With the birth of a baby, the family never lives the same life again, focusing maximum attention on the development of the little person. The vast majority of new parents are ready to spend hours on end discussing the achievements of their new child, boasting about new teeth, movements, and, of course, weight gain.
And everything would be fine, but not every baby regularly gains weight, and some even have a serious deficiency, which is determined according to a special table developed by the world's leading pediatricians, which gives approximate indicators of the norms for height and weight of children under 1 year.
Interesting facts about child growth
The growth zones of a child are the cartilaginous parts of the bones, which gradually “ossify” as they grow older. A well-known way to check whether a person will still grow or whether he has already reached his maximum “peak” is to take an X-ray of the hand, followed by an assessment of the degree of ossification of the wrist joint and the closure of growth zones.
The growth rate of a child directly depends on the presence in the little person’s body of the hormone responsible for this process. It is believed that children grow in their sleep, and this is true - growth hormone is produced during deep night sleep, so it is very important to put the baby to bed on time (at 9-10 pm).
What a child will be like when he grows up depends on the height of his parents, so if you are curious, this hypothetical value can be calculated using a simple formula, where M is the height of the mother and P is the height of the father:
Of course, such a calculation is very approximate and allows an error of up to 10 centimeters, both up and down. Just for fun, you can check the accuracy of the formula on yourself - after all, you know the height of your parents and your own height.
Babies gain hearing in the womb!
Whether babies can recognize the voice of their mother or father has not been proven by science. However, the fact that they hear everything that is happening outside is true. They do not pick up pure sound due to the amniotic fluid, but they are excellent at hearing muffled sounds.
Child growth in the first year of life
A person never grows as fast as at the beginning of his life.
In the first two months, the child on average stretches six to seven centimeters, growth occurs evenly. In subsequent months, the pace gradually subsides - two and a half centimeters at the age of three to four months and two from five to eight months. In the last three months before the first birthday, the child gains up to one and a half centimeters of height every month; this period coincides with the baby’s first attempts to learn to walk.
Thus, in the first year of life, the child grows by twenty to twenty-five centimeters . Please remember that the figures given are approximate.
| Growth standards for children under one year old according to WHO (average values) | ||
| Age | Girls | Boys |
| 0 months | 47.3 – 51.0 cm | 48.0 – 51.8 cm |
| 1 month | 51.7 – 55.6 cm | 52.8 – 56.7 cm |
| 2 months | 55.0 – 59.1 cm | 56.4 – 60.4 cm |
| 3 months | 57.7 – 61.9 cm | 59.4 – 63.5 cm |
| 4 months | 59.9 – 64.3 cm | 61.8 – 66.0 cm |
| 5 months | 61.8 – 66.2 cm | 63.8 – 68.0 cm |
| 6 months | 63.5 – 68.0 cm | 65.5 – 69.8 cm |
| 7 months | 65.0 – 69.6 cm | 67.0 – 71.3 cm |
| 8 months | 66.4 – 71.1 cm | 68.4 – 72.8 cm |
| 9 months | 67.7 – 72.6 cm | 69.7 – 74.2 cm |
| 10 months | 69.0 – 73.9 cm | 71.0 – 75.6 cm |
| 11 months | 70.3 – 75.3 cm | 72.2 – 76.9 cm |
| 12 months | 71.4 – 76.6 cm | 73.4 – 78.1 cm |
Child growth from one to seven years
At the age of one to three years, the intensive growth rate is maintained. During these two years, babies grow by about 20 cm, adding about 10 cm per year.
Starting from the age of three, the growth rate slows down, but remains stable - normally a child gains at least four centimeters per year.
Differences between the growth rate of boys and girls at this age have not yet been observed - all this will begin later, in early puberty.
By comparing a child of two to seven years old with his peers, one can judge with a high degree of probability whether he will be tall in adulthood or not.
