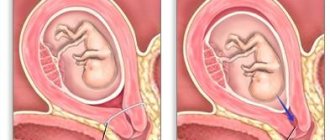
The most important point in the readiness of the female body for childbirth is the degree of maturity of the cervix, since if it is immature and unprepared, labor may not begin or surgical intervention may be required.
What does “naturally prepare the cervix for childbirth” mean? This process occurs thanks to special hormones - progesterone, the level of which decreases, and estrogens, the amount of which, accordingly, increases. The latter, together with prostaglandins (representatives of a group of hormone-like substances), are responsible for softening the cervix, which is necessary for childbirth to be easy, without injuring the baby and causing excessive blood loss to the mother. Prostaglandins are found in almost all organs of the human body, and they are also found in sperm. Therefore, if you continue to be sexually active during pregnancy, your body receives an additional external stimulus for normal cervical ripening.
How is the degree of maturity of the cervix for childbirth determined?
The degree of maturity of the cervix is determined using a special scale, taking into account the following four signs:
- cervical length;
- its consistency;
- patency of the cervical canal;
- its location relative to the pelvic wire line.
Then each feature is “assigned” from 0 to 2 points, the sum of which determines the degree of maturity of the cervix. Namely: a uterus that “scores” 5-6 points is considered mature, a uterus with 3-4 points is considered insufficiently mature, and a uterus with 0-2 points is considered immature. It should be understood that this assessment is subjective and depends on the degree of qualification and experience of the doctor.
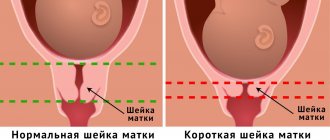
At the 38th week of pregnancy, a woman should be examined in the maternity hospital by a doctor to determine whether the cervix is ready for childbirth. This happens by examining the vagina. Based on the results obtained, the approximate due date is determined. Normally, the cervix before contractions should be soft, slightly shortened and located in the center of the pelvis.
If your pregnancy is already 38-39 weeks, and the doctor assessed the maturity of the cervix as 0-2 points, do not be upset - you still have time for it to fully ripen (sometimes this happens a day or two before birth).
Assessing the readiness of a woman’s body for childbirth.
⇐ PreviousPage 27 of 82Next ⇒In the last 1.5-2 weeks. Pregnancy ends the preparation of the woman’s body for the upcoming birth. This preparation covers all organs and systems, starting with the centers of higher nervous activity and ending with the executive organ - the uterus. The dominant of pregnancy is replaced by the dominant of childbirth, and the uterus turns from a receptacle for the fetus into an expelling organ.
The readiness of a woman’s body for childbirth is characterized by a number of signs, the appearance of which indicates the possibility of labor beginning in the near future. The most pronounced changes occur in the genitals. Unlike assessing the state of the central nervous system or hormonal status, which requires the use of special, usually complex, research methods, diagnosis of the condition of the reproductive system is carried out using conventional clinical methods of examining a pregnant woman and simple tests.
Methods for determining the readiness of a woman’s body for childbirth.
1. Determination of cervical maturity - determined by vaginal examination. The process of “maturation” is due to complex mechanisms of morphological restructuring of cervical tissue during pregnancy. Clinically, this is manifested by loosening and shortening of the cervix, gaping of the lumen of the cervical canal. The restructuring process begins from the area of the external pharynx and gradually spreads to the internal pharynx, therefore the softening of the internal pharynx in the process of “ripening” of the cervix occurs last. Acceleration of the processes of “ripening” of the cervix was noted in pregnant women after the introduction of estrogenic hormones and prostaglandins. During palpation assessment of the condition of the cervix, its consistency, the degree of its shortening, the degree of patency of the cervical canal, the location of the cervix in the pelvic cavity, the condition of the lower segment of the uterus during palpation through the vaginal fornix, changes in the shape of the cervical canal and the ratio of the length of the vaginal part of the cervix and the length of the cervix are determined. cervical canal. Based on the totality of these signs, 4 types of cervical condition are distinguished: “immature”, “ripening”, “not fully ripe” and “mature”.
