37, 38, 39 weeks of pregnancy are considered favorable for the onset of labor. This is normal for both the child and the mother. The baby is born full-term, and the mother’s body is ready for labor. To understand that a happy event is about to begin, you need to know what harbingers indicate it.
37, 38, 39 weeks of pregnancy are considered favorable for the onset of labor. This is normal for both the child and the mother. The baby is born full-term, and the mother’s body is ready for labor. To understand that a happy event is about to begin, you need to know what harbingers indicate it.
Now let's look at this in more detail.
The birth of a child rarely happens on the day set by the doctor. Such pregnant women make up only 16 percent of the total number, most of them are multiparous. This fact has been proven in practice, and women themselves who are preparing to give birth not for the first time know that this can happen a little earlier. Those who have had no more than three years since their previous birth often give birth a couple of weeks prematurely.
What are the birth signs of a second pregnancy?
The concept of precursors does not mean the onset of labor. They only suggest that the body is already preparing for it, and the mother must also mentally and physically prepare for the main event. Morally, it means understanding everything and consciously waiting for contractions; physically, it means being able to reduce the pain from contractions.
Abdominal prolapse. This phenomenon occurs according to the natural algorithm of pregnancy development. In the indicated three weeks, the fetus takes a position towards the exit. His head is located in the lower pelvic part. This is a normal birth presentation and indicates that the birth will be delivered without complications. This situation occurs a few days before giving birth.
It must be borne in mind that not everyone’s stomach drops during the prenatal weeks; for some, this happens already during labor. For multiparous women, this situation is not uncommon, so there is no need to worry that the belly has not dropped and other warning signs have appeared.
After uterine prolapse, the pregnant woman feels better. This concerns the stabilization of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory system.
It becomes easier to breathe, heartburn goes away, food is well digested. An inconvenience can be considered increased frequency of urination and pain in the symphysis pubis.
The pain is sometimes quite severe and interferes with full motor activity.
The dates for the descent of the abdomen for multiparous women are 38 and 39 weeks, less often this happens already at 37. After the uterus subsides, there is very little time left before giving birth, so the woman begins to prepare for the maternity hospital. There are times when the descent and the onset of contractions begin simultaneously. This is not a pathology, and is considered a common occurrence among women giving birth for the second time.
Weight loss. At the 37th week or already from 36, good changes occur when the pregnant woman gains weight; it begins to grow more slowly, and at 38-39 weeks in multiparous women it may stop completely or decrease. There are objective reasons for this:
- the child’s body weight has already formed and he has stopped increasing his parameters;
- swelling decreases, so the body eliminates everything unnecessary to make childbirth easier;
- The work of the kidneys is activated and moisture is removed from body tissues in an enhanced mode.
Weight loss should not frighten a pregnant woman, especially since it is minor. At week 39 it can be no more than a couple of kilograms. Losing body weight does not in any way affect the health of the mother and fetus. On the contrary, it becomes a little easier for a woman to move, and the disappearance of swelling in her legs ensures that shoes do not tighten them and normal blood circulation is restored. A woman’s face becomes prettier, this is also due to the elimination of swelling.
Removal of the mucus plug. An objective harbinger of imminent labor is the release of the mucous plug that closes the entrance to the uterus.
During pregnancy, it was a protection against penetration of any infection and harmful microorganisms into the uterus, and, consequently, into the fetus.
This substance is a mucous lump with a flesh-colored or brown tint.
The beginning of this process can be determined by the traces left by mucus on the laundry. With a complete and one-time release, the clot can be significant; with a partial release, small, odorless lumps are found, having a tight consistency and an admixture of blood streaks. A complete discharge is accompanied by some unpleasant phenomena, they consist of sensations of heaviness and nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar spine.
Multiparous women are characterized by the following features of the plug coming out:
- discharge is usually a close harbinger of the labor process;
- labor begins, as a rule, after a few hours;
- the uterus opens quickly after the plug comes out;
- A break of several days between the removal of the plug and contractions is rare.
Assessing these factors, we can say that births for multiparous women are faster than for those who become mothers for the first time.
"Nesting" syndrome. This term refers to a woman’s desire to prepare everything at home for the arrival of a baby. It is stated that this is done on an instinctive level, but the pregnant woman does it consciously and with love. Nature itself is helping her, because her condition has stabilized in recent weeks and she has a surge of vitality. Doing housework calms a woman down and gives her emotional positivity. She charges her household with her energy, they get involved in this work, the family unites, and a favorable environment appears in the house.
All these efforts are not mere vanity, but the creation of ideal conditions for the child. This concerns hygiene, comfort, and the preparation of necessary care products. The nesting instinct awakens in expectant mothers at 36-37 weeks and is one of the precursors of childbirth.
"False" contractions. This type of contraction is called Braxton-Hicks contractions. Multiparous women know about them, but do not always feel them. They have already understood in practice what true labor is, and weak spasms do not cause them anxiety. The woman lives her normal life, performs household duties and does not feel any discomfort.
