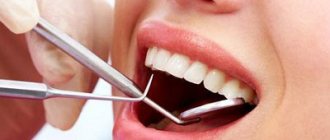
Is it possible to treat teeth with anesthesia for pregnant women?
Pregnant women are not immune from caries and other dental diseases.
Of course, it is better to sanitize the oral cavity when planning motherhood, but health problems can happen suddenly. What should women do in such a situation? If a pregnant woman has problems with her teeth, she cannot put off a visit to the dentist - expectant mothers have a weakened immune system, and advanced caries can easily cause purulent complications.
The doctor will tell you separately whether a woman can undergo this or that manipulation. Conditions that require urgent intervention must be treated immediately.
As for the permissibility of using anesthesia, a balance must be maintained between the intensity of pain from treatment and possible harm from the drug. Local anesthetics used in dentistry are almost not absorbed into the blood, so the main danger is an allergic reaction.
Anesthesia is needed when performing any painful manipulations in the oral cavity. Since non-urgent manipulations are rarely performed during pregnancy, pain relief is almost always necessary.
The choice of drug should be approached especially carefully - if the patient has already had her teeth treated with anesthesia, and remembers exactly what kind of anesthesia was used, then this particular drug should be used again.
The dosage should be observed very strictly; it should not be exceeded - this may provoke an allergic reaction.
Ideally, you should start sanitation of the oral cavity before pregnancy, but a joyful event may happen before the woman has time to complete treatment.
Carious teeth can become a source of infection for the baby, so even expectant mothers need to treat them, and the statement that this should wait until after childbirth is wrong.
And what can really be postponed are non-therapeutic procedures (bleaching, fluoridation, professional cleaning).
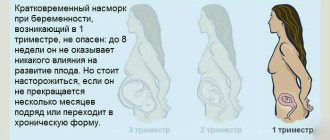
The best time for dental treatment during pregnancy is considered to be the second trimester. It is at this time that dental sanitation needs to be completed if the woman did not have time to do it before conception. Also, all dental problems that arise should be postponed until the second trimester or before childbirth, unless they require urgent intervention.
Wearing braces and any other structures is impractical. Expectant mothers often experience gingivitis (inflammation of the gums), teeth become more wobbly, so it is impossible to install the structures correctly, and their presence will cause pain and inconvenience. Dental prosthetics are postponed until after childbirth for the same reason.
Dental interventions, unless they are urgent, are not recommended to be performed before the 12th week of pregnancy. At this time, the formation of all the main organs and systems of the baby occurs, so the mother should refrain from additional stress factors.
If there is a need for urgent dental intervention that requires anesthesia, and even more so X-ray (in case of injury), the woman needs to perform the necessary procedures, then inform her gynecologist about this and undergo the prescribed tests - it takes time to understand whether the manipulation has harmed the baby .
If the pregnancy is so early that the woman does not yet know whether she is pregnant, it will not be possible to prevent harm from the effects of dental procedures. In some cases, it is a trip to the dentist and an unexpected reaction to treatment that turns out to be the factor through which a woman finds out that she will become a mother.
Until when
It is highly undesirable to carry out dental interventions after 36 weeks. At this stage, the half-sitting position that the woman occupies in the chair increases pressure on the lower abdomen. This can trigger premature birth. Therefore, all manipulations not related to the treatment of acute pain are prohibited during this period.
After 25 weeks (with the beginning of the third trimester), the tone of the uterus begins to increase, and any effects on the mother’s body, including dental treatment and associated stress, can cause early placental abruption and fetal hypoxia. To reduce stress levels, women are advised to wait until after childbirth for non-urgent procedures.
When treating teeth in pregnant women, the general rule applies, which applies to all diseases in expectant mothers - the benefit must outweigh the risk. And if you can do without manipulation or postpone it for several months, you should not risk your own health and the well-being of the unborn baby. However, acute pain, purulent inflammation and injuries must be treated at any time and as quickly as possible.
Is it possible or not?
A visit to the dental office is a mandatory procedure for every pregnant woman. This is due to the fact that the oral cavity plays an important role for the body. Diseases and infections can easily enter the bloodstream and cause complications for both the mother and the baby. How to treat teeth while carrying a baby?
Treatment for the first time in the early stages
The first trimester is an important time. It is during this period that the formation and laying of internal organs and life support systems occurs. Any negative impact can have serious consequences for the fetus. Therefore, doctors strongly recommend postponing any therapeutic measures that are carried out using strong medications. It is not advisable to remove a tooth, roots or nerve in the early stages. The doctor will try everything possible to postpone the surgery until a later date.