How can you tell if a child is growing normally? There is a formula that will help parents calculate the approximate growth rate at a specific age:
- For boys: 75 cm+n*7
- For girls: 75 +( n*7-1), where n is age in years (full)
It is important to remember that a child’s growth depends not only on heredity, but also on nutrition and lifestyle.
| Growth standards for children from 1 to 7 years old according to WHO (average values) | ||
| Age | Girls | Boys |
| 1 year | 71.4 – 76.6 cm | 73.4 – 78.1 cm |
| 1.5 years | 77.8 – 83.6 cm | 79.6 – 85.0 cm |
| 2 years | 83.2 – 89.6 cm | 84.8 – 90.9 cm |
| 2.5 years | 87.1 – 94.2 cm | 88.5 – 95.3 cm |
| 3 years | 91.2 – 98.9 cm | 92.4 – 99.8 cm |
| 3.5 years | 95.0 – 103.1 cm | 95.9 – 103.8 cm |
| 4 years | 98.4 – 107.0 cm | 99.1 – 107.5 cm |
| 4.5 years | 101.6 – 110.7 cm | 102.3 – 111.1 cm |
| 5 years | 104.7 – 114.2 cm | 105.3 – 114.6 cm |
| 5.5 years | 107.2 – 117.1 cm | 108.2 – 117.7 cm |
| 6 years | 110.0 – 120.2 cm | 111.0 – 120.9 cm |
| 6.5 years | 112.7 – 123.3 cm | 113.8 – 124.0 cm |
| 7 years | 115.3 – 126.3 cm | 116.4 – 127.0 cm |
| 7.5 years | 118.0 – 129.3 cm | 119.1 – 130.0 cm |
Growth disorders in children
The most common growth disorders in children are dwarfism and gigantism. The reasons lie in heredity, genetic disorders, and hormonal imbalances.
Gigantism is caused by excess growth hormone. The child (most often this happens with preschoolers ) is disproportionately tall and large. This problem can be identified using a blood test for hormones or magnetic resonance imaging.
Signs of dwarfism , on the contrary, reveal themselves early, as early as two or three years. The child is delayed in physical development and grows slower than his peers. At first this lag is not so noticeable, but every year it becomes more and more noticeable. For diagnosis in this case, MRI and blood tests are also prescribed.
These growth disorders are, to one degree or another, amenable to medical correction, so if you suspect any abnormalities, it is important to immediately consult a specialist.
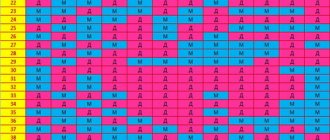
Here are the indicators of the ratio of height and weight of a child at different periods of age from 1 to 3 years. Particular attention must be paid to the RATIO of height and weight, which should be (in the table) in the same centile (in the same column of the table).
Anthropometric (centile) tables
The tables for height, weight and head circumference show ranges by group. The middle “blue” column shows the average for a given age. The “green” columns on the right and left show indicators within the normal range, which are slightly below or above the average. The “yellow” and “red” columns show indicators below or above normal that require special attention from parents and doctors.
- The average height of the child should be within the green and blue values (25-75 centiles). This height corresponds to the average height of children of this age.
- Growth, the value of which is between the yellow and green values (10-25 centiles) is also normal, but indicates a tendency for the child to be stunted.
- Growth, the value of which is between the blue and yellow values (75-90 centiles) is also normal, but indicates a tendency for the child to be ahead in growth.
- Growth, the value of which is between the red and yellow values - low (3-10th centile), or high (90-97th centile), which can be due to both the characteristics of the child and a disease with hormonal imbalance (usually endocrinological or hereditary ). In such cases, you should bring this to the attention of your pediatrician or family doctor, who, if necessary, will refer you to the appropriate specialist. Be sure to monitor the further growth, weight, and general condition of such a child.
- Growth that is beyond the red line (less than the 3rd or more than the 97th centile) indicates a pathology in the child’s growth. Such children must be consulted by appropriate specialists, primarily an endocrinologist, who will recommend further examination and prescribe appropriate treatment. Remember that diseases accompanied by impaired growth lead in the future to various disorders of physical and mental health.
