Causes of photophobia
The causes of photophobia of the eyes are the following:
- If the patient has been in a room with poor lighting for a long time, then after a sudden appearance of light, a temporary high sensitivity to bright light occurs. The pupil of the eye needs additional time to adapt. Such photophobia goes away quite quickly if there are no eye pathologies.
- Very often, photophobia occurs in diseases such as eye trauma, conjunctivitis, uveitis, keratitis, and iridocyclitis.
- The structure of an albino's body is different in that light can enter the eye not only through the pupil, but also through the iris, which has no pigment substances. Because of this, albinos often experience photophobia. This also applies to patients who have a light-colored iris.
- If a foreign object gets on the cornea and erosion occurs, photophobia may result.
- Photophobia can occur after the retina has been intensely exposed to ultraviolet or other rays for a long time. This occurs during gas or electric welding.
- During artificial dilation of the pupil, photophobia also occurs. The pupil is artificially dilated for a more accurate diagnosis of eye diseases.
- Sometimes photophobia occurs due to allergies or tuberculous-allergic conjunctivitis. In such cases, photophobia is expressed very sharply.
- Photophobia is a sign of brain damage as a result of mercury poisoning, as well as botulism, measles, and rabies.
- Sometimes, when taking medications such as belladonna, tetracycline, furosemide, doxycyline, quinine, photophobia occurs as a side effect.
- Very often, photophobia occurs with diseases such as migraines, viral infections or colds.
- Photophobia occurs with damage to the central nervous system or meningitis.
- Photophobia occurs with retinal detachment, refractive surgery, and sunburn of the eyes.
- This condition also occurs if contact lenses are chosen incorrectly.
Main causes of photophobia
The causes of photophobia are irritation of the following nerve systems:
Trigeminal nerve endings
which are embedded in the structures of the anterior part of the eyeball: the cornea and parts of the choroid. Such photophobia becomes a symptom:
- glaucoma;
- conjunctivitis;
- eye injuries;
- iritis, cyclitis or iridocyclitis;
- keratitis;
- uveitis;
- allergic keratoconjunctivitis;
- foreign body of the cornea;
- corneal burn;
- electric and snow ophthalmia;
- corneal erosions;
- flu;
- rubella;
- measles;
- incorrectly selected contact lenses;
- computer vision syndrome.
Visual-nervous structures of the retina:
- when the eyes are irritated by bright light;
- with albinism, when the iris is light and does not protect the retina from bright rays;
- when the pupil is dilated, especially persistently, caused either by a brain tumor or edema, or by eye drops (for example, atropine or tropicamide), or by the use of certain drugs, or by botulism;
- with complete or partial absence of the iris;
- with color blindness;
- retinal detachment.
Photophobia can also be caused by the following process (this is typical for severe lesions of the cornea):
- nerves coming from the inflamed cornea go to the necessary part of the brain;
- some of them, as intended by nature, fall not only into the area of subcortical structures that are “responsible” for the diseased eye, but also into the neighboring one, the one that should transmit impulses from the healthy eyeball to the cortex;
- in such a situation, only complete removal of the diseased eyeball can save the healthy one.
Increased photosensitivity that develops with migraine, retrobulbar neuritis (this pathology can develop as an independent disease, it is also characteristic of multiple sclerosis) or trigeminal neuralgia (it is most often caused by herpes zoster) is explained by this phenomenon. Impulses coming from the retina reach the subcortical nuclei. There they are collected and sent to the cortical structures. But, being previously summed up and amplified in the subcortical nuclei of the corresponding nerve (for example, trigeminal), they exceed the sensitivity threshold, which is why photophobia appears.
The mechanism of photosensitivity in brain pathologies such as an abscess, its tumor, hemorrhage into the cranial cavity or inflammation of the meninges (meningitis) is not fully understood, and therefore it is not presented here.
