During the normal functioning of the digestive system, the cardia of the stomach is in a closed state, but with pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, incomplete closure of the cardial region occurs. This is the cause of gastric disorders: heartburn, belching, pain. If the pathology is not treated in a timely manner, ordinary dyspepsia can develop into more serious diseases of the upper digestive system.
What is cardia?
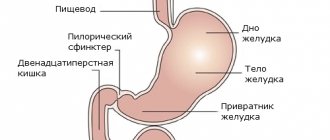
The human body contains a large number of sphincters - these are devices similar to a valve, in this capacity the circular muscle acts, which, when contracted, narrows and closes. The combination of folds of mucous tissue and the vascular system forms the sphincter apparatus.
Gastric cardia or lower esophageal sphincter (LES) - acts as an inlet valve into the stomach from the esophagus. Normally, it maintains a closed position, preventing acidic contents from refluxing into the esophagus. During eating, the cardia opens, allowing the food bolus to pass further.
It is important to note that the pressure in the stomach is higher than in the esophagus. Therefore, the anti-reflux barrier must exert force to resist the natural movement of stomach contents up the digestive tract.
When pathology appears, the cardiac sphincter stops closing, resulting in the backflow of gastric contents into the esophagus, and its walls are not adapted to the acidic environment. Failure to close the valve is insufficiency of the gastric cardia - a functional disease of the digestive tract in which reflux is observed.
Possible complications and prognosis
If treatment is started in a timely manner, the disease has a favorable prognosis. In most cases, it is not possible to completely cure it, and after entering a state of remission, it is necessary to continue monitoring with a doctor in order to prolong the period of remission. Without adequate treatment, the risk of developing severe complications from the affected organ increases.
These include:
- Reflux esophagitis (an inflammatory process in the inner wall of the esophagus due to reflux), which can also be complicated by erosions and ulcers.
- Stenosis and stricture of the esophagus is a pathological narrowing of its lumen.
- Barrett's esophagus is a precancerous condition characterized by local metaplasia of the epithelium (when instead of the squamous cell, normal for this organ, intestinal or gastric appears).
The symptoms and treatment of GERD differ in children and adults. The same applies to the various forms of the disease and the individual characteristics of each patient. Therefore, it is important that the treatment is carried out by a gastroenterologist.
The role of the diaphragm in reflux
The diaphragm plays an important role in preventing reflux. She, together with NSP, restrains the pressure so that there is no reflux higher in the gastrointestinal tract.
The antireflux barrier consists of the LES and the crura of the diaphragm. Since the pressure gradient between the stomach and esophagus is quite high, their coordinated action is necessary. The sphincter takes on a constant load, holding back pressure. The diaphragm helps him when he inhales, at this moment the pressure in the chest increases, and the legs of the diaphragm additionally put pressure on the walls of the esophagus, compressing them.
The formation of such a tandem is weakened by the formation of a diaphragmatic hernia. The cardia of the stomach moves upward, so the diaphragm is no longer able to participate in the antireflux barrier.
Degrees
There are 3 degrees of sphincter non-closure:
- 1st degree – the amount of incomplete closure of the cardia is about 1/3 of the diameter of the esophagus;
- 2nd degree – non-closure increases to half the diameter of the esophagus;
- Stage 3 – the valve stops closing completely.
As valve insufficiency develops and intensifies, the symptoms of GERD increase, esophagitis appears, and a serious complication may follow - degeneration of the esophageal mucosa: Barrett's esophagus.
Causes
Groups of factors can provoke cardiac failure:
Functional
- Increased pressure from the stomach on the sphincter, which occurs due to excessive gas formation, fermentation processes in the organ, or overeating.
- Stretching of muscle structures is the result of a chronic form of pancreatitis or obesity. Gradual muscle strain can also occur due to frequent gastritis.
- Disruption of the innervation of the lower esophageal sphincter may be associated with damage to the vagus nerve during surgical operations. This nerve is responsible for the tone and relaxation of the cardia.
- A sedentary lifestyle contributes to decreased muscle tone.
Organic
These reasons include factors associated with changes in the structure of organ walls due to:
- Diaphragmatic hernia. The sphincter moves into the chest and ceases to adequately perform its functions.
