In the last months of pregnancy, the female body is actively preparing for labor and the birth of a long-awaited baby. During this period, a woman should monitor her health more carefully and respond to various symptoms in a timely manner. Indeed, often in the last weeks, expectant mothers are faced with unpleasant surprises that can negatively affect the birth process.
Varicose veins, pressure on internal organs, heartburn, nausea, swelling, high blood pressure - all these are difficulties that pregnant women have to face. Hypertension is especially dangerous during the period of bearing a baby, so every expectant mother needs to know what factors provoke its appearance, as well as the dangers of this condition in the last weeks of pregnancy.
What is the reason for increased blood pressure at 39 weeks of pregnancy?
This is done to monitor your health and in case of deviations and abnormal behavior, immediately take the necessary measures. Strong jumps in blood pressure have a very bad effect not only on the well-being of the expectant mother, but also on her child, so knowing the normal pressure and monitoring it is very important.
It is believed that blood pressure at the 39th week of pregnancy should be no higher than 140 over 90 and no lower than 90 over 60. This is called normal blood pressure, which does not affect the condition of the mother and child. As already noted, you need to check your blood pressure every day with a special electronic tonometer; it is the most convenient and accurate. This device is capable of automatically measuring not only blood pressure, but also pulse. The advantage of this tonometer is that it has a memory function, and if the mother has lost her piece of paper with notes, she can compare the indicators through the device. Experts advise not to purchase old-style tonometers, since, firstly, it is very difficult to measure pressure with them yourself, and secondly, without experience, you can get incorrect readings.
Hypertension is high blood pressure at 39 weeks. It is accompanied by ringing or noise in the ears, as well as severe headaches. Hypertension at this stage can cause heaviness and fatigue in the legs, as well as nosebleeds. The main reason for this condition in pregnant women is strong changes in the woman’s body. In the woman's position, there is an increase in blood circulation, but its volume does not increase. When the blood volume begins to increase, almost by one liter, this condition becomes common. This happens already in the third trimester, closer to the birth itself.
So, increased blood pressure during pregnancy is not a very good sign, so you need to first review your diet. Doctors advise taking natural birch or beet juices.
An excellent way to lower blood pressure are cranberry juices or drinks. It is best to make freshly squeezed juices, then they have maximum effect. You should take one third of a glass of fresh cranberries, rinse them well and squeeze out the juice thoroughly. You can use the pulp to make cranberry mousse, which is very useful for lowering blood pressure. They need to be filled with a small amount of hot water and simmered over low heat for just five minutes.
Afterwards, you need to thoroughly strain the cake, and add a tablespoon of semolina to the resulting broth and again put it on low heat and boil for twenty minutes. Be sure to stir constantly so that the semolina does not stick to the pan and does not burn. After the specified time has passed, you need to add a little sugar for taste, bring to a boil again and turn off the heat. The resulting mass should be cooled well, then beat with a mixer, adding pre-squeezed cranberry juice. The mass should become light pink and have a viscous consistency.
Doctors advise you to wait and not take pills for blood pressure during pregnancy. Initially, you should try to give up strong coffee and black tea, even chocolate. These products can dramatically increase blood pressure. You can also get special massages by contacting specialists. But dangerous blood pressure during pregnancy will still have to be treated with medications prescribed by the doctor. And you shouldn’t self-medicate to avoid consequences.
The above tricks will help with the question of how to reduce blood pressure during pregnancy - freshly squeezed beet juice, birch sap or cranberry mousse. Also, if a woman suffers from this problem, then she needs to try to be in the fresh air more often, take evening walks before bed, and you can take chamomile teas at night, which will calm the nervous system and prevent an increase in blood pressure.
To prevent high blood pressure from bothering a woman, it is necessary to listen to the doctor’s advice, follow a daily routine, walk in the fresh air as much as possible, and exclude from the diet foods that can affect blood pressure readings.
In the last months of pregnancy, the female body is actively preparing for labor and the birth of a long-awaited baby. During this period, a woman should monitor her health more carefully and respond to various symptoms in a timely manner. Indeed, often in the last weeks, expectant mothers are faced with unpleasant surprises that can negatively affect the birth process.
Varicose veins, pressure on internal organs, heartburn, nausea, swelling, high blood pressure - all these are difficulties that pregnant women have to face. Hypertension is especially dangerous during the period of bearing a baby, so every expectant mother needs to know what factors provoke its appearance, as well as the dangers of this condition in the last weeks of pregnancy.