Photophobia symptoms
Symptoms of photophobia include convulsive closing of the eyelids that cannot be controlled, increased lacrimation, eye pain and headaches in bright light. Such symptoms can be caused by radiation from the sun, the screen of a mobile device, monitor, or fluorescent lamp.
If a patient has photophobia and works in a room with fluorescent lights, then migraine attacks and headaches are doubled.
For a person with increased sensitivity to light, exposure to the sun can cause a severe headache after 10 minutes.
Photophobia is not a disease in the literal sense of the word, but there are some signs that help identify photophobia:
- dizziness;
- internal swelling of the eyes;
- headaches or migraines;
- dry mucous membrane;
- sensitivity of the eyes to the light emitted by fluorescent lamps;
- eye fatigue;
- frequent inflammatory processes;
- dizziness;
- blinking or flashing in the eyes.
Also, increased sensitivity to bright light can cause chest tightness, shortness of breath, and nausea. There is also evidence that people who suffer from photophobia are more likely than others to suffer from depression, irritability, frequent mood swings, unreasonable outbursts of aggression and despair.
Symptom therapy
Treatment of photophobia is entirely based on the cause of this symptom. This requires ophthalmological diagnosis, since many eye diseases are similar to each other. To make a diagnosis, the following studies are needed:
- Ophthalmoscopy – examination of the fundus through a previously dilated pupil.
- Biomicroscopy - examination in a special slit lamp for changes in the vitreous body and areas of the fundus.
- Perimetry - checking visual fields.
- Tonometry is the measurement of intraocular pressure.
- Gonioscopy is an examination of the corner of the eye where the iris borders the cornea.
- Pachymetry is the measurement of corneal thickness.
- Ultrasound of the eye helps to examine the transparent media of the eye when it is impossible to perform ophthalmoscopy.
- Fluorescein angiography is a study of the patency of blood vessels that supply the structures of the eye.
- Optical coherence tomography - helps to identify changes in retinal tissue.
- Electroretinography - helps to carefully study the functioning of the retina.
- Sowing the discharge from the conjunctival sac for viruses (using the PCR method), bacteria and fungi.
If, according to the results of an ophthalmological examination, a person is healthy, an examination by a neurologist is necessary. This specialist also prescribes additional studies:
- MRI of the brain;
- electrocephalography;
- Dopplerography of the vessels of the neck, which are directed into the cranial cavity.
An ultrasound of the thyroid gland, determination of hormones produced by this gland in the blood, and radiography of the lungs are also prescribed. If signs of hyperthyroidism or diabetic retinopathy are detected, treatment is carried out by an endocrinologist. If there is evidence of a tuberculous process in the cornea and conjunctiva, therapy is prescribed by a phthisiatrician.
What can you do before consulting a specialist?
We do not recommend delaying contacting a doctor, as seemingly banal photophobia may hide a malignant brain tumor that is rapidly progressing. But while you're waiting for your appointment with a doctor or for a test, you don't have to suffer from daylight. To alleviate the condition, buy polarized sunglasses, which will make it possible to reduce the dose of ultraviolet radiation entering the eye. In addition you need:
- stop rubbing your eyes;
- reduce time spent sitting at the computer;
- use Vidisik drops containing artificial tears;
- for purulent discharge, use drops with antiseptics or antibiotics: “Okomistin”, “Levomycetin drops”, “Tobradex” and others. In this case, an examination by an ophthalmologist is mandatory, since the purulent process can affect the deeper parts of the eye, which the local antiseptic “does not reach”;
- If photophobia appears as a result of a bruise, injury or burn to the eye, emergency ophthalmological assistance is needed. First, apply antiseptic drops to your eyes, apply a sterile bandage on top, and call an ambulance.
Author:
Krivega Maria Salavatovna resuscitator
Photophobia in a child
Most often, the cause of photophobia in a child is congenital pathologies. In some cases, the child does not have the coloring pigment melanin (albinos). Also, the disease often occurs as a result of transferred viruses and infections. Fear of bright lighting develops with allergic or infectious conjunctivitis.
