All articles by the author
Author of the article: Maxim Fadovsky
Healthy and healthy lifestyle specialist.
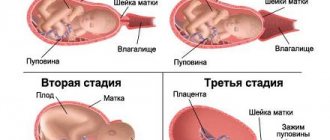
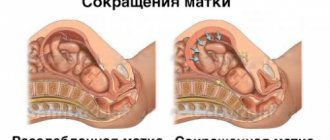
The threshold of labor is associated with certain changes affecting the muscular apparatus of the uterus.
A day before the baby is born, under the influence of hormonal levels, the organ begins to rapidly synthesize a special protein responsible for contractions. This is necessary to push the baby out of the birth canal.
In some cases, a woman feels false contractions. What kind of phenomenon is this, how to distinguish it from the onset of labor and how long such contractions can last, we will consider further.
What are false contractions during pregnancy?
Starting from the 20th week, the pregnant woman feels tension and spasms in the muscles of the uterus, which do not last long and without a certain rhythm.
In this case, as a rule, there is no pain, but the woman experiences discomfort. False contractions have other names - training, or Braxton Hicks. Doctors are still arguing about what false contractions are.
Some are of the opinion about their pathological nature, others - about the preparatory prenatal function.
It is undeniable that they saturate the placenta with oxygen and supply nutrients for the fetus, since during contractions the blood supply to the uterus increases.
Signs and symptoms
You need to understand that everyone's body is very different. And due to these individual characteristics, signs of false contractions may not appear the same in pregnant women. For some, they will be more intense, more regular, more painful. And some won’t even feel them until birth. However, it is useful for everyone to know about them in order to catch them in time.
Doctors call the following symptoms characteristic of false labor:
- Irregularity: many people are interested in how many days false contractions last - they can repeat every 5-6 hours, or maybe once every 2-3 days, they do not have any specific cycle;
- short duration: no more than a minute - this is how long false contractions last normally, usually a few seconds;
- the muscles of the uterus are tense;
- It should be noted that the timing of which week false contractions begin is very individual: it is considered equally normal if a woman felt them both at 20 weeks and at 38, for example;
- most often they wake up a woman in the middle of the night, since during the day, with business and worries, they are invisible.
Using these symptoms and signs, you can identify false contractions, which indicate the work and preparation of the uterus for the upcoming event. There is no need to be afraid: everything is going according to schedule. If there are about 2-3 weeks left before the appointed date, such harbingers warn the woman that it is time to prepare for the birth of the baby. At the same time, not the most pleasant sensations may await her.
Disagreements. Most doctors consider false contractions a necessary phenomenon, since they train and prepare the uterus for the upcoming birth. However, there are those who express a slightly different opinion: if they occur very often, the walls of the uterus risk becoming too soft, which will prevent it from becoming toned and opening during the birth process.
It is the physical sensations characteristic of false contractions at the end of pregnancy that will not allow a woman to confuse them with real ones. You just need to listen sensitively to your own body and understand what is happening to it at one time or another.
When the warning signs begin, the pregnant woman may feel the following:
- relative painlessness, although this symptom of false contractions manifests itself differently in each woman, since the pain threshold is not the same for everyone;
- discomfort;
- if you compare what false contractions are like, then they feel akin to a nagging pain in the lower abdomen during the menstrual cycle;
- the uterus seems to harden, and this can be felt or even felt if you place your palm on the lower abdomen;
- there is no clear rhythm of contractions;
- Quite unexpectedly, a feeling of compression occurs in a specific area of the abdomen or groin.
These sensations will allow the pregnant woman to distinguish false contractions from labor contractions, gather herself, not panic, and simply continue to patiently wait for the baby to be born soon. If you still have fears and doubts about whether these are real harbingers, a few useful recommendations will help you dispel them.
One more opinion. There is a point of view that false contractions have nothing to do with the training of the uterus, but are only the body’s response to the hormonal explosion that occurs during pregnancy.
Causes of false contractions
Doctors note that the occurrence of false contractions directly depends on the lifestyle of the expectant mother.