- Scar formations on the mucous membranes that occur after surgical interventions or injuries.
- Burn injuries or careless use of the endoscopic examination method.
- Consequences of removing polyps or cauterizing ulcers.
Reflux is often diagnosed late in pregnancy, which is caused by fetal pressure on the peritoneal organs. Do not panic, functional failure of the cardia is temporary and disappears on its own after childbirth.
Symptoms
Cardia insufficiency is characterized by a set of general signs that make it possible to identify pathology:
- Heartburn that occurs regardless of food intake or consumption of certain categories of food. It is the main symptom of the disease.
- Substernal pain in the area of the stomach.
- Belching of air and reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus, which are of a recurring nature.
- Nausea, ending with a gag reflex with bile impurities.
- General malaise, manifested by headaches and dizziness arising from physical activity.
- A chronic cough that often develops into asthmatic-type bronchitis.
In the absence of treatment, or its untimely start, the clinical picture will only worsen.
The severity of symptoms depends on the degree of cardia dysfunction:
- First. Incomplete compression of the valve is noted when the cardia rosette does not close completely, by one third. The symptoms are not severe. However, you should pay attention to frequent belching of air, which increases with poor chewing of food. Heartburn occurs periodically.
- Second. The clinical picture becomes more pronounced. At the same time, the pressure in the abdominal cavity increases, the number of heartburn attacks increases, and a folded neoplasm occurs on the gastric mucosa.
- Third. At the last stage, the sphincter completely loses its functions. Extensive inflammation of the esophageal mucosa appears. In a horizontal position, all symptoms intensify, sometimes interfering with restful sleep. Treatment at this stage should be inpatient.
Lifestyle
To ensure that the esophagus is freely passable and the cardia closes completely, certain rules must be followed:
- It is not recommended to overuse physical activity and bend over sharply, especially after eating.
- You should not wear tight clothes that fit your body, tight belts or waistbands.
- You should not go to bed immediately after dinner; it will be useful to move around a little.
- It is recommended to sleep with the head of the bed elevated.
- It is recommended to eat at least three hours before bedtime.
Diagnostics
In the diagnosis of gastrointestinal pathologies, instrumental examination methods, which are highly informative and accurate, play an important role. In order to identify it, the following diagnostic measures can be prescribed:
- Fibrogastroscopy. It is assumed that a probe equipped with a video camera is swallowed, through which a picture of the internal state of the organ being examined is displayed on a computer monitor. Through such diagnostics, it becomes possible to identify pathologies of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum.
- Daily pH measurements. It is carried out to determine the acid level of gastric juice over a daily period. The data obtained during the survey process is recorded in the form of a graph.
- Radiography. A contrast agent is used, most often barium. This examination is carried out on an empty stomach in the morning. The essence of the procedure is to drink contrast and then record images in various body positions.
- Monometry of the esophagus. Various indicators are taken from special sensors in the esophagus while taking a sip of water. Allows you to determine the contractile function of the esophagus, the coordination of peristalsis with the work of the sphincter. The duration of relaxation, residual pressure, duration and speed of contraction are assessed.
The reverse condition of cardia insufficiency is called achalasia, characterized by narrowing of the esophagus.
Treatment
Non-closure of the cardia of the stomach requires complex treatment, which is selected according to the cause that provoked the disease. A scheme is often used that combines drug and dietary therapy in conjunction with traditional methods.
Drug treatment
- Antibacterial drugs that are relevant when identifying Helicobacter, which is the main cause of inflammation.
- Antisecretory agents are prescribed in case of increased acidity.
- Enveloping drugs provide protection to the gastric walls.
- Preparations containing enzymes necessary for better digestion of food.
Medication therapy can be symptomatic in nature when it is necessary to relieve the unpleasant manifestations of sphincter dysfunction. Then the following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Antiemetics.
- Painkillers.
- Defoamers that suppress bloating and increased gas formation.
Folk remedies
To tone the cardiac sphincter, drinks containing caffeine are completely excluded from the diet. However, herbal infusions from medicinal plants valerian and St. John's wort are an alternative. Traditional medicine therapy is relevant only in the initial stages of the disease, when there are no complications, or during remission.
In the morning on an empty stomach, as well as before each meal, it is recommended to drink a glass of warm water.