“Pink disease” occurs very rarely in children.
In addition to high sensitivity to light, a child may experience the following symptoms:
- anorexia;
- excessive sweating;
- high blood pressure;
- too intense pink color of the feet and palms;
- stickiness of hands and feet.
If such signs appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Delay threatens complications and death.
Optic nerve palsy may occur in childhood. The eye pupil dilates and the upper eyelid droops. As a result, sensitivity to light increases.
Sometimes children complain that there is a foreign body in the eye, as well as a feeling of squeezing and photophobia. Such signs are characteristic of endocrine ophthalmopathy. The cause of the disease is disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland.
In order to prevent the development of photophobia in a child, it is worth finding out the cause of the disease in time, correctly diagnosing it and selecting treatment. It is also important to follow measures to prevent the development of the disease.
Causes
Photophobia is a painful reaction of the eyes to sunlight or artificially created light. In medicine, this condition is called photophobia .
The pathology is accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the visual organs. A person constantly squints his eyes in any light, but in the dark the feeling of discomfort disappears. There are certain reasons for this.
In adults
Disturbances in the functioning of the body provoke photophobia of the eyes; the causes in an adult may lie in the following problems:
- eye diseases;
- albinism;
- eye injury;
- viral and infectious diseases;
- presence of a foreign body in the eye;
- mental disorders;
- brain damage;
- pathologies of the central nervous system;
- taking medications;
- stress, lack of sleep.
Working at a computer monitor for long periods of time is bad for your eyes. The mucous membrane dries out, increasing the load on the visual organ. All this provokes a fear of light.
Serious pathologies are indicated by severe pain in the eyes, headache, redness of the whites, and blurred vision. If you have these symptoms, you should immediately consult a specialist.
In children
Photophobia in children has a variety of causes. The child’s body quickly reacts to infectious pathogens.
Pathologies such as meningitis, anthrax, scarlet fever, dysentery, and sepsis are manifested by a painful reaction to light.
The reason for this condition may also be:
- Inflammatory processes. These include conjunctivitis, keratitis, iritis, keratoconjunctivitis, iridocyclitis.
- Mechanical damage to the visual organ, entry of a foreign body.
- Color blindness. Color blindness is usually hereditary and is expressed in the inability to distinguish certain colors.
- Albinism. This is a congenital disease that is characterized by a lack or complete absence of melanin.
- Absence of the iris or part thereof. This pathology can develop as a result of injury or be observed in a child from birth.
- Heliophobia. This is the fear of being under the sun. Is a psychological problem.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system. They affect the child's perception of light.
- Abscesses, cysts and brain injuries. Neoplasms and inflammations are quite difficult to establish.
- The main signs of central nervous system damage are headache and photophobia in a child.
- The same symptoms are observed with meningitis, encephalitis, rabies, brain injury, botulism . Sometimes, along with photophobia and headache, a child may experience nausea and vomiting.
- Acrodynia is considered a fairly serious cause of photophobia . It occurs only in children and is accompanied by poor appetite, high blood pressure, and pink discoloration of the limbs.
- Photophobia in children can be observed with diseases such as rubella and measles .
Sometimes symptoms of photophobia appear after taking certain medications. Often in childhood, incorrectly selected optics are to blame for the problem.
If a baby's eyes hurt from bright light, this may be due to a sudden awakening, as well as certain diseases:
- brain abscess;
- vascular hematomas;
- migraine;
- ulcerative lesions of the cornea;
- glaucoma;
- keratitis;
- uveitis
If photophobia is caused by natural causes, then as reflexes decrease and after the formation of the visual organs, the child will be able to calmly be in brightly lit places. Lack of proper treatment in case of diseases can lead to loss of vision and even death.
Pathology can be recognized by the following sign: if visual impairment bothers one eye , most likely the reason is the structure of the organ, the presence of a foreign body, or disease. Both eyes cannot tolerate light in case of infection or brain damage.