As for easier procedures: fillings, caries treatment - this can be done. A carious tooth, even if it does not bother a woman, poses a potential threat. It creates a favorable environment for the development of bacteria and harmful organisms. Therefore, the problem must be eliminated immediately; no anesthesia is required at this stage. The only restriction is that arsenic cannot be used.
Fillings can be installed chemically or light-cured.
Often during pregnancy, stomatitis and gingivitis occur - inflammation of the root region of the tooth and gums. This is usually due to a rare hormonal imbalance. At the first symptoms you should consult a doctor.
In cases where periodontitis or pulpitis occurs, treatment with an anesthetic is required, and an x-ray is also required. Modern devices have a low radiation dose and will not harm the baby, but such a procedure in the early stages is done strictly as prescribed by the doctor, and as a last resort.
Tartar removal is also allowed at any time. The treatment does not require pain relief, but is performed using ultrasound or special instruments.
Safe drugs for local anesthesia
Local (local) anesthesia is the safest type of pain relief. It is used for women during pregnancy. As a rule, a lidocaine solution is used for injection. This drug in small doses can penetrate the placenta in early pregnancy, but it is quickly eliminated from the child’s body and does not cause harm.
Novocaine can also be used during pregnancy, but the dosage is usually reduced.
The anesthetics Ultracaine and Primacaine, containing adrenaline, are very popular in dentistry. However, they cannot be used during pregnancy. Accidental entry of adrenaline into the bloodstream can cause a sharp narrowing of blood vessels and disrupt blood flow to the placenta.
The dosage of the drug depends on the patient’s weight, her pain threshold and the complexity of the planned procedure. As a rule, women are given 1 ampoule or half, and for excess weight - 2 ampoules. The duration of action of the anesthetic is from 40 minutes to 2 hours.
First, let’s determine at what stage of pregnancy you can relatively safely treat teeth with anesthesia. The first and last trimesters (especially the ninth month) are considered the most dangerous in terms of external influences. In the early stages of pregnancy (1-3 months), the formation of fetal organs occurs, so the intervention of chemicals (medicines) is undesirable. In the last couple of months, the baby is also vulnerable, so it is also better not to “disturb” him with unnecessary medications.
It turns out that the second trimester is the safest, but this does not mean that a pregnant woman can drink handfuls of pills and undergo dental treatment with any anesthesia: there are still restrictions. But one thing is clear: pregnant women can have their teeth treated using painkillers.
If you have problems with your teeth, you should consult a dentist regardless of the time frame. Even if the tooth began to bother you in the first trimester, you should first visit the dentist to assess the situation. Afterwards, you need to contact your obstetrician-gynecologist and, together with him, think through further treatment tactics.
Painkillers, like other medications, harm the development of the fetus in the womb. The impact can range from minor to severe, including:
- the appearance of severe deformities in the child;
- fetal hypoxia due to insufficient oxygen supply;
- spontaneous miscarriage due to uterine tone.
During pregnancy, anesthesia with adrenaline is especially dangerous, which is sometimes added to the anesthetic solution to reduce its amount and increase the duration of the analgesic effect. Pregnant women can have their teeth treated only with adrenaline-free anesthesia, otherwise the risk of uterine tone and a general increase in pressure will increase.
Local (local) anesthesia is the safest type of pain relief. It is used for women during pregnancy. As a rule, a lidocaine solution is used for injection. This drug in small doses can penetrate the placenta in early pregnancy, but it is quickly eliminated from the child’s body and does not cause harm.
We suggest you read: Causes of burning tongue and its treatment
Novocaine can also be used during pregnancy, but the dosage is usually reduced.
The anesthetics Ultracaine and Primacaine, containing adrenaline, are very popular in dentistry. However, they cannot be used during pregnancy. Accidental entry of adrenaline into the bloodstream can cause a sharp narrowing of blood vessels and disrupt blood flow to the placenta.
The dosage of the drug depends on the patient’s weight, her pain threshold and the complexity of the planned procedure. As a rule, women are given 1 ampoule or half, and for excess weight - 2 ampoules. The duration of action of the anesthetic is from 40 minutes to 2 hours.