Scale for assessing the degree of “maturity” of the cervix according to G. G. Khechinashvili
| characteristic characteristic | degree of cervical maturity | |||
| "immature" | "ripe" | "not fully ripe" | "mature" | |
| consistency of the cervix | dense or softened only along the periphery | not completely softened, dense tissue is detected along the cervical canal | softened almost completely, with the exception of the area of the internal pharynx | completely softened |
| length of the vaginal part of the cervix and cervical canal | the vaginal part is preserved or slightly shortened, sometimes very long (4 cm or more) | the vaginal part of the cervix is slightly shortened (4-3 cm long), the cervical canal is longer than the vaginal part by more than 1 cm | the vaginal part of the cervix is shortened (3-2 cm long), the cervical canal is 1 cm longer than the vaginal part | the vaginal part of the cervix is sharply shortened (2 cm or less), the cervical canal corresponds in length to the vaginal part of the cervix or is no more than 0.5 cm longer than it |
| degree of patency of the cervical canal and its shape | the external os is closed or allows the tip of the finger to pass through | in primiparas, the external pharynx allows the tip of the finger to pass through (less often, we pass one finger to the internal pharynx); in multiparous women, we pass one finger to the internal pharynx; the cervical canal is curved, there is a sharp transition to the lower segment | the cervical canal is passed for one finger beyond the internal pharynx, there is no smooth transition of the cervical canal to the lower segment | the cervical canal is freely passable for one finger beyond the internal os, not curved, smoothly passes into the lower segment |
| thickness of the walls of the vaginal part of the cervix | 2 cm | 1.5 cm | 1 cm | 0.5 cm |
| condition of the lower segment of the uterus | the presenting part through the fornix is not clearly defined | the presenting part through the fornix is not palpated clearly enough | the presenting part through the fornix is palpated quite clearly, but landmarks on it cannot be determined | the presenting part of the fetus is clearly palpated through the fornix, landmarks are determined |
| location of the cervix in the pelvic cavity | located away from the wire axis of the pelvis (deviated posteriorly, less often anteriorly), the external pharynx is in the middle of the distance between the upper and lower edges of the pubic joint | deviated from the wire axis of the pelvis; the external pharynx is determined at the level of the lower edge of the symphysis or slightly higher | located closer to the wire axis of the pelvis; external os - at the level of the lower edge of the symphysis, sometimes slightly lower | located strictly along the wire axis of the pelvis; the external os is determined at the level of the ischial spines |
There is also a simplified scale for assessing the degree of “maturity” of the cervix according to E. H. Bishop (see the question “Harbors of labor”)
2. Oxytocin test.
a) Method for determining the reactivity of the myometrium to intravenous administration of a threshold dose of oxytocin capable of causing uterine contractions. The reactivity of the uterus to oxytocin gradually increases as pregnancy progresses and becomes maximum on the eve of birth. Before performing the test, the woman being examined must be in a horizontal position for 15 minutes in a state of complete emotional and physical rest in order to exclude the possibility of uterine contractions under the influence of other factors. An oxytocin solution is prepared immediately before the oxytocin test (0.01 IU of oxytocin in 1 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution). Then, draw 10 ml of the prepared solution into a syringe and inject it intravenously “push”: 1 ml at intervals of 1 minute. The administration of the solution is stopped when contraction of the uterus appears, recorded hysterographically or by palpation. However, more than 5 ml of solution or 0.05 units of oxytocin should not be administered. The test is considered positive if uterine contractions in response to the administration of oxytocin appear within the first 3 minutes. It is believed that a positive oxytocin test indicates the possibility of spontaneous labor within the next 1-2 days. b) A method for predicting the date of birth based on the amount of oxytocin solution administered. If uterine contraction occurs after internal administration of 2 ml of oxytocin solution (0.02 units), then labor will occur within 1 day. c) Method for assessing the sensitivity of the uterus to oxytocin in Montevideo units (EM). EM is the average contraction amplitude multiplied by the number of contractions in 10 minutes. This technique allows you to determine 3 degrees of sensitivity of the uterus to oxytocin: 1 - inertia of the uterus; 2 - low sensitivity - up to 40 units; 3 – good sensitivity – more than 40 units. Uterine activity exceeding 40 IU indicates complete readiness for childbirth. d) A method for assessing the sensitivity of the uterus to oxytocin in relation to the duration of contractions (DS) to the pause between contractions (PMS). With PS/PMS equal to 0.1-0.3, birth is predicted in 1-3 days. With a coefficient of 0.4-0.6 - later than 5 days. The oxytocin test is not without its drawbacks, which include invasiveness, the possibility of developing uterine hypertonicity, hypertension in the pregnant woman and hypoxia in the fetus. 