The intrauterine development of the fetus is influenced by many factors, and deviations from the norm of iron in the blood during pregnancy in a woman are considered especially dangerous. Hemoglobin is a very important indicator for any person, regardless of gender and age. Thanks to its special protein composition, this substance performs the function of transporting oxygen throughout the body. When there is a lack of iron, it negatively affects the general well-being of the patient.
Daily iron requirement during pregnancy
Experienced, competent medical workers have found that the human body contains at least 4.5 grams of iron. Most of it is part of the hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the erythrocyte, the rest are components of other cells of the human body.
Iron for pregnant women main functions:
- Transportation of carbon dioxide and oxygen, that is, they participate in gas exchange.
- Iron for pregnant women is involved in metabolism, since without it biochemical reactions will not occur inside the human body.
The daily requirement of iron during pregnancy is the number of milligrams of iron that a woman should receive daily; such criteria depend on gender, general condition of the body and age.
Consequently, during pregnancy, the need for iron in a woman’s body increases based on the growth of the intrauterine child. It is also important to know that the female body creates a certain supply of iron during this process, that is, to prepare for birth loss of blood or a long period of lactation.
How dangerous is anemia for mother and fetus?
The development of anemia in the first trimester threatens miscarriage. If in the early stages of pregnancy iron deficiency anemia was not detected due to the hidden nature of the course, then in the second trimester the disease takes on a more expressive appearance in the form of fetoplacental insufficiency, underdevelopment of the chorion and amnion, and placenta previa.
First of all, the negative consequence of prolonged iron deficiency anemia is oxygen starvation of the baby. Prolonged fetal hypoxia is fraught with developmental delays in the baby and the acquisition of congenital pathologies of various organs, but the saddest thing is that prolonged hypoxia leads to intrauterine death of the child.
For the mother, anemia can cause early toxicosis or severe gestosis, the appearance of which only aggravates fetal hypoxia.
Iron deficiency can also lead to premature birth. The risk of complications during childbirth also increases. Women in labor with anemia often experience weak labor and bleeding during and/or after delivery, especially during cesarean section.
In addition, a lack of iron in a pregnant woman’s body can cause anemia in her child after birth.
Serum iron: normal
Serum iron during pregnancy is a type of test that determines the concentration of iron in the blood of a woman carrying a baby. It is important to note that the level of such iron can vary depending on the time of day. Doctors indicate that the highest rates in women are observed in the morning. An increased level of serum iron during pregnancy causes various ailments, which can subsequently negatively affect the general well-being of the mother and the development of her unborn child.
It is possible to diagnose the iron level of a woman carrying a baby using various complex laboratory diagnostics and studies that make it possible to determine the metabolic processes of this macroelement in the woman’s body, as well as its level of distribution. It is also necessary to know that if a woman does not have enough serum iron in her body, she may develop anemia, which is accompanied by pronounced symptoms.
Indications for testing
A blood test for serum iron is prescribed by a doctor in the following situations:
- Establishing diagnosis;
- Confirmation of the suspected diagnosis;
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of the treatment;
- Monitoring indicators after therapy.
Indications for taking a serum iron test are the following conditions::
- Deviation of hemoglobin and red blood cells from the norm in the general analysis;
- Suspicion of anemia. In this case, the analysis can determine the type of anemia;
- Food intoxication;
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Suspicion of hidden gastrointestinal bleeding;
- Diseases of infectious and inflammatory nature;
- Identification of signs of hypo- and vitamin deficiency;
- Heavy or prolonged bleeding in women;
- Termination of anemia therapy. An iron test helps evaluate the effectiveness of treatment;
- Suspicion of the presence of a genetic pathology associated with metabolic disorders in the body.
Iron is low during pregnancy
Iron deficiency in the body of the expectant mother can occur as a result of insufficient consumption of this microelement. As a result, the level of hemoglobin decreases, and manifestations of anemia are also possible.
Factors causing iron deficiency:
- Insufficient iron level before pregnancy.
- Chronic illnesses.
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Pronounced toxicosis in early pregnancy.
- Long and heavy periods during pregnancy.
Symptoms if iron levels are low during pregnancy:
- Fatigue.
- Irritability.
- Weakness.
- Dizziness.
- Frequent severe headaches in the morning.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Dry mucous membranes.
- Stomatitis.
