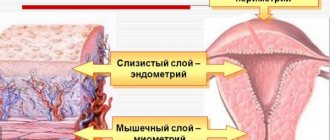
The mucous layer of the uterus lining it from the inside is called the endometrium. It undergoes a number of changes regarding its thickness and structure in certain phases of the cycle, which is due to the physiological need to create conditions for an egg ready for fertilization. Any deviation from the norm in the condition of the endometrium leads to problems with conception and pregnancy. Too thin endometrium and pregnancy are a difficult combination, since the pathological condition of the endometrium in the form of its thinning causes problems with the successful implantation of the fertilized egg, but even if this is successful, carrying such a pregnancy is unlikely.
On certain days of the cycle, the thickness of the endometrium varies from 5 to 10 mm, before the onset of menstruation it increases to 1.5 cm. A thickness of 7 mm is considered the norm for reliable strengthening of the egg. In the case when a woman’s endometrial layer thickness is recorded at a level lower than 0.5 cm, we speak of the pathology of endometrial hypoplasia (thinning), which negatively affects the ability to become pregnant and bear a baby.
Causes of pathology of the thin endometrial layer
Predisposing factors contributing to thinning of the endometrial layer include:
- deviations in hormonal function, endocrine disruptions;
- impaired blood supply to the uterine layers;
- inflammatory diseases of the genital area;
- incorrect use of contraceptives;
- previous manipulations in the uterine area (curettage, abortion);
- hereditary predisposition to underdevelopment of the uterine epithelium.
The course of the pathology of hypoplasia does not differ in the severity of symptoms, so it is often diagnosed during the examination of women experiencing problems with conception and pregnancy. Symptoms can be in the form of scanty, painful periods, cycle disruptions, and the presence of clots during menstruation. But if a woman has no plans related to pregnancy, then she may not suspect that she has a pathology.
Treatment
Before prescribing treatment for thin endometrium and planning pregnancy, you need to undergo a comprehensive examination. To do this, the woman is examined by a gynecologist and sent for the following tests:
- blood test for hormones;
- smear from the vagina and cervix;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
Based on the results of the study, it will be possible to confirm the thin endometrium, as well as establish the cause of this disorder. Further treatment will directly depend on the cause of the pathology.
If thin endometrium was detected during pregnancy, then the likely cause of the disorder is a lack of progesterone in the body. If hormone deficiency has been confirmed, then hormonal support with progesterone preparations, for example, Duphaston, Utrozhestan, will be prescribed.
Medication
If we are talking about preparing for pregnancy and a woman is thinking about how to grow the endometrium, then she definitely needs to be examined. If inflammation is detected, the woman will be treated with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. It is quite possible that by eliminating inflammation, it will be possible to normalize the functioning of the uterus.
In case of hormonal disorders, you will need to visit an endocrinologist. If endocrine disorders are detected, therapy will be specific, depending on the pathology found. In general, combined contraceptives are usually prescribed. Such products help restore the menstrual cycle and grow the endometrium.
To improve blood circulation in the body, Actovegin is prescribed. It is also possible to use homeopathic medicines, for example Hormel. In complex treatment, women are prescribed vitamin complexes to strengthen general immunity.
Physiotherapeutic
To grow the endometrium, it is necessary to improve blood circulation in the uterus. Physiotherapy helps with this. Such procedures improve the nutrition of the tissues of the genital organs, eliminate inflammatory processes, but physiotherapy is necessary in complex treatment under the supervision of a gynecologist.
For thin endometrium, the following physiotherapy methods are used:
- Magnet;
- Ultrasound;
- Laser;
- Balneotherapy.
Massage is useful for thin endometrium. Physical therapy is mandatory, with a focus on the pelvic area and pelvic floor. The following exercises are effective:
- Deep squats, lunges;
- Abdominal exercises;
- Exercise bike, scissors;
You need to exercise every day to have an effect. If a woman doesn’t really like strength exercises, you can sign up for aerobics, dancing, or the pool. It is not so important what kind of sport the patient will engage in. The most important thing is for a woman to move. Then blood circulation will be restored and the endometrium will begin to grow normally.
Nutrition
A woman’s reproductive function largely depends on her lifestyle, and especially nutrition. Eating fatty, sweet foods, with dyes, carcinogens and chemical additives is one of the causes of obesity, hormonal imbalance and thin endometrium. Hunger strikes and strict diets also do not have the best effect on the patient’s fertility.
According to statistics, overweight and too thin women suffer from infertility much more often than women with a normal physique. Therefore, nutrition should be healthy and balanced.
If a woman wants to grow the endometrium and become pregnant, she needs to normalize her weight. If you are obese or malnourished, a proper balanced diet will help. To follow it, you need to follow the following recommendations:
- Eat 5-6 times a day in small portions, 3 main meals, 2-3 snacks.
- You need to steam, boil, bake or grill without oil.
- Sugar is excluded from the diet and replaced with fruits, dried fruits, and honey.
- Only fresh and healthy foods are consumed; there should be no ready-made meals with unknown ingredients in the diet.
- It is recommended to give up alcohol and smoking. Bad habits disrupt blood circulation in the uterus and negate treatment.
There is no need to exclude fats or carbohydrates from the diet; all microelements are necessary for the normal functioning of the body. But you need to eat healthy carbohydrates, that is, cereals, bran, and not sugar and flour. And fats should be healthy, vegetable, for example, nuts, olive oil, flaxseed oil, etc. Oils should not be heated; they are added to salads.
Proper nutrition significantly increases the chances of successful conception and helps a woman bear a healthy child.
Folk
Treatment of thin endometrium is best done under the supervision of a doctor, because it is important to eliminate the exact cause of the disorder. Self-medication blindly can only complicate the situation and worsen the woman’s condition. For example, if a patient starts drinking herbs with phytohormones during a hormonal imbalance, it can only increase the imbalance.
Folk remedies are used in complex therapy of thin endometrium; the following remedies can be used:
- Sage decoction;
- Pumpkin juice;
- Raspberry leaves, etc.
Before using folk remedies, you must make sure that you are not allergic to the components of the product.
The mucous layer of the uterus lining it from the inside is called the endometrium. It undergoes a number of changes regarding its thickness and structure in certain phases of the cycle, which is due to the physiological need to create conditions for an egg ready for fertilization. Any deviation from the norm in the condition of the endometrium leads to problems with conception and pregnancy. Too thin endometrium and pregnancy are a difficult combination, since the pathological condition of the endometrium in the form of its thinning causes problems with the successful implantation of the fertilized egg, but even if this is successful, carrying such a pregnancy is unlikely.
On certain days of the cycle, the thickness of the endometrium varies from 5 to 10 mm, before the onset of menstruation it increases to 1.5 cm. A thickness of 7 mm is considered the norm for reliable strengthening of the egg. In the case when a woman’s endometrial layer thickness is recorded at a level lower than 0.5 cm, we speak of the pathology of endometrial hypoplasia (thinning), which negatively affects the ability to become pregnant and bear a baby.
Possibility of pregnancy
With thin endometrium, women are usually diagnosed with infertility. This is explained by the fact that the endometrium is 3 or 4 mm thick, which does not allow the egg to become firmly established in the uterus. Implantation will be successful if the thickness is over 5 mm; the best thickness is considered to be 7 mm, 9 mm, 10 mm, 11 mm. It is important to consider that the indicated thickness of the endometrial layer is considered normal only on certain days of the cycle. It will be the smallest immediately after menstruation, on average the norm is 5-7 mm, in some women it may be less than 2-3 mm, which is thinner than normal.
A graph of the linear dependence of endometrial thickness on cycle days on average looks like this:
- Phase 1, initial proliferation (days 5-7) - from 2 to 6 mm, average 0.5 mm;
- Phase 2, average proliferation (8-10 days) - from 4 to 9 mm, average endometrium 8 mm;
- Phase 3, late proliferation (days 11-14) - from 8 to 14 mm, average 0.11 cm;
- Phase 4, early secretion (days 15-18) - 10-15 mm, average 12.5 mm;
- Phase 5, medium secretion (days 19-23) - maximum endometrial thickness, on average it can be 16 mm;
- Phase 6, late secretion (24-27 days of the cycle) - the endometrial layer becomes thinner, up to 0.11 cm.