In order to achieve a therapeutic effect, it is useful to use the following recommendations:
- Plantain juice helps normalize digestion.
- Between main meals, it is useful to drink an infusion made from calamus root. To do this, 5 grams of raw materials are poured into a glass of boiling water.
- Three times during the day, drink a medicinal infusion for the stomach, which is prepared from peppermint, plantain, St. John's wort, chamomile and yarrow.
- Dandelion flowers, which are covered with sugar and ground and then decanted, have a high therapeutic effect. The resulting syrup is diluted with water.
- Cumin is an indispensable remedy for restoring and maintaining proper functioning of the stomach. It can be consumed as a decoction or crushed and added to breakfast cereals.
Diet food
Proper and healthy nutrition for gastric sphincter insufficiency is the basis of the entire therapeutic approach. In order to quickly recover and prevent exacerbations of the disease, you should:
Write in the comments. Feel free to understand the problem that interests you together. >>>
- Avoid consuming foods that can cause a decrease in tone. These include: chocolate products, carbonated drinks, pepper, tea, coffee, seasoned foods.
- Avoid spicy and fatty foods.
- Completely eliminate the consumption of alcohol and tobacco products.
Meat protein, on the contrary, helps to increase the tone of the LES and reduce symptoms.
The main condition for the complete absorption of food is its frequent consumption in small portions. A minimum 4-hour interval should be observed between main meals. At the end of the meal, refuse to take a lying position, and preferably sleep with the head end raised.
Prevention
Humans are designed in such a way that preventing disease is not about them. Most often, you have to first treat the disease, and even in an advanced form, and then think about prevention. Diseases of the esophagus and the entire gastrointestinal tract are easy to prevent with the help of proper, moderate nutrition, normal drinking regimen, active lifestyle, giving up bad habits, and timely, regular medical examination. But from theory to practice in matters of such prevention there is an abyss.
I read somewhere that the fear of not having enough to eat and eating for future use is a genetically embedded fear in the subconscious of the descendants of those generations who experienced long times of famine. And, nevertheless, when it comes to health and quality of life, it is worth making an effort and gradually correcting eating behavior by reducing portions and giving up unhealthy foods. It is even more difficult to avoid frequent stress and maintain emotional calm. But these are important factors in maintaining the health of many organs and systems of the human body. This means that issues of strengthening mental health and the nervous system also need to be given constant attention.
We recommend: Why does bile reflux into the esophagus and how to cure it?
Physiotherapy
The muscular structures of the gastric cardia can be easily strengthened. For this purpose, specially designed breathing exercises are used. Particularly popular is Strelnikova’s gymnastic method, which involves performing training twice during the day: in the morning and in the evening before a meal, and also after an hour and a half after its end, for 1500 breaths.
As a preventive measure, gymnastics is performed in the morning or evening period. Such breathing exercises help strengthen the body and improve the health of internal organs due to increased blood flow.
Regular breathing exercises for insufficiency of the gastric cardia will be no less useful:
- The training should be carried out on an empty stomach, since any activity performed on a full digestive organ weakens the sphincter, which is explained by the pressure of gastric contents on the valve.
- The lungs are perhaps the only organ that can be controlled externally. For this reason, you need to start gymnastics with normal inhalations and exhalations.
- Exercises should be performed simultaneously with thoracic and abdominal breathing, when the muscular structures of the abdominal cavity become involved in the respiratory process.
- Inhalations and exhalations must be carried out in compliance with different speed limits.
If the disease occurs in the final stages, then the listed gymnastic exercises become useless.
Diet
Treatment of chalazia will be 100% effective only if a special diet is used along with conservative therapy. Its main principles:
- eating food only in fractions. Eating this way will reduce the load on the sphincter;
- Meals must be taken at the same time;
- after eating, you should walk or be in a sitting position for two hours;
- include cereal porridges and homogenized dishes in your daily diet;
- It is strictly forbidden to eat too hot or chilled foods;
- a proper diet should contain a lot of vegetables and fruits;
- You should not consume salty, smoked, fatty foods, alcoholic drinks and seasonings.
Treatment of cardia insufficiency is a long process that requires strict adherence to the instructions of the attending physician.