Abuse of alcoholic beverages, smoking, and addiction to coffee provoke their appearance. Excessive emotional and physical stress lead to muscle strain and spasms of the uterine muscles.
Contractions appear after intimate relationships, increased motor activity of the fetus.
False contractions can also be caused by:
- eating chocolate or other sweets;
- lack of sleep;
- travel by any type of transport;
- fear, excitement;
- dehydration;
- bladder fullness;
- lack of vitamins, micro- and macroelements.
Symptoms of false contractions
The sensations of false contractions during pregnancy are vaguely reminiscent of real contractions.
The uterus contracts, and quite noticeably. This forces the child to move actively. During real contractions, the child begins to pass through the birth canal and performs only the necessary movements.
Symptoms of false contractions during pregnancy:
- contraction of the smooth muscles of the uterus;
- painlessness;
- noticeable discomfort due to rapid sudden movements of the fetus;
- pulling sensations without sharp pain;
- the spasm appears in one place and does not radiate to the lower back;
- short duration of spasm;
- Irregularity of contractions - they occur at different times of the day and last for different periods of time.
When is it time to go to the maternity hospital?
A couple of weeks before the start of labor, the pregnant woman is full of energy, the whole apartment shines perfectly, everything is washed, ironed, prepared, and even the unreplanted flowers haunt her at night. The so-called “nesting syndrome” is already the first signal that you will soon be going to give birth.
The amount of discharge increases, the nose is stuffy. Minor weight loss is possible as the body gets rid of excess fluid. False contractions may occur. The baby calms down and gains strength. The mucus plug comes off (can happen either a week or a couple of hours before birth). There may be an upset stomach, so the body gives itself a natural enema and cleanses the stomach. The main thing is to collect everything you need for yourself and your baby while you are in the maternity hospital and don’t forget about the documents.
If your water breaks and contractions become more frequent, it is important to notify your doctor and call an ambulance. It doesn’t matter what time of day or night, there is no need to worry, and they will be embarrassed, the child will not wait.
How to identify false contractions
A special consultation with a gynecologist on how to distinguish false contractions from real ones is not required at all. Even a first-time mother will not confuse true contractions with anything.
Real contractions are periodic - they occur at a certain interval.
At first they last a minute or two, followed by a rest of 20-30 minutes - everything is very individual for each pregnancy. After some time, the duration of contractions increases, and the interval between them decreases.
During real contractions, it is impossible for women to be distracted by anything else - the pain increases and radiates to the lower back and below.
During Braxton Hicks contractions, a woman can be distracted by watching an interesting movie; a change in body position leads to the cessation of muscle spasms.
False contractions occur at different times and go away quite quickly on their own or after taking antispasmodics. True ones do not stop after the use of antispasmodics.
During training contractions, the fetus moves a lot, unlike real ones.
Harbingers of childbirth
Abdominal prolapse
Towards the end of pregnancy, the baby in the womb descends, its head is pressed against the entrance to the pelvis. This is a harbinger of labor in first-time mothers, which appears several weeks before birth, and in multiparous women, it can happen already during labor.
The expectant mother can detect this by changes in the size of the abdomen, especially its upper part. It seems to “lower”, freeing the diaphragm, reducing heartburn and making breathing easier. At the same time, pressure on the bladder increases, so the problem of the first trimester - frequent urination - returns again.
"Stalk"
The large volume of the abdomen, its downward displacement and the load on the spine leads to the formation of a special posture. A pregnant woman walks with her back tilted back to maintain balance with a shifted center of gravity. Such a precursor before childbirth is not obligatory and specific. It depends on the size of the abdomen, the weight of the pregnant woman and baby, as well as the woman’s physical fitness. During the third birth, weakening of the ligamentous apparatus can lead to altered posture already at 20-25 weeks.
Changes in well-being and mood
Shortly before giving birth, the expectant mother may feel drowsiness, some apathy and a desire to retire from the noisy world. This is partly due to the inability to move easily and quickly, with a general change in condition. But this is partly influenced by the functioning of the brain. Gradually, the dominant of pregnancy turns into the dominant of childbirth, the body adjusts to a difficult stage, the woman is completely immersed in her own experiences. For the same reason, nervousness and tearfulness may appear, especially if family members underestimate the degree of anxiety of the pregnant woman.