The mechanism of action of modern drugs for local anesthesia is the disruption of the formation and conduction of impulses in nerve endings and fibers. In addition to pain, all types of sensitivity are temporarily reduced. A person ceases to feel touch and temperature.
The therapeutic effect is realized by local injection of an anesthetic solution into soft tissues, penetrating into the structures of the nervous system. If a large amount of the compound enters the blood, the anesthetic affects the functional state of the heart and blood vessels. This is manifested by a change in heart rate and rhythm, as well as an increase or decrease in blood pressure.
Anesthetics, when ingested by a developing fetus, can have a negative effect:
- disruption of the processes of formation and maturation of various organs;
- the formation of developmental defects, the most severe of which are changes in the heart and structures of the nervous system;
- disruption of the functional state of the heart and structures of the fetal nervous system.
After the birth of a child, exposure to anesthetics in utero can lead to delays in growth and development.
There are several drugs on the modern pharmaceutical market that have minimal negative effects on the developing fetus. The most commonly used are primacaine and ultracaine.
Despite the fact that drugs with such active ingredients have minimal negative effects, their use is allowed only for strict medical indications. First, the dentist prescribes a consultation with a gynecologist, who will assess the balance of benefits for the mother with the potential risk for the developing fetus.
Review of popular painkillers: risks, timing, replacement options
Pregnant women should approach the choice of painkillers responsibly and carefully. Always read the instructions! Allowed drugs in the first two trimesters may be prohibited in the third, and suitable medications in the last stages of pregnancy are not always used in the early stages of gestation.
The modern pharmacological market offers a wide range of painkillers. But among them there are “people's leaders.”
Lidocaine
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic drug available in the form of a solution for intravenous administration and injection, spray, ointment, and eye drops. Depending on the purpose of use of the drug, one or another form of the drug is used.
FDA category of action of lidocaine on the fetus (when applied topically) is B. The instructions include pregnancy as a limitation for the use of the drug.
The active substance of this anesthetic is lidocaine hydrochloride. Water for injection is used as an auxiliary component in the solution for intravenous administration, and water and sodium chloride are used in the solution of Lidocaine for injection. The spray, along with the main component, contains 96% ethanol, propylene glycol and peppermint oil, and the eye drops additionally contain water, sodium chloride and benzethonium chloride.
Lidocaine in the form of a spray can, if necessary, be used for local anesthesia no earlier than the second trimester of pregnancy.
The principle of action of Lidocaine is to block sodium channels in nerve endings, which has a beneficial effect on the inhibition of the conduction of nerve impulses.
During pregnancy, Lidocaine is often used to a limited extent, most often in the form of an injection solution for dental treatment, but it is important to know that today there are safer anesthetics for pregnant women . In gynecology, the drug is used for local anesthesia when suturing the cervix or installing a pessary, if necessary. In this case, doctors use an injection solution of Lidocaine or a spray. Expectant mothers may also need pain relief in case of injuries, stretch marks, dislocations, as well as minor surgical procedures (for example, when suturing wounds).
Lidocaine has a number of contraindications:
- intolerance to the components of the drug;
- bradycardia or chronic heart failure;
- low or high blood pressure;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- lactation period.
Side effects from using Lidocaine may include:
- allergic reactions (itching and rash on the skin);
- disorders of the nervous system (insomnia, depressed and weak state);
- headache and dizziness;
- disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract (diarrhea, nausea, vomiting);
- changes in blood pressure;
- heart pain.
The combined use of lidocaine with other drugs can have a toxic effect on the body, strengthen or weaken the effect of one of the drugs, and lead to adverse reactions of various types. Therefore, independent use of lidocaine is excluded. Only a doctor can determine the dose for using the drug, and also select additional medication if necessary.
Anesthesia with lidocaine is not recommended in the first trimester of pregnancy, since the placenta is not yet formed at this time and there are risks of a negative effect on the development of the fetus. From the second half of pregnancy, lidocaine is eliminated from the baby’s body thanks to the functioning of the placenta much faster than from the mother’s blood.
Baralgin and Analgin and other preparations of metamizole sodium
Baralgin is a non-narcotic analgesic that has an analgesic and antipyretic effect on the body. The drug is available in the form of tablets, drops, rectal suppositories and solution for intramuscular and intravenous administration. For pregnant women, it is more preferable to use tablets of this painkiller, since Baralgin injections are painful and can provoke uterine tone.
