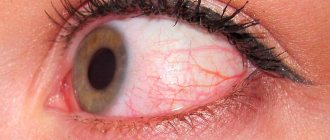
Reasons for appearance
Dacryocystitis occurs in the presence of physiological pathologies, namely congenital narrowing of the duct (stenosis). Sometimes doctors detect a complete blockage of the tear duct.
The main causes of the disease:
- Trauma to the eyes or paranasal sinuses.
- Inflammatory process of the nose, which provokes swelling of the tissues around the eye.
- An infectious process caused by bacteria and viruses, which leads to blockage of the duct.
- Getting foreign particles into the eye or working in dusty and smoky rooms. As a result, the channel becomes clogged.
- Allergy to exposure to an irritant.
- Reduced protective properties of the body.
- Overheating and hypothermia.
- Presence of diabetes mellitus.
Very often this pathology occurs in newborn babies. This is due to the structural features of the tear ducts. When the baby is in amniotic fluid, the tear duct is closed with a special membrane, which must rupture during or after childbirth. This process does not occur if pathology occurs. Tears collect in the canal and this provokes an inflammatory process. It mainly develops in women. Men are also no exception, but this pathology is detected very rarely in them. The reason is differences in the structure of the lacrimal canal. Women use cosmetics, most of which cause inflammation.
Complications of dacryocystitis
Complications usually involve the spread of an infectious process, which can be superficial (eg, cellulitis), deep (orbital cellulitis, orbital abscess, meningitis) or generalized (sepsis).
If dacryocystitis is present, intraocular surgery (for example, cataract removal) should be postponed until it is cured, since there is a high risk of developing endophthalmitis. There are also complications associated with dacryocystorhinostomy:
- unsuccessful operation;
- formation of scars on the skin;
- nosebleeds;
- cellulite;
- discharge of cerebrospinal fluid through the nose.
The acute form of both acquired and congenital disease is dangerous due to complications. For example, it does not cause lacrimal sac abscess, orbital phlegmon, or brain abscess. In the absence of adequate treatment, death is possible. The chronic process does not often provoke complications.
Stones in the tear ducts often appear in 13-16% of people suffering from this disease. Those with a history of acute form of the disease are at higher risk than those with chronic dacryocystitis.
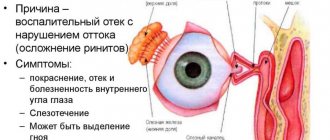
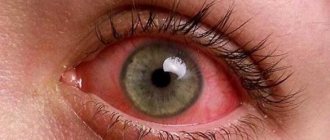
Symptoms of the disease
Tears are necessary for the normal functioning of the visual organs. They moisturize the cornea of the eye, protect against mechanical irritants, and perform an antibacterial function.
Sometimes tears stop flowing, this is the first sign of tear duct obstruction. Treatment is one way to cope with the problem and prevent the development of canaliculitis. Sometimes massage of the tear duct helps.
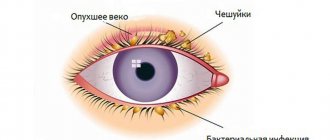
Main symptoms:
- painful and unpleasant sensations in the eye area;
- redness of the skin around the eye;
- feeling of squeezing and bursting;
- swelling of the skin;
- lacrimation;
- edema;
- vision problems;
- increased secretion of mucus, which smells bad;
- formation of pus;
- high body temperature;
- intoxication of the body.
The acute stage of dacryocystitis appears as an inflammatory process affecting one eye. In the chronic stage, the tear duct swells, the eye turns red and the number of tears increases.
If you experience such symptoms, you should consult a doctor. Blockage can occur in both acute and chronic stages. The accumulation of tear fluid increases the likelihood of infectious processes.
About pathology
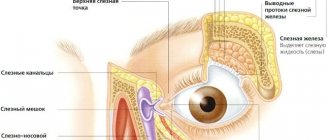
The lacrimal sac stores secreted tears. They are needed not only so that the baby can make a stronger impression on his parents during whims, but also for natural disinfection and protection of the organs of vision. Normally, excess tears drain through the nasolacrimal duct, which connects the lacrimal sac and the nasal cavity. This is why toddlers sniffle when crying.
If this canal is too narrow, the tear fluid cannot flow freely and leave the lacrimal sac. The eyes of such a child look watery and unhealthy. Meanwhile, bacteria begin to multiply in the lacrimal sac due to lack of drainage. Due to this, inflammation and suppuration occur.
In newborns, dacryocystitis differs from the disease that can develop in older children. It is more physiological, since in infants the obstruction of the canal is associated with its congenital narrowness. Often it goes away on its own, but the parents’ task is to still help the baby.
In children who are no longer considered newborns by age, but belong to the category of infants (children up to one year old), obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct can develop during influenza, an acute respiratory viral infection. Sometimes such unpleasant symptoms are the consequence of a prolonged runny nose of any origin, as well as the presence in the nose.
Children who fall and injure their nose also often suffer from dacryocystitis, since the location of their septum may be disrupted. Advanced dacryocystitis is dangerous due to the development of an abscess or phlegmon, which will require serious surgical treatment.
