Premature aging of the placenta is diagnosed in almost 20 percent of expectant mothers. This pathology is a serious pregnancy complication, and can even become an indication for early delivery if the gestational age allows it. The main danger with this diagnosis is the insufficient supply of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus.
In the absence of timely treatment (in cases where it is necessary), there is a possibility of retarded fetal growth, the development of pathologies, as well as chronic hypoxia, which can cause intrauterine death of the baby.
Placenta - what is it?
In Latin, the word “placenta” means “pie, flatbread.” It's all about how the placenta looks: the organ received this name due to its flattened shape, because in appearance it resembles a flat disk.
When does the placenta form during pregnancy?
Its formation begins only when conception occurs, and when the child is born, it is excreted along with the membranes.
The placenta performs the following functions:
- respiratory - through it oxygen enters the fetus and carbon dioxide comes out;
- barrier – protects the fetus from those harmful substances that are in the mother’s blood;
- nutritious - nutrients come from mother to fetus;
- hormonal - produces a number of hormones that determine the normal development of pregnancy;
- excretory - waste products of the fetus are excreted through it.
Development of the placenta
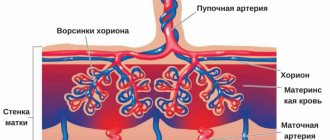
The development of this organ does not occur immediately after conception. In the fourth week of pregnancy, the fertilized egg is surrounded by the chorion - this is a special villous tissue. The formation of the early placenta occurs around the ninth week. It is formed by chorionic villi that penetrate the upper layer of the uterus and connect with the blood vessels there.
By the end of gestation, the placenta already weighs about half a kilogram, and its diameter is 15-20 cm. The permeability of the placenta membrane increases until the 32nd week of pregnancy. After all, every week the size of the fetus increases, and it requires more and more oxygen and nutrients.
Accordingly, in order to provide such nutrition, the number of vessels in the child's place increases, and the membrane becomes thinner. After the thirty-second week, the development of the placenta stops and it begins to age. If this happens earlier, then early aging of the placenta .
Stages of pathology
To determine the degree of aging of the placenta, doctors use ultrasound diagnostics. With its help, the structure, condition of the organ and the thickness of its walls are visualized, which are compared with the gestational age. Premature ripening of the placenta is classified into 4 stages:
Stage 0. It is characterized by the normal structure of the organ, in which it fully carries out all its functions. Normally corresponds to 20-30 weeks of pregnancy.
I degree. It has a second name - the active growth phase. At this time, the placenta performs its functions well, but degenerative processes begin in it. Normally, this period begins from 27-31 weeks and lasts until 32-33 weeks.
II degree. It is called the maturity phase. By this time, quite strong structural changes occur in the placenta, its walls become thicker, and gas exchange decreases. The mature “baby place” is normally diagnosed from 34 to 39 weeks of pregnancy.
III degree. This phase is called “aging”. The placenta is preparing for the upcoming birth; in the physiological course, this period begins after the 37th week of pregnancy.
If structural changes in the “baby place” do not correspond to the duration of pregnancy, the doctor diagnoses “premature aging of the placenta.”
Degrees of placenta maturity
During the development of pregnancy, the doctor looks for all internal changes during an ultrasound examination. And the degree of maturity is also determined during the ultrasound process, taking into account certain parameters.
Based on the duration of pregnancy, the degrees of maturity are determined as follows:
- degree of maturity 0 – up to 30 weeks;
- degree of maturity of the placenta 1 – 27-36 weeks;
- degree of maturity of the placenta 2 – 34-39 weeks;
- degree of maturity of the placenta 3 – after 36 weeks.
To determine what degree of aging - first, second or third - the doctor determines its thickness, looks for calcium deposits and cysts.
Not so long ago, the maturity of a child's place was viewed differently than it is now. Thus, it was believed that with premature aging, miscarriages , there is a high risk of antenatal fetal death, and low-weight children are born. However, after scientists conducted a series of studies, such interdependence was refuted.
If a woman has a third degree of maturity before 35 weeks (for example, at 32 weeks), she is considered to be at increased risk.