Contraindicated in the first and third trimesters of pregnancy. Use in the second trimester is only for strict medical reasons. Breastfeeding is contraindicated within 48 hours after taking Baralgin M.
Register of medicines: Baralgin: Active substance
https://www.rlsnet.ru/tn_index_id_468.htm#primenenie-pri-beremennosti-i-kormlenii-grud%60yu
The active ingredient of Baralgin is metamizole sodium, and the auxiliary components are macrogol and magnesium stearate. The drug prevents the transmission of pain impulses to the nerve center. Thanks to this mechanism, the pain is dulled, but the cause of its occurrence does not disappear, so the pain may recur after the painkiller is removed from the body.
The category of action of metamizole sodium on the fetus according to the FDA has not been determined, however, in a number of countries this substance is prohibited, since its toxic effect on the body as a whole has been proven.
General indications for the use of Baralgin:
- headache;
- toothache;
- muscle pain;
- joint pain;
- intestinal colic;
- neuralgia;
- radiculitis;
- arthritis;
- injuries;
- febrile syndrome (infectious-inflammatory diseases, insect bites).
Contraindications for the use of Baralgin include:
- intolerance or hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- I and III trimester of pregnancy and breastfeeding period;
- age under 15 years;
- disturbances in the functioning of the liver, kidneys, heart, and respiratory organs.
The use of Baralgin together with other analgesics can mutually enhance the toxic effects, and with sedatives - lead to severe hypothermia. The simultaneous use of Baralgin and acetylsalicylic acid leads to a decrease in the effectiveness of the latter.
In the first trimester, it is prohibited to use Baralgin due to possible damage to the child’s nervous system; in the third trimester, when using the drug, a pregnant woman faces possible complications during childbirth and the postpartum period (heavy bleeding, weak labor), as well as impaired respiratory function in the baby. The second trimester is the only relatively safe time for taking Baralgin, but subject to strict adherence to the dosage selected by the doctor and a short course of treatment .
Baralgin can be used with caution only in the second trimester of pregnancy
Another popular painkiller from the group of non-narcotic drugs is Analgin. The active ingredient of Analgin is the same as that of Baralgin - sodium metamizole. Analgin is produced in tablets and ampoules. During pregnancy, if there is an urgent need, it is possible to use both forms of the drug, depending on the situation.
Contraindications to the use of Baralgin and Analgin:
- renal and liver failure;
- intolerance to the components of the drug;
- dysfunction of the bone marrow;
- age up to 10 years;
- I and III trimester of pregnancy;
- breastfeeding period.
Adverse reactions from the use of metamizole include headaches and dizziness, fever, anemia, skin rash and much more.
In case of urgent need and the unavailability of other medications, the doctor may prescribe Analgin to the expectant mother in a certain dosage, subject to short-term (ideally one-time) use.
Analgin should not be abused during pregnancy, as the risk of negative consequences exists at any stage of gestation
Ketorol and Ketanov
Ketorol (analogue - Ketanov) is an analgesic non-narcotic drug produced in the form of tablets, solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration, as well as gel (ointment). In the first six months of bearing a baby, ointment is considered the safest form of the drug to use. The use of Ketorol in the form of tablets, solution and gel in the last trimester of pregnancy is prohibited.
The main active ingredient of the drug is ketorolac. Additional components in the ointment include propylene glycol, carbomer, dimethyl sulfoxime, tromethamine, glycerol, ethyl alcohol, sodium methyl parahydroxybenzonate, purified water and flavoring.
Category of action of ketorolac on the fetus according to the FDA is C.
Ketorol has analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects. The gel affects peripheral tissues, preventing the biosynthesis of prostaglandins, which are responsible for the pain threshold of sensitivity.
Ketorol is strictly forbidden to be used in the third trimester of pregnancy
The ointment is used for toothache, myalgia and neuralgia, bruises, sprains and rheumatic lesions, pain from injuries, as well as radiculitis and inflammation of soft tissues.
Ketorol, like many other painkillers, does not eliminate the cause of pain, but only muffles the pain.
Contraindications to the use of ointment may include:
- skin diseases (dermatosis, eczema, infected abrasions);
- bronchial asthma;
- age up to 12 years;
- intolerance to the components of the drug;
- third trimester of pregnancy;
- breastfeeding period.
Side effects from the use of Ketorol may include allergic reactions (itching, peeling of the skin, redness, urticaria) and gastrointestinal disorders - heartburn, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea.