What to do
Swelling occurs during pregnancy not only in the legs, but also on the face. To establish the truth, it is necessary to take tests that will reflect all the violations. Additionally, doctors use special herbal teas. They help strengthen the functioning of the kidneys, which remove excess fluid from the body, including sodium.
You should give preference to loose shoes with comfortable soles and a small heel. It is possible that the legs swell due to very tight elastic socks, excessively tight clothing; close attention is also paid to this circumstance.
If not only the legs, but also the nasal cavity swell, during pregnancy not only the mother, but also the child experiences a lack of oxygen, which is very negative at 39 weeks.
To eliminate this situation, special nasal drops are used, which narrow the vessels of the nasal cavity, normalizing normal breathing. At the same time, the pregnant woman takes diuretic teas; they eliminate not only swelling from the legs, but also the nasal cavity.
You also need to pay attention to the position in which the pregnant woman sleeps or lies. As already mentioned, the uterus is large; in a certain position, it can compress the inferior vena cava, leading to edema. This condition is isolated into a separate disease, which is called “inferior vena cava syndrome.” You will need to find the optimal position or change it frequently.
Blood pressure during pregnancy: normal and pathological
In a normal state, a person’s blood pressure should be within 120/80. During pregnancy, the concept of normal has a wider range of values - from 90/60 to 140/90.
Almost every tenth pregnant woman experiences hypertension, so this category of patients must always be under strict medical supervision. When visiting an antenatal clinic, the expectant mother must have her blood pressure measured. If the indicators are outside the normal range, then doctors urgently take measures to normalize it in order to eliminate all kinds of complications.
What factors provoke an increase in blood pressure
There can be many reasons for hypertension during pregnancy:
- stress on the female body, which does not have time to adapt to new conditions and reacts to changes with high blood pressure;
- Stressful situations are a common cause of increased blood pressure;
- genetic predisposition when there are hypertension in the family;
- insufficiency of the compensatory forces of the female body during pregnancy, when the heart should be responsible for increased blood circulation, but it cannot fully cope with the task;
- diabetes mellitus - the disease itself does not increase blood pressure during pregnancy, but can become a provoking factor;
- abuse of tobacco products (smoking). Everyone knows that there are few health benefits from a bad habit, and besides, nicotine has a negative effect on the cardiovascular system;
- weak physical activity, as a result of which the heart does not fully cope with the load;
- problems with excess weight. During the nine months of pregnancy, every woman is obliged to control her weight, because excess weight or a tendency to obesity will certainly affect blood pressure indicators;
- disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys can also provoke pressure surges;
- hormonal imbalance caused by dysfunction of the thyroid gland, pituitary gland or adrenal glands.
Who is at risk
Of course, not all pregnant women have problems with blood pressure. However, there are also patients who are especially susceptible to this condition. These include:
- women who have had miscarriages;
- pregnant women over 35 years of age;
- women who had problems with blood pressure during a previous pregnancy;
- overweight and obese pregnant women;
- patients suffering from hormonal disorders.
Variant of the norm
Doctors often reassure expectant mothers, saying that this is a normal phenomenon that will go away on its own. Swelling of the legs at 39 weeks of pregnancy is the result of a combination of several factors, each of which contributes. Let's list them briefly:
- Excess body weight. Not at all uncommon when carrying a baby.
- Abuse of salty foods.
- Drink a large amount of liquid.
If the swelling is severe, the doctor will insist on hospitalization, and already in the hospital, specialists will study urine tests and decide what to do. Leg swelling at 39 weeks is not always a reason to panic. Diuretic herbs and a water-salt diet are often prescribed. This way you will be able to reach the deadline.
What signs indicate high blood pressure?
It would not hurt for every expectant mother, especially if she has problems with blood pressure, to have a tonometer in the household - a special device that measures blood pressure. It is easy to use and allows you to find out accurate indicators at any convenient time.
If it is not possible to measure blood pressure, then pregnant women should listen to their body: it will always tell you when something is going wrong. The occurrence of symptoms such as headache, ringing in the ears, attacks of nausea and even fainting indicates high blood pressure.
But there are cases when hypertension is asymptomatic and does not bother the pregnant woman, but is diagnosed only with the help of a tonometer. This is why it is so important to monitor blood pressure readings during pregnancy and regularly attend antenatal clinics.