Greetings, dear readers! All parents strive for their children to grow up healthy and develop normally. But how can you tell if everything is okay with your baby? Doctors recommend focusing on such important indicators as the child’s weight and height by month. Compliance with the standards proposed by WHO on the basis of research, doctors determine the degree of full term of the baby and the quality of its further development.
What to do if the indicators differ from the norm, should I worry?
The indicators, as already mentioned, do not always correspond to the norm and may deviate slightly in one direction or another. The mother’s nutrition during breastfeeding, the baby’s lifestyle and other factors matter, so the table does not always indicate the truth that should be.
Parents need to regularly show their child to the pediatrician so that the doctor can determine the real cause of underweight or overweight, as well as slow or accelerated growth. The specialist will definitely ask a number of questions and give parents recommendations on nutrition, lifestyle, may prescribe a massage, any tests or diagnostic methods, and advise doing children’s yoga or infant swimming.
Also for the pediatrician it will be important how the child goes to the toilet, whether he cries often, and whether he eats the required amount of food. In general, if the baby feels well, eats normally, receives all the necessary vitamins and microelements with breast milk or formula, begins to hold his head up, crawls and sits on time, does not suffer from colic and bloating, there is no reason to worry: such babies eventually catch up with their peers.
In any case, you cannot draw any conclusions on your own: only a pediatrician can judge the norms and pathologies, so a timely visit to a pediatrician will help to identify various pathologies in time and take measures to eliminate them.
Where do the norms come from?
World Health Organization, or WHO in the period 1997-2003. conducted a number of studies on the development of children under one year old, as well as a parallel analysis of the height and weight of children aged 1.5 to 6 years. The focus of the world organization was not only on indicators, but also on their ratios and monthly increases.
Why was such a global study needed? The latest data on indicators of physical development of children were recorded back in the 70s. 20th century. Since then, not only the rhythm and lifestyle of people has changed, but also the nature of infant feeding.
If during the Soviet period most babies were bottle-fed, then with the improvement of working conditions for nursing women and the opportunity to receive paid leave after childbirth for 1.5 years, more and more babies are now breastfed, which is otherwise reflected in the increase in body weight and length.
Data collection was carried out in different countries and ethnic groups: European countries, the USA, India, Brazil, Oman, etc. The study showed that each nation has its own parameters, therefore, to derive the average value of length and weight, for example, for European and Indian children, it is forbidden.
What do the values depend on?
Mothers who have at least once had a monthly check-up with their babies at the clinic know that the nurse not only measures and records indicators, but also pays attention to associated development factors:
- past viral and infectious diseases;
- presence of dehydration;
- teething;
- presence of appetite;
- conditions of education.
Pregnant women should not eat for two!
If the expectant mother eats a lot, the fetus will begin to push against the stomach even more, which will cause heartburn. Also, a large amount of food threatens pregnant women with excess weight and compaction of the fat layer. As a result, it will be more difficult for the baby to get enough oxygen.
Child growth by months
Child growth standards depend primarily on the gender of the child, so WHO has created separate tables with average indicators for girls and boys. Depending on the age of the baby, the ratio of length and body weight, as well as the increase, will also differ.
First year
The table shows approximate growth indicators for babies at birth and up to one year; you can also track how many centimeters the child will grow within a month.
Children under one year old are characterized by a special change in indicators, and every month of life during this period is significant. But before you take measurements and count, you should make sure that your baby meets the indicators of a full-term baby:
- The birth took place at 38-40 weeks of pregnancy.
- Height is at least 45 cm with a weight of 2.5 kg.
- Head circumference – from 34 to 36 cm.
- Body parts are proportional.
- The skin is smooth and delicate.
- Hair length from 1 cm.
- Clear rhythmic pulse.
- Developed sucking reflex (you can read about unconditioned reflexes in my article).
If a baby was born premature, there are separate height and weight indicators for him depending on what week of pregnancy he was born. Here is a table of height and weight of a premature baby:
Features of growth increase in the first year of life are as follows:
- On average, the baby gains 3 cm over a monthly period.
- The total increase in the first year of life should be at least 25 cm. Thus, the normal figure for a one-year-old baby is from 74 to 76 cm.