After consultation with your doctor, Ketorol can be used externally with caution until 27 weeks of pregnancy, avoiding ingestion of the drug. In the last three months of expecting a child, this painkiller can lead to negative and irreversible consequences - uterine bleeding and labor disturbances, which pose a threat to the life and health of mother and baby.
Spazgan and Spazmalgon
Spazgan and Spazmalgon are analgesic, antispasmodic and antipyretic drugs that have identical active substances in the same proportions:
- metamizole sodium (500 mg);
- pitofenone hydrochloride (5 mg);
- fenpiverinium bromide (0.1 mg).
Methods of administration and doses, indications and contraindications, as well as side effects for these two analgesics are the same.
Painkillers are available in tablets and in the form of an injection solution. While waiting for the baby, in case of acute one-time need, the acceptable form of the drug is tablets; injections are given in rare cases.
Use is contraindicated during pregnancy (especially in the first trimester and the last 6 weeks) and during breastfeeding, because possible premature closure of the ductus arteriosus and perinatal complications due to the effect of metamizole sodium on the ability of maternal and fetal platelets to aggregate.
Register of medicines: Spasmalgon: Active substance
https://www.rlsnet.ru/mnn_index_id_4365.htm#primenenie-pri-beremennosti-i-kormlenii-grud%60yu
Spazgan and Spazmalgon are painkillers with the same active substance
The medicine helps relax the smooth muscles of internal organs, reduce their tone, and relieve inflammation. Spazgan and Spazmalgon are prescribed for stomach pain, intestinal and renal colic, muscle pain, neuralgia and sciatica.
Recent Entries
Is it possible to give a mirror: how to protect yourself from bad omens It became known about the influence of cell phone towers on human health Is it possible to eat bananas bought in Russia?
If a woman has certain diseases or conditions, these medications should not be taken. These include:
- pregnancy in the first trimester and the last month and a half of gestation;
- lactation period;
- individual intolerance to the components of the drug;
- anemia;
- intestinal obstruction;
- liver and kidney diseases;
- bronchial asthma;
- tachyarrhythmia;
- diseases of the heart, gall bladder.
Among the complications caused by taking Spazmalgon and Spazgan, the following stand out:
- allergic reactions;
- constipation or exacerbation of gastritis;
- tachycardia and dysfunction of the cardiovascular system;
- anemia;
- renal failure, etc.
While carrying a child, the drug is strictly contraindicated for a woman in the first three months, as this risks a pathological condition of the fetus (for example, abnormal development of internal organs) or miscarriage. Use of this medicine in the last weeks of pregnancy may weaken labor and result in birth injuries.
Taking Spazgan or Spazmalgon together with other analgesics can lead to toxic damage to the body.
No-Shpa and Drotaverine
The active component in No-Shpe and Drotaverine is drotaverine hydrochloride, and the excipients are povidone, magnesium stearate, corn starch, talc, lactose. The drugs have the same chemical composition and concentration and are available in the form of injections and tablets. No-Shpa and Drotaverine differ only in manufacturer and cost (Drotaverine is cheaper than No-Shpa).
The drugs belong to the group of antispasmodics, which reduce the tone and motor activity of the smooth muscles of internal organs. Also, the active substance relieves spasm of blood vessels and has no effect on the nervous system.
As shown by studies on reproductive toxicity in animals and retrospective studies of clinical data, the use of drotaverine during pregnancy had neither teratogenic nor embryotoxic effects. Despite this, when prescribing drotaverine to pregnant women, caution should be exercised and it should be used only in cases where the potential benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus, while prescribing the injectable dosage form of No-shpa® in pregnant women should be avoided.
Register of medicines: No-shpa
https://www.rlsnet.ru/tn_index_id_2337.htm#primenenie-pri-beremennosti-i-kormlenii-grud%60yu
Most often, pregnant women take No-Shpu or Drotaverine when there is uterine hypertonicity and the threat of premature birth, as well as for diseases of the gall and bladder, intestinal and renal colic.
The use of Drotaverine and No-Shpa during pregnancy is possible at any stage, but with great caution and after the doctor’s permission
No-Shpu and Drotaverine are not prescribed to expectant mothers with severe heart failure, eye disease (glaucoma) and hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Adverse reactions from these drugs include:
- headaches and dizziness;
- nausea or vomiting;
- constipation;
- changes in blood pressure;
- tachycardia.