Causes
Doctors recommend measuring blood pressure regularly during pregnancy. This is especially true for those women who have previously experienced an increase in it.
A tonometer is used for this. Some doctors believe that a mechanical device shows more accurate indicators. But at home it will be much more convenient to use an electronic tonometer.
You can suspect that you have high blood pressure based on the following signs:
- frequent headaches;
- dizziness;
- the appearance of “floaters” before the eyes;
- deterioration of general condition;
- nausea, which can even result in vomiting;
- sensation of tinnitus;
- redness of the skin (most often in individual areas on the face or chest).
Although it is possible that hypertension during pregnancy will not manifest itself in any way and will be detected only during a routine visit to the doctor.
Why is this happening? High blood pressure during pregnancy may be due to the following reasons:
Why is high blood pressure dangerous in the last weeks of pregnancy?
High blood pressure levels before the happiest and most long-awaited moment of pregnancy do not bode well. First of all, this condition can signal the occurrence of gestosis - late toxicosis. This is a very dangerous complication during pregnancy, which is accompanied by fluid retention in the pregnant woman’s body, edema, and increased protein content in the urine. Preeclampsia is dangerous for a child due to insufficient oxygen supply.
Even if high blood pressure is not caused by late toxicosis, then it should not be left without due attention, since with regular high blood pressure, vascular tone increases, which in turn can lead to fetoplacental insufficiency. In this case, the child will not receive enough oxygen and nutrients, which can lead to delays in intrauterine development.
In addition, if blood pressure surges are regular and the readings are above 140, then premature placental abruption is possible. Such a process may result in termination of pregnancy or premature onset of labor.
Also, hypertension in the last weeks of pregnancy can provoke eclampsia, a condition characterized by convulsive seizures, which is also dangerous for the woman and her baby.
Diagnostic methods
When determining the reasons for the increase in blood pressure, the doctor will recommend that the pregnant woman undergo kidney sonography.
High blood pressure must be diagnosed and eliminated in a timely manner; this is the only way to prevent dangerous complications. If you experience characteristic symptoms, a pregnant woman should immediately consult a doctor. The doctor will conduct an initial examination, measure blood pressure, and collect important information. To find out the causes of hypertension and an accurate diagnosis, a referral is given for the following diagnostic measures:
- general clinical analysis of blood, urine;
- electrocardiography;
- myocardial ultrasonography;
- Vascular ultrasound;
- Kidney sonography.
What to do if you have high blood pressure?
As you already understand, high blood pressure during pregnancy, especially before birth, is a dangerous symptom that signals pathology and requires immediate medical intervention. Self-medication in this situation is simply unacceptable. Based on the examination results, the doctor will prescribe drug therapy. Your task is to strictly follow all medical prescriptions, observing the dosage of medications and the duration of therapy.
If the pressure rises slightly, then you can resort to alternative therapy. Antihypertensive drinks can help normalize blood pressure: cranberry juice, beet juice, pumpkin decoction, viburnum infusion, birch sap. Of course, folk remedies will not completely eliminate the problem, but they can be an excellent preventive measure.
>
In severe cases, the only correct solution may be hospitalization, where the patient will undergo therapy under strict medical supervision until the upcoming birth.
While expecting a child, the female body becomes very vulnerable, long-standing diseases worsen, previously unknown sensations appear, and sometimes not always pleasant ones.
Quite often, one of the symptoms of the development of pathologies during pregnancy is high blood pressure. Therefore, during examinations, obstetricians-gynecologists monitor the pressure of the expectant mother every time.
Blood pressure norms during pregnancy
Normal blood pressure during pregnancy, in which the heart and blood vessels perform their functions without experiencing excessive stress, are considered to be:
- 110-120 mm. Hg Art. for upper (heart) pressure – diastolic;
- 70-80 mm. Hg Art. for the lower (vascular) – systolic.
For chronic hypotensive patients, these limits may be lower: 90/60 mm Hg. Art.
It is important that a woman, when registering for pregnancy at a medical institution, knows the “working” values of her pressure.
Indeed, often (as, for example, in hypotensive patients) increased blood pressure is determined based on an increase in values: more than 30 mm. Hg Art. for the upper indicator and 15 mm Hg. Art. for the lower one, it means that blood pressure has risen beyond the permissible level.
Of course, a one-time increase in blood pressure for some reason is not a reason for the diagnosis of hypertension. But if an elevated level is recorded at least twice in a row, then this is already a reason for concern.
Why does blood pressure rise?