- Children grow more rapidly in the first months after birth, after which this process slows down. So, in the first 3 months the increase will be 3.5 cm per month, from 3 to six months - 3-2.5 cm, from 7 to 9 - about 1.5 cm, from 9 to one year - 1 cm.
- It is not only the overall increase in height that is important, but also its relationship to the weight and proportionality of body parts.
For doctors, the indicator of normal development of a baby is not so much its height as its head circumference. If the head is large and disproportionate to the body, doctors may suspect a disease such as hydrocephalus, an accumulation of fluid in the brain.
From 2 to 17 years
When a baby turns one year old, parents, as a rule, pay little attention to how much his growth is within normal limits. However, before the onset of puberty, this indicator is no less important than in the first months of life.
After a year, children's growth begins to slow down. Up to 2 years of age, the baby grows by an average of 9-12 cm, depending on gender and other factors. Until the age of 5 years, his height will increase by only 20-22 cm.
By the age of 10, the average height of a boy is 138-139 cm. From 11 to 17 years, during puberty, the growth of girls slows down, and in boys, on the contrary, it increases after 12-13 years. By the age of 17, the average for a girl will be 155-160 cm, for a boy - 166-171 cm.
How to determine a child's height?
To determine how tall your baby is under one year old, you will need a measuring tape or meter ruler:
- Place the baby on the crib so that the back of his head rests on a hard surface.
- Extend your legs and place your feet at a 90-degree angle.
- Mark where the heels end.
- Raise the child and measure the distance from the mark to a hard surface.
If the child can already stand, to measure his height, place him near the wall so that his heels touch a hard surface. Then take a hard ruler and place it on the child's head so that it forms a right angle with the wall. Make a mark where they touch and measure the distance from the floor to the mark.
What happens in the 1st trimester
The fertilized egg moves through the fallopian tube and on days 5–9 it descends into the uterus and attaches to its walls. Until the 10th week, the fetus nourishes the yolk sac formed in the fertilized egg. From the 11th week, through the umbilical cord and placenta, the fetus receives everything it needs for development. The fetus receives oxygen through the blood.
- On days 10–14, the fetus begins to increase in size.
- The nervous system begins its formation on the 20th day.
- On the 21st day after fertilization of the egg, you can already hear the baby’s heart beating on an ultrasound.
- On the 28th day, the formation of the spine already occurs, which is visible on ultrasound. Along with it, the rudiments of arms and legs are already visible.
- Day 30 The embryo has already grown noticeably and continues to develop. The amount of blood in the fetus increases.
- On day 35, the production of pigment is already visible, as evidenced by darkening of the eyes. On an ultrasound, the phalanges of the baby’s fingers become visible.
- 40th day. The fetal brain begins to actively work.
- 8 weeks The outermost part of the spine (tail) lengthens and bends. The embryo reaches a size of 15 mm.
- Week 10 The future teeth and jaw, as well as all parts of the ear, begin to form. The eyes are covered with lids. The baby begins to move in the womb, but the mother does not hear it due to its small size.
- At the 11th week, you can already see an almost full-fledged person whose kidneys are functioning, all the functions of the stomach are functioning, and facial expressions are developed. Joints have formed. At this stage, the child’s blood type is already determined.
The 12th week is the most interesting, when parents can try to find out the sex of the child. The length of the fruit is about six centimeters.
Baby's weight by month
WHO strongly recommends that parents pay attention not only to the height and proportionality of body parts, but also to weight gain. Many parents believe that the more a baby weighs before one year, the better. But this statement is fundamentally wrong. Unhealthy obesity can affect both teenagers and infants, especially those who are formula-fed.
Up to a year
For children under one year old, the weight norm is determined by month, and it should be taken into account that bottle-fed children gain weight much faster:
- 1 month. During this time, the child gains on average about 0.6 kg. To maintain normal developmental indicators, it is ideal if the mother feeds the baby every 3 hours. The volume of mixture consumed ranges from 80 to 120 ml per feeding.
