Content:
- What is bilirubin?
- Total bilirubin in pregnant women: norm and deviations
- Causes of elevated bilirubin
- What to do with increased bilirubin
← Proper nutrition for high levels of bilirubin in the blood
What to do if the level of basophils increases and what could this mean? →
Throughout pregnancy, the expectant mother regularly undergoes laboratory tests that allow her to monitor the progress of pregnancy. One of the important indicators of blood tests, which doctors pay special attention to, is bilirubin. As a rule, the amount of bilirubin in the blood increases slightly during pregnancy, which is considered normal. If the amount of bilirubin exceeds the norm, the expectant mother requires a thorough examination, since such indicators can be dangerous for both the woman and the fetus.
Important! During gestation, bilirubin in pregnant women may be slightly elevated and is not considered a pathology by the doctor. Its quantity can increase along with the growth of the fetus, while the level of increase is insignificant and practically imperceptible in the transcript of the analysis.
What problems increase bilirubin
An increase in bilirubin, first in the blood, and then in the urine, occurs against the background of pathological processes in the liver. Outwardly, this manifests itself in jaundice, and the urine takes on darker, richer shades. At the same time, the reasons for the increase in bilirubin may vary, in addition, they can be combined with each other.
If the problem is improper outflow of bile, then it is directed not towards the stomach, but into the blood. Such an incorrect outflow can be provoked by:
- chronic hepatitis;
- autoimmune type hepatitis;
- housing and communal services;
- acute viral hepatitis;
- hepatitis of bacterial nature, toxic and much more.
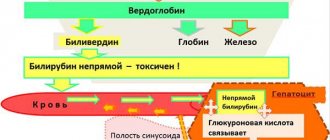
It is important to emphasize that in this case one cannot exclude problems of an oncological nature and various syndromes. It is important to note that there are two types of bilirubin: direct and indirect. If we are talking about an increase in the indirect fraction, then the reasons may vary, but in most cases they are associated with incorrect breakdown of indirect bilirubin or with too rapid a cycle of erythrocyte life.
Since indirect type bilirubin is not able to dissolve in water, the presence in the blood of a significant difference from the norm upwards may go unnoticed in a urine test. If indirect bilirubin in the blood has increased, problems may be associated with anemia of a hemolytic nature, which is congenital, with secondary hemolytic anemia, drug-induced anemia, of a toxic nature. Against the background of poisoning with harmful substances or poisons. Various syndromes cannot be ruled out.
Elevated levels of bilirubin in urine are most often associated with problems that damage liver cells. These include hepatitis of various natures, liver injuries and cirrhosis, liver damage due to metastases.
Total bilirubin in pregnant women: norm and deviations
The pigment bilirubin is directly related to the liver and gall bladder, which is why when it increases, an enlarged liver and yellowness of the skin are observed. During pregnancy, a woman’s body experiences enormous stress; all internal organs work in an intense mode, which often leads to various disorders. Changes also occur in the liver and gallbladder, which are responsible for processing and excreting bilirubin. The norm of bilirubin in pregnant women is from 8.5 to 20.5 mmol/l. In case of deviations, the indicators are increased.
If you are interested in a table of bilirubin norms in women by age, you can find it in the article on our website.
Video TV show with Dr. Komarovsky about neonatal jaundice
With minor deviations, the woman will not have jaundice, but if the norm is exceeded significantly, then there is pronounced jaundice of the skin, which alarms doctors and becomes the reason for ordering a number of tests.
Important! High bilirubin during pregnancy can be a sign of quite serious diseases: cholecystitis, viral hepatitis, hemolytic anemia and other pathologies that can be dangerous for both the woman and the fetus.
When bilirubin is elevated during pregnancy, there is a high probability that the baby will also have this pigment above normal after birth. Such children are born with yellow skin, they may have an enlarged liver, and they are prone to various allergies.