The problem of thinning of the endometrial uterine layer worries women who are just planning to conceive, as well as those patients who are faced with spontaneous termination of pregnancy. They are interested in whether it is possible to get pregnant when they have a thin layer of endometrium, what thickness is enough for pregnancy.
Each organism is individual, the natural process of conception is complex and depends on many factors, so pregnancy if a woman has a thin endometrium is quite possible. Another question is that the developed pathology of hypoplasia can interrupt it at an early stage. Sometimes pregnant women, when very little time has passed since conception, begin menstruation, and they even suspect that a miscarriage has occurred.
If the process of fertilization of the egg is successful, then it is implanted into the mucous layer. At the same time, the endometrial layer continues to increase its thickness. During the first trimester it can reach 2 cm or more.
The endometrium also tends to grow during an ectopic pregnancy. Regardless of whether the fertilized egg is normally fixed in the thickness of the uterus, or for various reasons its advancement into the uterus was disrupted and it remained in the fallopian tube, growth of the endometrial layer is observed. This is explained by the action of hormones that affect the endometrium, preparing it for the formation of the placenta during the further development of pregnancy.
Many people ask: In gynecological practice, there have been cases where pregnancy occurred in patients with an endometrial thickness of only about 4 mm. If hypoplasia is diagnosed, it is important for specialists to carefully monitor the condition of the endometrial layer in the event of pregnancy, since there is always a threat of miscarriage, which must be prevented in time.
Consideration of the feasibility of conducting an IVF procedure for endometrial hypoplasia deserves a separate discussion. The chances of an egg implanting during artificial insemination are minimal if the endometrial layer is small and its thickness on favorable days does not exceed 0.5 cm. The percentage of successful implantations is less than 15%. Patients are advised to delay preparations for IVF and undergo a course of treatment in order to increase the endometrium to 7-9 mm in thickness.
Lifestyle for growing endometrium
No matter how carefully all the doctor’s prescriptions are followed, increasing the endometrium for conception is possible only with an integrated approach. The lifestyle a woman leads plays an important role. Proper nutrition and sufficient physical activity are conditions for the health of the body in general and the reproductive system in particular.
A balanced diet helps maintain endometrial thickness and functionality. For successful conception, a woman’s daily nutrition should include:
- sources of vitamin E
: leafy vegetables, unrefined grains, bran, vegetable oils; - sources of vitamin C
: black currants, lemons, bell peppers, grapefruit, kiwi; - sources of salicylates
(substances that prevent the formation of blood clots): strawberries, raspberries, honey, raisins, prunes, thyme, curry, paprika, ginger, cinnamon; - sources of omega-3 fatty acids
: rapeseed and flaxseed oil, tuna, nuts, salmon.
If there is insufficient blood supply to the pelvic organs, moderate physical activity is necessary. Swimming, running, fitness, and oriental dancing can help thicken the mucous membrane. There are special exercises that lead to strengthening the muscles of the perineum and pelvis (Kegel technique, wumbling). But before starting classes, you should consult a doctor; in some cases, physical activity can aggravate the situation.
A doctor can give an exact answer to the question of how to grow the endometrium. He will conduct all the necessary examinations and, based on the results obtained, will create an effective treatment program. A modern approach to restoring the functions of the uterine mucosa includes the use of medications, folk remedies, as well as adherence to the rules of nutrition and physical activity.
The inner layer of the uterus plays an important role - it nourishes the fetus. But there is such a pathology as thin endometrium. It is because of this that the embryo cannot develop and grow normally. It is necessary to find out the causes and prescribe the correct treatment.
The endometrium is the inner mucous layer of the uterine wall with a large number of blood vessels. It takes an active part during pregnancy - the embryo is attached to it and feeds from it.
It is this that allows the fetus to breathe and eat, and most importantly, to develop properly. Thin endometrium is a pathology during gestation and needs to be treated.
The fewer female hormones in the body, the smaller the layer.
With a thin endometrium, a woman does not feel discomfort in everyday life, but when planning a pregnancy it is extremely undesirable, as it can cause a miscarriage or non-attachment of the fetus.
Most often, the normal inner layer of the uterus, increased to 10-13 mm in the last days of the cycle, helps the egg to attach more easily.
This means that it is easier to get pregnant. But a small layer, on the contrary, does not allow this to be done. In this case, a long course of treatment is required.
Diagnosis and treatment measures
After considering the complaints made by the patient and collecting an anamnesis, the woman is recommended to undergo a series of examinations.
Prescribed:
- submit blood and urine samples for general tests;
- conducting tests to determine hormone levels;
- conducting a transvaginal ultrasound to determine the condition of the uterus and ovaries in different phases of the menstrual cycle;
- taking a sample from the uterine layer for histology;
Therapeutic measures to eliminate hypoplasia are a whole range of procedures aimed at eliminating hormonal imbalances, improving blood circulation in the uterine layers, eliminating the consequences of chronic inflammatory processes, which are carried out with the help of medications and surgical interventions.
Therapy with hormonal drugs, their regimen and dosage is performed only by an experienced specialist based on the results of a comprehensive examination. With the help of physiotherapeutic treatment, hirudotherapy, acupuncture, and special gymnastic exercises, it is possible to improve the blood supply to the pelvic organs, which will have a positive effect on the condition of the uterine layers. The above-mentioned treatment methods make it possible to improve the condition of the uterine layer when the endometrium grows 6 mm or more.
Some cases of pathology require a surgical treatment method, when the pathological layer is removed, which contributes to its complete renewal and stabilization of its normal thickness.
The normal functioning of the uterine layers and the balance of hormones are the key to a good pregnancy and the birth of a healthy child.
Article outline
What is thin endometrium and why is it so dangerous? The endometrium is a mucous layer lining the inside of the uterus necessary for the implantation of the egg. But if there is too thin a layer of mucous membrane in the uterus, the egg simply will not have anything to attach itself to, that is, the woman will not be able to get pregnant.
Why is this pathology observed? There are many causes of the disease, the main one is hormonal imbalance, but there may be others - inflammatory processes, abortion. What to do in this case can only be determined by a doctor after an examination. The causes and treatment are very closely interrelated; to normalize the thickness of the endometrium, it is necessary to determine what caused the disease, and then begin appropriate treatment.
Attention: You cannot start taking medications on your own without consulting with your supervising doctor!
Diagnostics
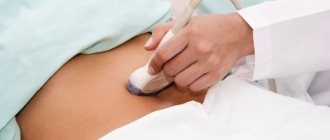
If a woman complains of infertility and scanty, painful menstruation, the doctor, by examining with mirrors and palpation, determines the presence or absence of abnormalities in the development of the genital organs. To determine the thickness of the mucosa, the patient is sent for an ultrasound. The study is carried out using the transvaginal method.
New growths in the uterus are detected using diagnostic hysteroscopy. Often, polyps and small myomatous nodes are immediately removed.
The blood is tested for the content of various hormones. If the presence of inflammatory processes is suspected, a smear is taken from the vagina and cervix, and the composition of its microflora is examined. A blood test is also performed to determine the presence of antibodies to various types of infection.
Video: How the endometrium grows
Why does the endometrium shrink?
The reasons for thin endometrium are various; among the main factors why the endometrium does not have the proper thickness are the following:
- hormonal imbalance;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- chronic inflammatory diseases;
- disturbances in the blood supply to the uterus;
- congenital anomalies of the uterus;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- frequent use of Postinor (emergency contraception).
The condition of the endometrium is affected by reasons such as surgical interventions on the uterus, including abortion. Often a similar problem is diagnosed in women with insufficient physical development of the body, short stature, and narrow pelvis. This does not mean that insufficiency of the endometrial layer will be determined in all these cases, but the inability to become pregnant for a long time against the background of these factors should be the reason for visiting a doctor.