A gynecologist will explain in more detail about the characteristics of maturity, for example, the degree of placenta maturity 2, what this means.
In the table below you can clearly see the degrees of ripeness by week.
Table of degrees of placenta maturity by week of pregnancy
| Chorionic part (the one that is adjacent to the fetus) | Structure | Are there calcium deposits? | |
| 0 tbsp. (up to 30 weeks) | Completely smooth | Homogeneous | Virtually none |
| I Art. (27-36 weeks) | Wavy | A little seal | Microscopic |
| II stage (34-39 weeks) | There are indentations | There are seals | Visible |
| III Art. (after 36 weeks) | Recesses to the basement membrane | Cysts | A large number of |
Danger
The most dangerous variants of the course of premature ripening of the placenta are stage 2 at 32 weeks and earlier, or stage 3 before the 37th week of pregnancy. Milder forms of pathology in the absence of progression of the process do not lead to serious consequences. Typically, 1st degree of premature ripening of the placenta does not affect the development of the fetus, or causes mild growth retardation - malnutrition.
In severe cases, premature aging of the placenta is dangerous due to the development of fetal hypoxia. The unborn child receives little oxygen, harmful metabolic products accumulate in its organs, and adequate cell respiration does not occur. Sometimes this pathology threatens severe retardation in the growth and development of the fetus.
Attention! To prevent the development of premature aging of the placenta, the expectant mother is recommended to prevent abortions, promptly treat urogenital diseases, and lead a healthy lifestyle while carrying a child.
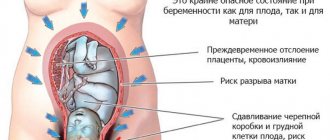
The third degree of premature aging of a child's place can lead to even more serious pathologies. Due to a strong decrease in blood circulation processes, rupture of amniotic fluid and placental abruption may occur, which will lead to premature birth. In rare cases, intrauterine fetal death is observed.
Placenta thickness
This parameter is a very important point in the diagnosis, since deviations from the norm can be evidence of pathologies. There is a special table of placental thickness by week, which indicates the normal limits.
The thickness of the placenta by week is determined by ultrasound, which is performed after 20 weeks. If the process of bearing a baby proceeds normally, then the greatest thickness of the placental tissue is observed at 34 weeks, and at 36 weeks. its growth stops, and its thickness may even decrease slightly.
If the placenta is too thin, placental hypoplasia . However, as a rule, this is not a very threatening phenomenon, unless a significant decrease in size is noted. Very often, such deviations are associated with genetic disposition, the influence of unfavorable factors, and diseases of the woman. If this is due to illness, treatment is carried out; in all other cases, supportive therapy is practiced.
This indicator is also influenced by the physique of the expectant mother. Short, thin women have smaller baby seats than tall, curvy women. If thickening of the placental tissue is diagnosed, this condition can threaten the termination of pregnancy. But with the right approach to treatment, pregnancy can be saved.
Thickening can occur due to Rh conflict , diabetes mellitus , gestosis , iron deficiency anemia , or previous infections . In case of serious deviations, careful monitoring of the expectant mother is important. The fact is that with the rapid growth of a child's place, its active aging occurs. When thickened, hormonal function is disrupted, which can negatively affect pregnancy.
However, if after a series of additional examinations the doctor concludes that the fetus is developing normally, only careful observation will be needed.
Deviations of placental thickness from the norm: causes, consequences and treatment tactics
Pregnancy does not always proceed smoothly; in some cases, the development of the placenta does not correspond to normal indicators. If the thickness of the child's place is less than normal, but they speak of hypoplasia, otherwise hyperplasia occurs.
Thickening of the placenta or hyperplasia
The diagnosis of hyperplasia is made when the width of the placenta in its thickest place exceeds the upper limit of normal, and the greater the deviation, the more dangerous the situation. This pathology develops for various reasons:
- sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, syphilis, gonorrhea and others);
- diabetes;
- viral infections, including ARVI;
- Rhesus conflict;
- fetal malformations;
- anemia;
- gestosis;
- pregnancy with twins.
Pregnancy with twins is a situation where hyperplasia is a variant of the norm. In order to provide two fetuses with oxygen and all the substances they need at once, the baby’s place becomes larger and the volume of placental tissue increases.
