3 liters is alarming.
- Acetone smell in exhaled air. Acetone, as one of the metabolites, is normally removed from the body in the urine. In type 1 diabetes, the toxin remains in the tissues and poisons them.
In women over 30 years of age, additional symptoms may appear over time, such as:
- Low temperature (35.5-36.1° C).
- Itching, especially in the groin area.
- Infection of the vagina.
- Convulsions, loss of sensitivity, numbness of the toes, pain in the heart, pain in the calves due to damage to the peripheral nerves. In the absence of timely treatment, gangrene often develops.
- Dry skin with plenty of fluids and good nutrition, deterioration of the upper layer of skin, poorly healing wounds and microcracks.
- Weakening of the immune system and, as a result, frequent colds, skin lesions with fungal infections, thrush, furunculosis.
- Apathy, fatigue, nervousness, depression, headaches due to hormonal instability.
Laboratory blood testing in insulin-dependent patients shows a glucose concentration of more than 6.1 mmol/l, while the normal blood sugar level is 4.1-5.9 mmol/l. But elevated sugar levels also occur during pregnancy, after illness or stress.
Repeated tests a week later help clarify the diagnosis. When the threshold level of 8 to 11 mmol/l is reached, glucose is present in the urine. When there is excess sugar in the blood, some of it combines with the hemoglobin of red blood cells. This protein is called glycosylated hemoglobin. Normally it is 4.5-6.5%.
See also: Symptoms of pancreatic diseaseul
Type 2 diabetes
If the pancreas maintains normal insulin levels, but the cells do not perceive the hormone, they speak of relative insulin deficiency or type 2 diabetes. In this state, cells feel starved for energy, even if insulin and glucose are present. The manifestation of pathology is characteristic of a more mature age. What are the signs of diabetes in women after 40 years of age?
Along with the general signs of diabetes mellitus in women, the second type of diabetes is characterized by symptoms unique to it, such as:
- Osteoporosis. Impaired bone density is more common in women over 60 years of age, but with diabetes, this condition can also occur in women after 40 years of age.
- Weakness of muscle tone due to impaired functioning of peripheral nerves and physical inactivity.
- Weight gain, against which all diets are powerless.
- Hair loss on the legs and appearance on the face.
- Yellow growths on the skin are xanthomas.
- Deterioration of vision.
Type 2 diabetes occurs in 90% of cases. With a healthy lifestyle, the disease can be prevented and this does not require intense physical activity or “starvation” diets. Another thing is female type 1 diabetes, against which there are no effective preventive methods.
ul
The effect of diabetes on the body
Type 1 diabetes mellitus has a clear clinical picture and rapid development. A progressive disease often provokes the development of the following pathological changes:
- Blood thickening. Since excess glucose causes dehydration, the blood becomes thicker. There is a tendency to thrombosis. Mostly small vessels are affected, the legs are especially affected.
- Retinopathy. The retina of the eye is damaged, vision decreases to the point of blindness.
- Polyneuropathy. A feeling of colic in the legs, over time – numbness and insensitivity of the limbs.
- Diabetic foot. Non-healing ulcers and abscesses and necrotic areas appear. A serious complication of diabetes mellitus is gangrene. Unfortunately, in a neglected state, the leg must be amputated.
- Nephropathy. Due to the increased load on the kidneys, the functioning of this organ is disrupted.
Type 1 diabetes is an incurable disease. It is dangerous due to its complications, which turn a person into a disabled person. There is also a constant threat of diabetic coma. But all these manifestations of the disease can be brought under control and the quality of life can be maintained at a normal level. This requires constant intake of insulin in doses prescribed by the doctor, regular glucose measurements, and special nutrition. Also follow all medical recommendations related to lifestyle.
Knowing the symptoms of diabetes will allow you to seek medical help in time and prevent the development of complications.
Share link:
Treatment of diabetes
If you have diabetes, you cannot engage in amateur activities. Only qualified medical care can improve a woman’s quality of life. Treatment of diabetes mellitus is more successful in the early stages of the disease. That is why women need to monitor the changes occurring to them and the sensations that accompany them. At the first signs of diabetes in women over 50 years of age, it is necessary to undergo tests to determine:
- cholesterol and blood sugar;
- level of ketone bodies in urine;
- pancreatic enzymes.
When glucose levels are above 7 mmol/L, a doctor may diagnose prediabetes. An accurate diagnosis can be made after reviewing the results of all other tests. At a level of 10 mmol/l and above, we can talk about serious problems with insulin secretion.
See also: Medicinal properties of boron uterus
Diabetes can have different degrees of severity: from first to fourth. The disease is incurable, so it is treated under constant medical supervision.
The treatment course for type 2 diabetes includes:
- blood glucose tracking;
- diet;
- taking medications that lower blood glucose levels and improve cell sensitivity to insulin.
If you strictly follow all the doctor’s prescriptions, insulin injections may not be necessary, because the hormonal levels gradually normalize.
Treatment for type 1 diabetes includes:
- insulin injections;
- diet;
- physical education classes.
When remission occurs, it must be supported by exercise and a therapeutic diet. The doctor chooses the treatment tactics, taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient, his age, type of diabetes and other factors. Symptoms become more severe with age. At the age of 60, it is even possible to develop a lactic coma, problems with the kidneys, vision, and skin. It is advisable to include an experienced ophthalmologist, cardiologist and nephrologist on the medical team. As an addition to the main treatment, traditional methods can also be used, but only those approved by the attending physician.
If left untreated, diabetes can cause disability and early death. It’s not for nothing that the disease has another name: “the silent killer.” The results of one large-scale study showed that diabetes shortens a woman’s life by an average of 8 years and increases the risk of developing pathologies of the heart and blood vessels by 6 times, while in men the latter figure is 2-3 times less.
ul