"Nesting" instinct
If you conduct a survey among young mothers on the topic “what did you do when labor began?”, then many will probably give similar answers. Gluing wallpaper, dismantling the wardrobe, washing the tiles in the bathroom - these are just a few of the things a woman decides to do at the end of pregnancy. This “arrangement of the nest” is akin to the instincts of many animals, when before the appearance of offspring they need to take care of the home. If such troubles do not tire the expectant mother too much, then they should be treated positively. After all, homework distracts a little from worries and worries about the upcoming birth.
Weight loss
Often, a few weeks or days before giving birth, a woman loses 1-2 kg. This is associated with a decrease in the amount of amniotic fluid. But you can’t rely on this sign. After all, weight strongly depends on nutrition, so a pregnant woman may stop eating because of worries or, on the contrary, she will start running to the refrigerator at night, eating up her anxiety (which, by the way, is very undesirable).
Reducing the number of baby movements
When the uterus becomes too crowded for the growing fetus, its range of motion is reduced. This is also caused by hormonal changes in the mother’s body before childbirth. Therefore, a week before an important event, the baby seems to “quiet down.” This happens often, but not always. In addition, a sharp decrease in activity may indicate oxygen starvation of the child, which is a reason to immediately consult a doctor. Such a harbinger of labor appears rarely before 37 weeks.
Removal of the mucus plug
Throughout pregnancy, the cervix is closed and filled with mucous secretion. It protects the fetus from infection. A few days before giving birth, the cervix becomes so smooth that the mucous plug simply cannot stay in it and begins to come out. At this time, a woman may notice mucous or mucous-sacral discharge on her underwear. Sometimes the cork comes out right away, and sometimes it comes out little by little and gradually. It cannot be confused with anything. This event indicates that labor is steadily approaching, so it is worth notifying your obstetrician-gynecologist.
Training contractions
The notorious Braxton-Hicks (false) contractions are a common occurrence in the last weeks of pregnancy, a harbinger of labor in most women. They can cause discomfort to some, while others do not even understand that uterine contractions are occurring. The essence of such contractions is the gradual preparation of the cervix for the process of childbirth and “tuning” the coordinated work of the muscles. Braxton Hicks contractions usually begin 1-2 weeks before birth. The main task of a pregnant woman and a doctor is to distinguish them from real labor, since false contractions do not require any medical measures.
What to do if false contractions start
Training contractions are not considered pathological conditions during pregnancy, but serve as a reason to change your lifestyle.
You should rest more, worry less, and reconsider your diet. If false contractions cause discomfort, you need to lie down, trying to find a comfortable position. Usually, in a lying position, the muscles come to a state of rest and the spasms stop. Taking no-spa will relieve stress.
Other ways will help:
- warm bath for 5-7 minutes;
- breathing exercises - frequent breathing “like a dog”;
- leisurely walk;
- an interesting read or an exciting (not scary!) movie.
To prevent training contractions, you need to urinate in a timely manner, not have sex, and drink water during the day.
At a time close to childbirth, the number and duration of contractions are recorded. Up to six an hour is no cause for alarm. True contractions have a clear rhythm that will not allow mistakes.
If you notice bloody discharge, leakage of water, or sharp pain in the lower abdomen, you should urgently seek medical help. These are pathological abnormalities that do not occur during healthy pregnancy and childbirth.
Fact #9
Training contractions feel similar to periodic pain during menstruation. Moreover, many (but not all) expectant mothers discover that if their menstruation is usually painful, then false contractions are also strong.
What else, besides unpleasant sensations similar to menstrual pain, can a woman feel or see if she has false contractions:
- tension in the abdomen, similar to cramps, in different parts of the abdomen (upper, lower, or even closer to the groin area), but not all at once
- during them it is not difficult to palpate the uterus; it, as is often said, “turns to stone”
- sometimes you can see clear contours of a tense uterus
- contractions gradually “fade out” and their intensity decreases (while the strength of prenatal contractions normally only increases)
Most often, training contractions occur in the morning and evening, although, of course, not always and not for everyone. Moreover, if the contractions began in the evening, then at night they, as a rule, subside, and in the morning they can resume again.