During pregnancy with identical twins, only one placenta is formed, which ensures the supply of all necessary substances and oxygen to them, therefore an increase in its size is considered a variant of the norm
. Hyperplasia is the body’s response to the influence of external factors, an attempt to protect pregnancy. When the child’s oxygen supply is insufficient and capillaries die, the network of blood vessels increases in order to prevent oxygen starvation of the fetus. Therefore, in modern medicine, a thick placenta is not an independent diagnosis, but a consequence of some other pathology.
Hyperplasia is detected during ultrasound. In most cases, no associated symptoms are observed. Doctors consider the pathology dangerous for the fetus when, in addition to thickening of the child’s place, there is reason to talk about a violation of its functions. If the placenta does not fulfill its role fully, there is a high probability of consequences for both the baby and his mother:
- the child does not receive the amount of oxygen he needs, which affects all his organs and systems; in severe cases, fetal death is possible;
- the onset of premature labor or the need for a caesarean section may arise;
- weakness of labor due to disruption of the hormonal function of the child's place can lead to complicated childbirth and birth injuries;
- in the postpartum period, the risk of bleeding in the mother increases, and there is a possibility of problems with breastfeeding.
The expectant mother needs to pay attention to the movements of the fetus: with a lack of oxygen, the baby’s motor activity increases. A dangerous signal is a decrease in the number of movements. If alarming signs appear, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Detection of hyperplasia requires mandatory medical monitoring of the woman. First of all, it is necessary to establish the cause of the pathology and treatment tactics will depend on this. A comprehensive examination of the mother's health is carried out, cardiotocography and Dopplerometry are prescribed to determine the child's heart rate and determine abnormalities in the placental circulation. Even if the functioning of the baby’s place is not impaired, doctors often prescribe drugs that improve blood circulation in the placenta (for example, Actovegin, Curantil). Treatment can be carried out both in a hospital and at home.
Hypoplasia or thin placenta
Hypoplasia occurs when the thickness of the placenta does not correspond to the norm, but is beyond its lower border. In this case, the fetus experiences oxygen starvation, the heart rate and placental blood flow slow down. All this leads to developmental delays, premature birth and even intrauterine death of the baby, so medical intervention is required.
A lag in the thickness of the placenta from normal values can be caused by various reasons:
- fetal malformations;
If the cause of hypoplasia lies in genetic abnormalities, then in this case doctors talk about the primary form of pathology. It is not amenable to medical treatment. In all other cases, hypoplasia is considered secondary, that is, caused by a concomitant disease, and is corrected with medications.
- high pressure;
- atherosclerosis;
- gestosis;
- bacterial and viral infections;
- drinking alcohol, drugs, smoking.
A thin placenta as a normal variant can only be found in petite women; in all other cases it is a sign of pathology.
Hypoplasia is detected only on ultrasound. Women with this diagnosis are hospitalized and prescribed medications to improve blood flow in the placenta, prevent the formation of blood clots, affect blood clotting, vitamins and others, depending on the causes of the pathology.
Placental hypoplasia requires constant medical monitoring of the condition of the woman and child, so the pregnant woman is hospitalized
Why does the placenta age too early?
If an old placenta is diagnosed during pregnancy, this may be due to various factors.
Hypertension
Gestational hypertension , that is, increased blood pressure during pregnancy, is very often associated with the function of the placenta. Due to various reasons, defective blood vessels are formed in the child's place, and this affects both the condition of the fetus and the health of the woman. As a result, the expectant mother develops edema , high blood pressure, and sometimes, in severe cases, preeclampsia . A child, developing in the womb, does not receive enough oxygen due to defective blood vessels. As a result, the placenta has to “work” at full capacity, which is why it ages prematurely.
Infections
If the expectant mother falls ill with any infectious disease, then the placental tissue works more actively. It filters the mother's blood from viruses, allows more oxygen and antibodies to pass through to the baby in order to intensify the fight against the disease. As a result, its maturation and, accordingly, aging accelerates.