- Dyspnea.
- Deviation.
Having such symptoms, you should urgently visit a doctor to diagnose a deficiency of this element, which can be done using an analysis of iron levels.
If, after diagnosis, a qualified gynecologist discovers an iron deficiency, then the girl will be prescribed iron supplements and iron vitamins for pregnant women.
How to take a blood test to determine iron?
To determine the iron/hemoglobin content in the blood, a pregnant woman needs to undergo a general blood test.
Blood is donated exclusively in the morning and on an empty stomach. Before this, the pregnant woman should get at least 8 hours of sleep at night. If a pregnant woman enters a medical facility with a threat of miscarriage, then blood is taken for a general analysis at absolutely any time of the day.
The day before donating blood, you will need to completely eliminate fried, spicy, and fatty foods from your diet. Also, it is not permissible to drink alcohol.
There should be no physical activity for about a day before we donate blood. If you are taking any medications, be sure to tell the laboratory assistant about it.
All blood tests must be taken within the same laboratory, since the units of blood measurement are different in different laboratories.
Why can anemia occur during pregnancy? Every woman should be aware of these reasons.
The first and most common reason is an insufficiently balanced diet during pregnancy. If a pregnant woman does not receive the vitamins and minerals she and her baby need from food, then it is imperative to pay attention to vitamin complexes that are sold in pharmacies.
The second reason for anemia in pregnant women is if a pregnant woman works in hazardous chemical production before maternity leave.
Other causes of anemia during pregnancy may include:
- Infections;
- Chronic inflammatory processes that a woman had even before pregnancy;
- Pathologies of the urinary system;
- Endocrine system disorders;
- Threat of miscarriage during pregnancy, namely bleeding from the uterus;
- Multiple pregnancy;
- Immunity impairment.
To increase hemoglobin during pregnancy, the patient must additionally take medications that contain iron (as prescribed by the doctor) and carefully follow a diet.
A therapeutic diet implies complete nutrition, which will contain all the necessary vitamins and minerals. The diet should be filled with meat (pork, pork liver, turkey, veal), fish, cottage cheese, cheese, dairy products, egg yolk, almonds, apples, spinach, and cocoa.
If we are talking about medications, then the emphasis should be on taking medications such as Sorbifer, Totema, Ferrum Lek, Maltofer.
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract that interfere with the absorption of iron;
- severe toxicosis, causing regular profuse vomiting, which removes necessary substances from the body before direct absorption;
- multiple pregnancies requiring more iron than a normal pregnancy;
- problems with nutrition, fasting, dieting, general exhaustion of the body.
The usual hemoglobin level for pregnant women is in the range from 110 to 140 g/l. In the initial stages, hemoglobin should not fall below 120; women who experience lower levels during the first trimester should be under special supervision by their attending physician.
| Analyzed indicator | Change in level relative to normal |
| Hemoglobin | Mild anemia: from 110 to 90 |
| Moderate anemia: from 89 to 71 | |
| Severe anemia: less than 70 | |
| Red blood cells | Less than 3.5 |
| Hematocrit | 0.3 – 0.33 or less |
| Color index | 0.85 or less |
| Iron | Less than 10 |
In addition, there is a significant increase in iron binding capacity. It is the test for its level that is the decisive diagnostic tool if there is a suspicion of the development of iron deficiency in the body, since changes in other indicators may be insignificant or not occur at all.
To obtain the most accurate results, before taking serum iron tests you should:
- Do not eat at least 8 hours before the test.
- The day before the test, avoid fried foods and alcohol.
- The test must be taken before starting a course of medication or no earlier than 10 days after its completion. If this is not possible, it is important to notify your doctor.
- The analysis is not performed immediately after x-rays, fluorography, or ultrasound.
- The analysis is due no later than 10 am.
The average serum iron level ranges from 50 to 160 mcg/dL. If it is reduced, this is a sign of anemia.
The symptoms caused by iron deficiency during pregnancy are quite noticeable and pronounced.
- general weakness, dizziness, lethargy, high level of fatigue;
- poor condition of skin, hair and nails;
- development of shortness of breath;
- digestive problems;
- sudden changes in taste preferences and the desire to eat something not intended for food, for example, chalk or paper;
- impaired sense of smell, addiction to strong unpleasant odors;
- the appearance of involuntary urination.