The duration of the period of false contractions usually does not exceed two to three hours, but there are also exceptions to this rule. What can we do - we are all different, and the female body, as one of the Orthodox priests noted, can be compared to the most complex computer, while the male body, in his own funny expression, is just a typewriter.
Not all women experience training contractions. Or rather, not everyone feels them. Since the frequency, intensity, duration of contractions, as well as the individual pain threshold, are different for everyone. Therefore, some pregnant women can feel them after 20 weeks, others only towards the end of the nine-month wait, and still others do not even know what it is.
So there is no need to worry if things are steadily moving towards the “performance”, but the “dress rehearsal” has not yet taken place. Most likely, you simply do not feel false contractions.
Although you can often read in specialized literature that training contractions do not cause pregnant women much discomfort, many mothers categorically disagree with this far from indisputable statement.
Often false contractions are quite long in time and strong. They can exhaust even very persistent and positive-minded expectant mothers. And, if you are going to give birth for the first time, you may well mistake them for real contractions. Therefore, if in doubt, go to the doctor or call an ambulance.
Yes, training contractions are completely normal, but if they last long (longer than 3-4 hours in a row) and exhaust you, then you should definitely tell your doctor about them. Perhaps this is a symptom of some kind of trouble.
It is difficult to predict the occurrence of training contractions. However, it has been noticed that they often occur:
- with a full bladder (so try not to let it get to that point)
- after an orgasm or during active sexual activity
- if the expectant mother is stressed
- during heavy physical exertion experienced by a pregnant woman
- in cases of maternal dehydration
Although everything, of course, is individual. What causes your girlfriends or even your sister to start training fights may well have no effect on you. Just try to observe your feelings and, perhaps, you will be able to discern the relationship between some of your actions and the subsequent onset of training contractions.
Many people fear that, having gotten used to training contractions, they simply won’t understand when it comes to action.
Do not worry! It is difficult to confuse precursor contractions (even if they are quite strong) with real ones. But you shouldn’t relax either. After all, training contractions may well turn into prenatal contractions. Therefore, even if false or precursor contractions have become commonplace and familiar to you, still listen to your body, pay attention to the frequency, duration and regularity of contractions.
You can distinguish training contractions from the onset of labor by the following signs:
- intervals between contractions of varying lengths
- contractions are irregular
- pain often decreases or even disappears when changing body position; try to lie down if you were sitting or standing, or get up and walk around if, on the contrary, you were lying down
If the “rehearsal” continues, albeit intermittently, for several days, then even the most persistent and calm expectant mothers begin to fear that this is not a training session, but the beginning of labor. And they have a fear of not being able to get to the maternity hospital in time.
Don't worry, doctors say that training or precursor contractions never precede a quick (4 - 5 hours) or rapid (3 hours) labor. So you will definitely have time to get to the maternity hospital. And this, you see, inspires some optimism.
Often the appearance of training contractions of the uterine muscles provokes:
- Excessive activity of a pregnant girl.
- Excessive activity of the fetus in the womb.
- Insufficient amount of moisture in the female body.
- Full bladder.
- Nervous overstrain.
- Stress, anxiety, overwork.
- Performing sexual intercourse.
- Frequent touching and stroking of the abdomen.
If this process brings discomfort, you should:
- Control the amount of liquid consumed.
- Reduce physical activity.
- Stop having sex for a while.
Possible complications
In some cases, training contractions are painful, but otherwise they differ from real contractions - there is no rhythm. There are no changes in the cervix (does not soften, shorten, or open).
This means a pathology called false birth. It is observed in 10-15% of women in labor and is associated with weakness of labor contractions.
Risk factors for a pathological prenatal period:
- emotional or mental instability instability - women with a labile nervous system;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system (heart disease), chronic kidney and liver diseases;
- hypertension;
- diseases associated with hormonal imbalance - diabetes, obesity, infantility of the genital organs;
- fear of childbirth;
- large fetus or multiple pregnancy;
- a history of repeated abortions;
- gestosis;
- little and polyhydramnios;
- the age of the woman in labor is about 17 and over 35;
- incorrect position of the child's place and fetus;
- anatomical features - narrow pelvis.