Diagnostics
Dacryocystitis is detected without much difficulty. At the appointment, the doctor performs a visual assessment of the eye and palpation of the lacrimal sac.
Additional events:
- Test using paint. The eye is instilled with a solution containing a dye. If pigment appears in the eye after a few minutes, this indicates a blockage of the tear ducts.
- Probing. Using a probe with a needle, the ophthalmologist penetrates the duct, which helps to expand it and get rid of the problem.
- Dacryocystography. Carrying out an X-ray examination with the introduction of a dye. In the picture you can see the structure of the eye system and identify the problem.
- Patency can also be checked with the West test. A cotton swab is placed in the nasal passage, on the affected side. Collargol is instilled into the eye. The condition is considered normal when after 2 minutes the tampon turns dark. If the swab remains clean or stained after 10 minutes, there is a problem.
Treatment
Eyes are the mirror of the soul. When an eye problem arises, there is no need to take risks. Treatment should be prescribed by a doctor after preliminary diagnosis. The treatment method is selected depending on the form and cause of the pathology that provoked it, and age characteristics.
Treatment methods:
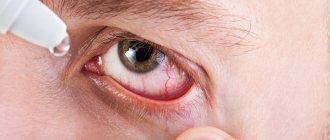
- Rinsing the eyes with antibacterial and disinfectant solutions.
- The use of special drops and ointments.
- Massage procedures and compresses to help clean the canal.
Eye rinsing with antiseptic solutions is carried out several times a day. The procedure is performed by an ophthalmologist in a hospital setting.
Ointments and drops that have an antibacterial effect:
- Phloxal . Antibacterial drug with a wide spectrum of effects. Fights the inflammatory process. The course of treatment is 10 days, two drops twice a day.
- Dexamethasone . Drops with an antibacterial effect. Effective against infectious processes. Instill 5 times a day. The required dosage and course of treatment are selected by the doctor individually for each patient.
- Levomycetin is a hormonal drug. Used for allergic reactions and inflammations.
- Ciprofloxacin . Prescribed for infections of the lacrimal duct. Buried every three hours.
The drugs have contraindications and side effects. Drug therapy is carried out under the supervision of the attending physician.
If the treatment does not have a positive effect, bougienage is performed - cleaning the lacrimal canal from purulent contents;
You can quickly cope with the disease only if treatment is started in a timely manner. If symptoms are negative, you should visit an ophthalmologist.
How does acute and chronic inflammation manifest?
The principles of eliminating pathology consist of symptomatic treatment:
- pain;
- swelling;
- purulent foci.
Treatment with antibiotics is carried out. All other conditions are determined by the attending physician. If symptoms of the disease occur, painkillers are prescribed. Pain syndrome can be treated with medications, but their action is not always effective.
Much attention is focused on the treatment of suppuration; for this purpose, rinsing the nasolacrimal canal is prescribed. For symptoms of dacryoadenitis, the washing process takes half an hour.
It is recommended not to rush into treatment with surgery. Traditional medicine methods are suitable. In addition to solutions that relieve swelling, antihistamines are used.
Radical ways to fight
If there is no positive effect from drug treatment, or if the cause is a tumor or cyst, surgical treatment is performed.
Surgical intervention happens:
- Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy I. A device with a camera is inserted into the duct. A puncture or incision is made using an endoscope. A special valve is created, the main purpose of which is drainage. The recovery period is 7 days. In parallel, antibiotic therapy is carried out to prevent the risk of developing an inflammatory process. The main advantage is the absence of visible marks after the operation.
- Balloon dacrycytoplasty is an intervention that, due to its safety, is performed even on newborns. A conductor with a reservoir filled with liquid is inserted into the channel. Allows you to expand the area, thereby breaking through it. The procedure is carried out under local anesthesia. During the rehabilitation period, special drops and antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
brief information
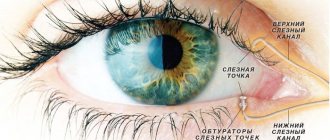
The lacrimal glands are responsible for producing fluid and draining it into the nasal cavity.
These are paired organs that perform tear secretion and tear drainage functions. The lacrimal ducts are presented in the form of: lacrimal stream, lake, puncta, canaliculi, sac and nasolacrimal duct. The functioning of the glands is regulated by the fibers of the facial and branches of the trigeminal nerves. The lacrimal apparatus is supplied with blood through a special artery, and return flow occurs through the vein adjacent to the gland.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oM9B3LzPvow
The tear fluid contains water, urea, mineral salts, protein, mucus and lysozyme. The latter is an antibacterial enzyme, thanks to its properties it cleanses and protects the eyeball from harmful microbes.
The secreted liquid washes away grains of sand and foreign small objects from the eyes. In the presence of irritants such as smoke, excessively bright light, psycho-emotional states, severe pain, lacrimation increases.
Massage
Prepare your hands before the procedure: wash, disinfect or wear gloves.
Massage scheme:
- Press on the outer corner of the eye, turn your finger towards the bridge of the nose.