Among the consequences of untreated iron deficiency there are quite serious ones. Some of them affect the course of pregnancy:
- The likelihood of miscarriage or premature birth, as well as frozen pregnancy, increases.
- Labor contractions become weaker and may be accompanied by heavy bleeding.
- Anemia harms the formation of the fetus and causes developmental delays.
- The frequency and intensification of toxicosis is provoked.
Immediately after pregnancy and childbirth, a number of complications may also occur:
- Tendency to purulent-septic infections.
- Development of gestosis.
- Lack of breast milk.
- Complications in the child, his extremely low immunity and tendency to allergies and anemia.
The level of anemia immediately after childbirth is often further exacerbated by significant blood loss and subsequent lactation. Therefore, what seemed like a minor decrease in the indicator can become a real problem.
Under no circumstances should you take the presence of anemia lightly. It is important to increase your blood iron levels and take prescribed medications.
If the indicator decreases slightly during pregnancy, as well as before it during planning, it is important to eat foods containing large amounts of iron.
Among them:
- liver;
- red meat;
- dairy products;
- apples and apricots;
- nuts;
- buckwheat;
- beans
- eggs;
- fish and other seafood.
There are also foods that, on the contrary, should be avoided because they interfere with the absorption of iron.
- cow's milk;
- cheese;
- tea;
- coffee;
- flour products;
- cereal-based dishes.
It is important to remember that iron is absorbed from foods in extremely small quantities, no more than 2% of each, so there should be a predominant amount of them in the diet. From this it is clear that, as a rule, changing the usual diet alone is often not enough to effectively increase the iron content in the blood.
It is necessary to take additional medications, among which the most popular are vitamin complexes and medications based on ferrous iron.
| Type of anemia | Content of ferrous iron, mg |
| Lightweight | 50-60 |
| Medium to heavy | 100-120 |
Increasing the dose to a greater extent is not recommended: this can cause unwanted complications for both the mother and the fetus.
Often, taking iron supplements is combined with taking the following medications and vitamins:
- vitamin E;
- methionine;
- garlic preparations;
- ascorbic acid;
- vitamin B
They have the most effective effect an hour or two before meals. Pectin-containing products should not be consumed at the same time.
All these substances should be taken exclusively as prescribed by a doctor; only in this case can they achieve their optimal effect and be sure that there are no contraindications.
When a woman suffers from chronic alcoholism, then her affected internal organs cannot function normally. Therefore, the spleen, liver, and pancreas can worsen metabolic processes.
This leads to an increase in the amount of iron and a malfunction of the body systems:
- Severe fatigue, apathy, poor health appear, and the woman experiences a loss of strength.
- A severe headache begins to bother me.
- There is a deterioration in appetite and weight loss.
- Pain in the epigastric region and heartburn develop.
- Diarrhea or constipation occurs.
- Sometimes nausea and vomiting bother you.
- Cardiac activity is disrupted, and atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels develop.
- The functioning of the liver and kidneys changes, up to the development of renal failure.
- Diabetes may develop.
- Inflammation occurs in the joints with the development of arthritis.
- The tendency to allergies and infections increases due to a decrease in the body's defenses.
- An increase in this microelement can provoke the development of malignant neoplasms.
If these symptoms are present, a thorough examination and treatment of the woman is carried out by correcting nutrition, filtering water, and bloodletting.
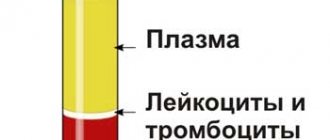
During pregnancy, the female body begins to produce 1.5-1.7 times more blood. It forms blood for the unborn child.
And, as you know, blood consists of red blood cells, which are based on hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is the very iron necessary to transport oxygen throughout the body. Lack of iron during pregnancy can cause anemia. This disease is caused by insufficient oxygen supply to a certain area of the body.
If the body does not receive enough iron, it can cause premature birth. Therefore, expectant mothers need to choose the right diet so that it contains the optimal amount of iron microelements.
The need for iron with the growth of the fetus in expectant mothers constantly increases. The larger the fetus becomes, the more blood the woman’s body begins to form.
And the more blood is formed, the more iron the hematopoietic systems need. Therefore, here is a list of the basic needs of the expectant mother’s body in ferum at different stages of pregnancy:
- In the first trimester, the optimal amount of daily iron is 15 mg.