Such contractions can appear at different times of the day, last longer than a week and deplete the woman in labor to the limit. Subsequently, labor is weak and the fetus suffers from oxygen starvation.
Due to the tension of the uterus, it is not possible to palpate the fetal head; it does not enter the birth canal.
The baby's movements are painful for the mother. In this situation, the water breaks prematurely and the course of labor becomes more complicated.
False contractions can be a sign of uterine hypertonicity and warn of a possible termination of pregnancy or premature birth.
If there is accompanying nagging pain in the lower back and lower abdomen, or bloody vaginal discharge, you should immediately contact an antenatal clinic.
What is it?
It should be noted that not all expectant mothers feel training contractions, because such uterine activity indicates a sharp hormonal change in a woman’s body. And in a young and healthy body, all this should go absolutely smoothly and unnoticed.
Many mothers wait for them completely in vain, asking “experienced” friends and acquaintances how long before birth there are training contractions. If there are some disorders in the internal secretion organs, then false contractions may begin in the second half of pregnancy. And yet, the answer to the question that worries almost all women - how many days before birth can they be felt, will be this: about fourteen, that is, two weeks. After all, it is during this period that the hormonal system of the expectant mother begins to closely “command” the biochemical reactions that will be simply necessary during labor. It happens that this kind of harbinger appears if the baby has grown large.
If the expectant mother suffers from some health problems, and she has a history of abortions, fibroids, and the like, she should not be surprised that such contractions will await her while carrying the baby. There is no need to be afraid. You just need to listen sensitively to everything that is happening inside her. She must remember how the birth process itself goes and compare it with the observed sensations. This should be enough for her to be able to determine whether she is in labor or just false contractions.
Diagnosis of pathology
Upon admission to the maternity ward or at a consultation, the gynecologist will perform a vaginal examination and ask the pregnant woman about the duration of contractions and the time of occurrence. During the examination, the doctor will determine the degree of readiness of the cervix.
If the cervix is immature and contractions are painful, labor will be induced. To get a more complete picture, the doctor may prescribe NGG.
External hysterography is a painless study in which, using sensors, a gynecologist will reliably determine the truth or falsehood of contractions.
Simultaneously with NGG, cardiotocography is performed to listen to the fetal heartbeat and determine hypoxia.
Treatment of false contractions
If Braxton Hicks contractions do not cause any noticeable inconvenience and are painless, the woman just needs to lie down for a while, rest, and her health will improve.
Taking antispasmodics will eliminate spasms of the uterine muscles.
Otherwise, in case of painful arrhythmic contractions after 36 weeks, the woman is hospitalized in the maternity ward.
Treatment depends on the characteristics of the specific case:
- the length and condition of the tissues of the cervix - its maturity;
- painful contractions;
- maternal and fetal conditions;
- duration of pathological contractions (painful and ineffective).
If the uterus is mature and contractions last less than 6 hours, the amniotic sac is opened and labor is induced.
With the same duration of contractions and the cervix is not ready, sedatives and gels containing prostaglandins are prescribed intravaginally to prepare the cervix.
If contractions lasted more than 12 hours, the pregnant woman is put into medicated sleep to restore strength. After awakening, labor is stimulated.
What does the appearance of false contractions signal?
Training contractions prepare a pregnant woman psychologically and physically for childbirth.
The uterus contracts and smooth muscles are trained. The woman in labor gets used to the thought of the upcoming event, and waits for the moment of the birth of the child without fear.
With prolonged Braxton Hicks contractions, expectant mothers become impatient and want to give birth sooner.
By the time training contractions begin during pregnancy, gynecologists judge the approach of labor. Typically, labor occurs one to two weeks after the onset of Braxton Hicks contractions, also called pre-labor contractions.
False contractions, which are painful and start too early (at 20-22 weeks), are most likely a symptom of uterine hypertonicity.
Author: Irina Petrovna, obstetrician Specially for the site kakrodit.ru