Causes of insufficient endometrial thickness
In order to determine how to quickly grow the endometrium for successful conception, you need to find out the reasons for its reduced functionality. A thin lining of the uterus may be due to the following factors:
- pathologies of the endocrine system present from birth;
- dysfunction in the production of endocrine glands, leading to a discrepancy between the level of hormones and the period of the menstrual cycle;
- insufficient blood supply to the uterus, bladder, pelvic floor muscles and rectum, as a result of inflammation, surgery, injury, as well as congenital nature;
- damage to the mucous layer of the uterus, most often resulting from abortions and curettage;
- underdevelopment of the pelvic floor and uterine muscles;
- infectious diseases of the uterus;
- use of birth control pills.
Currently, researchers are suggesting that the cause of insufficient thickness of the mucous membrane may be heredity. But there is not yet enough clinical data to support this theory.
Thin endometrium
Signs
A thin layer of endometrium often manifests itself as the following:
- cycle is irregular;
- discharge during menstruation is scanty, the duration is extremely short;
- there is frequent spotting between separate periods (you need to pay attention to the color of the discharge; brown and black require immediate medical attention);
- miscarriages, infertility.
Signs of endometrial thinning may include weak secondary sexual characteristics and anorgasmia. Outwardly, symptoms may not appear, but it should be remembered that such a disease is quite dangerous and can lead to the most negative consequences.
The first symptoms of endometrial thinning
If the endometrium is small, a woman may notice certain characteristic signs. If the following symptoms occur, you should consult a gynecologist:
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle, frequent delays or changes in duration;
- painful periods;
- too little discharge.
Since it is very difficult to get pregnant with a thin endometrium, in the presence of pathology, women complain of infertility. Long unsuccessful attempts to conceive a child become the reason for an examination.
With a thinned endometrium, women may experience anorgasmia and weak expression of secondary sexual characteristics. The first menstruation occurs at age 16 or later.
Uterine discharge with a thin mucous membrane, even during menstruation, is scanty. The duration of menstruation is reduced, the volume of blood released decreases. Since this disorder is often provoked by hormonal imbalance, the “red” days of the female calendar can move several days forward or backward.
Ovulation in a woman with a thin endometrium and an imbalance in hormones does not occur every month, and it is difficult to accurately determine these days.
Thin endometrium and pregnancy
A normal pregnancy can occur even with a thin layer of endometrium, but it is much more difficult to bear and the risk of miscarriage is very high. Conception usually occurs normally if ovulation has occurred. However, the ability of the embryo to settle in the uterus and receive nutrition at first is in question.
Progesterone and estrogen levels change during the menstrual cycle. If pregnancy occurs, then under their control the growth of the tissue layer does not come out, and favorable development conditions are created for the fetus.
How to identify
Only diagnostics can determine how thin the epithelium is and how this can affect the possibility of natural pregnancy. The following research methods are usually prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the uterus;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- urine and blood tests;
- study of hormonal levels;
- biopsy of uterine tissue;
- histology of uterine tissue.
Diagnostics will help answer the question of what caused the disease and how to treat the thinning of the epithelium. Most often, a hormonal imbalance is determined, in which case appropriate therapy will be indicated. If the examination reveals inflammatory processes, then treatment will be aimed, first of all, at eliminating the root cause, after which measures will be taken to build up epithelial tissue.
How to bring the endometrium back to normal
In order to establish all the processes occurring in the thickness of the endometrial layer, an accurate diagnosis of its condition is necessary. Diagnosis is carried out using ultrasound and other techniques that allow one to assess the thickness of the functional layer by week, and sometimes by day of the cycle. Tests are required to determine hormone levels and determine the presence or absence of concomitant pathologies.
In order for a woman to become pregnant, it is necessary to completely cure all pathologies that impede the process of conception. Hormone replacement therapy helps to cope with the condition of hypoplasia. It helps to “grow” the endometrial layer (sometimes by 6 mm), which increases the chances of the egg to firmly penetrate the uterine layer. Additionally, to stimulate the growth of thin endometrium, physiotherapy is used, mainly aimed at improving blood microcirculation.
The progression of hyperplastic processes is stopped by medication or surgical methods (hormone therapy, curettage of the uterine cavity). How many days, what courses and medications are needed for hormone therapy is determined for each patient individually. It is necessary to monitor the thickness of the endometrial layer over time in order to assess the effectiveness of treatment and timely prevent relapses of the disease.
The successful development of the fetus largely depends on the condition of the endometrium, so every woman should know as much as possible about the state of her female health. And this is possible with regular visits to the gynecologist and following his recommendations.
One of the important criteria for the birth of a healthy child is the endometrium during pregnancy, namely its condition, on which both successful conception and the process of bearing a baby depend. At the stage of pregnancy planning, every woman is recommended to undergo a diagnostic examination to identify possible pathologies and their subsequent elimination. If you pay attention to this issue before conception, the risk of developing abnormalities during pregnancy will be minimal.
Treatment with drugs
Drug treatment of thin endometrium involves taking the following medications:
- Duphaston (a synthesized drug similar to progesterone, reduces the tone of the uterus, prevents exfoliation of the epithelium, taken on days 11-25 of the cycle, prescribed only by a doctor);
- Melsmon (contains placenta, is used to eliminate symptoms of inflammatory processes, normalize the cycle, has a number of contraindications);
- Actovegin (normalizes blood circulation in the genital organs, accelerates the growth of the endometrium, the general course lasts 4-6 weeks, the exact regimen is calculated only by the supervising doctor);
- Hormel (a homeopathic remedy, the duration of treatment may vary, the dosage regimen is calculated only by a doctor).
Taking any medications, especially hormonal ones, can be prescribed by a doctor after an examination. It is not recommended to start taking it on your own, as this can cause a serious deterioration in the condition.
How to grow the endometrium
If thin endometrium is diagnosed based on various studies and tests, before proceeding directly to treatment, it is necessary to determine the cause of its occurrence. To grow a small endometrium in case of hormonal disorders, drugs containing progesterone are used, such as Duphaston.
If hypoplasia is a consequence of a chronic inflammatory process of the genital organs, the first thing you need to worry about is not how to increase the thickness of the upper layer of the endometrium, but how to eliminate the cause of its occurrence. When the problem of pathology is insufficient uterine blood supply, in order to build up the endometrium, along with medications, non-drug treatment methods are used, such as:
- healthy eating,
- massage,
- special therapeutic exercises.
You can grow the endometrium without hormones, using herbs and such folk recipes and alternative medicine methods as.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies includes the following:
- raspberry leaf tea, which you can drink several times a day;
- tinctures of boron uterus (sold in a pharmacy, taken daily, the duration of the course is determined by the doctor);
- natural pumpkin and pineapple juices, which can be consumed in any quantity;
- tinctures of sage, which should be taken in the first half of the menstrual cycle (course duration - four months);
- combined decoctions of chamomile, elderberry inflorescences, nettle, mint, medicinal cap, yarrow (take thirty minutes before meals, three to four times a day).
It will take at least four to six months to reach the required thickness, but the first results will be clearly visible within a couple of months from the start of treatment. However, the use of folk remedies must be agreed upon with the supervising physician and combined with traditional medicine methods. This is the only way to get a reliable and sustainable result.
Endometrial thickness by day of the cycle (normal)
The endometrium is the inner mucous lining of the uterine cavity. During the menstrual cycle, the structure and thickness of the endometrium undergoes significant changes.
The thickness of the endometrium by day of the cycle is determined using ultrasound.
In the first two days of menstruation, the endometrium is visualized as a structure of heterogeneous consistency, slightly increased sound conductivity and has a thickness of 0.5-0.9 cm. During this period, there is no clear layer-by-layer structure.
On days 3-4, the endometrium looks like a formation with increased echogenicity and a small thickness of 0.3-0.5 cm.
On days 5-7 of the cycle, a slight thickening of approximately 0.6 - 0.9 cm is noticeable, echogenicity decreases and its sound conductivity increases.