- The norm of iron in the body of pregnant women in the second trimester is 20-30 mg/day of this microelement.
- In the third trimester - 33-35 mg/day.
To correctly adjust the above values, you should consult your doctor. Each female body is unique, and pregnancy proceeds differently for each, so it is not advisable to independently set the rate of ferum consumption per day. During pregnancy, you need to eat right and take plenty of vitamins.
Causes of deficiency
The danger of anemia
Most pregnant women do not pay attention to such a diagnosis as anemia. However, it is worth noting that such a disease has a high risk of causing various abnormalities:
- An insufficient amount of this element leads to a decrease in hemoglobin, which in turn can lead to oxygen starvation and delayed development of the baby.
- Preeclampsia or late toxicosis may occur. In the absence of effective or timely medical treatment, it can lead to death of the mother.
- The risk of blood loss may increase during labor or after the baby is born. Subsequently, a woman may give birth to a baby with a sharp development of allergic diseases, colds and low immunity. Therefore, iron plays an important role for pregnant women.
Increased iron during pregnancy
Increased iron levels in the blood during pregnancy can cause various pathologies and changes that will indicate a number of serious diseases:
- Bronze diabetes is a type of hereditary pathology that does not allow getting rid of the accumulated reserve
- Hemolytic anemia is a dangerous disease that can be fatal.
- Various abnormalities associated with metabolic processes in a woman’s circulatory system, which can result in aplastic anemia;
- Kidney pathologies;
- , iron-containing preparations for pregnant women can cause lead poisoning, that is, a toxic condition.
Consequently, increased iron during pregnancy is a dangerous condition for a woman, so it is necessary to contact a qualified specialist to control iron in the body in order to prevent its decrease or increase.
Iron supplements for pregnant women
Iron supplements during pregnancy can restore iron levels in the body and cure anemia. The peculiarity of drugs that restore iron during pregnancy is that they must be safe for the body of a pregnant woman and not harm the child. Drugs are prescribed based on the results of a blood test.
Most often, pregnant women are prescribed Sorbifer Durules tablets. This preparation contains vitamin C and 100 mg of iron. "Totema" is an iron-containing solution. Each ampoule of the drug contains 50 mg Fe. "Fenuls" - capsules containing 45 mg of Fe. This drug is used for anemia and to prevent Fe deficiency.
The dosage of iron supplements is prescribed by the doctor (from 30 to 100 mg per day). Fe intake causes changes in the functioning of the body, most often this is expressed in a change in the color of the stool to a darker one. Many drug packages say ferrous sulfate. In order for the body to receive 30 mg of Fe, you need to take 150 mg of ferrous sulfate. Your doctor will help you accurately calculate the dosage and time of administration.
It is worth noting that under no circumstances should an expectant mother prescribe iron supplements on her own. This can only be done by a doctor and only based on the results of a blood test. If a pregnant woman takes in more iron than she needs, this can lead to serious complications during pregnancy and fetal development. Especially often in this situation, pathologies such as gestational diabetes, oxidative stress and miscarriage develop.
There are many medications that can be used to supplement iron during pregnancy. A wide group of such drugs is made on the basis of divalent iron. However, these medications can cause many side effects, in particular, nausea, heartburn, constipation, and exacerbation of chronic diseases of the digestive system.
The drug Ferrocyton is especially not recommended for women expecting a baby. At the same time, such drugs as Ferronal, Ferroplex, Ferrocal are approved for use. However, their disadvantages include the need to take fairly large doses - two tablets 3-4 times a day. More convenient to take are those medications that are taken as a tablet (capsule) 1-3 times a day, for example, Conferon, Tardiferon, Sorbifer Durules.
The new generation of medicines contain ferric iron and do not have many of the side effects of the previous generation of medicines. These medications include Ferlatum, Maltofer and Ferrum Lek.
A normal level of iron in the blood during pregnancy is one of the conditions for its successful course and the birth of a healthy baby. Therefore, the expectant mother should regularly undergo medical examinations, take the necessary tests and follow all the advice of a specialist.
What foods contain iron?
Iron for pregnant women is the most important element that is necessary for the mother and her intrauterine baby. This element is involved in the formation of red blood cells, which in turn are responsible for oxygen supply to the body of the future woman. With the help of a balanced diet, that is, foods that are rich in iron, you can satisfy the body's need for this element during the period of bearing a baby.