Eating Excessive Calcium
Calcium deposits are one of the main signs of aging in a child's place. The closer to the end of pregnancy, the more calcifications are detected in the placenta. And if a woman’s body constantly receives a large amount of this microelement, then gradually calcium replaces the placental tissue, which provokes its active premature aging. This often happens if a pregnant woman takes vitamin supplements uncontrollably.
Causes
The reasons why the placenta “wears out” faster than necessary for the proper development of the fetus may be related to the mother’s health or bad habits.
- Smoking.
Cigarettes have a negative effect on the condition of blood vessels and cause spastic reactions. In addition, if a woman inhales tobacco smoke (even with “passive” smoking), the fetus’s need for oxygen increases, which means that the vascular system of the placenta must work harder.
- Chronic metabolic diseases of the mother.
Some diseases (diabetes, thyrotoxicosis, high blood cholesterol) lead to blockage of blood vessels. The same fate befalls the newly formed vessels of the placenta.
- Heart or kidney failure in the mother.
In this case, the blood circulation of the expectant mother herself is impaired, and this affects the functioning of the placenta. If the mother is at risk, therapy to improve blood flow may be prescribed in preparation for pregnancy.
- Internal infections.
Hidden infections such as toxoplasmosis, herpes, cytomegalovirus, etc. have a toxic effect on tissue, thereby causing premature aging of the placenta.
Some of these infections may be dormant and become more active due to decreased immunity during pregnancy.
That is why it is important to undergo PCR diagnostics of common infections at the planning stage and, if necessary, treat them.
- History of abortion.
Pregnancy or uterine surgery leads to thinning of the endometrium. In this case, the placenta initially develops with a lag, does not reach the required thickness and ages faster than usual.
- Rhesus conflict.
Rh conflict between mother and child leads to the formation of antibodies in the blood. In turn, antibodies can also act as toxins, complicating the work of the placenta and causing premature aging.
- Toxicosis.
Prolonged toxicosis, especially in multiple pregnancies, usually leads to accelerated maturation of the placenta. The presence of more than one embryo in the uterus is usually diagnosed already at the first ultrasound.
A woman carrying twins is taken under special control and preventive medications are prescribed in advance to regulate blood clotting and support blood vessels.
Other reasons that can lead to aging of the placenta include:
- violations of the regime and diet;
- swelling;
- overweight;
- living in areas with unfavorable ecology.
If risk factors are known in advance, preventive treatment is necessary to maintain normal placental function and slow tissue aging.
What does early maturation of the placenta lead to?
For every expectant mother who is interested in the dangers of early maturation of the placenta during pregnancy, it is important to realize that this phenomenon in itself is not a threat to the health of the mother and baby. Only if other signs of fetal aging are observed during aging can a health threat be noted. Such signs are the following manifestations:
- Severe intrauterine developmental delay.
- Violation of the fetal-placental and uteroplacental blood supply.
- Presence of signs of Rh conflict in the fetus.
- Severe hypertension in the mother.
- Diabetes mellitus in a pregnant woman (decompensated).
It is important to understand that even if there is no premature maturation of the placenta at 32 weeks of pregnancy or at another period, the conditions listed above are dangerous in themselves. In such conditions, special therapy is required, and in some cases, urgent delivery is necessary.
How is premature ripening of the placenta diagnosed and what is done when it is detected?
Only a doctor can diagnose the condition of premature aging of the placenta using an ultrasound examination. This does not affect the woman’s well-being and does not appear externally. If the specialist suspects something is wrong with the ultrasound, then an urgent CTG procedure (cardiotocography) is prescribed, where the fetal heartbeat is listened to, its tone and clarity are assessed, and the baby’s activity is analyzed. Using these indicators, the specialist determines whether the fetus suffers from a lack of oxygen.
It makes sense to prescribe CTG in late pregnancy, when the baby’s heart muscle is fully formed. Both ultrasound and CTG are necessary and absolutely safe procedures for mother and baby.
If at the 32nd week of pregnancy a pregnant woman is diagnosed with significant aging of the placenta, she is urgently hospitalized in the pathology department of the maternity hospital. There the woman is examined, laboratory assistants take the necessary tests, and specialists examine the fetus. The purpose of these activities is to find out whether the maturation of the organ somehow affects the child, whether he feels nutrient deficiency and oxygen starvation.