On days 8-10 of the cycle, a clear hyperechoic structure finally begins to appear in the central part of the endometrium, approximately 0.1 cm thick, which persists almost until the end of the menstrual cycle. Above and below this formation there are zones of average sound conductivity and echogenicity 0.3 cm thick. All structures are surrounded by a thin echo-negative rim 0.1 cm thick. The thickness of the endometrium itself, together with the echo-negative rim, at this time is 0.8-1 cm.
The echographic picture on days 11-14 is similar to the previous one, but between the echo-negative rim and the zone of medium echogenicity, a thin echo-positive structure begins to appear, having a thickness of about 0.1 cm. The entire endometrium in this phase of the cycle has a thickness of 0.9-1.3 cm Throughout all subsequent stages of the secretion phase, the endometrium has the same structure, only a slight thickening is noticeable.
Already on days 15-18, the endometrium reaches a thickness of 1-1.6 cm.
On days 19-23 – 1-2.1 cm.
And on days 24-27 of the cycle, the thickness of the endometrial layer begins to decrease to 1-1.8 cm.
A healthy endometrium that corresponds to the day of the cycle is one of the main conditions for reliable implantation of the fertilized egg.
Reasons for the discrepancy between the endometrium and the day of the cycle:
– luteal phase deficiency – dyshormonal conditions; – endometrial injury (as a result of curettage surgery); – congenital hypohormonal condition, uterine hypoplasia; – impaired blood supply in the pelvic area and uterus. This problem can be either congenital or acquired (with diseases of the genitourinary system, after inflammation or abortion).
As a result of identifying the cause of impaired maturation and development of the endometrium, therapeutic measures are prescribed. A gynecologist-endocrinologist diagnoses and treats the endometrium. Vitamin E is most often prescribed.
Folk remedies for endometrial growth
A very good remedy for the growth and maturation of the endometrium is boron uterus and red brush (Rhodiola colda). These herbs must be consumed according to a special regimen, dividing the menstrual cycle into two phases. The first half is after the end of menstruation and until the middle of the cycle, at which time it is necessary to take a red brush. In the second half of the cycle, it is recommended to drink boron uterus. By the beginning of new menstruation, the volume of medicinal decoction consumed must be reduced until it is completely discontinued. If pregnancy does not occur, it is recommended to take a break during menstruation.
To prepare the decoction you need 1 tbsp. l. pour a glass of boiling water over the herbs and leave for four hours, preferably in a thermos or any other closed container. It is best to store in a cool place and drink 1 tbsp. l. every 6 hours.
Also, fresh or canned pineapple helps to enlarge the endometrium.
Normal endometrial thickness in early pregnancy
For egg implantation, the thickness of the endometrium must be at least 7 mm. And directly during pregnancy, the thickness of the endometrium will be the same as it was during implantation (since the growth of the endometrium stops due to changes occurring in the body).
Proper nutrition
To return the normal thickness of the mucous membrane, proper and nutritious nutrition is necessary. Products high in vitamins E and A and salicylates are mandatory. The diet should include vegetables, fatty fish, berries, apples, honey, various dried fruits, cinnamon, paprika, thyme. The amount of tea and coffee should be limited, as well as excessively fatty, sweet foods, fast food should be excluded altogether.
Along with a nutritious diet, we must not forget about maintaining physical fitness. You should walk more, dance, play various sports, and visit swimming pools.
Why is thin endometrium dangerous for the female body?
A fully developed endometrium is necessary for normal conception and a healthy pregnancy. Hypoplasia is one of the most common causes of infertility. Even if a woman with a thin endometrium manages to become pregnant, early miscarriages in this case are quite common. In pregnant women with hypoplasia, labor is more pronounced, labor is much weaker and there is a risk of heavy bleeding during and after childbirth. In some cases, the only way for women with this diagnosis to find the joy of motherhood is IVF.
If thin endometrium is diagnosed in a pregnant woman, it is necessary to provide her with maximum rest. Often expectant mothers with this diagnosis are admitted to hospital care in the early stages and remain there for quite a long time. A woman has to take care of herself, lead a sedentary lifestyle and regularly take medications prescribed by a specialist to maintain pregnancy.
Thin endometrium and pregnancy
When planning pregnancy, the thickness of the endometrium is decisive; too thin a layer makes the attachment of the egg simply impossible. It should be taken into account that the maximum thickness of the mucosa is observed on days 24-27 of the cycle, this is 1-1.3 cm in a normal situation. For conception, 0.9-1.3 cm is enough; this thickness is achieved at approximately 11-14 days. But if there are problems with the endometrium, its thickness will be the same as in the early stages of the cycle, that is, within 0.3-0.5 mm.
What are the dangers of this during pregnancy? In the first trimester, spontaneous miscarriage is likely, which may be accompanied by severe uterine bleeding. It is also a big question whether it is even possible to get pregnant. Even after a successful IVF procedure, a woman is prescribed treatment to return the thickness of the endometrium to normal. Usually these are folk methods that are safe for pregnant women, vitamin complexes and some physiotherapy measures. Therefore, when deciding whether pregnancy can occur and what measures should be taken, you must immediately contact a specialist who will conduct an examination and prescribe a treatment regimen before IVF and during the most dangerous first trimester.
Structure and functions of the endometrium
Endometrium
– mucous membrane of the uterine cavity. How quickly and successfully the fertilized one can establish itself depends on its thickness, integrity and functionality.
The structure of the endometrium includes:
- epithelium - the cellular layer lining the uterine cavity;
- capillaries, glandular ducts;
- stroma - supporting connective tissue that produces collagen during menstruation.
The main function of the endometrium is to create conditions favorable for the consolidation and normal development of the embryo in the uterine cavity. Normally, after this the mucous membrane begins to change: its blood supply and secretory functions increase. Subsequently, endometrial vessels take part in. Thanks to them, the developing fetus receives the right amount of oxygen and all the substances necessary for development.
Another function of the endometrium is a barrier. It prevents the development of adhesions: it does not allow the walls of the uterus to stick together, despite their constant contact.
The likelihood of pregnancy depends on the thickness and structure of the endometrium, as well as the maturity of the glandular layer. The functionality of the mucous membrane is determined by the presence of estradiol, a hormone produced by follicles. During this process, the endometrium matures and further produces progesterone.
IVF for thin endometrium
In some cases, it may not bring results; the only solution for thin endometrium is IVF. This is an artificial insemination procedure that may require a long time and compliance with hormonal therapy. But in most cases, women manage to get pregnant normally, although the doctor must monitor the patient all the time before giving birth.
The endometrium is the upper mucous layer lining the uterus. A characteristic feature of the endometrium is the abundance of blood vessels. The endometrium is extremely sensitive to the amount of female hormones in the body, the lack of which leads to its thinning.
The main function of the endometrium is to create favorable conditions for the engraftment of the blastocyst in the uterus. In addition, the thickness of the endometrium is also extremely important for women’s health.
It is considered normal to gradually increase the size of the endometrium from 0.5 centimeters on the first day of the cycle, and to 1-1.3 centimeters by the 27th day of the cycle.
Naturally, for a woman’s normal healthy sex life, the size of the endometrium is not significant, but for women, these values are extremely important, since the possibility of pregnancy itself directly depends on them.
In a physically healthy woman who is in the last phase of the menstrual cycle, the size of the endometrium increases, which leads to its enrichment with iron and greater blood flow, and increases the chances of rapid implantation of the embryo.
Women whose endometrium is not thick enough cannot become pregnant for a long time and are forced to undergo a long course of treatment.
Cause of thin endometrium
The main and most common cause of thin endometrium in modern living conditions is long-term. Being interested in why the endometrium is thin in a particular woman, the doctor will definitely send her to check the level of hormones in the body.
The second most common cause of thin endometrium is considered to be a violation of the uterine mucosa, which occurred as a result of curettage after an abortion and other operations on the uterus.
In addition, some women have a congenital circulatory disorder in the uterus, which also affects the thickness of the endometrium.