Factors contributing to the appearance of high blood pressure during pregnancy differ little from the causes of hypertensive conditions in the “non-pregnant” period:
- excess weight (obesity);
- bad habits (alcohol, smoking);
- chronic diseases of internal organs, which are accompanied by high blood pressure;
- diabetes;
- hereditary predisposition;
- hypertension as an independent disease (in the absence of endocrine disorders or diseases of internal organs).
Since the period of bearing a child for the female body is a period of increased stress, if there is a known predisposition, problems with blood pressure in the expectant mother are quite expected.
Moreover, if the expectant mother has already suffered from high blood pressure (including during a previous pregnancy), then in the vast majority of cases (about 80%) high blood pressure is inevitable during the next pregnancy.
However, it also happens that a jump in intracranial pressure in a woman was first noted during the current pregnancy. The reason for this may be:
- Developing gestosis. Then hypertension is one of the symptoms of the triad of this pathology (along with proteinuria and edema).
- Gestational hypertension, which is not combined with other symptoms of gestosis. It occurs after the 20th week of pregnancy and, as a rule, heals itself after childbirth.
How does hypotension manifest?
During early pregnancy, the disease manifests itself in different ways.
The symptoms noted are:
- lack of oxygen;
- drowsiness;
- dizziness;
- loss of appetite;
- increased sweating;
- trembling in hands;
- headaches;
- irritability and apathy;
- weakness throughout the body;
- memory impairment;
- pallor of the skin;
- decrease in body temperature (about 36 degrees).
In the second trimester, hypotension is worst tolerated in spring and summer. Stress can aggravate its symptoms. Low blood pressure at week 39 can also manifest itself as unmotivated irritability.
The most striking symptom is headache. It can be sharp, aching, bursting, with mild and severe accompanying dizziness. In some cases, short-term fainting occurs.
People suffering from hypotension tend to wake up already tired. They can work for a couple of hours, and after that they are left completely exhausted. They become active only in the evening.
Did you know that hypotensive people do not tolerate stuffiness well. It is much easier for them to walk along the street than to sit indoors, although low atmospheric pressure is also contraindicated for them. They often experience shortness of breath after exercise. People with hypotension do not tolerate weather changes well. They don't like windiness, high humidity, etc.
Hypotension in some cases manifests itself in a special way. In particular, symptoms such as nausea, constipation, heartburn, etc. may occur.
In the later stages, many unpleasant symptoms occur due to hypotension. Blood pressure problems usually occur in about 15% of women. They usually appear due to stress, heredity, and age (over 40 years old).
Signs of high blood pressure
The insidiousness of hypertension is that its initial stages can easily not be recognized.
This is especially true for expectant mothers, for whom high blood pressure is common.
The body has adapted to this state and is in no hurry to react to it. Therefore, at every routine examination by an obstetrician-gynecologist, a woman is monitored using a tonometer.
With mild hypertension, its signs may be mild:
- mild headache, dizziness;
- rapid pulse;
- increased sweating;
- bright “blush” on the cheeks;
- anxiety.
The severity of these symptoms progresses with a further increase in pressure. Added to them:
- dyspnea;
- areas of redness on the skin throughout the body;
- "tinnitus;
- weakness;
- attacks of nausea, vomiting;
- “flies”, “fog” before the eyes.
Pain in the left sternum, insomnia, and excessive nervousness may appear, which are so easily mistaken for characteristics of a “pregnant” body.
Perhaps this is true, but the doctor must confirm or refute the suspicions.
At what pressure does one feel sick: vomiting and nausea if the pressure rises
In people suffering from surges in blood pressure, nausea is a sure sign that their health will soon worsen.
An attack of nausea always appears suddenly, and sometimes vomiting is observed. It is impossible to cope with the problem using conventional methods. Often, nausea with high blood pressure is a signal of an approaching hypertensive attack. The first thing you need to do is measure your blood pressure using a tonometer. Take a quick-acting antihypertensive medication.
When the pressure is slightly increased, for example, 130-140/95-100 mmHg, then nausea as a symptom is rarely detected. However, as blood pressure rises, due to the progression of the disease, the intensity of nausea increases.
At what pressure does one feel sick? All hypertensive patients feel sick at different numbers; this is due to the body’s adaptability to surges in blood pressure. Some will feel sick at 150/90mm, others feel fine at 170/100mm.
Why do you feel sick with high blood pressure?