Photophobia in cats and dogs
Photophobia is normal in small cats and dogs. This is due to the fact that the organs of vision are not sufficiently developed, and the baby looks for a darker place. Also, sometimes a cat or dog on the eve of giving birth looks for a darker and more protected place in order to give birth there.
Sometimes animals have eye diseases that lead to increased sensitivity to light. In such cases, there is cloudy discharge from the eyes, inflammation of the tissues around the organs of vision, redness of the conjunctiva, and swelling. Sometimes a foreign object gets into the eye. It is also common for eye diseases to cause cloudiness or white spots on the surface of the eyes. If you have such signs, you should contact your veterinarian and undergo a course of treatment.
Rabies is sometimes the cause of photophobia. This disease is caused by a pathogen that can survive in animal corpses. Under successful circumstances, the pathogen retains vital activity for two years and dies only at temperatures above 100°C. Rabies is carried by dogs, cats, foxes, hedgehogs, and bats.
Rabies affects the spinal cord and brain. The nervous system is so affected that death occurs. The virus enters the body through open wounds or upon contact with the mucous membrane (eyes, mouth). It can be found in the animal's saliva and internal organs. Rabies is dangerous for all warm-blooded animals and humans. The rabid animal is aggressive, easily excited and afraid of light. Also, with the disease, spasms, convulsions occur, and salivation increases.
In adults, the incubation period lasts from three to six weeks. In children, the first signs of the disease may appear as early as a week after the virus enters the body.
If signs of rabies appear, the animal is euthanized and the corpse is burned. There is no cure for this disease. Owners of sick pets are required to undergo vaccination.
In order to prevent an unpleasant situation, dogs and cats need to be vaccinated against rabies once a year.
Prevention
To prevent photosensitivity, you must first protect your eyes from bright light. To do this, you need to purchase polarizing sunglasses that will filter ultraviolet radiation, preventing large amounts of it from entering the organs of vision.
In addition, you must:
- rub your eyes as little as possible, especially on the street, in the hospital and other public places;
- Rest your eyes more often while working at the computer;
- use artificial tears (Vidisic);
- if purulent inflammation occurs, use antiseptic or antibacterial drops (Okomistin, Levomycetin, Sulfacyl, etc.).
If photophobia is the result of mechanical damage to the eye (trauma, burn, blow, etc.), the patient must immediately consult an ophthalmologist. To do this, call an ambulance, then treat the eyes with an antiseptic, and apply a sterile bandage over the visual organ. You should not delay your visit to the doctor, since ordinary and, at first glance, harmless photophobia may hide diseases that can pose a mortal danger to the patient.
A symptom such as photophobia gives a person a lot of unpleasant sensations. In this case, any ray of light, daylight or artificial, on the area of the eyeball brings a feeling of discomfort, and sometimes even acute pain. Sometimes this manifestation is accompanied by lacrimation and redness of the eyes. What are the causes of photophobia? What to do in this case?
Definition of disease
Photophobia, or photophobia, is called discomfort in the eyes that appears in artificial and natural light conditions. At the same time, at dusk or in complete darkness, the eyes of a sick person feel normal.
Photophobia should be distinguished from a pathological fear of exposure to the sun, which is called heliophobia and is a mental illness that is in no way related to disruption of the functioning of the visual organs.
Causes
There is congenital photophobia, in which the eye reacts to daylight or artificial light due to a lack of melanin pigment or its complete absence in the body.
The causes of photophobia can be completely different:
- Diseases of the organs of vision;
- Features of the structure of the eyes (for example, albinism);
- General diseases;
- Adverse environmental influences (excess UV radiation).