The first symptoms of possible problems with the endometrium
The thickness of the endometrial layer can be determined with reliable accuracy solely by ultrasound of the uterus, but each woman can make a preliminary diagnosis for herself, guided by the following signs and symptoms:
- Menstrual irregularities. Irregular, painful periods almost always indicate a problem with the endometrium;
- in a healthy woman they are quite abundant. The lack of a sufficient amount of blood during menstruation should make you think and lead you to the gynecological office for examination.
Consequences of thin endometrium
For a non-pregnant woman, it does not matter significantly how thick her endometrial layer is, but for a pregnant woman this circumstance is extremely important, since the main and most unpleasant consequence of a thin endometrium is spontaneous miscarriage in the early stages of pregnancy.
In addition, thin endometrium can cause severe uterine bleeding during a medical or conventional abortion.
How to prevent the risk of thin endometrium
Thin endometrium in women almost always poses a threat to future pregnancy, which is why gynecologists advise, before thinking about children, to undergo a small examination to determine the thickness of the endometrium. Statistics show that thin endometrium is observed today in every 3rd woman. This problem has long acquired global proportions, so all the means of modern medicine are being used to solve it. Thin endometrium and pregnancy are inextricably linked.
Treatment of thin endometrium
Let's take a closer look at what to do with thin endometrium:
- First of all, undergo an examination and determine the reason why the endometrium is thin;
- Determine together with your doctor how to treat thin endometrium;
- To identify the possible impact of thin endometrium on pregnancy.
The course of treatment for thin endometrium is very complex and lengthy, as it involves restoring the normal functioning of the entire reproductive system of a woman by taking various hormonal medications, as well as homeopathic remedies. In the fight to increase the size of the endometrium, the following treatment methods are used:
— physiotherapeutic;
- medicinal;
- surgical.
Traditional medicine in combination with special physiotherapeutic procedures aimed at increasing blood flow to the pelvis and, accordingly, increasing the size of the endometrium are very effective in the fight against thin endometrium. It is considered especially useful for thin endometrium.
Naturally, the use of any medications, including herbal ones, should be strictly under the supervision of a doctor and on his recommendation. There is no hope for a complete cure after using infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs, but they are still good to use as a supplement to basic medical procedures.
It should be noted that treatment of thin endometrium is not possible in all cases; for example, if congenital or acquired uterine hypoplasia is detected, a woman is physically unable to become pregnant naturally. For such women, the only solution is artificial insemination, which involves implanting an already formed and fertilized egg into the uterus. Thus, thin endometrium and IVF are directly related.
So, the endometrium is an extremely important component of the lining of the uterus, without the proper thickness of which a woman will not be able to get pregnant normally and bear a healthy child. When planning a pregnancy, you should definitely check the thickness of the endometrium; it should not be less than 7 millimeters. Any deviations from this figure indicate the need to begin immediate treatment.
Content
Many women of reproductive age are faced with the problem of infertility, which appears due to a thin endometrium. This is the inner layer located in the uterine cavity.
The uterus is considered a unique organ that allows a woman to carry out the function of childbearing. The uterus includes the following structural parts:
- body;
- neck.
The body of the uterus consists of several layers.
- The outside of the uterus is covered with a serous membrane.
- The myometrium is a muscular layer that allows the uterus to stretch during fetal growth and contract during menstruation and childbirth.
- The inner layer or lining of the uterus, the endometrium, allows for implantation of the fertilized egg.
The endometrium is supplied with blood vessels. Under the influence of hormones during the cycle, the functional layer of the endometrium grows, preparing for the implantation of a fertilized egg. If conception does not occur, under the influence of sex steroids, the functional layer is rejected and leaves the uterine cavity in the form of menstruation.
Any fluctuations in hormonal levels lead to changes in the thickness of the endometrium, which can become either thin or thick. Thin endometrium causes infertility and miscarriage.
The lower limit of normal endometrial thickness for implantation of the fertilized egg is 7 mm. This pathology occurs quite often among women in the reproductive cycle.
Causes of insufficient development of the endometrium
Poor development of the uterine lining can occur for a number of reasons.
Endocrine pathologies.
The endometrium is thin as a result of a lack of estrogen in the body. The reasons for the decrease in their level are:
- disruption of the pituitary gland, lack of FSH hormone, which stimulates the production of estrogen in ovarian cells;
- hyperthyroidism (excessive production of thyroid hormones);
- increased content of androgens in a woman’s body;
- unhealthy diet (drastic weight loss);
- long-term depression;
- smoking;
- uncontrolled use of progesterone drugs.
Poor circulation in the uterus
. Insufficient blood supply leads to a lack of oxygen and nutrients necessary for the development of epithelial cells. The cause of the disorder may be vascular and heart diseases, improper development or damage to the vascular network, as well as compression of the uterine vessels by tumors.
Underdevelopment of the uterus.
If its volume is too small, then the full development of the mucosa becomes impossible.
Damage to the basal layer.
The formation of a new endometrium occurs from the basal cells of its lower layer, adjacent to the wall of the uterus and having a constant thickness. If the basal layer is partially removed during curettage, abortion or diagnostic procedures, then the normal development of the functional layer will become impossible, and the endometrium will be thin.
Inflammatory and infectious processes in the uterus.
They cause damage to the structure of the basal layer, the formation of scars and adhesions on it, which impede the normal development of the new endometrial layer.
Causes
Gynecologists note that the thickness of the endometrium varies on different days of the cycle. At the beginning of the cycle, the endometrium is quite thin, its thickness ranges from 5 to 9 mm. Before menstruation, the endometrium is normally not thin. Thickness is up to 1.3 cm.
The endometrium is considered thin if its thickness does not exceed 5 mm. Gynecologists call thin endometrium hypoplasia or thinning of the inner layer of the uterus.
There are many reasons for thin endometrium. Among the main causes of thin endometrium, experts identify:
- hormonal disorders;
- endocrine pathologies;
- violation of the blood supply to the uterus, which is congenital;
- inflammatory pathologies in chronic form;
- PCOS;
- underdevelopment of the uterus;
- repeated use of drugs related to emergency contraception, for example, Postinor.
Surgical interventions negatively affect the inner layer of the uterus, causing the appearance of thin endometrium. Curettage is extremely undesirable, especially as part of a surgical termination of pregnancy. It should be remembered that abortions can cause thin endometrium.
Thin endometrium is often found in girls with underdeveloped uterus. In such cases, a thin endometrium is combined with a narrow pelvis, short stature, late onset of menstruation and small volume of mammary glands.
Enlargement of the endometrium with the help of medications
In order to grow the endometrium in a short time, it is necessary to use medications. Their prescribing should be done exclusively by a doctor, since only he will be able to select the most effective drugs and correctly draw up a treatment regimen.
Since the growth of the endometrium occurs with the help of an increase in the amount of estradiol, hormonal drugs can quickly cope with the problem. The regimen for taking them is determined by the phases of the cycle.
In the first half, injections of Divigel, Estradiol, Femoston and Proginova tablets are prescribed. These medications increase the thickness of the endometrium by increasing blood circulation and gland activity.
In the second phase, it is necessary to take Duphaston and Utrozhestan. These drugs promote the formation and maturation of the endometrium. Both contain large amounts of progesterone, a hormone necessary for the implantation of the embryo in the uterine cavity and a successful pregnancy.
In addition to hormonal medications, the doctor may prescribe medications necessary to treat diseases that cause thin endometrium. The main objectives of such therapy are the restoration of damaged mucous membranes and the elimination of infectious and inflammatory processes in the uterus. If a woman is taking birth control pills, they will need to be discontinued.
Clinical picture
There are no specific signs of such a pathology as thin endometrium. Many women, before planning a pregnancy, do not pay attention to some manifestations and are not aware of the presence of a thin endometrium.
As a rule, women are diagnosed with “thin endometrium” when planning pregnancy. Usually the diagnosis is made when a specialist is looking for the reason why pregnancy does not occur. In some cases, thin endometrium causes miscarriage.
Signs of thin endometrium include:
- scanty periods;
- cycle disorders;
- painful periods;
- clots in menstrual flow;
- acyclic menstrual flow;
- bleeding.