Practice shows that nausea occurs both with high and low blood pressure. This symptom is encountered not only by hypertensive patients, but also by hypotensive patients. However, the reasons are different.
If you begin to feel sick against the background of high blood pressure, then an additional “bouquet” of negative symptoms is added. An increase in body temperature, headaches, and diarrhea are often detected. Feeling of heartbeat, painful sensations in the sternum area.
With high blood pressure and vomiting, the danger lies in the fact that this combination of symptoms can develop into a hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke. The consequences of these conditions are unpredictable.
Attacks of nausea and vomiting with high blood pressure are caused by a disorder of blood circulation in the brain. Due to swelling, irritation of the vomiting center is observed - this is the main reason leading to the symptom.
In addition to the fact that brain activity is disrupted, high blood pressure leads to panic and fear, increased anxiety, as a result, a large concentration of adrenaline is released into the blood. The tone of the sympathetic nervous system increases. If the tension is not relieved, repeated vomiting occurs.
Signs of a hypertensive attack:
- Numbness of the limbs.
- Shortness of breath, facial skin becomes red.
- Lethargy, apathy.
- Headache (temple and back of head hurt).
- My head is spinning.
- Vomit.
If nausea and vomiting with pressure are a symptom of a hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke, then the patient’s speech slows down, severe weakness, and intense headache appear.
When the tongue sticks out, it deviates to the side. Such signs require emergency medical care.
Why do you feel sick when your blood pressure is low?
on
We figured out why vomiting occurs with high blood pressure. However, a person can feel sick even with low blood pressure. This condition does not depend on food in any way, and it is difficult to get rid of it.
Once diagnosed, hypotension can cause nausea for various reasons. The main thing is to establish the source of the pathological condition and eliminate it.
With a sharp decrease in systolic and diastolic values, headache, weakness, dizziness, impaired coordination of movement, and slow pulse are observed. Some people experience chills and fever.
The normal blood pressure is 120/80 mm. With a slight deviation within 15 mm, alarming symptoms are rarely detected. When a large difference occurs, the patient experiences a whole range of negative manifestations.
Causes of nausea with low blood pressure:
- Severe exhaustion of the body, which is caused by prolonged fasting.
- Nausea and decreased blood pressure may indicate internal bleeding.
- Pathologies of internal organs - kidneys, liver, stomach.
- Physical or mental exhaustion.
- Sleep deficiency, chronic neurosis, depression.
During pregnancy, low blood pressure is caused by hormonal changes that occur in the first trimester. In the 2-3 trimester, DM and DD increase. No treatment is required. It is enough to follow a daily routine, eat right, and constantly monitor your blood counts.
Dangerous consequences of high blood pressure during pregnancy
Of course, high blood pressure is a pathology and requires immediate correction.
Careful monitoring of blood pressure values by specialists is due to the likelihood of dangerous consequences for mother and child.
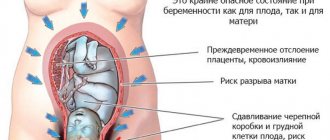
- High blood pressure in pregnant women is a “response” to the narrowing of blood vessels, including in the uterus and placenta. This leads to difficulty in blood circulation in the “uterus-placenta-fetus” system, and, consequently, to fetal hypoxia. Prolonged hypoxia is the cause of intrauterine growth retardation.
- Placental insufficiency, which also develops due to vasospasm, can cause spontaneous abortion.
- Due to increased blood pressure in the channel between the uterus and the placenta, detachment of part of the placenta may occur, which will lead to insufficient nutrition of the fetus, and, depending on the scale of the detachment, may cause premature termination of pregnancy.
- Long-term hypertension can cause functional failure of a woman’s vital organs, which poses a danger to the health and life of the mother and her unborn baby.
- Severe hypertension, as a manifestation of gestosis, can lead to the development of complications dangerous for the mother and her unborn child - preeclampsia and eclampsia.
- A significant jump in pressure, especially during childbirth, can cause retinal detachment (and subsequent blindness) or even a stroke.
How does hypertension affect the expectant mother and child?
Why is high blood pressure dangerous during pregnancy and why is it recommended to constantly monitor it?
Elevated blood pressure readings may indicate the development of gestosis. This is a dangerous disease, the insidiousness of which lies in the disruption of the functioning of vital organs. First of all, the cardiovascular system begins to suffer.
