Adenoviral infection in children at the household level is more often called ARVI. As a rule, parents do not bother themselves much with identifying the virus that caused the disease. The main thing is that the child is sick.
Experience with infectious diseases suggests that adenovirus can infect even if someone’s child has already been ill. Within 25 days after illness, adenovirus can infect a healthy child upon contact with a carrier.
The situation is typical for kindergartens and schools. It is almost impossible to protect children from communication in these groups. This is why wave-like infection occurs within a couple of weeks from the start.
Features of adenovirus infection in children
Adenovirus infection in children is much more common than in adult patients. Also, in children and adolescents, the infection occurs with a more vivid clinical picture.
Symptoms of the infectious process may include:
- lymphoid structures,
- respiratory tract,
- ocular conjunctiva,
- mucous and lymphatic structures of the intestine.
For reference. In addition to specific symptoms, the disease is accompanied by the appearance of intoxication and febrile symptoms, as well as catarrhal manifestations with pronounced exudative components (productive wet cough, discharge of mucus from the nasal passages).
Features of the disease in newborns
Up to six months, immunity is supported through breastfeeding. With mother's milk, the baby receives a full set of antibodies. In this regard, passive immunity does not provide opportunities for a serious viral attack.
Having stable immunity in the event of illness reduces symptoms and consequences.
However, over time, the body's protective properties decrease. In the period from 6 months to a year, the risks of an infectious disease gradually increase.
Attention. After one year of age, the risks of adding a bacterial component increase, which will intensify the course of the disease in case of infection.
The consequences of the disease also become more complex.
Etiology of the infectious process
The causative agents of the disease are distinguished by high rates of resistance in the OS (environment). Pathogens tolerate freezing well. When released into water (at temperatures up to four degrees), the pathogen can remain viable for two years.
Attention. On household items and clothing, adenoviruses can remain active for from ten to forty-five days.
Also, the causative agent of the infectious process is not destroyed when treated with ethers and lipid solvents.
When exposed to ultraviolet radiation, treated with chlorine-containing disinfectants. means or at temperatures above fifty-six degrees, the virus is inactivated within half an hour.
How is adenovirus infection transmitted in children?
The source of the causative agent of adenoviral infection (AI) is a patient with an active form of pathology or a healthy virus carrier. At the same time, healthy carriers of viruses play a critical role in the development of outbreaks of adenovirus infection in children and adults.
A patient without symptoms of the disease continues to actively release viruses into the OS, contributing to the infection of others.
Attention. Virus shedding can be observed up to forty to fifty days after infection.
The causative agent of adenoviral infection can be released into the OS with mucus and feces. In the first days of the disease, viruses are most actively released with mucus particles (coughing, sneezing, etc.). In the later stages of the disease, as well as in intestinal forms of the disease, viruses are actively excreted in the feces.
The most common mechanisms of infection transmission are:
- fecal-oral;
- contact and household;
- food.
Also, in rare cases, intrauterine infection of the fetus is observed.
The natural level of susceptibility to the pathogen in children is high. In adults, the disease is registered less frequently and often occurs in mild forms (due to the formation of species-specific immune reactions).
For reference. Outbreaks of adenovirus infection in children are most often recorded in the cold season. The exception is outbreaks of pharyngoconjunctival fever and epidemic keratoconjunctivitis, often recorded in the summer.
The form of the disease depends on the serotype of adenovirus that has entered the body.
Prevention
It comes down to improving overall health so that the immune system itself can quickly cope with the adenovirus.
The following contribute to increasing the body’s resistance to diseases:
- normalization of work and rest regimes. A person should not be overly tired or overworked. It is necessary to sleep at least 7 - 8 hours at night;
- proper nutrition. Eat a variety of foods, because with it we get the necessary vitamins and minerals. The diet should include fish, different types of meat, fruits, vegetables, seafood, dairy products, and bread. Food should be tasty and enjoyable. Proper eating also has its own characteristics. Better in small portions, but often! Optimally – 5 – 6 times a day. You should eat in a calm environment, silently, enjoying and chewing your food thoroughly;
- Regular physical exercise strengthens the body and guarantees health. Walking, running, gymnastics, dancing, swimming, etc.