- 2 month. During this period, the increase will be about 0.7-0.8 kg. The intervals between feedings can be increased to 3.5 hours. If in the future you decide to wean your baby from feeding at night, keep in mind that his weight will begin to decrease.
- 3 month. An increase of 0.8 kg is maintained. The intervals between feedings remain, but it is worth considering that up to 3 months the baby is bothered by intestinal colic, so appetite may decrease.
- 4 month. The child gains an average of 0.75 kg, and further indicators will decrease.
- 5 month. By the end of the fifth month, the baby already weighs 0.7 kg more.
- 6 month. In six months, Baby gains 0.65 kg. During this period, complementary foods in the form of vegetable purees begin to be introduced, which can replace one feeding.
- 7 month. Body weight increases by 0.6 kg. At seven months of age, babies can be given gluten-free porridge in the morning.
- 8 months. Weight gain is about 0.55 kg. The baby's menu includes a variety of vegetables, lean meat, cereals, and egg yolk.
- 9 months . The weight gain is half a kilogram. Purees from several components and fermented milk products appear on the menu.
- 10 months . The baby weighs 0.4 kg more than last month. He already tolerates fresh fruit well. You can add butter or vegetable oil to porridge.
- 11 months. Weight increases by 0.4 kg. You can include low-fat fish in the menu.
- 12 months . The weight increase occurs by 0.35-0.4 kg.
The following chart will help you determine if your baby is developing normally:
You can independently calculate the optimal weight of a child using the formula:
- For the first half of the year. Multiply 800 by the number of months for the calculation period and add the weight of the baby at the time of birth.
- In the second half of the year. M+800×6+400x(N-6), where M is the birth weight, N is the number of months.
After a year
In the future, not only the indicators prescribed by WHO will be important for girls and boys, but also the body mass index, which shows whether the weight is insufficient, normal or excessive. To determine your mass index, you need to divide your body weight by your height.
For boys and girls, the range of permissible body weight may differ, but on average the indicators are summarized in the following table:
It should be borne in mind that for girls, body weight during puberty is a significant indicator. You need to carefully monitor your diet and avoid overindulging in sweets and starchy foods. Boys are recommended to eat protein foods, since from the age of 12-13 there is a sharp increase in growth and muscle mass.
When should you sound the alarm?
Based on the indicators proposed by WHO, one must take into account that they are averaged, and minor fluctuations in one direction or another are acceptable. Parents need to sound the alarm if weight values are significantly underestimated or overestimated.
If the levels are low, it is recommended to reconsider your diet and daily activity. For example, if until the age of 5 the child steadily gained weight, and by the age of 6 he began to lose weight sharply, the changes may be associated with preparation for school and a stressful state, a violation of the usual daily routine.
For infants up to one year old, vomiting, leading to dehydration, can be a dangerous phenomenon. The problem may arise due to improper nutrition, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and nervous system. In this case, you should definitely see a doctor.
In adolescence, boys, as a rule, experience pronounced thinness associated with intensive growth. Girls should eat more plant foods, since during the period of hormonal maturation there is a high probability of becoming obese.
Deviations from normal body weight at any age in a child should be a signal for parents that it is time to sound the alarm and seek help from doctors if you cannot help the baby on your own.
If the article was useful to you, leave a link to it on social media. networks. See you soon!
What happens in the 2nd trimester
Week 14. While the child is awake, he actively trains his muscles, and the sucking reflex develops. The baby's vestibular apparatus is developing and he orients himself in space. Reacts to sounds from the outside world. The eyes are able to react to light.
Week 16 The placenta is actively functioning - the connection between mother and child. The weight of the fruit is 150 grams. Hair on the head, eyelashes and eyebrows begin to actively grow.
Week 20 Mom already feels how the baby inside her is making movements, moving in the hem of the uterus. The baby's height is 25 cm. The child responds to a sharp sound from the external environment and to the mother’s experiences with a sharp push.
At the 24th week, the baby is already showing his character. Facial expressions reflect his emotions. An ultrasound in the second trimester can tell you when the baby is happy or sad. The child already weighs about 0.5 kg, his skin is pink, which is protected by a special lubricant, since it is still very tender.