- With gestosis, microscopic holes can appear in the walls of blood vessels, through which liquid and protein from the plasma penetrate into the tissues, which leads to their swelling. They mainly affect the extremities;
- A very dangerous condition can be placental edema, as a result of which the fetus experiences an acute oxygen deficiency;
- The most severe form of gestosis is eclampsia - this is a pathology in which serious damage to the nervous system occurs, which leads to loss of consciousness or even coma.
High blood pressure during pregnancy in the 1st trimester may indicate chronic or gestational hypertension.
Gestational hypertension can occur as a reaction to pregnancy itself. At the same time, in the initial stages, the blood vessels narrow, and the fetus begins to experience a deficiency of oxygen and nutrients.
The cause of chronic hypertension can be various pathological processes in the maternal body. Most often it appears in response to dysfunction of the kidneys or organs of the endocrine system.
High blood pressure during pregnancy in the 2nd trimester is the least common and may be associated with the development of gestosis.
Know! Women who are primarily at risk are those whose bodies develop an infection, become intoxicated, or are often stressed.
High blood pressure during pregnancy in the 3rd trimester may be due to hereditary factors. Therefore, if you also have this predisposition, you should monitor your condition more carefully.
Read about what changes occur in a woman’s body during this period in the article 3rd trimester of pregnancy>>>.
Important! If elevated blood pressure levels are observed over a long period of time, there is a risk of placental abruption.
High blood pressure in late pregnancy can cause premature birth.
During childbirth, hypertension can cause convulsive syndrome - a negative condition that can threaten both mother and child.
Is hospitalization necessary?
Since hypertension is an extremely dangerous phenomenon for a pregnant woman, it is unreasonable to refuse the proposed hospitalization. In addition, it is very likely that with a favorable prognosis, the period spent in the hospital will be short.
If hypertension was included in a woman’s medical history even before pregnancy registration, a referral for hospitalization will be issued at the first appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist.
In the hospital, the degree of hypertension will be determined, the risk of possible complications for the woman’s health will be predicted and treatment methods will be selected.
When hypertension is initially detected during pregnancy, hospitalization is also indicated to search for the causes that caused the increase in pressure.
If an increase in indicators occurred in the second trimester, it is important to exclude the development of gestosis or diagnose it in a timely manner.
If the degree of hypertension is mild, the pressure is stable and does not adversely affect the well-being of the expectant mother, then the next hospitalization as planned will follow at the beginning of the third trimester, since during this period the likelihood of a crisis increases.
At 38-39 weeks of pregnancy, the expectant mother with high blood pressure moves to the hospital until the birth.
During this time, she will undergo an examination in order to clarify her condition and choose a method of delivery, as well as preparatory procedures.
In case of exacerbation of a hypertensive condition in a woman, going to the hospital is mandatory. This is necessary to determine the factors that caused the worsening of hypertension and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Additionally useful
When the legs become severely swollen, a woman cannot move normally, and her quality of life is disrupted. A sedentary lifestyle not only negatively affects future births, but also contributes to increased swelling. Along with taking medications, it is recommended to walk more, especially in the fresh air. This will help increase blood flow, along with it the swelling of the legs will go away, and it will be easier to give birth to a child.
Another important factor that will help prevent swelling is to reduce the amount of fluid consumed. Along with salt, spices, pickled and pickled vegetables, and salted foods are limited. The doctor prescribes special preparations that will help reduce swelling and its negative manifestations.
How to reduce blood pressure during pregnancy
Depending on the causes of arterial hypertension, the doctor chooses tactics for further pregnancy management and treatment methods aimed at normalizing blood pressure.
As a rule, a combination of drug and non-drug therapy is used.
Non-drug method
The non-drug method consists of limiting physical and social activity, namely:
- refusal to participate in stressful situations.
- creating a comfortable psychological environment.
- excluding excessive physical effort, therapeutic exercises and swimming at a calm pace are allowed.
- Maintaining a sleep and rest schedule.
General recommendations
In addition, it is important to follow some nutritional principles aimed at:
- adjustment of potassium-sodium metabolism (to prevent fluid retention in the body);
- prevention of further excessive weight gain (if overweight).
- To improve water metabolism in the body it is necessary:
- limit or completely eliminate the use of table salt with food, as a source of sodium, leading to fluid retention in tissues;
- include in your diet foods rich in potassium, which reduces vascular tone, and magnesium, which also has a mild diuretic property.