The usual name for this phenomenon is training contractions; their appearance occurs between 32 and 37 weeks. Only women carrying a child for the first time can confuse them with labor pains. They may experience contractions of the uterus and the onset of training contractions even in the second trimester.
In second-time mothers, false contractions can usually appear in the last two weeks; in this case, even experienced mothers in labor make mistakes and take them not as harbingers, but as the beginning of labor. In order not to confuse false and true contractions, you need to know what their difference is. Signs of real labor pains are:
- regularity of contractions;
- first equal time intervals between them;
- then the intervals between contractions become shorter;
- increasing the duration of the contraction;
- increasing pain, inability to calm it by changing position;
- rupture of water preceding uterine contractions.
“False” contractions are not so painful, do not have a regular pattern, and do not develop progressively to increase in duration and pain.
That is, they do not have a specific development algorithm; they are essentially chaotic. Second-bearing women know how to stop them; to do this, just do breathing exercises or find a comfortable position.
Colostrum release. Colostrum is droplets of liquid, white like milk but clear, that appear on a pregnant woman's nipples. In second-born women, they may not form in the last weeks, but earlier - in the second trimester. But such an early appearance is rare, but at 38-39 weeks they will definitely stand out from the nipple, and your bra will be wet.
This phenomenon is completely natural and there is no need to fight it; moreover, it is not recommended to interfere with the release of colostrum. Unpleasant moisture should be removed using water procedures - showering, wiping, blotting. At the same time, observe hygiene rules so as not to introduce an infection into the nipple.
Remember to use soap as little as possible when treating your nipples. It dries out the delicate skin on the nipples, which can subsequently cause them to crack during feeding. Cracks bring significant suffering to a nursing mother, so the skin of the nipples must be protected.
The appearance of wet spots on clothes from secreted colostrum can be avoided. There are special inserts in the bra that absorb colostrum. Use them and your blouses will remain clean, without discomfort. Pads are needed not only during pregnancy, they will protect your clothes during lactation. Milk is also released from the nipples when the mammary gland is full.
Some women try to save their clothes by squeezing out colostrum before going outside. This is strictly prohibited. In this way, you can infect the nipple and harm yourself and the baby.
Reducing tremors. In recent weeks, there has been a decrease in the number of movements. This is a completely understandable phenomenon - the baby in the womb has grown so much that it is already difficult for him to actively move his limbs. His body is preparing for difficult work - passing through the birth canal, it needs strength, so motor activity decreases.
But despite the physiological need to reduce the number of kicks, their number should be controlled by the mother. The child should push at least a dozen times a day. If the baby moves less often, then undergo an examination and CTG. A woman can be calm only when the examination reveals the normal condition of the fetus, and the doctor concludes that nothing threatens it.
If during the examination it turns out that movements have decreased because the child does not have enough oxygen, then the right solution would be to artificially stimulate contractions and begin the labor process.
Stool disorders. The appearance of diarrhea, as a harbinger in multiparous women, is typical in the last days before childbirth. This is a physiological process of cleansing the body. You need to help cleanse your intestines; to do this, you should switch to a light diet. It will be well absorbed and excreted in a timely manner, without lingering in the digestive organs.
Your intestines should be free during pushing; nature has provided for the removal of feces through loose stools during the prenatal period. What does not come out naturally will be removed with an enema. During diarrhea, harmful toxins and waste are eliminated, which helps to improve the health of the mother's body. Ridding the intestines of feces helps reduce the load on the organs and makes the birth process easier.
Reviews
According to reviews from mothers in labor, sometimes it is not possible to recognize contractions, and women either come to the maternity hospital in advance, or only when there is no doubt left, but by this time multiparous women already have a fairly large opening of the cervix. The fact is that a pregnant woman intuitively expects the same sensations to appear as the first time, but most often they are completely different.
Corrections for the relative speed of each stage must be made.
Also, don't trust your sensitivity. Some mothers indicate that even the pain was completely different and began not from the back, but from the lower back.
Harbingers of the onset of labor
These include two main features:
- regularity of strong contractions;
- waste of amniotic fluid.
During contractions, which are very painful, the woman understands that labor has arrived, but with the water breaking, not everything is so simple. The ideal scenario for bladder rupture is when it occurs during childbirth with an open uterus. But there are cases of outpouring of water before the start of contractions or during them, that is, at home. Then the woman needs to remember how much water there was, what it smelled like, what color it was. This is necessary so that the doctor correctly assesses the situation and chooses the correct algorithm for managing labor.
A dangerous precedent is the gradual leakage of water; this phenomenon indicates damage to the amniotic sac and the risk of infecting the child with infections. If you suspect leakage, you should definitely consult a doctor, and you can monitor this phenomenon without constantly using sanitary pads. They absorb moisture and do not make it possible to timely determine the rupture of the bladder shell.
Thus, there are two types of precursors - on the eve of an imminent birth and with the onset of labor. If you learn to distinguish between them, you will feel calmer in the last weeks of pregnancy and will know in time when you need to get ready for the maternity hospital.