In the first half of pregnancy, No-Shpa promotes the preservation and normal development of the fetus by relaxing the muscular lining of the uterus. At later stages of gestation, No-Shpu and Drotaverine are used with great caution, since their active substance can provoke relaxation of the cervix and its sudden dilatation, which leads to premature birth.
Ibuprofen and Nurofen
Nurofen and Ibuprofen belong to the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that reduce pain, body temperature and febrile seizures. The active ingredient in both medications is ibuprofen.
Expectant mothers are allowed “simple” ibuprofen preparations without additional active substances in the composition
The drugs are presented in the form of capsules, tablets, syrup and oral solution, gel. For pregnant women, the drug in pediatric form with the lowest content of active substance is more suitable for use.
Contraindicated in the third trimester of pregnancy, in the first and second trimesters - with caution.
Register of medicines: Active substances: Ibuprofen
https://www.rlsnet.ru/mnn_index_id_100.htm#primenenie-pri-beremennosti-i-kormlenii-grud%60yu
Ibuprofen is prescribed for rheumatoid pathologies (rheumatism, articular syndrome, arthritis, osteoarthritis, etc.), feverish conditions caused by inflammation and infections, as well as for toothache and headaches.
Contraindications to the use of the drug are:
- acute stomach ulcer;
- ulcerative colitis;
- depressed hematopoietic function;
- heart failure;
- optic nerve diseases.
Common adverse reactions include:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- heartburn;
- bloating;
- changes in blood pressure;
- allergic reactions.
During pregnancy, Ibuprofen and Nurofen can be used as a pain reliever in the second trimester . The rest of the time, the medication can lead to negative effects on the development of the fetus, as well as complications during the birth process. Using ointment and gel is safer than taking tablets.
Along with Paracetamol and Drotaverine, ibuprofen drugs are the most common among pain pills prescribed to expectant mothers.
Nimesil
Nimesil belongs to the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and is produced in the form of a powder intended for dissolution in water. The main active ingredient of the drug is nimesulide, auxiliary ingredients are ketomacrogol, molasses, sucrose, E330 and flavoring.
During pregnancy, the use of Nimesil is fraught with negative consequences for mother and baby
Nimesulide reduces the production of prostaglandins, which leads to a decrease in elevated body temperature, pain relief and prevention of inflammation in the body. Nimesil can be used during pregnancy only in case of emergency and only by the decision of the attending physician to eliminate acute pain of any nature.
Like other drugs of the NSAID class that inhibit the synthesis of PG, nimesulide can adversely affect the course of pregnancy and/or the development of the embryo and lead to premature closure of the ductus arteriosus, hypertension in the pulmonary artery system, impaired renal function, which can progress to renal failure with oligohydramnios, to an increased risk of bleeding, decreased contractility of the uterus, and the occurrence of peripheral edema. In this regard, nimesulide is contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation.
Register of medicines: Nimesil
https://www.rlsnet.ru/tn_index_id_13172.htm#primenenie-pri-beremennosti-i-kormlenii-grud%60yu
The drug has a number of contraindications:
- hypersensitivity to the components of the product;
- increased bleeding;
- acute ulcer of the duodenum or stomach;
- intestinal diseases;
- cardiac, renal, liver failure;
- poor blood clotting;
- alcoholism and drug addiction;
- children under 12 years of age;
- pregnancy and lactation.
Common side effects from the drug:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- dizziness;
- tachycardia;
- change in blood pressure;
- dyspnea;
- itching and rash on the skin.
Treatment with Nimesil is dangerous for pregnant women, as the drug can provoke abnormalities in the development of the fetus, as well as lead to spontaneous abortion. Therefore, when choosing a painkiller, you should give preference to safer medications.
Is there an alternative
If we take it as an axiom that the use of local anesthesia in dentistry for pregnant women will greatly harm the child, theoretically there are two options left. But, unfortunately, both of them are obviously even more dangerous for the baby. First: do not treat your teeth yet and wait until childbirth. In this case, mommy will suffer from toothache, and this is unnecessary stress for her and the baby.
Second option: treat without anesthesia. For simple superficial caries, treatment is carried out without anesthesia. For more serious problems (inflammation of the canal, nerve), dental anesthesia is necessary, because the painful shock for a pregnant woman will be more dangerous than the administration of medications.
When is pain relief required?
In dentistry, modern local anesthetics are used, which are practically not absorbed into the blood and do not cause systemic complications.