To diagnose the functions of the placenta, the following are used:
- laboratory tests for the level of placental hormones;
- analysis of enzyme activity in plasma;
- listening with a simple gynecological stethoscope or CTG procedure;
- Dopplerometry (control of blood supply in the vessels of the uterus and umbilical cord).
If the placenta has stopped supplying the fetus with useful microelements from the mother, then the woman is prescribed medications that stimulate the functioning of the placenta. But therapy must be prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication is simply unacceptable here. After a course of medications, the pregnant woman is sent for repeated studies.
Possible prescription of drugs:
- antibacterial agents;
- vitamin complexes, minerals and iron-containing preparations;
- drugs that stimulate the uteroplacental blood flow, namely Curantil, Actoverin.
If acute fetal hypoxia is detected, a decision is made on an urgent cesarean section. Labor is also artificially induced when a child is found to have severe developmental delays.
If at 32 weeks of pregnancy the deviation from the norm is insignificant, then treatment is not prescribed. But it is important to understand at what speed the placenta will mature. To do this, the woman is monitored more carefully and additional examinations are carried out throughout the remaining period of gestation.
Doctors advise a woman to eliminate all risk factors:
- stabilization of body weight, proper diet;
- getting rid of cigarettes (according to studies, the overwhelming percentage of women who were diagnosed with early placental maturity were smokers);
- taking medications to reduce the child's exposure to harmful toxins;
- treatment of late gestosis and edema;
- therapy against infectious diseases and diseases transmitted through sexual intercourse;
- walks in the fresh air for three or four hours a day;
- introduction of a balanced diet, including dairy products, vegetables, fruits, grains, wholemeal bread, dried fruits;
- eliminating possible sources of infection;
- elimination of physical activity;
- protection from emotional and stressful situations;
- timely and long rest, sleep at least ten hours;
- It is recommended that pregnant women sleep on the left side.
The placenta is a rather complex mechanism that takes on enormous functionality in the body of a woman carrying a baby. Like any impressive system, it tends to fail for a variety of reasons. As a preventive measure, a pregnant woman should take care of herself and the baby and do everything possible to avoid premature aging of the placenta. To do this, the first thing you should do is give up bad habits and take care of your health.
What is an immature placenta and why is it dangerous?
If the placenta does not reach 2-3 degrees of maturity by the end of pregnancy, it is considered immature. This is a fairly rare occurrence; as a rule, it is associated with errors in the diagnostic process.
For example, if there is a Rh conflict between mother and fetus, then the baby’s place may “swell.” When an ultrasound examination is performed, due to the edematous smoothness, the placenta looks like it is at 0 degree of maturity. Therefore, an immature placenta is not a dangerous phenomenon, but such signs can often mask dangerous complications for the mother and child.
What additional research methods are practiced?
To determine the degree of maturity of the fetus and placenta and to diagnose or exclude dangerous conditions, additional research methods are practiced.
Ultrasound with Doppler
It is impossible to assess the child’s condition based on information about the degree of maturity of the placenta. Therefore, it is the data obtained from Doppler ultrasound that is considered to be indicators of a normal pregnancy.
Data is obtained due to the reflection of ultrasonic waves from a variety of biological media. They make it possible to assess blood circulation through the placenta. Provided that everything goes well, after 20 weeks the blood resistance in the vessels that connect the uterus, fetus and baby's place decreases. Thanks to stable resistance, oxygen and nutrients are constantly supplied to the fetus. If a good result was obtained during an ultrasound with Doppler, then there is no need to be afraid, even if during an ultrasound examination the placental tissue looks older than it should be at this moment.
It is also important to take into account that the opposite situation is possible: placental tissue may be of normal maturity, but it may not perform its functions as needed. Accordingly, this will negatively affect the child’s condition. Therefore, it is important to carry out regular examinations.
Cardiotocography CTG
This method is good because it makes it possible to assess the baby’s current condition. With the help of special sensors, it is possible to detect the fetal heartbeat, count the number of its movements, and register how the uterus contracts. The totality of the data obtained allows us to determine even the most minor disturbances in the functions of the placenta.