Specific prevention of adenovirus infection
Vaccines have now been developed against some of the adenovirus serotypes that most often cause the disease. They are used to prevent mass diseases in the army. The drug is available in tablet form. For complete protection you only need to take 2 tablets. However, this vaccine is not available in the Russian Federation! And you can't buy it either. This vaccine is used only by the United States Army. We can only hope that one day it will appear in our country.
Pathogenesis of adenovirus infection in children
After the virus enters the body, the process of its active reproduction in the affected cells begins. After this, it penetrates the blood, triggering a wave of viremia.
Clinically, this process can be manifested by the development of such specific symptoms of adenoviral infection in children as:
- pharyngoconjunctival fever;
- catarrh of the respiratory tract (in mild forms of the disease, the upper respiratory tract is affected, and in moderate and severe infections, adenoviral bronchitis and pneumonia can develop);
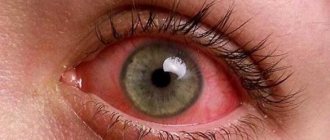
- keratoconjunctivitis;
- diarrheal symptoms;
- damage to lymphoid structures;
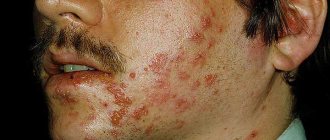
- widespread exanthema (rash due to adenoviral infection in children is much more common than in adults).
What are adenoviruses?
Adenoviruses are viruses whose genome consists of double-stranded DNA. They belong to the genus Mastadenoviruses (lat. Mastadenovirus). Adenoviruses show high resistance to environmental factors. To date, 51 serotypes of adenoviruses have been identified, but only a third of them are pathogenic for humans. Some serotypes have been shown to be oncogenic in rodents, but no association has yet been demonstrated between adenoviruses and their transformation into tumors in humans.
Research is currently underway on the use of adenoviruses as a DNA vector in gene therapy. Adenoviral infections affect the respiratory, digestive and visual systems. They can be especially dangerous for newborns and people with weakened immune systems. Infection usually occurs by droplet or fecal-oral route. The reservoir of the virus is humans.
Places such as kindergartens, nurseries, boarding schools, hospitals and military barracks contribute to the spread of infection.
Conjunctival infection (conjunctivitis) may occur from contact with sick people's towels, contact lenses, or swimming pools. Remaining an infection on a particular serotype of a virus creates permanent resistance to that particular serotype (but not to others).
Infection occurs through the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract, conjunctiva and cornea.
Adenoviruses also have a special affinity for lymphoid tissue, and infiltrates of lymphocytes form in infected tissues and organs.
Adenoviral infection in children - symptoms
Attention. The infectious process caused by adenoviruses always begins acutely. The first manifestation of adenovirus infection in children is intoxication symptoms.
Intoxication manifestations can vary from moderate to severe. Patients are concerned about the appearance of headaches, severe weakness, lethargy, muscle and joint pain. Nausea and vomiting are also common.
Appetite is reduced. Young children may experience moodiness and tearfulness.
The temperature during adenovirus infection in children rises from the first days of the disease. The maximum severity of fever is usually observed in the first two to three days of illness.
However, elevated temperature in children can last from five to ten days.
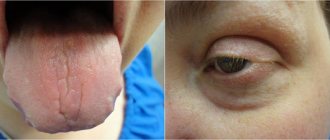
The most specific tetrad of symptoms for adenovirus infection in children is the presence of:
- acute rhinitis;
- acute pharyngitis;
- acute inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eyes (conjunctivitis);
- severe febrile symptoms.
For reference. Diarrheal symptoms are common in young children.
A typical manifestation of adenoviral infection is also catarrhal inflammation of the respiratory tract. Exudative components predominate in the inflammatory process, so patients experience:
- copious discharge of non-viscous and non-purulent mucus from the nasal passages;
- productive, wet coughs.
Young children often cannot blow their nose or cough normally, so they experience copious amounts of mucus running down the back of the throat. It is due to the constant flow of mucus that children vomit more often.