Those. if a woman is not allergic to a specific drug, then pain relief affects her in the same way as before pregnancy - it numbs the jaw and does not cause unwanted effects.
You should be wary of hypersensitivity. Pregnancy is accompanied by hormonal changes, which can cause allergies in cases where they were not previously observed.
To avoid unwanted reactions, the patient needs to remember what medicine was used to relieve pain before, and during treatment, inform the doctor about deterioration in well-being.
Anesthesia in dentistry during pregnancy involves the use of specific agents that have a minimal effect on all processes associated with the safe bearing of the baby. Pregnant women can be given local anesthesia with the following drugs:
- ultracaine;
- ubistezin;
- novocaine (if there is no allergy).
Lidocaine, popular today, affects cardiac activity, so it is not suitable as an anesthesia for pregnant women.
A woman who comes to the doctor early, when the tummy is still invisible, must definitely warn the doctor about her situation. You should also make assumptions about a possible pregnancy, for example, if you had unprotected sexual intercourse and your next menstruation has not yet begun. This will allow the doctor to determine what anesthesia can be used to minimize the negative effects of the medications on the fetus.
Modern dentistry allows the use of general anesthesia, but not during pregnancy. A “cocktail” of medications that enters a woman’s body during drug-induced sleep is extremely dangerous for a child at any stage.
Before deciding on the possibility of using anesthesia during pregnancy, consider whether you really need it? After all, for example, the treatment of an uncomplicated carious cavity can be done without its use. The dentist will be able to carefully clean the canals without affecting the nerve itself, and there will be no need for dental anesthesia, which is undesirable for pregnant women.
Treatment of an uncomplicated carious cavity can be done without the use of anesthesia
Among pregnant women, there is a widespread belief that any type of anesthesia is harmful during fetal development. In this regard, most pregnant women prefer to postpone a visit to the dentist's office.
When carrying a child, it is necessary to check with your attending physician about the possibility of dental treatment using anesthesia.
It is often allowed if
- there is no individual intolerance;
- painkillers are carefully selected;
- treatment is carried out in the second or third trimester of pregnancy.
It is important to understand how pain medications affect women who are pregnant. Dentists often use medications containing adrenaline, which helps to constrict blood vessels, which leads to an analgesic effect.
These drugs are prohibited during pregnancy, as they increase uterine tone and provoke an increase in blood pressure. It is because of this that expectant mothers should receive treatment using only modern medications containing a minimal amount of adrenaline.
Expectant mothers should receive treatment using only modern medications containing a minimum amount of adrenaline
When treating teeth during pregnancy, painkillers are administered by injection, which begins to have an effect after a short period of time. A pregnant woman usually does not feel any pain from medical procedures, which allows for a variety of procedures, including the removal of a diseased tooth. Neither mother nor child will feel any negative emotions.
When carrying a child, it is prohibited to perform anesthesia:
- in the first trimester of pregnancy;
- in the last month of pregnancy;
- if you are allergic to the constituent components of the anesthetic drug;
- if there is a danger to the mother and child from the type of painkiller used.
When treating teeth during pregnancy, painkillers are administered by injection.
There are some types of anesthesia that are prohibited during pregnancy. The consequences of their use may be irreversible.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Gummy smile: reasons for development, how to correct it,
| View | Influence |
| Local anesthesia with lidocaine | A sharp decrease in blood pressure, difficulty breathing, seizures and muscle weakness |
| General anesthesia | The woman is in a state of artificial coma, which is very dangerous for the child |
How to use the drug correctly and safely during pregnancy?
Depending on the period of development of the child, the age of the expectant mother, her body weight and the complexity of the intervention, an individual dosage of the medication is selected.
A single dose for pain relief is from 100 to 200 milligrams of solution. If the procedure is quite minor and does not require strong anesthesia, then the amount of the drug is reduced to 50-60 mg.
Lidocaine (spray) is applied topically during pregnancy. It is often used in dentistry. Particular care must be taken when doing this. Due to loss of sensitivity, the expectant mother can damage the tongue and mucous membranes of the oral cavity with her teeth.
Dental problems during pregnancy
Is anesthesia harmful during pregnancy? Doctors say yes. This type of anesthesia can lead to a sharp decrease in blood pressure in a pregnant woman, while oxygen saturation in the blood deteriorates.