3. Non-stress test. Using a cardiotocograph, spontaneous contractile activity of the uterus and cardiac activity of the fetus are recorded for 40-60 minutes. When the pregnant woman’s body is ready for childbirth, rhythmic contractions of the uterus are recorded on the hysterogram; At the same time, the condition of the fetus is assessed, taking into account its reaction to the contraction. 4. Mammary test. A non-drug test is based on the appearance of endogenous oxytocin during irritation of the nipples and areolas in a pregnant woman. The response of the uterus is recorded using a cardiotocograph. The mammary test is assessed positively if uterine contractions appear within the first 3 minutes from the onset of nipple irritation and 3 contractions are observed within 10 minutes. 5. Colpocytological test. Cytological examination of vaginal smears allows us to assess the hormonal balance of a woman in the last days of pregnancy. There are 4 cytotypes of vaginal smears, which can be used to judge the degree of a woman’s biological readiness for childbirth. 1 cytotype - late pregnancy or navicular smear type. It is typical for a normally progressing pregnancy, starting from the 2nd trimester. In the smear, scaphoid and intermediate cells predominate in the form of clusters in a ratio of 3:1. The cytoplasm of the cells is strongly basophilic. Leukocytes and mucus are absent. Eosinophilic cells are found in 1%, with pyknosis of nuclei - 3%. The onset of labor with this cytotype can be expected no earlier than 10 days later. Cytotype 2 - shortly before birth. The smear reveals a decrease in the number of scaphoid cells and an increase in the number of intermediate cells. Their ratio is 1:1. The cells begin to settle in isolation. Cells of the superficial layers of the vaginal epithelium appear. Eosinophilic cells among them account for 2%, with nuclear pyknosis - 6%. Childbirth can occur in 4-8 days. Cytotype 3 - due date. The smear is dominated by cells of the intermediate (60-80%) and superficial (25-40%) layers. Scaphoid cells occur in 3-10%. Cells lie isolated. The number of eosinophilic cells is 8%, with pyknosis of the nucleus - 15-20%. Leukocytes and mucus appear. The onset of labor is possible in 1-5 days. Cytotype 4 - undoubted due date. Cells of the superficial layers predominate in the smear (40-80%). There are few intermediate cells. The scaphoids are absent or sporadic. Superficial eosinophilic cells may be without nuclei (“red shadows”). The cytoplasm is poorly stained, the edges of the cells are of low contrast. The smear takes on a “erased” or “dirty” appearance. The number of eosinophilic cells is 20%, with pyknosis of nuclei - 20-40%. Leukocytes and mucus in the form of clusters. Childbirth occurs either on the same day or within the next 3 days.
Induced labor.
Induced labor is an artificially induced birth for maternal or fetal indications, as well as for combined indications.
Indications : post-term pregnancy, oligohydramnios, the presence of meconium amniotic fluid, hypertension syndrome, severe gestosis, intrauterine growth retardation, chronic fetal hypoxia, Rh-negative blood in a pregnant woman with sensitization, diabetes mellitus and other extragenital diseases that cannot be treated and complicate the course pregnancy.
Contraindications : anatomically narrow pelvis of degree II-III degree of narrowing, severe fetal suffering, severe somatic diseases of the mother, high myopia, suspected failure of the uterine scar, uterine fibroids (cervical location of the node, suspicion of degeneration of the node, etc.).
In case of a complicated pregnancy that threatens the health of the mother (severe forms of gestosis, extragenital diseases that have not responded to therapy) and the fetus (post-term pregnancy, diabetes mellitus in the mother, isosensitization), as well as in case of intrauterine death of the fetus or abnormalities of its development, it becomes necessary to artificially induce labor. Artificial, or induced, childbirth is carried out before the expected due date or during a full-term (post-term) pregnancy. Some obstetricians and gynecologists prefer to conduct so-called programmed childbirth, the essence of which is to induce labor during a full-term pregnancy, a mature fetus and a prepared cervix at a randomly selected time that is optimal for the mother, fetus and medical staff.
The main criterion for success during labor induction is the readiness of the female body for childbirth (see question “Assessing the readiness of the woman’s body for childbirth”), according to which you can choose delivery tactics and outline adequate corrective therapy.
