What is dacryocystitis called?
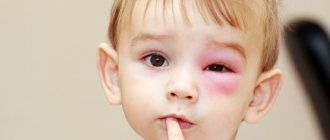
Tear duct obstruction is a condition in which the natural outflow of tears is disrupted. The disease is characterized by the development of an inflammatory process in the lacrimal sac of a newborn.
How does the nasolacrimal duct work in a baby?
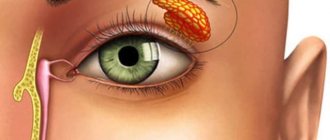
The structure of the nasolacrimal duct gives a complete picture of the process of development of tear obstruction. The lacrimal fossa contains a gland that is responsible for the production of tear fluid in a newborn.
A tear goes through a difficult journey. Washing the eye, it enters the area of the inner corner, where it flows through the channels into the lacrimal sac. Excessive tears enter the nasopharynx through the nasolacrimal duct. A feature of its structure in a newborn is its short length. This contributes to the penetration of infection into the organs of vision.
How does tear obstruction form?
When the baby is in the womb, the tear duct is blocked by a vestigial film. It blocks the flow of amniotic fluid into the respiratory and visual organs. As soon as the child is born, the membrane ruptures, and the visual apparatus begins to function normally.
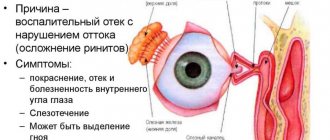
Sometimes there is no breakthrough. The tear stream, blocked by a plug in the canal, begins to look for other passages. Such stagnation in the lacrimal sac begins to become inflamed, which leads to the development of dacryocystitis.
Risk group among newborns
Most often, obstruction of the lacrimal duct is diagnosed in infants under the age of 2 months. Any newborn, due to the specific structure of the visual organ system, is susceptible to this disease.
But there are factors that contribute to the development of dacryocystitis in infants:
- injuries received during passage through the birth canal;
- abnormal development of the lacrimal duct.
The danger of dacryocystitis
An advanced disease can provoke the transition of dacryocystitis to the chronic stage. In addition, the lack of proper treatment leads to the development of diseases of the visual organs and the newborn’s body as a whole.
Causes of obstruction
Dacryocystitis can develop for a number of reasons:
- Congenital defect.
Due to underdevelopment of the drainage system in the eye, a plug appears in the lacrimal canal. The mucus can resolve on its own, but sometimes probing is used to remove it.
- Abnormal skull shape.
The provoking factor is the presence of serious diseases in the newborn with visible defects. Such diseases include Down syndrome.
- Infectious eye diseases.
- Mechanical damage to the bones located in the area of the lacrimal canals.
- Formation of tumors and cysts in the eye drainage system.
- Application of eye drops.
Symptoms of the disease
Dacryocystitis is often confused with conjunctivitis.
Indeed, the external signs are similar, but there are significant differences, due to which the diagnosis of obstruction of the lacrimal duct is made:
- often changes are visible only in one eye;
- swollen and red lower eyelid;
- the appearance of pus when pressing on the lacrimal sac;
- the sore eye is watery all the time;
- restless sleep;
- refusal to eat;
- possible increase in body temperature.
Diseases with similar symptoms
- Conjunctivitis.
- Blood in tear fluid.
- Allergic reactions.
The diseases described above are often confused with blocked tear ducts in newborns, because the symptoms are very similar. Young, inexperienced mothers often mistake contamination for conjunctivitis and most often limit themselves to pharmaceutical medications, as well as local anti-inflammatory and antiseptic treatment. Ordinary conjunctivitis can be quickly cured with proper treatment by specialists, but obstruction of the lacrimal duct cannot.
With conjunctivitis, there is no phenomenon of tearing, and there is also no purulent discharge or redness of the skin. Doctors are inclined to believe that obstruction is still a congenital disease, and conjunctivitis is infectious and acquired. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. Remember that at the first symptoms of obstruction and inflammation, the child should be urgently shown to a pediatric ophthalmologist who can make an accurate diagnosis.
How to recognize tear duct obstruction in a newborn?
To make an accurate diagnosis, the newborn undergoes a comprehensive examination. Only after identifying dacryocystitis can a doctor prescribe one type of treatment for the disease.
Examination of the child by a specialist
The doctor carefully examines the baby's eyes and feels the affected area. To make a more accurate diagnosis, the doctor compares all the obvious symptoms.
Be sure to examine the child's second eye for signs of dacryocystitis. If both organs of vision are affected, treatment tactics change.
Taking a nasal sample
The Vesta nasolacrimal test can provide comprehensive information about the degree of patency of the canals in the system. For the procedure, a 3% solution of Collargol is used. It is instilled into the conjunctival area of the eye, and a cotton turunda is inserted into the nasal passage.
If the cotton wool becomes stained within 5 minutes, then the permeability is considered good and the test is positive. When staining the turunda after a longer period, we can talk about the presence of weak patency of the lacrimal canals.