If an ultrasound examination reveals premature aging of the placental tissue, then it is necessary to perform CTG and Dopplerography to determine the condition of the child.
Why does premature maturity of this organ occur?
This question is asked by all mothers who have been diagnosed with this. And experts answer it like this:
- A pregnant woman does not take care of her health, which also affects the child. Neglect can be expressed in smoking or systematic consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- The mother does not have enough nutrients, therefore, the child does not receive enough of them;
- The pregnant woman has late toxicosis;
- Diseases that are caused by viruses and bacteria can also lead to the fact that the degree of maturity of the placenta does not correspond to the norm;
- If the mother is expecting several children;
- Damage that is observed in the uterus;
- There were abortions or unsuccessful pregnancies (miscarriages);
- Chronic diseases of the endocrine system;
- Individual characteristics of the body.
However, this is an open list of reasons; there are a lot of them, and yours specifically can be found out only after a complete and professional examination.
How to stop the aging process?
If the doctor, based on research results, has concluded that the placental tissue is aging prematurely, then pregnant women, of course, worry about this and try to find out how to “rejuvenate” it. If it is diagnosed that aging of the placenta is stage 3 during pregnancy, or aging of a lesser degree, any attempts at “rejuvenation” are pointless.
Every expectant mother needs to be aware of the following:
- Immediately early maturation of the child's place is not a threatening condition for either the mother or the baby.
- If ultrasound reveals aging of the placental tissue, additional studies must be performed - CTG and Dopplerography. However, this fact is not a reason to worry.
- In the process of determining the maturity of a child's place, diagnostic errors occur quite often.
- If, in the course of additional studies, normal indicators of the fetal heartbeat and placental blood flow are determined, then the expectant mother has no reason to worry about the aging of the placenta.
- Provided that severe fetal hypoxia , then the condition of the pregnant woman and child must be monitored. The doctor makes a decision on treatment or emergency delivery.
- There are no drugs or methods to slow down the aging process of placental tissue.
- Currently, there is no evidence base regarding the use of Curantil , Actovegin , Pentoxifylline , multivitamin complexes, etc. for this purpose.
Diagnostics
The assumption that the placenta is aging prematurely can be made by a specialist during a routine ultrasound examination.
Detection of morphological changes in the structure of a child's place is a reason for undergoing an additional comprehensive examination.
The pregnant woman receives referrals for the following procedures:
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs (in particular the uterus and placenta);
- Dopplerometry of uteroplacental blood flow.
Ultrasound examination allows you to determine such signs as:
- structural changes in the placenta;
- tissue compaction;
- the appearance of salt inclusions;
- change in shell thickness;
- formation of lobules.
Doppler testing is aimed at examining the blood vessels of the placenta.
Using this procedure, you can determine the speed of placental blood flow and the quality of blood supply to the fetus. In addition, the woman is recommended to undergo additional procedures to diagnose the cause of placental aging.
How to prevent early aging of the placenta?
To prevent such manifestations, a woman must be very careful in planning her pregnancy and in her lifestyle while carrying a baby. It is important to practice the following preventive measures:
- plan pregnancy;
- do not drink alcohol or smoke;
- practice moderate physical activity;
- to walk outside;
- carry out screenings, CTG, Doppler ultrasound in a timely manner;
- take Folic acid ;
- for anemia, take iron supplements;
- try to avoid crowds of people to prevent infection with infectious diseases.
If a woman is worried about certain indicators obtained during the examination, she should definitely seek additional advice from a doctor. Perhaps he will order additional examinations.
Signs and symptoms
There are no objective symptomatic signs of the development of this pathology. Only a specialist can diagnose premature aging of the placenta using ultrasound diagnostics. However, observing the movements of the fetus, the expectant mother is able to suspect abnormalities
during pregnancy.
Increased or decreased movements of the child may be a symptom of hypoxia - oxygen starvation of the fetus. This pathology occurs due to premature aging of the placenta stage II-III. If the expectant mother notices unusual fetal activity, she should seek medical attention and undergo an ultrasound examination.