If the cervix is immature or not mature enough:
a) create a hormonal background by administering folliculin or estradiol dipropionate (20,000 units), sinestrol (10 mg) for 3 days or more
b) administration of glucose, calcium, vitamins B1, C, galascorbine.
c) intravenous drip infusion of 2% sigetin solution (10 ml), diluted in 300 ml of isotonic NaCl solution or 5% glucose solution at a rate of 8-12 drops per minute. Sigetin enhances uteroplacental blood flow and the transport function of the placenta, increases the sensitivity of the myometrium to oxytotic substances.
d) to prepare a pregnant woman’s body for childbirth (with a whole amniotic sac), the use of prostaglanlins F2a and E3 is effective. For this purpose, 5 mg of prostaglandin F2a (enzaprost) or 1 mg of prostaglandin E2 are diluted in 500 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution or 5 %
glucose solution and administered intravenously at a rate of 8-10 drops per minute. Vaginal, intracervical and extra-amniotic administration of prostaglandins with gel can be successfully used.
d) non-drug methods of preparing the body of pregnant women for childbirth and induction of labor, such as electrical stimulation of the cervix, stimulation of the nipples of the mammary glands, introduction of kelp into the cervical canal, intrauterine extra-amnial insertion of a Foley catheter, etc. The positive effect of preparatory therapy for childbirth serves as the basis for subsequent induction of labor .
In the presence of an intact amniotic sac and a mature cervix, amniotomy is an effective method of inducing labor (in 50 %
cases).
Indications for amniotomy: polyhydramnios, oligohydramnios, late gestosis, hypertension of any etiology. Since amniotomy itself promotes the development of labor, there is no need to simultaneously prescribe uterine contractions. This is also justified because amniotomy is accompanied by disruption of uteroplacental blood flow, which returns to its original value no earlier than 40 minutes after amniotomy, and the condition of the fetus depends on uteroplacental blood flow. The most justified is to wait after amniotomy for 2-3 hours. In the absence of regular labor, you should begin administering one of the oxytotic agents - oxytocin or prostaglandin or a combination thereof. If, despite the use of oxytotic drugs, labor does not develop within 3-5 hours, it is necessary to perform delivery by cesarean section. Sometimes, for the purpose of inducing labor, they resort to exfoliation of the lower pole of the amniotic sac, but this method has no independent significance and can be used before amniotomy.
If the amniotic sac is intact and the amniotic fluid is moderate and the cervix is mature, a gentle and effective method of inducing labor is the use of oxytocin, prostaglandins, or a combination thereof. When labor has developed, an early opening of the amniotic sac is performed. If, under the influence of oxytotic drugs with a whole amniotic sac, labor does not develop within 3-5 hours, then the administration of the drugs is stopped, and the next day they resort to amniotomy, followed by the introduction of uterotonic drugs, and in case of failure, a cesarean section is performed.
Obstetric tactics for premature rupture of water are determined by the readiness of the woman’s body for childbirth.
a) If the cervix is immature , measures are taken to promote ripening of the cervix and increase the excitability of the myometrium. For this purpose, they resort to creating the usual hormonal-glucose-vitamin-calcium background, but for faster absorption, estrogens are administered 3-4 times a day at a dose of 20,000 units together with ether (0.5-1 ml) intramuscularly with an interval of 1- 2 hours. With this route of administration, estrogens enter the mother’s bloodstream within 20-25 minutes and promote faster ripening of the cervix. After successful preparation, labor induction begins.
b) In case of premature rupture of amniotic fluid and a mature cervix in women with infantilism, post-term pregnancy, breech presentation of the fetus, as well as when the primigravida is over 30 years old, has a burdened obstetric history and other aggravating factors, labor induction begins immediately after the rupture of the waters.
c) If the cervix is mature and there are no factors aggravating pregnancy, and the mother and fetus are in good condition, labor induction begins no later than 6 hours after the amniotic fluid is released.
Active tactics of labor management - programmed childbirth -
used for uncomplicated full-term pregnancy, in pregnant women with extragenital and obstetric pathologies, as well as in extreme situations to prevent maternal and perinatal mortality. It provides for the possibility of delivery during the daytime, with careful monitoring of the condition of the woman and the fetus, in conditions of optimal organization of the work of the maternity unit with the involvement of highly qualified specialists. For this purpose, an early amniotomy is performed (at 6-7 a.m.) after preliminary administration of antispasmodics (30-40 minutes before amniotomy). In the absence of labor, after 3 hours, the administration of uterotonics (oxytoin, prostaglandins) begins, the duration of administration of which is no more than 3 hours. If there is no effect from the induction of labor or if the obstetric situation changes (fetal hypoxia, deterioration of the mother's condition), surgical delivery is performed.