If symptoms of hormonal disorders occur, you should visit a gynecologist and undergo an examination.
Treatment to build up a thin functional layer of the endometrium
To increase the thin endometrium, hormonal drugs of various effects are used in treatment. Estradiol preparations (Divigel, Dermestril, Progynova). They are taken in the form of tablets for oral administration or treated with vaginal suppositories. Such drugs stimulate cell division and accelerated growth of the mucous membrane.
Some homeopathic remedies, such as hormel drops, help enhance the production of estrogen. Drugs (menopur and others) are used that stimulate ovulation and improve the production of gonadotropic hormones of the pituitary gland (they regulate the functioning of the ovaries).
Warning:
All of these remedies have serious contraindications. They can only be used as prescribed by a doctor. Any independent use of hormonal drugs in order to increase the thin endometrium can not only have the opposite effect, but also lead to severe cycle disorders, the formation of tumors in the uterus and mammary glands, and disturbances in blood composition.
Physiotherapy methods such as electrical stimulation, acupuncture, special massage and therapeutic exercises are used to improve blood circulation. General strengthening treatment with vitamins and immunomodulators is carried out. If necessary, anti-inflammatory therapy with antibiotics is carried out. Sometimes, in order to remove tumors in the uterus and restore normal development of the mucous membrane, it is necessary to perform a procedure of curettage of the uterine cavity.
Folk remedies based on medicinal plants (hogweed, red brush and others) are also used for treatment. They are used only after consultation with a doctor.
Thin endometrium
- is one of the reasons preventing natural conception. Its thickness is determined by several factors, including hormonal changes. It becomes most functional during the premenstrual period. The question of how to grow the endometrium is most relevant for women planning to become mothers.
Probability of pregnancy
Pathology of the internal uterine layer has a negative impact on the likelihood of pregnancy. Hypoplasia prevents the fertilized egg from attaching. However, in gynecological practice, there are cases of conception with a thickness of the inner layer of 4 mm. When pregnancy occurs, there is a risk of spontaneous abortion, toxicosis, uterine bleeding, and weak labor.
After conception occurs, the inner layer gradually increases. This allows the doctor to suspect pregnancy even in the absence of visualization of the fertilized egg. During short-term pregnancy, the thickness of the inner layer is subject to close influence by the gynecologist. With pathologies such as hypoplasia, miscarriage may occur. In order to prolong pregnancy and eliminate pathology, special medications are used.
The IVF procedure is not performed for hypoplasia, since the percentage of successful implantation is extremely low. Initially, the causes of pathology and hypoplasia are eliminated, and then the IVF procedure is performed.
Uterine prolapse during pregnancy from A to Z
The uterus is the hollow muscular reproductive organ of a woman in the pelvis. With each pregnancy and childbirth, the ligaments that hold the uterus in its normal position weaken. Women who have given birth multiple times are often diagnosed with uterine prolapse during pregnancy.
Uterine prolapse during pregnancy symptoms
Uterine prolapse and pregnancy
If the uterus is lower than it should be during pregnancy, this can have serious consequences. The risk of miscarriage increases 10-20 times. With a prolapsed uterus, pregnancy fading and intrauterine fetal death often occur. Almost every such pregnancy ends in premature birth. Prolapse of the uterine wall or cervical prolapse in early pregnancy has a worse prognosis than its onset in the last trimester. Visits to the gynecologist should not be neglected; it is important to follow all his instructions.
Childbirth with a prolapsed uterus
Childbirth with cervical prolapse is possible, but the postpartum period is often accompanied by complications. A woman is often hospitalized for a long period of time in order to maintain pregnancy during uterine prolapse and to determine management tactics.
Due to improper blood supply and location, the risk of endometritis and abscess formation increases. If the prolapsed uterus becomes infected, it will have to be amputated or extirpated.
Treatment
With a slight prolapse, the birth of a baby is possible, but the woman will have to wear a bandage all the time. If there is a pronounced downward displacement of the uterus, starting from 3-4 months of pregnancy, strict bed rest must be observed.
A woman should not gain much weight during pregnancy. It is necessary to limit the amount of food taken, otherwise the weight of the fetus may go beyond the normal range.
To make pregnancy easier and strengthen the pelvic muscles, you need to do special gymnastics. Most often recommended
Source
Diagnosis and treatment
Detection of a pathological condition is possible through various research methods. The doctor carefully examines the patient’s complaints and medical history, and then prescribes an examination:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs in different phases of the cycle;
- hormonal diagnostics;
- blood and urine tests;
- aspiration biopsy.
Diagnostics allows us to determine hypoplasia and the causes of its occurrence. Treatment is prescribed in accordance with the diagnostic results.
In a significant number of cases, hypoplasia is caused by hormonal reasons. Pregnant patients are recommended to take appropriate hormonal medications, in particular those containing progesterone.
If the cause of the pathology is an inflammatory process, it is advisable to prescribe drugs to eliminate the source of infection. Sometimes there is a need for surgical intervention. The patient undergoes curettage and is prescribed hormonal therapy. Surgical intervention promotes the process of renewal of the mucous membrane of the uterine body, allowing it to normalize its thickness.
If the cause of the pathological condition is circulatory disorders, patients are recommended physiotherapy, massage, hirudotherapy, therapeutic exercises and acupuncture.
Drug therapy
In the treatment of disorders of the thickness of the inner layer of the uterine body, drug therapy is widely used. The basis of drug treatment is hormonal drugs and other agents.
- Duphaston. The drug is an artificial progesterone, which prepares the uterus for conception, eliminates increased tone, and prevents abruption. It is advisable to use duphaston as prescribed by a doctor.
- Melsmon. This is a placenta-based drug that is used to normalize the cycle and eliminate inflammation. The medicine is not used during pregnancy, endocrine disorders, hypertension.
- Actovegin. The drug improves blood circulation in the genital organs, which helps eliminate hypoplasia. During pregnancy, the drug begins to be taken from the sixteenth week.
- Gormel. This is a homeopathic remedy that is used to activate the production of estrogen. The drug contains natural ingredients. Due to its alcohol content, Hormel is not used during pregnancy. The drug should not be used if you have kidney failure or are planning pregnancy.
- Estradiol preparations are prescribed in the first phase of the cycle to build up the endometrium, since its hypoplasia is a consequence of low estrogen production. They use both tablets (Proginova) and local ones (Divigel, Ovestin).
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment have a fairly beneficial effect on the condition of the mucous membrane. As part of complex treatment, they have a gentle effect. The main advantage of the procedures is the absence of pronounced side effects and a minimum of contraindications.
For hypoplasia, the following physiotherapeutic methods are used:
- magnetic therapy;
- ultraviolet;
- ultrasound;
- mud baths;
- massage.
Physical exercise, walks in the fresh air and proper balanced nutrition are useful.
Diet
It is known that poor nutrition often causes various diseases. Insufficient intake of nutrients into the body is one of the causes of hypoplasia.
Gynecologists note that the diet must necessarily include foods rich in proteins and vitamins A and E. Fatty fish, vegetables, fruits and berries are very useful.
Eating dried fruits, honey, and red wine has a good effect. Sweet and fatty foods, processed foods, and strong drinks should be limited due to their negative impact on the body.
Proper nutrition should be combined with moderate physical activity.
Every woman suffering from infertility has her own treatment history, her own causes of the disease, but everyone has the same dream. Gynecologists and pharmacists are constantly searching for new drugs and methods of treating this disease. After all, the main thing is not only to make the correct diagnosis, but also to select individual treatment, the result of which will be the birth of a healthy baby.
Thin endometrium - what to do?
A common cause of female infertility is a thin layer of the endometrium, and treatment in this case can be carried out with hormonal medications, pseudohormones, and herbal decoctions. Going towards your goal will not be easy, but getting there is quite possible.
How to treat thin endometrium with herbs?