- Gently press and massage the lacrimal sac, removing purulent masses from it.
- Instill a warm solution of furatsilin and remove the discharge.
- Carry out pressing and massaging movements along the tear ducts.
- Jerky movements along the nasolacrimal sac with some force to open the canal and extract the discharge.
- Instill a solution of chloramphenicol.
In case of obstruction, the technique is carried out up to five times a day.
General information
Phlegmon of the lacrimal sac (acute purulent peridacryocystitis) in most cases is a complication of chronic dacryocystitis. The disease is diagnosed in 3-5% of newborns suffering from inflammation of the tear ducts.
According to statistics, with timely surgical treatment, 96.9% of patients experience a complete recovery, only 3-4% of patients experience a relapsing course. In 12.5% of cases, multi-stage surgical interventions are required. Males and females get sick with the same frequency. The pathology is widespread.
Cellulitis of the lacrimal sac
Folk remedies
After prior approval from a doctor, traditional medicine is successfully used at home.
Folk remedies:
- Aloe. For inflammation, it is good to instill freshly prepared aloe juice, half diluted with saline solution.
- Eyebright. Cook in the same way. Use for eye drops and compresses.
- Chamomile. Has an antibacterial effect. You need to take 1 tbsp. l. collection, boil in a glass of boiling water and leave. Use to wash eyes.
- Thyme . Due to its anti-inflammatory properties, the infusion is used for dacryocystitis.
- Kalanchoe. Natural antiseptic. Cut off the leaves and keep in the refrigerator for two days. Next, extract the juice and dilute it in a 1:1 ratio with saline. This remedy can be used to treat children. Adults can instill concentrated juice into the nose, 2 drops each. The person begins to sneeze, during which the tear duct is cleared of pus.
- Leaves from a rose . Only those flowers that are grown on your own plot are suitable. You will need 100 gr. collection and a glass of boiling water. Boil for five hours. Use as lotions.
- Burda ivy-shaped . Brew a tablespoon of herb in a glass of boiling water, simmer for 15 minutes. Use for rinsing and compresses.
- Bell pepper . Drink a glass of sweet pepper fruit every day. adding a teaspoon of honey.
Which drops to take based on age
Ophthalmologists prescribe the following drops for dacryocystitis in newborns and children under 3 years of age:
- Collargol;
- Vitabact;
- Levomecithin;
- Phloxal;
- Vigamox;
- Tobrex.
In addition to the listed drugs, adults are prescribed:
- Dexamethasone;
- Ciprofloxin.
Description of drugs
All drops described should be taken only if prescribed by a doctor. They are sold in pharmacies by prescription.
Drops are the basis of drug treatment for dacryocystitis.
- Collargol. Antimicrobial agent. Helps relieve inflammation and stops the formation of mucus. These eye drops are indicated for children from birth and adults. The drug contains 30% albumin and 70% silver. Drops are contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to their components.
Collargol is available in powder form, which is diluted with distilled water. At the pharmacy, the patient should indicate his diagnosis. Based on it, the pharmacist will dilute the powder in the required proportions.
- Vitabact. Antibacterial agent. Used as drops for dacryocystitis in newborns, older children and adults. The active component of the drug is picloxidine dihydrochloride. Excipients: distilled water, polysorbate and glucose. The drug is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to its components.
- Vigamox. Antimicrobial agent with antibiotic. Used as drops for dacryocystitis in children from birth and adults. The active component of the solution is moxifloxacin hydrochloride. Excipients: boric acid, water for injection and sodium chloride.
- Phloxal. Antimicrobial drug with antibiotic. The active component of the drops is ofloxacin. They also contain sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide, benzalkonium chloride, hydrochloric acid and purified water. Floxal is used for dacryocystitis in adults and children over one year old.
- Levomycetin. Antibacterial and antiviral agent with antibiotic. It is rarely prescribed for children under two years of age, only in severe cases of dacryocystitis. The active substance of the drug is chloramphenicol. Excipients: boric acid and distilled water. Drops are contraindicated for children under one year of age, pregnant women and patients with their personal intolerance.
- Tobrex. Antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drug with antibiotics. Contraindicated for children under 3 years of age. The active ingredients of the drops are dexamethasone and tobramycin. Excipients: benzahexonium and sodium chlorides, hydroxyethylcellulose, distilled water. Tobrex should not be used by pregnant women.
- Ciprofloxin. Antimicrobial agent with antibiotic. It is prohibited for use by children under 18 years of age. The active substance of the drug is ciprofloxacin hydrochloride. Excipients: mannitol, purified water, acetic acid, sodium acetate. Drops treating dacryocystitis are contraindicated in pregnant women and patients with hypersensitivity to their components.
- Dexamethasone. Anti-inflammatory drug. May help relieve allergic symptoms. If the patient has severe or chronic dacryocystitis, drops ease its course. The drug is contraindicated for children under 12 years of age. The active component of the drug is dexamethasone. Excipients: ethanol, dihydrogen phosphate and sodium chloride, purified water, etc. The drug should not be used in case of hypersensitivity to its components and intraocular pressure.