To prevent excessive weight gain you should:
- limit fat intake to 40 g per day, giving preference to vegetable fats;
- minimize the presence of simple carbohydrates in the diet: sugars, refined foods, treats;
- adjust your food intake towards fractional meals.
Traditional methods
Among the non-drug ways to combat high blood pressure, folk methods have also found their place:
- Grind and mix an equal amount of rose hips, hawthorn, red viburnum, linden flowers, calendula, blueberry and heather shoots and motherwort herbs. Separate 2 tbsp. l. , pour 2 cups of boiling water over them, simmer for 15 minutes. in a water bath and leave at room temperature. Drink 100 g of the strained mixture with honey after meals 3-4 times a day. The duration of the course is 1.5 months.
- Mix half a glass of cranberry juice with the same amount of honey. Take 1 tsp. 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 14 days.
- Mix an equal amount of crushed valerian root, cudweed herb, heather shoots and viburnum flowers. Pour 2 cups boiling water over 2 tbsp. l. mixture and leave in a thermos for 2 hours. Sweeten the warm, strained infusion with honey and take ¼ cup 4 times a day. The course of treatment is 1-1.5 months.
Before using herbal remedies, you should obtain approval from the doctor monitoring the pregnancy to exclude possible contraindications.
Medication method
In addition to non-drug measures recommended to lower blood pressure, the doctor will prescribe medications.
With a slight increase in pressure, herbal remedies that have a calming, mild sedative effect, based on motherwort, valerian, lemon balm, mint, etc., will be sufficient.
With persistent hypertension, there is a need to use more serious pharmacological agents.
The most common remedy, due to its availability and safety at the same time as its effectiveness, is methyldopa (“Dopegit”).
The blood pressure medication is approved for use from the earliest stages of pregnancy. Methyldopa does not have a negative effect on placental blood circulation, does not pose a threat to the intrauterine development of the fetus, and does not cause adverse effects for the unborn child in the future.
The effect of the substance occurs within 2-6 hours and manifests itself:
- in a relaxing effect for the central nervous system;
- in suppressing the activity of hormones that cause an increase in blood pressure;
- in suppressing the activity of a blood plasma enzyme (renin), which can affect blood pressure levels and sodium metabolism;
- in relieving vascular hypertension;
- in general sedative effect.
For high blood pressure in late pregnancy, when protein is detected in a urine test and taking into account all possible risks to the fetus, β-blockers are prescribed.
The action of the tablets is based on the blockade of receptors sensitive to the action of the “stress hormones” adrenaline and norepinephrine. Taking β-blockers has an antihypertensive effect on a woman’s body and also reduces the frequency of proteinuria.
Cardioselective β-blockers are often prescribed to pregnant women as a medicine for blood pressure, because they have fewer side effects compared to non-selective ones.
In the fight against high blood pressure, the effect they have directly on cardiac activity is important:
- the frequency and strength of heart contractions decreases;
- the body's sensitivity to stress decreases;
- renin activity decreases;
- conductivity in the AV node decreases to the desired level, normalizing the contractile-conducting activity of the cardiac sections;
- the oxygen demand of the heart muscle is normalized (anti-ischemic effect);
- the risk of cardiac arrhythmias is reduced.
Popular β-blockers prescribed to pregnant women help lower blood pressure during pregnancy: atenolol, metaprotolol, labetalol, nebivolol, bisoprolol.
Currently, bisoprolol is more preferable due to its ease of use (1 tablet per day), reliable round-the-clock action, possibility of use in diabetics and less pronounced “withdrawal syndrome” compared to other drugs.
Calcium antagonists or calcium channel blockers are similar in effectiveness to β-blockers.
But they do not act on the nervous system, but on the channels in the cardiac and vascular muscles through which calcium enters the muscle cells.
The force of muscle contraction depends on the calcium concentration in its cells. Activation of calcium channels occurs under the influence of adrenaline and norepinephrine. Blockade of calcium channels prevents spasm of the heart muscles and blood vessels.
Based on the direction of action of calcium antagonists, they can be divided into groups:
- acting only on smooth vascular muscles (nifedipine, normodipine, amlodipine, etc.) and therefore recommended for use simultaneously with β-blockers;
- acting on the muscles and heart and blood vessels (verapamil) and therefore prohibited for use simultaneously with β-blockers.
Taking calcium antagonists during pregnancy does not exclude a possible detrimental effect on the fetus and is often accompanied by unpleasant side effects.
Therefore, they are prescribed when taking other groups of antihypertensive drugs is impossible.