Many women refuse to treat thin endometrium hormonally, since treatment with folk remedies also helps with this problem. Sage gives very good results for follicles when the endometrium is thin; you need to brew 1 teaspoon in a glass of water and drink it throughout the day in the first phase of the cycle. The boron uterus also helps well with thin endometrium, being a pseudohormone that transforms in a woman’s body. It also has an anti-inflammatory effect. Modern medicine also offers homeopathic drops “Tazalok” to solve this problem, which normalize the menstrual cycle and regulate the synthesis of endogenous gonadotropic hormones. This drug has virtually no side effects.
How to increase thin endometrium with the help of drugs?
The endometrium grows within 14 days, its growth is stimulated with estradiol drugs. To build up the endometrium, doctors prescribe the drug Proginova, Estradiol or femoston in the first phase of the cycle; in the second phase they recommend taking duphaston. With thin endometrium, Duphaston helps form its structure, acts as synthetic progesterone - “accompanies” the growing endometrium, it should be taken in the second half of the cycle. All of these drugs are synthetic and have many contraindications, so their use should be discussed with your doctor and the risk assessed yourself.
Often, thin endometrium is detected after taking OCs, but here everything depends on the woman’s body. Abandoning oral contraceptives and taking Regulon for two months can lead to positive results in restoring the growth of optimal endometrium.
Treatment of the disease
If such a pathology is detected, treatment should be prescribed immediately. The disease is detected through an ultrasound procedure (ultrasound), where the maturity and thickness of the endometrium is determined. Its permissible values must be at least 7 mm, only in this case pregnancy can occur. It is quite possible to get pregnant with a thinner layer of the endometrium, but the thinner it is, the lower the chance.
Productive treatment can be: medication (hormonal therapy) and surgery (direct removal of the endometrial layer). During surgery, hormonal treatment is also used to eliminate internal imbalances in the female body.
It is almost impossible to identify thin endometrium on your own, because this type of pathology is completely asymptomatic, only in rare cases accompanied by bleeding. That is why it is necessary to systematically prevent this disease. To do this, you need to carefully monitor your health, promptly eliminate any irregularities in the menstrual cycle, intensively fight obesity (if necessary), restore your emotional background and try to minimize stress. It is also recommended to conduct a routine ultrasound of the pelvic organs, and if there is the slightest concern, seek advice from a qualified specialist. In this way, the progression of the disease can be prevented.
A successful pregnancy is possible only if the endometrium of the uterus has a certain thickness sufficient to hold the embryo in it. When its development is insufficient, a woman experiences menstrual disorders, infertility, or problems with bearing a fetus. If the endometrium is too thin, treatment is required to regulate the hormonal levels in the body, since its disruption is the main cause of this pathology. An examination helps determine the presence of a deviation from the norm.
Content:
Extension methods
How to quickly grow the endometrium? After finding out the reasons for the underdeveloped endometrium, the doctor makes a decision on how to improve the endometrium: what medications need to be prescribed, in what dosages, recommend physical exercises or physiotherapeutic procedures, etc. Pharmacological drugs prescribed for insufficient development of the endometrium:
- Hormonal drugs based on estradiol (Divigel).
- A medicine containing salicyl (Aspirin).
- Hormonal drugs that activate estrogen production (Gormel).
- Hormonal medications containing synthesized progesterone help improve the process of endometrial maturation (Duphaston, Utrozhestan).
- Drinking sage decoction.
- The use of tinctures of boron uterus.
Alternative medicine methods that help improve blood circulation in the pelvic organs and improve the process of endometrial growth:
- Acupressure.
- Acupuncture is the impact on certain points of the body with special needles.
- Hirudotherapy is a treatment method that involves applying medicinal leeches to certain areas of the body.
A woman who wants to get pregnant quickly is interested in how quickly the endometrium can grow. The answer depends on many factors: on the causes that caused the disorder, on the degree of development of the pathological process. The main thing is to contact a competent specialist and follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
The endometrium is sensitive to the hormonal background of a woman, and it is this feature that affects its size. The endometrium becomes noticeably thicker and is enriched with glands, which provide improved blood supply to the tissue in the last, premenstrual phase of the cycle. This ensures a successful pregnancy – that is, it ensures the possibility of conception.
Conception with abnormalities
There is confirmed data in which pregnancy was formed with an endometrial volume of four millimeters, with normal gestation and subsequent childbirth. Experts note that with such indicators, the likelihood of the formation of obstetric pathology increases, leading to complications of pregnancy or its termination.
Thick endometrium
Hyperplasia is characterized by thickening of the surface layer of the mucous membrane up to 26 mm, changes in its standard structure. The pathology interferes with the strengthening of the egg in the wall of the uterus, and the embryo is not able to develop normally.
Thin endometrium
Hypoplasia prevents conception, and when it occurs, it does not allow the egg to attach to the wall of the organ.
The endometrium is the mucous layer of the uterus that lines its cavity, has a complex structure and an abundant vascular network, which grows during pregnancy. The function of the endometrium is reliable implantation of the embryo in the uterus, but this is only possible with normal thickness of the mucosal layer.
- Table of contents
If the endometrium is thin, then the blastocyst will literally have nothing to “catch onto” and will have nowhere to receive nutrients for its growth.
Until the placenta is formed, the embryo will be nourished and supplied with blood from the endometrium. If pregnancy does not occur, the functional layer is rejected with the onset of menstruation and the egg is released, which dies.
Treatment
Thin endometrium is a condition that requires mandatory treatment, which can be conservative or surgical. If the cause of the disease is a hormonal imbalance, the patient is prescribed therapy with drugs containing progesterone. Drug treatment of thin endometrium is a rather lengthy process that requires an average of 1-3 months, depending on the individual characteristics of the woman’s body. Along with taking medications, the patient is recommended to undergo physiotherapeutic procedures and therapeutic exercises. In cases where the disease was caused by other pathologies of the pelvic organs, it is imperative to treat them.
If the development of hypoplasia is caused by more serious factors, then surgical intervention will be required, which involves surgical removal of the thin inner layer of the endometrium. Next, you will need to ensure an increase in the required thickness of the inner membrane using intensive hormone therapy.
Do not be afraid of taking hormones; only first-generation drugs had serious side effects. If you take medications correctly and follow all doctor's recommendations, you can achieve a positive result. Unfortunately, exact statistics on how many women managed to become pregnant after treatment are unknown, since auxiliary factors such as age, lifestyle, and diseases of the reproductive system play an important role in this process. Healthy young women without bad habits, abortions, or a history of serious gynecological diseases have a greater chance of conceiving a child in the first months after hormone therapy.
Traditional medicine is also effective in treating thin endometrium. Doctors recommend taking a decoction of sage three times a day for the entire duration of treatment. Only with a responsible and comprehensive approach will you be able to achieve a positive result and get rid of such an unpleasant diagnosis as thin endometrium.
Symptoms and diagnosis of the endometrial layer
The pathology has no obvious signs and is manifested by pain and scanty menstrual flow, cyclicity disorders, and the presence of blood clots. When seeking professional help, the patient undergoes a diagnosis:
- Ultrasound;
- taking samples for histological examination.
Drug therapy
Prescribed by the attending physician based on the examination data obtained.
Products for external use
To increase endometrial volume, it is recommended to use:
The drugs are made in the form of a gel or suppositories and are classified as estrogen drugs.
Preparations for oral administration
Patients can be prescribed combined oral contraceptives - in order to stabilize hormonal metabolism, medications containing progesterone - Duphaston, Utrozhestan.
Physiotherapy
Common physiotherapeutic procedures to combat thinning endometrium are:
- magnetotherapy;
- ultrasonic exposure;
- massage sessions;
- mud therapy.
It is recommended to undergo them on the first day after the end of menstruation. Manipulation is included in complex therapy.
Traditional methods
Home methods for combating anomalies are widely used:
- Infusion of sage - take a glass of fresh boiling water per teaspoon of plant material and leave for 2-3 hours. The finished medicine is used in the first half of the cycle for 4 months.
- Infusion of boron uterus - pharmacy bags are filled with boiling water, wait 25 minutes and used daily.