Against the background of constant ingestion of mucus containing viruses, children are also more likely than adults to experience damage to the lymphoid structures of the intestine (mesadenitis).
Adenoviral pharyngitis is manifested by sore throat (increased when swallowing), an increase in the size of the tonsils (thin filmy deposits may be noted), granularity and hyperemia of the posterior wall of the pharynx.
For reference. Young children also often experience severe symptoms of adenoiditis (nasal voice, night snoring, severe nasal congestion, mucus running down the back of the throat, etc.).
On the second to fourth days of the disease, children often experience the development of adenoviral bronchitis or pneumonia.
Damage to lymphoid structures is accompanied by an increase in the submandibular, cervical, occipital, etc. lymph nodes
Lymph nodes are dense, moderately painful on palpation, not fused and mobile. The skin over the inflamed lymph nodes is not changed.
Suppuration of the lymph nodes is uncharacteristic. The suppurative process can develop only with the addition of a secondary bacterial component.
In this case, the appearance of sharp pain in the lymph node, hyperemia of the skin over it, softening in the center of the lymph node and a symptom of fluctuation are noted.
Stenosing laryngotracheitis
For reference. Also, a common symptom of adenovirus infection in young children is acute stenosing laryngotracheitis. Obstructive symptoms may persist for up to three weeks.
The manifestation of signs of stenosing laryngotracheitis is an indication for mandatory emergency hospitalization in a hospital.
The development of stenosing laryngotracheitis is accompanied by the appearance of:
- hoarseness of voice;
- rough barking cough;
- noisy breathing;
- severe anxiety or lethargy of the patient;
- mixed shortness of breath;
- pallor of the face and cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle;
- retraction of intercostal spaces;
- retraction of the supraclavicular and/or subclavian fossa.
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis is made based on clinical symptoms and epidemiological data. A general blood test is also performed.
If necessary, to exclude the development of complications, ultrasound, ECG, chest x-ray, etc. are performed.
A consultation with an ENT doctor (sinusitis, otitis) or a surgeon (mesadenitis) may also be indicated.
To confirm the diagnosis, rapid diagnostics (ELISA, RIF), etc. can be performed.
Adenoviral infection in children - treatment
For mild cases of the disease, treatment is symptomatic. Bed rest for the period of fever and vitamin therapy are indicated. According to indications, antiviral drugs, interferons and interferon inducer drugs can be used.
If necessary, antipyretics, mucolytics, vasoconstrictor nasal drops, eye drops with interferon, etc. are used.
Attention! Antibiotics for adenoviral therapy in children are used only in complicated forms of the disease and the addition of a bacterial component.
Treatment
Dr. Komarovsky’s main advice regarding the treatment of adenovirus infection is to provide suitable conditions for the sick baby. To make you feel better, you can use symptomatic medications, but only after examination by a specialist.
Parents should pay attention to the fact that most drugs are approved for use at 2-3 years of age. Therefore, you must carefully read the instructions before using medications.
Treatment of adenovirus infection:
- Eliminating a runny nose
At this stage, you can use rinsing or instillation, depending on what the child tolerates better. From infancy, it is allowed to use drops containing sea salt. For example, Aquamaris, Aqualor. Some of them have a vasoconstrictor effect and stop a runny nose in a short time, for example, Snoop (used no earlier than two years of age). This group of medications should be used for no more than a few days, as local dysbiosis and addiction develop.
- Elimination of relevant symptoms
The temperature should be brought down if it rises above 38.5 degrees for 3 days. If there is no improvement within this period and the child continues to have a fever, it is necessary to consult a doctor again. Paracetamol or Nurofen are most often used for children. These substances, in addition to antipyretic, have an analgesic effect. These drugs can be found on pharmacy counters in the form of sweet emulsions, so taking the medicine will not be difficult.
- Additional measures
The children's room must be ventilated at least 3 times a day, and wet cleaning must also be carried out. In addition, you should provide the child with plenty of warm drinks and try to maintain bed rest. If the baby is sick, the mother must ensure uninterrupted access to breast milk.