Diagnosis of pathology
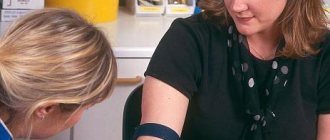
The level of bilirubin in the blood can be determined using a biochemical test of blood or urine. But the last option is not always informative. For example, if indirect bilirubin increases, the levels may be normal. That is why pregnant women are recommended to take a biochemical blood test. There is no need to worry too much if the symptoms listed above are absent and bilirubin is elevated. Perhaps the recommendations for taking the test were not followed:
- Blood should be donated strictly on an empty stomach. The last meal should be no later than 20:00 the previous day.
- 2-3 days before the expected date of the test, you should avoid spicy, smoked and salty foods.
- The expectant mother should try to relax and not be nervous, as stress can negatively affect the results.
- Blood should be donated strictly on an empty stomach. The last meal should be no later than 20:00 the previous day.
- 2-3 days before the expected date of the test, you should avoid spicy, smoked and salty foods.
- The expectant mother should try to relax and not be nervous, as stress can negatively affect the results.
Causes of elevated bilirubin
If bilirubin is increased during pregnancy, the reasons may be quite different, but basically it increases with intrahepatic cholestasis, when the outflow of bile from the liver is impaired. When the indicator is increased or decreased, this is always a reason to consult a doctor and determine the reason for its deviation.
The reasons for this most often are the following pathologies:
- hepatitis of viral, bacterial etiology;
- autoimmune disorders;
- cholelithiasis;
- biliary cirrhosis;
- gestosis in pregnant women;
- severe toxicosis;
- hemolytic anemia.
Increased bilirubin in pregnant women in the early stages may be present with severe toxicosis, and in later stages it can be associated with excessive enlargement of the fetus. Often, the cause of deviations of bilirubin from the norm in pregnant women is the use of certain medications or an incorrect daily routine and diet.
A diet with increased bilirubin can help reduce this indicator in the blood in pregnant women. causing the woman to worry.
Important! In some cases, increased bilirubin may occur due to improper blood sampling or improper preparation. Doctors recommend that women, on the eve of testing, avoid fatty and spicy foods, as well as overeating.
When is a test ordered and how to prepare for it?
The bile pigment bilirubin is formed during the breakdown of red blood cells. To find out its concentration, a biochemical analysis of venous blood is prescribed. The reason for referring a pregnant woman for diagnostics is suspicion or monitoring of the condition due to existing pathology of the liver or gallbladder:
- hepatitis;
- cirrhosis;
- cholecystitis;
- cholelithiasis.
During pregnancy, it is also recommended to donate blood for bilirubin in case of pancreatitis, hemolytic anemia, or poisoning.
Diagnostics does not require complex preparation. A woman needs to come to the laboratory in the morning without having breakfast beforehand. If you are suffering from unbearable hunger, you can have a snack no later than 4 hours before donating the biomaterial.
3-4 days before diagnosis, you should stop taking choleretic drugs (if they were previously prescribed).
What to do with increased bilirubin
A slight increase in bilirubin in the blood does not require treatment, but when the indicators are pathological, the doctor will first prescribe a full examination: a repeat blood test, urine test, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, which will help examine the liver, gall bladder and ducts, evaluate their work, and identify changes. Therapeutic therapy for elevated bilirubin in pregnant women is prescribed individually for each patient, depending on the test results.
Drug treatment is prescribed only as a last resort. If a woman is diagnosed with liver or gallbladder disease, then treatment is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause.
A healthy lifestyle normalizes the level of bilirubin in the blood of a pregnant woman
In some cases, the doctor may prescribe infusion therapy, after which the bilirubin level will return to normal. If a pregnant woman has a history of severe liver disease, then the pregnancy will proceed with complications, and in some cases the question of termination may arise.
When there are no serious diseases, the doctor advises the expectant mother to be more attentive to her health and nutrition, and may prescribe herbal decoctions: motherwort, chamomile, mint, St. John's wort. It is recommended to spend as much time as possible in the fresh air and avoid sources of stress. If bilirubin is elevated, it is important to follow all the doctor’s recommendations, regularly take blood tests and remember that the growth and development of the fetus, as well as the baby’s life after birth, depend on the woman’s health.