Lifestyle
Doctors advise switching to a specialized diet, taking walks in the fresh air more often, and doing therapeutic exercises to the best of your ability. It is necessary to exclude all harmful influences - alcohol, cigarettes.
Folk recipes
How to grow the endometrium using folk remedies? For these purposes, it is recommended to use medicinal herbs that normalize hormonal levels, promote the production of certain hormones, and help improve the condition of the uterine mucosa. Sage, hops, clover, lovage, mistletoe have a positive effect on the endometrium.
The simplest and most effective folk remedies for a poor, thinned mucous layer:
- Sage decoction for endometrial growth.
Plant hormones stimulate follicular activity and help increase estrogen levels. Sage for growing the endometrium is easy to prepare. It is necessary to pour 1 tbsp. a spoonful of chopped herbs with a glass of boiling water, boil and let it brew for about 15 minutes. How to drink sage correctly? It is recommended to consume the filtered decoction 4 times a day. The treatment course begins immediately after the end of the critical days and continues until the ovulatory period.
- Sparrow decoction
improves blood circulation, microcirculation, and helps restore mucous membranes. Art. pour a spoonful of herbs into a glass of boiling water and leave for 3 hours. Drink the prepared decoction in small sips, 3 times a day, a quarter of a glass. - Infusion of raspberry leaves.
Raspberry leaves are useful for the endometrium because they include estrogen, which stimulates ovarian functions. Brew the leaves with boiling water and drink instead of tea. Most women who built up the mucous layer using this product were satisfied with the results.
Enlargement of the endometrium using traditional recipes is recommended to be discussed with your doctor. Although medicinal plants have fewer contraindications and side effects, they have a certain effect on the hormonal system, which does not always give a positive effect.
Causes and symptoms
The top layer of the endometrium is functional, it is the one that is shed during menstruation, the bottom is basal, it serves as the basis for the growth of a new layer for the next cycle. The thickness of the uterine mucosa develops gradually. If the required amount of epithelium does not grow, then a thin layer of endometrium is formed, which in most cases does not allow pregnancy.
What is the cause of endometrial thinning? The main provoking factors are identified:
- hormonal imbalance, which may be caused by diseases of the thyroid gland, disorders in the hypothalamic-pituitary system, pathologies of other endocrine glands that affect the production of estrogen;
- PCOS;
- vascular diseases leading to disruption of the blood supply to the uterus;
- chronic infectious lesions of the genitourinary organs, resulting in the formation of scars and adhesions;
- endometritis – 50% of women with endometritis suffer from infertility;
- hypoplasia (underdevelopment) of the uterus;
- frequent surgical procedures, use of a uterine contraceptive, leading to mechanical damage to the endometrium;
- tumors of the pelvic organs, compressing the uterus, tumors of the gonads, as a result of which the production of hormones is disrupted;
- chromosomal disorders leading to deviations in the development of the genital organs;
- mental disorders, depression caused by frequent stress;
- regular use of emergency contraception.
If the thin functional layer is of congenital origin, then such girls are delayed in sexual development, menarche occurs late (after 16 years of age), breast underdevelopment, a narrow pelvis, and short stature are observed. With a thin endometrium, there are no specific symptoms, so a woman is unlikely to be able to identify the disease on her own.
The following signs may indirectly indicate a thin endometrium:
- failure of the menstrual cycle is the most common symptom, expressed in scanty periods, pain, uterine bleeding, shortening of the cycle, discharge outside the cycle;
- spontaneous pregnancy loss in the first trimester;
- decreased libido;
- inability to get pregnant.
The symptoms of thin endometrium depend on the factors that caused the disease. Thus, with a hormonal imbalance, a woman will be bothered by mood swings, depression, headaches, weather dependence, increased blood pressure, poor sleep, deterioration of the skin and appearance in general.
What factors related to the endometrium affect pregnancy?
Thickness changes during the menstrual cycle, but this value also depends on factors such as age and the woman’s health. Changes in thickness and structure are regulated by the woman’s hormonal system, namely the hormone estradiol. There are standard indicators of what the thickness and structure of the endometrium should be at a certain age, and a certain phase of the cycle. These indicators ensure successful attachment of the fetus.
Endometrial indicators in different phases of the menstrual cycle:
- 5-7 days - 3-6 mm, homogeneous structure;
- 8-10 - 5-10 mm, thickening of the functional layer;
- 11-14 - 7-14 mm, ;
- 15-18 - 10-16 mm;
- 19-23 - 14 mm or more;
- 25-28 (on the eve of menstrual bleeding) - about 12 mm.
When pregnancy occurs, the endometrium thickens. Reaching 20 mm by 4-5 weeks, then transforms into the placenta. During menopause, hormonal changes in the body occur, in particular, the endometrium begins to atrophy, its thickness is about 3-4 mm.
Vitamins C and E, salicyl improve the process of endometrial maturation, so sufficient intake of them into a woman’s body is an important condition for treatment. To do this, it is recommended to include the following foods in your diet: citrus fruits, fresh vegetables, milk, raisins, grapes, prunes, ginger, dill. It is also possible to prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures and exercise. Physiotherapeutic procedures include: laser therapy, thermotherapy, alternating current treatment. In some cases, traditional medicine has an effective effect.
If it is insufficiently thick or hypoplastic, the fertilized egg cannot attach to the wall of the uterus, which causes infertility or miscarriage in women. In such cases, endometrial augmentation may be necessary. Causes of impaired maturation of the lining mucosa:
- In case of disturbances in the hormonal system.
- Congenital uterine hypoplasia is a discrepancy between the size of the uterus and the woman’s age.
- The presence of inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs.
- Insufficient blood supply to the uterus.
- After curettage of the endometrium.
- Curettage is a procedure that is prescribed for miscarriages, for the purpose of artificial termination of pregnancy, to obtain a sample of the endometrium (diagnostic purposes), in the presence of polyps in the uterus, endometrial hyperplasia (thickening) and other diseases.
- Consequences of surgery.
Drug therapy
If the endometrium does not grow, the woman needs to undergo a medical examination to identify the reasons that provoke low levels of layer thickness. In the treatment of identified pathologies, physiotherapeutic procedures and medications are used to eliminate the underlying disease.
Direct preparation for conception involves a course of drug therapy. For these purposes, drugs are prescribed to increase the thickness of the endometrial layer:
- Products that promote normal hormonal balance. The use of Divigel for endometrial growth has a good effect. This drug includes estradiol, which increases the level of progesterone, which increases the mucous membrane of the uterine layer.
- Utrozhestan
is a natural drug containing the hormone progesterone. Utrozhestan promotes optimal maturation of the uterine mucosa, improves its structural and functional state. Utrozhestan has earned numerous positive reviews from patients and doctors. - Hormel drops
are a hormonal remedy. Drops increase levels of the hormone estrogen and help grow the uterine mucosa. The use of drops may be recommended for hormonal disorders if there is no ovulation. - Curantil
is an effective drug that increases the processes of microcirculation and blood circulation, and increases the size of the endometrial layer. Curantil is a very effective drug, but it has a wide range of contraindications and possible adverse reactions. Before taking Curantil, you should consult your doctor. - Proginova for growing the endometrium
- improves uterine blood supply. This product includes estrogens and estradiol, which increase the density and quality of the mucous layer.
Which drug to choose to accelerate the growth of the uterine inner layer is decided by the doctor individually. Among the safest drugs that have a minimal range of contraindications and possible adverse reactions are Utrozhestan, Duphaston, Curantil.
How to quickly grow the endometrium without the use of medications? Traditional medicine, which has many safe recipes, can be a good solution.
Thin endometrium - symptoms indicating pathology
If infertility or early termination of pregnancy has been diagnosed, especially after illnesses or gynecological procedures, it is imperative to monitor the condition of the endometrium. This is done using an ultrasound of the uterus.
Symptoms indicating a possible problem with the thickness and condition of the endometrium:
- scanty infrequent menstruation;
- menstrual irregularities - amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea with displacement, loss or absence of menstruation;
- previous abortions, endometritis, adnexitis, surgical interventions and gynecological procedures;
- habitual early pregnancy loss.