In some cases, a double nasal test is used with the insertion of a cotton swab moistened with a weak solution of adrenaline into the nasal opening.
Other studies to clarify the diagnosis
Parents should not be alarmed if the doctor takes a smear from the conjunctival area. This is necessary to identify the causative agent of the eye infection and the severity of the disease.
Sometimes a newborn may be prescribed an additional test - dacryocystography. During the procedure, the child is given a series of control images that will allow the patency of the lacrimal canal to be assessed.
Preparing a child for sounding
Before performing surgery and cleaning the canal, the doctor must make sure that the symptoms did not arise as a result of viruses or bacteria entering the baby’s body. If the diagnosis of “dacryocystitis” is established, the specialist prescribes an examination of the child, during which:
- Blood is taken from the baby to test the rate of clotting.
- Bacteriological culture is performed to examine the fluid in the lacrimal sac
- Biomicroscopy of the diseased eye is prescribed
- A sample is taken to check the patency of the canal. At the same time, a special colored liquid is dripped into the baby’s eye, which normally should easily penetrate into the nasal cavity. The doctor carefully examines the nasal passage with a cotton swab, on which colored traces should be detected. If the cotton wool remains uncolored, the patency is impaired and requires restoration through surgery.
When the decision to carry out probing is made, the doctor gives the mother recommendations, on compliance with which the success of the treatment depends. For several days it is necessary to follow a certain diet, and 3 hours before the sounding the baby should not eat (this prevents regurgitation of food in the infant).
| During the operation, medications will be used, so during this period you cannot use medications that are incompatible with the medications necessary for the procedure. |
The mother should prepare a diaper in which to wrap the baby and limit the movements of his arms during medical procedures.
Most often, bougienage is carried out in an outpatient clinic, but sometimes you have to go to a hospital. During the recovery period, the child will be monitored by an ophthalmologist and a therapist.
Return to contents
How to treat dacryocystitis?
The disease is treated with complex therapy. It includes hygienic eye rinsing, the use of medications and, in special cases, surgery.
Taking medications
Medicines prescribed to a newborn for dacryocystitis are necessary to block the spread of infection.
Widely used medications are eye drops:
- Vitabact;
- Tobrex;
- Vigamox;
- Phloxal;
- Levomycetin.
Albucid drops are not used to treat obstruction of the lacrimal canal in young children. This is due to the likelihood of complications that will inevitably lead to surgery.
Method of washing a diseased organ
Furacilin solution is used as an eye wash. A cotton pad is moistened with it and the damaged organ is wiped, as a result of which the eyelid is cleared of purulent discharge.
Chamomile decoction has an excellent antimicrobial effect. Wash the affected eye with a swab soaked in the prepared solution at least 2 times a day.
Carrying out the operation
Surgical intervention is performed if actions to remove the plug in the tear duct have not brought the desired result. Over time, the gelatinous film thickens and becomes difficult to break. A qualified ophthalmologist comes to the rescue.
The operation to clear the tear duct is called probing, or bougienage. This manipulation is carried out in children whose age has reached 6 months. Probing can be accompanied by both local and general anesthesia.
For surgical intervention, a special probe is inserted into the lacrimal canal. The essence of the operation is to break through the film with a very thin needle. The surgical action is performed quite quickly - within a few minutes. At the end of the operation, the surgeon injects a special antiseptic solution into the tear duct. A positive outcome of the manipulation is the flow of fluid into the nasal passage and nasopharynx.
The need for massage for dacryocystitis
The purpose of massage for obstruction of the tear duct is to break the gelatinous plug in the tear duct. The membrane breaks through the creation of pressure. Therefore, the most appropriate time for a massage is considered to be the period when the baby is crying.
Before starting the procedure, the newborn's sore eye is washed with furatsilin solution. Massage movements should not be rough or harsh. A newborn's nasal bones have not yet fully formed, so they are easily damaged.
Finger movements during the massage should be made with gentle jolts or vibrations in the direction from top to bottom. The action must begin from the inner corner of the eye, gradually moving along the projection of the lacrimal canal. 5-10 movements are enough, after which the purulent discharge is wiped off with a cotton pad.
Massage for dacryocystitis should be performed at least 5 times a day for 2 weeks. Do not forget that after each procedure, the newborn needs to drip the eyes with drops that have an anti-inflammatory or antibacterial composition.
From the video you will learn clearly with an example of how to massage a baby with dacryocystitis.
Prohibited actions in the treatment of a disease
Sometimes mothers, despairing of the current situation, resort to independent actions that are not approved by medical specialists. Such manipulations can aggravate the development of the disease, causing serious consequences. Under no circumstances should you:
- drip breast milk into the eyes;
- use tea when washing the eyes;
- use antibiotic drugs without doctor's approval.
When a baby starts crying
Tears do not appear immediately in newborns. At what exact moment this occurs depends on physiology. Some babies develop faster, and some slower. Immediately after birth, tears do not flow from any baby.