If during pregnancy there is a reduced number of lymphocytes in the blood, then you can find out information about the reasons for this deviation in the article on our website.
Important! Every pregnant woman should know that increased bilirubin in the blood is not a disease, but only a symptom that indicates other diseases or disorders occurring in the body of the expectant mother.
In order to avoid unpleasant “surprises” during pregnancy, a woman needs to prepare for this well before conceiving the baby. This is the only way to avoid complications during pregnancy. In addition, it is also important to regularly undergo tests during pregnancy, which will help monitor the health of both the woman herself and her unborn child.
← Proper nutrition for high levels of bilirubin in the blood
What to do if the level of basophils increases and what could this mean? →
We recommend studying similar materials:
- 1. Causes and dangers of increased basophil levels in children
- 2. Reasons for an increase or decrease in neutrophils in a blood test in children?
- 3. Functions and possible causes of pathologies of segmented neutrophils
- 4. What do elevated eosinophils mean in a blood test in adults?
- 5. Proper nutrition for high levels of bilirubin in the blood
- 6. What to do if the level of basophils increases and what does this mean?
- 7. Low level of total bilirubin in the blood: reasons for the decrease
Ways to reduce bilirubin
Therapy for reducing the amount of pigment in the blood depends on the cause of the increase in bilirubin. To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to re-donate blood for biochemistry, following all recommendations.
After re-screening, it is necessary to consult a gastroenterologist. After conducting an examination and reviewing the test results, the doctor will prescribe the necessary therapy. Usually the specialist’s prescription is very simple and harmless to the unborn child:
- proper nutrition, balanced with vitamins and microelements necessary during pregnancy;
- taking medications that do not harm the fetus;
- daily exposure to fresh air;
- elimination of bad habits: smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages and narcotic substances;
- compliance with the regime;
- taking medicinal decoctions based on chamomile. But you should not self-medicate, since even basic motherwort or valerian root can harm the unborn child. Before using traditional methods, it is necessary to consult a doctor who will assess the patient’s condition and be able to allow or prohibit the use of the infusion;
- healthy and adequate sleep, the duration of which is 7-8 hours a day;
- avoiding taking medications that affect the pigment index, since it is because of them that bilirubin can increase;
- prescribing infusion therapy in a hospital.
The type of medication depends on the disease that caused the increase in bilirubin:
- hemolytic anemia - blood transfusion is possible or the deficiency is filled with washed red blood cells. If the case is advanced, an artificial termination of pregnancy is performed. This disease is treated by a hematologist or infectious disease specialist, who may prescribe drug or surgical therapy;
- hepatitis - many drugs are contraindicated for pregnant women (including interferon and ribarivin), therefore those that are safe for the fetus are prescribed: Essentiale, Chofitol, Karsil. There is another way to cause premature birth. The birth takes place in a specialized hospital for hepatitis patients.
You should not ignore changes in the amount of bilirubin in the blood in pregnant women, since this is one of the main symptoms of severe liver diseases. If the bilirubin level is increased or, conversely, decreased, it is necessary to undergo examination and treat the disease at an early stage.
Consequences for the expectant mother and fetus
Most often, an increase in bilirubin in the blood occurs in the last trimester of pregnancy. This is due to the enormous load on the liver as a result of an increase in the size of the uterus. In turn, this condition leads to stagnation of bile and increased bilirubin. The consequences for pregnancy can be very different:
- With a slight increase in bile pigment (within 8.4-20.5 µmol/l), there is no danger for mother and child. Bilirubin levels return to normal immediately after childbirth, when the load on the liver is less.
- With a sharp increase in pigment, a real threat arises to the condition of the mother and fetus. If bilirubin levels are not lowered in time, there may be a risk of premature birth or stillbirth. For the mother, a high level of bile pigment may mean the development of hemolytic anemia or hepatitis.
We suggest you read: Pilates for pregnant women: how to do the exercises correctly