Water
Childbirth in multiparous women, as in primiparous women, begins with the breaking of the waters. They can “break through” quickly without causing any pain. Some describe this moment as involuntary urination. In this case, the liquid has neither color nor odor. Water may also leak. This is usually accompanied by frequent wetting in the perineum, which causes some discomfort, but not pain. In any case, in the last stages of pregnancy, it is necessary to monitor everything that happens in the body, reporting to the gynecologist in charge of the pregnancy. It is worth remembering that a fetus that is not surrounded by water cannot “breathe”, which means it begins to strive to be born. Once your water breaks, you are only a few hours away from giving birth.
Frequency of contractions
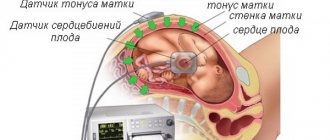
The frequency of contractions is divided into 3 phases depending on their duration and the break time between them.
- Initial. The duration of contractions is 20 seconds, and the break between them is 15 minutes.
- Active. The duration of the contraction is increased to 1 minute, and the break time is reduced to 3 minutes. In this phase, the cervix dilates to 7 cm.
- Deceleration phase. The shortest phase, during which the cervix dilates to 12 cm.
With repeated births, the process proceeds 2 times faster, so doctors recommend going to the hospital when contractions occur every 5 minutes.
Real and false contractions
Before real contractions, which dilate the cervix by 12 cm, Braxton-Hicks training contractions occur. They prepare the body for natural childbirth. Until the end of the second or beginning of the third trimester, training contractions are not noticeable due to the low weight of the fetus. The appearance of intrauterine contractions becomes noticeable at 32 weeks, and in primigravidas - at 20 weeks.
False contractions cause contractions of smooth muscles without dilation of the cervix and they are very easy to distinguish from real ones by the following signs.
- Lack of pain and regularity. Their intensity gradually decreases, and all signs disappear on their own after some time.
- The short duration of the process. The contraction lasts only 30–60 seconds.
- Localization of muscle tension. All sensations are concentrated in a certain part of the uterus, and not throughout the entire organ. There is also no painful kickback in the lower back.
- Disappearance of uterine contractions after changing position. Changing body position does not affect actual contractions.
- No discharge. During real contractions, the discharge looks like clear mucus or bloody fluid.
The intensity of training contractions depends on external and internal factors. Their appearance is connected:
- with intense physical activity. Don't chase your figure and limit your activities in the gym. Sign up for yoga or swimming. Closer to childbirth, reduce your activity to leisurely walks outside;
- with insufficient water in the body. Install a special application on your phone to track the amount of liquid you drink;
- with stress and any worries of the expectant mother. Do not try to work until the birth and go on maternity leave according to established standards;
- with active movements of the child in the womb and diseases of the urinary system;
- having sex after 38 weeks. Exclude intimate life in later stages or limit it as directed by your doctor;
- with a full bladder. Be sure to go to the toilet at the first urge and do not try to endure it for a long time.
To eliminate the sensations that arise, take a warm shower, try to lie down and relax with your eyes closed, or do a few breathing exercises.
How do contractions begin in multiparous women?
A couple of days before giving birth, a pregnant woman loses up to 2.5 kg in weight and complains of deterioration or lack of appetite. Additionally, psychological changes are noted. A woman often worries about trifles, tries to keep the house clean and especially carefully arranges the sleeping place of the unborn child. Soon other symptoms are added:
- changes in posture and gait;
- the appearance of false contractions;
- prolapse of the abdomen;
- gastrointestinal upset (diarrhea, nausea);
- increased frequency of urination associated with fetal pressure.
Before contractions, discomfort appears in the abdomen, accompanied by gas formation and diarrhea.
The first real contractions are accompanied by tension in the abdomen, reminiscent of menstrual cramps, and “petrification” of the uterus. Pressure on the lower back may cause pain and shortness of breath. At this time, it is important not to forget about frequent and deep breathing to avoid fetal hypoxia.
After the discharge of amniotic fluid, painful spasms worsen. During the second birth, when the body is already prepared, unpleasant feelings are less pronounced than the first time. The approach of imminent labor can be determined by:
- according to the regularity of contractions. Carefully calculate the intervals at which new contractions occur. It should be at least 10–15 minutes and gradually reduced to 3–5 minutes. The appearance of brownish discharge will indicate an early birth, which is no more than 10 hours;
- removal of the mucus plug. In some cases, this factor is false, and labor begins after 1.5–2 weeks, and in others, soon after the release of pinkish or reddish vaginal mucus;
- discharge of amniotic fluid. A sudden release of a large amount of amniotic fluid indicates rupture of the membranes. Regardless of the amount of water released, rush to the maternity hospital. It is dangerous for a child to be left without the protection of amniotic fluid for a long time.
Please note that if you experience excessive watery or bloody discharge, you should consult a doctor.
After the signs described above appear, try to relax and count how long the contractions last. If the time of each contraction steadily increases, and the interval between them decreases, go to the hospital. Multiparous women usually give birth faster, so delaying may result in childbirth in an ambulance.