Tears do not appear in a child immediately, but their prolonged absence indicates a pathology that requires treatment.
First tears and physiology
For the first months of their lives, babies cry without tears. They can make a dissatisfied face, corresponding to a crying state, but their eyes will remain dry. This is because children's tear ducts open only 1-1.5 months after birth.
Tear ducts do not form in the womb because the baby's eyes are washed there by amniotic fluid, and tears are not needed in this case.
When a child is comfortable, he does not express any emotions. The facial muscles are not yet fully developed to express feelings in any special way. But if the child is not comfortable, he is hungry or cold, he announces his dissatisfaction by screaming. In this case, the baby’s face resembles a cry, but there are no tears in the eyes. This is because the facial muscles develop faster than the tear ducts.
Until the child begins to cry, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the baby's eyes.
The mucous membranes of a newborn's eyes are very dry and thin. It is necessary to examine the child’s eyes daily to ensure that they do not turn red. Before tears appear, the baby’s eyes need to be washed by the parents. Otherwise, they will dry out or dust will accumulate in them, which will lead to inflammation. The child's eyes need to be washed regularly 2 times a day: morning and evening. This can be done with an ordinary cotton swab dipped in boiled water. Instead of plain water, you can use an infusion of chamomile. It is prepared from 1 tsp. dried chamomile flowers and 1 cup of boiling water, infuse for 30 minutes.
Whatever eye solution you choose, it should be at room temperature. Hot or cold liquid can cause the eye to fester. You need to wipe your eye with a wet cotton swab, from the outer corner to the inner. If the mother is breastfeeding, then the baby's eyes can be instilled with breast milk. You need to drip 2 drops into each, and directly from the chest.
When the baby starts to cry, the mother should make sure that they flow from both eyes. If fluid does not appear on one side, this may indicate that the space of the lacrimal canal is too narrow, its suppuration or dysfunction of the lacrimal glands. Therefore, you need to consult a doctor for help and start an examination to find out the cause.
The sooner the cause of dysfunction is identified, the greater the chances of successfully treating it. If the tears appear white, this also indicates the development of an infection. In this case, it is recommended to instill the child’s visual organs with a solution of furatsilin.
It is necessary to diagnose the cause of the child’s lack of tears as quickly as possible and begin treatment.
If tears don't appear for a long time
There is no clear definition in how many months tears should appear. It all depends on the baby’s development: for some a little earlier, for others a little later. But by 4 months, tears should appear in all babies. If this does not happen, then this may indicate a blockage of the tear ducts. The first tears should soften the plugs of amniotic fluid that plug the canals. But in 5% of babies, the canals may be narrow, and the plug simply cannot come out. In this case, you need to consult an ophthalmologist. He will prescribe special softening drops to clean the canals.
In addition to using drops, you can give your child a special massage that stimulates the excretory tract. To do this, you need to gently massage the inner corner of the eye clockwise with your little fingers 5 times a day. If drops and massage do not help, and suppuration occurs, a bougienage procedure may be prescribed. Its essence lies in the fact that a small probe is inserted into the tear duct, which clears the paths for tears and makes the ducts wider.
If there are no problems with tear production, then this is not at all a reason not to visit an ophthalmologist. The doctor should regularly examine the baby's vision organs to check whether they are developing normally. He will look at whether the eyelids function well, whether the child is able to see, whether the optical media are transparent.
Complications of obstruction
The most dangerous thing that can happen to a newborn is the spread of pus throughout the body due to untimely treatment of dacryocystitis.
Infection, in turn, provokes the development of such serious diseases as:
- phlegmon of the eyelid, lacrimal sac or orbit;
- dacryocystocele;
- meningitis;
- panophthalmitis.
An advanced stage of the disease can lead to vision loss in a newborn. Therefore, it is easier to seek treatment at the initial stage of tear duct obstruction.
Possible complications
If pathogenic bacteria enter the clogged duct, the baby may develop purulent conjunctivitis.
If the lacrimal canal in newborns is not open or too narrow, due to the accumulation of pathological fluid, overstretching of the lacrimal sac occurs, which becomes clearly visible upon visual examination. Soon a bacterial infection occurs, as a result of which the child progresses to chronic purulent conjunctivitis. If the clogged lacrimal sac is not cleaned and the disease is not treated, the risk of cellulitis formation increases, which can cause brain abscess and sepsis.
The role of preventive action
There is no guaranteed protection for a baby from obstruction of the lacrimal duct, but parents can take care of the health of the newborn in advance:
- Maintain newborn hygiene.
- Rinse your eyes thoroughly after suffering from dacryocystitis. Pay special attention when treating organs of vision that contain discharge.
- Contact your doctor promptly for advice or treatment.
At the first manifestations of obstruction of the lacrimal canal, you must immediately show the child to the doctor. Only a specialist can accurately determine the diagnosis and recommend to parents one or another treatment method. With the most dangerous prognosis, it is possible to normalize the condition of the newborn and completely cure dacryocystitis.