Increased eye sensitivity to light can be caused by taking certain medications. For example, to effectively diagnose the fundus of the eye, doctors instill drugs into the eyes that dilate the pupil, as a result of which the retina is exposed to increased exposure to light rays for some time. Photophobia can also become a side reaction to taking medications such as:
- Quinine;
- Tetracycline;
- Doxycycline;
- Belladonna;
- Furosemide.
In recent years, the cause of photophobia of the eyes has increasingly become a long stay at the computer (“computer syndrome”). Increased sensitivity of the eyes to light and wind occurs against the background of constant drying out and visual stress.
Some diseases can also cause a heightened reaction to light in the eyes, such as:
- Conjunctivitis;
- Ulcers and damage to the cornea;
- Tumors;
- Eye keratitis (inflammation of the cornea);
- Iritis (inflammation of the iris);
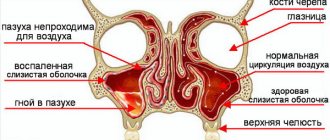
- Meningitis;
- Diseases of the central nervous system;
- Acute attack of glaucoma ICD 10;
- Retinal detachment (photo);
- Refractive eye surgery.
Photophobia can also occur due to damage to the eye by bright light (for example, with snow ophthalmia, welding without glasses, when looking at the sun, etc.).
Long-term wearing of lenses can also lead to photophobia, especially if they were incorrectly selected. In rare cases, doctors encounter photophobia caused by botulism, mercury poisoning, chronic fatigue, and depression.
Symptoms
A person suffering from photophobia, when exposed to an illuminated space, squints, closes his eyes, and tries to protect his eyes from the light with his hands. When wearing sunglasses the situation improves slightly. Increased photosensitivity may be accompanied by additional symptoms, such as:
- Headache;
- Watery eyes;
- Pupil dilation;
- Redness of the eyes;
- Feeling of “sand” or “stinging” in the eyes;
- Impaired visual acuity;
- Unclear outlines of objects.
Treatment of photophobia
Treatment for photophobia begins only when the cause of this condition is determined. First of all, the cause of the disease is eliminated, and most often photophobia goes away on its own.
If the cause of photophobia is taking medications, then you should consult a doctor and replace the medications with safer ones.
If the cause of the condition is a congenital pathology, then special contact lenses are often used to solve the problem, which do not differ from the natural color of the eyes, but do not transmit light.
The most commonly prescribed treatments for photophobia are:
- artificial tears if you have dry eye syndrome;
- eye drops to treat various diseases that cause sensitivity;
- if the cause of photophobia is hemorrhage, then it is worth removing excess blood;
- antibiotic drops if the cornea is damaged;
- migraine medications;
- antiviral drugs and antibiotics if the diagnosis is conjunctivitis;
- anti-inflammatory drugs if mild encephalitis is diagnosed.
In order to choose the most effective method of treating photophobia, you should consult an ophthalmologist. The type of treatment depends on the cause of the sensitivity to light.
But quite often it is difficult or impossible to identify the cause. There are also cases when treatment does not bring the desired result. In such cases, special glasses with pink lenses are used to protect the eyes. They reduce the amount of light that enters the eye. But not all patients can use this method. For some people, these glasses cause even greater light sensitivity. In such cases, it is necessary to consult an ophthalmologist.
You can also use glasses with UV protection and wide frames.
Causes
Photophobia is not considered a disease, but is a symptom of other health problems, such as infections or inflammation, that affect the eyes. The best way to deal with photophobia is to periodically visit an ophthalmologist and treat its causes.
In fact, photophobia is a neurological problem that involves the communication system between the eye and the brain, not just the eye. The part of the eye that sends the light sensitivity signal to the brain is different from the part that transmits vision, which is why some people, even if they are blind, may suffer from photophobia.
Conditions that affect the brain and may cause photophobia as a symptom include:
- Encephalitis . Encephalitis occurs when the brain becomes inflamed due to an infection, which may be viral or bacterial. If not treated quickly, the disease can be fatal.