⇐ Previous27Next ⇒
What signs are indicators for artificial preparation of the cervix for childbirth?
Unfortunately, what is thought out and laid down in our body by nature itself and should be done naturally does not always happen by itself. Sometimes you still have to make a decision about preparing the cervix for childbirth using artificial methods, indicators of which are the following factors:
- unsatisfactory condition of the fetus (for example, intrauterine growth retardation);
- gestosis is a complication that affects the normal course of pregnancy. The expectant mother may experience increased blood pressure, the appearance of edema, and the kidneys begin to work poorly, as a result of which spasms may occur in the placenta and uterus, from which the baby may also suffer. This complication can be treated with medication, but if it does not produce results, delivery must be resorted to;
- artificial preparation of the cervix for childbirth may be due to hemolytic disease of the fetus, the development of which is provoked by Rh conflict between the fetus and mother (the female body begins to produce antibodies that have a detrimental effect on the child’s red blood cells). If the number of these antibodies is too high and they interfere with the further normal intrauterine development of the baby, a decision is also made about planned delivery;
- post-term pregnancy.
More on the topic
How does the cervix dilate?
Causes of shortening of the cervix and possible threat of pregnancy
Pregnancy after cervical conization
Cervical erosion during pregnancy
Causes and consequences of cervical rupture during childbirth
Dilatation of the cervix before childbirth
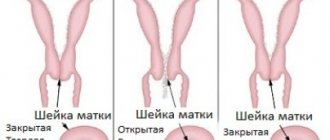
Normally, throughout pregnancy, the cervix has a dense consistency, length from 3 to 5 cm, the cervical canal is closed and filled with a mucous plug, which serves as additional protection against infection. In multiparous women or in the presence of cervical scars from previous births, the canal may pass a finger to the internal pharynx.
From about 34-36 weeks of pregnancy, the cervix begins to ripen. The maturation process includes:
- shortening of the cervix;
- softening consistency;
- centering the cervix along the axis of the birth canal;
- gradual opening of the external and internal pharynx.
The closer the due date, the more pronounced the processes of ripening and dilatation of the cervix. Multiparous women and women with good labor dominance may already have a dilatation of the cervix of up to several centimeters at the time of the onset of labor in the absence of other signs of labor.
What artificial methods do they use to prepare the cervix for childbirth?
First of all, by creating an appropriate hormonal background using estrogen drugs. Most often, Sinestrol is used for this, which is administered intramuscularly (injections) twice a day for several days (from 2 to a maximum of 12 days). Foreign doctors do not use estrogens for these purposes.
Secondly, this is done by introducing prostaglandins, which are injected into the cervical canal in the form of an intracervical gel (“Prepidil”), or intravenously in the form of a solution (“Enzaprost”). The doctor should regularly assess the condition of the cervix every 3 hours, monitor the woman’s blood pressure, pulse and breathing rate.
The third (most popular) recently is a mechanical method of preparing the cervix for childbirth, such as the introduction of kelp - seaweed, which is also known as seaweed.
Laminaria have a wide spectrum of action and are used in many branches of medicine, including in obstetrics, where they are used in the form of special sticks called burzhi (they are inserted into the cervical canal).
They need to be inserted so that they are completely in the cervical canal, but at the same time slightly protrude beyond the external os. Being in the cervical canal, they become saturated with mucus, swelling greatly, which provokes its mechanical opening.
Laminaria have this effect due to the content of a specific substance in them - arachidonic acid, which affects the production of prostaglandins. It is allowed to administer from one to five burji sticks in one session. The results are assessed by a doctor within 24 hours. This safe procedure can be repeated if necessary.
In what cases is artificial preparation of the cervix for childbirth contraindicated?
The above methods of cervical preparation cannot be used for women for whom vaginal delivery is contraindicated (in case of a planned cesarean section).
Making a decision on medical preparation of the cervix for childbirth is very responsible and requires a serious approach. This is especially true in cases where a woman in labor suffers from bronchial asthma, epilepsy, impaired renal (or liver) function, and vascular and heart diseases.
Especially for beremennost.net Anna Zhirko