You can get iron during pregnancy by eating the following foods:
- Lentils.
- Buckwheat.
- Beet.
- Walnut
- Dried fruits such as dried apricots, figs, dates and prunes.
- Sea kale not only has a high iron content, but at the same time it is an easily digestible product that contains various microelements and vitamins, which has a beneficial effect on the health of the expectant mother.
- Fish and seafood.
- Meat and liver, however, do not need to be abused;
- Fruits such as persimmon, banana, apple, apricot, and plum.
- Broccoli.
- Fresh grapes, cherries or pomegranates.
By consuming such foods in moderation, a woman can control the level of iron in her own body during pregnancy, but do not forget that such foods should not be abused so as not to increase the level of iron in the blood during pregnancy.
Symptoms and causes of anemia
Often pregnant women who have pre-existing iron deficiency suffer from anemia before conceiving a child.
And with the appearance of the baby in the womb, the iron reserves in the woman’s body are depleted, because the baby takes some of the iron and other substances it needs from the mother’s body reserves, and by the second trimester, iron deficiency begins to become more serious. According to the decreased level of hemoglobin in the blood, there are three degrees of severity of the disease:
- Light degree – 90-109 g/l;
- Average degree – 70-89 g/l;
- Severe degree – less than 70 g/l.
In the first two stages, iron deficiency does not appear as such. All that is possible is the appearance of weakness in the muscles, perversion of taste, dizziness, frequent headaches, tinnitus, flashing “spots” before the eyes, fatigue, sleep disturbance, decreased appetite, weakened immunity.
With severe anemia, the patient may complain of shortness of breath, tachycardia (rapid heartbeat), chest pain, weakness in the legs, and severe headaches.
The following may indicate the course of latent anemia: a woman’s addiction to the use of chalk or clay, frequent appearance of jams (cracks) in the corners of the mouth, a burning sensation on the tip of the tongue, rapid physical and mental fatigue, drowsiness and weakness in the arms/legs.
This concerns iron deficiency (anemia), but there is also such a thing as iron excess (hemochromatosis), which has somewhat similar symptoms.
So, hemochromatosis is a disease characterized by elevated levels of iron in the human blood. Its symptoms are pain in the joints, general weakness, body aches, fatigue, heart rhythm disturbances, and decreased libido (i.e., sexual desire).
Only a special set of blood tests, a description and explanation of which is given at the end of the article, will help determine exactly whether a woman suffers from excess or deficiency of iron.
Causes of IDA. Anemia caused by a lack of iron in a woman’s body is observed when:
- constant small uterine blood loss (with endometriosis, the presence of an ovarian cyst);
- chronic hidden bleeding (for example, with hemorrhoids, erosive or polypous gastritis, ulcers in the gastrointestinal tract);
- diseases manifested by systematic nosebleeds (thrombocytopenic purpura, thrombocytopathy);
- the presence of chronic infectious and inflammatory processes;
- consuming insufficient amounts of iron-containing foods (for example, vegetarianism), fasting (anorexia) or an unbalanced and monotonous diet;
- increased need for iron during multiple pregnancy;
- impaired absorption of iron (due to inflammatory or atrophic processes in the small intestine) or its transport (due to diseases of the liver, spleen);
- disruption of red blood cell formation;
- congenital iron deficiency.
Pregnant women at risk for developing anemia include:
- with low blood pressure, early toxicosis or gestosis;
- with placenta previa or premature placental abruption;
- primigravida young girls and women aged 30 and older.
Prerequisites for the development of anemia are a history of pregnancy failure, multiple births and short intervals between them. All this depletes the iron depot (reserves) in a woman’s body.
Pregnancy vitamins with iron
Basically, all women are trying to find iron vitamins in tablets for pregnant women, which would represent a complex of all the necessary vitamins and microelements for pregnant women. However, highly qualified, competent and experienced medical workers note that at different stages of pregnancy, the expectant mother and her baby need different complexes of vitamins and elements.
That is why doctors distributed iron vitamins for pregnant women as follows:
First trimester of pregnancy intake:
- Folic acid.
- Vitamin A.
- Vitamin E.
- Vitamin C.
- Yoda.
- Calcium.
Second trimester of pregnancy: intake:
- Gland.
- Yoda.
- Calcium.