- Meningitis . Meningitis is an infectious disease caused by bacteria that causes inflammation of the membranes surrounding the spinal cord and brain. The disease can also cause serious complications such as hearing loss, brain damage, seizures and even death.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage . Subarachnoid hemorrhage occurs when there is bleeding between the brain and layers of surrounding tissue. This bleeding can cause brain damage, stroke, or death.
Severe brain injuries, pituitary tumors, and supranuclear palsy can also cause photophobia.
Photophobia is also very common due to the following conditions that affect eye health:
- Abrasions on the cornea of the eye . Corneal abrasions and scratches are damage to the cornea, the outermost layer of the eye. This type of injury occurs when small particles such as dirt, sand or other substances get into the eyes. This buildup of intrusive particles can cause a very serious problem called a corneal ulcer.
- Scleritis . Scleritis is characterized by inflammation of the white part of the eye. This problem mainly affects adults between 30 and 50 years of age, especially women. In most cases, scleritis is caused by pre-existing autoimmune diseases and also causes symptoms such as eye pain, photophobia, watery eyes and blurred vision.
- Conjunctivitis . Conjunctivitis occurs when the layer of tissue covering the white part of the eye becomes infected or inflamed. This infection is most often caused by viruses, but it can also be caused by bacteria or allergies. In addition to photophobia, conjunctivitis can cause itchy, painful, and red eyes.
- Dry eye syndrome . This disease is characterized by problems with tear ducts that cannot produce enough tears to lubricate the eyes or that produce poor quality tears. This results in the eyes remaining extremely dry.
Other health conditions such as iritis, cataracts, macular degeneration, keratitis, uveitis and blepharospasm may also present photophobia as one of its symptoms.
- Migraine . Sensitivity to light is a common symptom of migraines. About 80% of people with migraines experience sensitivity to light. Migraines can be caused by many factors, such as hormonal changes, diet, stress, and even environmental changes. When migraines cause very severe headaches, symptoms include throbbing in the head, photophobia, nausea and vomiting.
- Mental health problems . Some people with mental health problems such as agoraphobia, depression, bipolar disorder, anxiety and panic attacks may also experience photophobia.
- Operation . There is evidence that some surgeries to correct vision problems may also make the patient more sensitive to light than before.
- Medications . Some types of medications present photophobia as one of its side effects. Some of these include antibiotics such as doxycycline and tetracycline, furosemide, which is used to treat heart failure, kidney or liver disease, antihistamines, estrogen-containing oral contraceptives, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, sulfonamides, tricyclic antidepressants, and quinine, which is used to treat malaria .
- External damage . Photophobia can also be caused by problems such as retinal detachment, improper or prolonged contact lens wear, and sunburn.
Drops for photophobia
Sometimes increased sensitivity to bright light occurs periodically and is not a sign of a serious illness.
In order to reduce the degree of discomfort, the doctor prescribes special drops for photophobia. Here is a list of the most popular drops that will help get rid of photophobia:
- Levomycetin;
- Tobradex;
- Dexamethasone;
- Indocollier;
- Oksial;
- Cationorm;
- Okumetil;
- Visine;
- Artificial tear.
If photophobia is a consequence of excessive stress on the organs of vision, then drops containing vitamins are used.
If sensitivity to light is a consequence of inflammatory processes, then anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents will be used.
All medications can be used only after consulting an ophthalmologist.
Folk remedies are also used to treat photophobia. The eyes are washed with infusion of plantain leaves or flax seeds. A tablespoon of raw material is poured into a glass of boiled water and infused for 20 minutes. The infusion is filtered and used to wash the eyes in the morning and before bed.
Treatment of fear of light
Treatment tactics for photophobia of the eyes are determined only after a reliable diagnosis has been made. Therapy is aimed at eliminating the provoking factor.
Drug treatment is used for bacterial or fungal infections or acute chronic diseases that have caused the development of a functional failure.
In this case, the following drugs are prescribed:
- "Okomistin";
- "Tobradex".