Third trimester of pregnancy intake:
- Gland.
- Vitamin C.
- Vitamin D.
Thus, qualified medical workers have identified which vitamin and element a woman needs in a particular trimester of pregnancy. It is also important to note that iron is not always necessary for pregnant women in the first trimester of pregnancy. Therefore, before purchasing this or that complex of vitamins for pregnant women at the pharmacy, it is necessary to consult with a gynecologist or obstetrician-gynecologist, so that the complex of vitamins will benefit the mother and the unborn baby.
If you liked the article, tell your friends
ShareShareShare
SALID © When copying material in full or in part, a link to the original source is required.
Found an error in the text? Select the desired fragment and press ctrl+enter
ADVERTISERS
- Course authors
- Offer
- Help
MARKETPLACE
- Placement in the catalog
- Course authors
- Course catalog
- Articles
WEBmasters
- CPA network
- Rules
- Help
Salid
- Blog
- Documentation
Personal account Contacts
2013-2020 LLC "Eight" INN 7718898626 Privacy Policy
Causes of decreased serum iron
Serum iron in blood plasma can decrease for many reasons. Some of them are caused by external factors, while others are a consequence of internal changes. The most common of them are the following:
iron deficiency anemia - the disease can be caused by chronic blood loss, lack of iron intake into the body or impaired iron absorption;
chronic systemic diseases - lupus erythematosus, tuberculosis, rheumatoid arthritis, endocarditis, Crohn's disease;
Causes of serum iron imbalance
Sometimes a change in the quantitative state of hemoglobin occurs against the background of various conditions of pregnant women, for example, Rhesus - conflict. Anti-Rhesus serum during pregnancy is administered according to the child’s vital indications, i.e. if there is a threat of miscarriage or placental abruption. The use of serum affects not only the condition as a whole, but also the quality of the blood.
Relatively simple causes of imbalances in red blood cells and hemoglobin in the body that can be quickly corrected are:
- minimal consumption of foods containing iron;
- disruption of the small intestine, where the process of microelement absorption in the body occurs;
- vitamin deficiencies;
- increased need (pregnancy);
- insufficient compensation of iron compared to consumption.
The serum iron norm in pregnant women is considered to be 10 units higher than the usual value, and is monitored by taking a clinical blood test 2 times a month. Given the serious changes in blood parameters, blood sampling occurs more often as prescribed by the treating gynecologist. In some cases, it is recommended to stay in the hospital to monitor the pregnant woman’s condition and blood counts twice a day.
More complex causes of impaired formation of the required amount of serum iron, requiring constant monitoring, are the following pathologies:
- diseases of the hematopoietic organs;
- chronic liver and kidney diseases;
- endocrine diseases;
- chronic intestinal pathologies;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- taking medications for too long.
Serum iron levels during pregnancy can not only decrease, but also increase. Deviation towards increase is also a pathology. The blood becomes too thick, oxygen is poorly distributed throughout the cells, the blood cells become denser and the baby and mother are starved of oxygen.
If iron levels are too high, the liver becomes enlarged and the skin may turn yellow. Weight loss and heart dysfunction occur. Sometimes cramps in the calf muscles occur.
If the numbers are lower
less than normal is considered an independent disease and is characterized by the term iron deficiency anemia. This type of anemia is considered the most common among all anemias. This disease accounts for 90% of cases.
In this case, 3 degrees are distinguished depending on the severity of the disease.
- A mild degree corresponds to a decrease in indicators to the level of 112-128 g/l. This condition does not cause pathological changes or deterioration in health and can be discovered by chance during a medical examination.
- The average degree leads to disruption of the general condition of the body; complaints of dizziness, darkening of the eyes with sudden movements, and periodic headaches are possible. With this degree, the amount of hemoglobin is at around 85-111 g/l.
- Severe anemia is characterized by a decrease in hemoglobin below 85 g/l and is accompanied by serious changes in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. This condition is life-threatening and requires immediate treatment. Symptoms of this disease are shortness of breath with minor exertion, rapid heartbeat, fatigue, memory loss and attention associated with oxygen deprivation of the brain.
In addition to iron deficiency anemia, hemolytic anemia, in which there is increased breakdown of red blood cells, as well as posthemorrhagic anemia, associated with the loss of a large amount of blood, can lead to a decrease in hemoglobin levels.