Glasses for photophobia are prescribed by an ophthalmologist as a temporary or preventive measure.
Prevention of photophobia
If measures are not taken and photophobia is not treated, the quality of life can worsen.
To protect yourself from excessive sensitivity and lead a normal life, you should follow preventive measures against photophobia:
- keep the room clean so that dust does not scatter light;
- install an application on electronic devices that will reduce the amount of light;
- Carry eye drops with you at all times to prevent your eyes from drying out;
- use only those sunglasses recommended by an ophthalmologist;
- reduce the influence of computer and TV screens to a minimum;
- wear a wide-brimmed hat;
- Take regular breaks when working with a computer;
- remove from the interior all objects that are brightly colored;
- When outdoors, protect your eyesight with special glasses.
Despite the fact that with high sensitivity to light, there is a desire to constantly be in the dark, it is worth exposing your eyes to light that is controlled and limited. If you are constantly in dark rooms without light sources, then photophobia will increase. There is also a high risk of developing depression and anxiety.
Characteristics of photophobia
The symptom is extremely easy to recognize - it hurts to look at the light. There is a dominant desire to close your eyes, cover your eyes with your hands, and be in a darkened room. In addition, photophobia is accompanied by a number of other mandatory signs:
- lacrimation;
- frequent blinking;
- feeling of pain, “sand” in the eyes;
- accompanying headache, dizziness;
- possible decrease in visual acuity.
Pupil dilation, which is also present in photophobia, can be difficult to determine on your own. Mainly due to the subjective perception of the reflection in the mirror. And checking the pupillary reflex involves directing a beam of light into the eye.
What to do if a symptom suddenly appears
If a child's tears flow when the light is on, or there is an unpleasant sensation, you need to show it to an ophthalmologist. The doctor identifies the cause of the disorder by resorting to:
- to ophthalmoscopy;
- fundus examination;
- to the analysis of corneal scrapings.
If the baby has conjunctivitis, drops, means to strengthen the immune system, medications for allergies or viruses are prescribed. In case of a congenital defect, lenses are selected that obscure the light. If no abnormalities are found in the visual organ, a neurologist examines the baby. Acrodynia is treated with antihistamines, anticholinergics, sedatives, and vitamins.
Fundus examination - ophthalmoscopy
An adult should contact an ophthalmologist if the following signs are present:
- In poor lighting, your eyes and head hurt.
- There is abnormal sensitivity to sunlight.
- The image becomes blurred.
If photophobia occurs due to prolonged sitting in front of a monitor, it is enough to adjust the brightness of the screen and work in a dark place.
You can get rid of photophobia only by eliminating the pathology or disorder that accompanies it.
It is important for young mothers to be on the alert - a detailed list of reasons why a child’s eyes fester.
Photophobia is often accompanied by a headache during twilight.
A dangerous degenerative disease of the retina is retinoschisis.
Treatment
Symptom therapy is prescribed after determining the causes of the pathology. Doctors advise patients to follow simple rules:
- on sunny days do not leave the house without sunglasses;
- use eye drops;
- During migraine attacks, it is advisable for the patient to go to a dark place.
Timely treatment of photophobia and the causes of its occurrence contributes to the rapid relief of this symptom.
However, quite often the symptom is not formed against the background of any disease, but is congenital. In this case, doctors recommend adhering to the above rules.
Symptoms
Since heliophobia is only a symptom of photophobia, this symptom is accompanied by other symptoms:
- lacrimation - manifests itself in rabies, neuralgia, keratoconjunctivitis;
- headache – symptoms are characteristic of the development of migraine, headache, meningitis, stroke, encephalitis;
- high body temperature - appears with meningitis, encephalitis, hemorrhagic fever;
- vomiting and nausea - indicates meningitis, migraine, meningoencephalitis.
Photophobia itself causes the following symptoms in the patient:
- feeling of burning and stinging;
- desire to squint or close your eyes.