Dangerous consequences of general anesthesia:
- teratogenicity (impaired development of tissues and organs of a child, which can cause congenital deformities);
- intrauterine asphyxia of the fetus (suffocation), which occurs due to maternal hypoxia (oxygen starvation);
- increased risk of miscarriage.
Operations under anesthesia are carried out in extreme cases when there is a threat to the life of the mother. Superficial sedation (inhalation of nitrous oxide) is also contraindicated. Therefore, only local anesthesia is used for dental treatment.
If a woman is afraid of injections, then you can first numb the mucous membrane with an anesthetic gel, and only then inject into the gums.
Private dental clinics have a large selection of anesthetic drugs indicated during pregnancy. If you are looking for reliable dentistry, we suggest using the convenient search engine on our website.
Hormonal changes in the body of expectant mothers also affect teeth, which may begin to decay. This doesn't always happen, but some pregnant women suffer from hair loss and dental deterioration:
- the enamel wears away, which increases sensitivity to cold and hot;
- teeth crumble, become loose;
- Gums bleed and become inflamed.
Not only hormones affect the condition of the teeth of pregnant women. A lack of vitamins can also cause their condition to worsen. The fetus develops and needs calcium. And if mommy doesn’t get enough of it, she has to “pay” with healthy teeth. Gums suffer due to vitamin C deficiency.
And, of course, changing your diet. Pregnant women often crave sweets and other fast carbohydrates. This also affects the condition of the teeth, which become more susceptible to caries.
Is anesthesia harmful during pregnancy? Doctors say yes. This type of anesthesia can lead to a sharp decrease in blood pressure in a pregnant woman, while oxygen saturation in the blood deteriorates.
Dangerous consequences of general anesthesia:
- teratogenicity (impaired development of tissues and organs of a child, which can cause congenital deformities);
- intrauterine asphyxia of the fetus (suffocation), which occurs due to maternal hypoxia (oxygen starvation);
- increased risk of miscarriage.
Operations under anesthesia are carried out in extreme cases when there is a threat to the life of the mother. Superficial sedation (inhalation of nitrous oxide) is also contraindicated. Therefore, only local anesthesia is used for dental treatment.
If a woman is afraid of injections, then you can first numb the mucous membrane with an anesthetic gel, and only then inject into the gums.
Private dental clinics have a large selection of anesthetic drugs indicated during pregnancy. If you are looking for reliable dentistry, we suggest using the convenient search engine on our website.
A large number of studies have made it possible to identify drugs with the least amount of the hormone adrenaline in their composition.
For example, the following are preferred as anesthesia for pregnant women:
- Ultracaine;
- Primacaine;
- Ubistezin and others.
The drug Ultracain
The use of these drugs does not pose a risk to the health of pregnant women, since all the harmful substances contained in them cannot penetrate the walls of the placenta, which means that they are not able to penetrate the baby’s body. Primacaine and Ultracaine are the most common painkillers. Some experts are not against their use even in early pregnancy.
The attending physician individually determines all necessary doses of medication according to the stage of pregnancy, the state of health and the age of the woman. Primacaine enters the placenta minimally and, moreover, has a short half-life, which is why conduction anesthesia with the use of this drug is permitted when carrying a child.
In what cases is the drug contraindicated during pregnancy?
The drug should never be taken by expectant mothers who are hypersensitive to the main component. Also among the contraindications are the following situations:
- severe heart failure;
- high blood pressure;
- lactation and short-term pregnancy;
- complications of liver and kidney pathologies;
- during bradycardia;
- with blockade of the transverse vessels of the heart, and so on.
Doctors strongly do not recommend using the spray form if there is a possibility of an epileptic seizure in the expectant mother.
During use of the product, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the pregnant woman. In case of overdose and improper use of the drug, the following reactions may occur:
- skin itching and severe rash;
- shortness of breath and pressure disturbances;
- weakness and dizziness;
- insomnia and headaches;
- nausea, vomiting and digestive disorders;
- pain in the heart and stopping the functioning of this organ.
If one of the reactions occurs, symptomatic treatment should be performed immediately. In some cases, even emergency early delivery or hospitalization of the expectant mother may be required.
Safe drugs for local anesthesia
Not all medications used in dentistry are approved for expectant mothers. In some cases, it may be advisable to refuse anesthesia - if the procedure itself is not too painful. But not all women can tolerate pain, even minor pain, and pain is more stress for the fetus than the risk of an allergy to anesthesia.
During treatment
List of approved drugs for dental treatment:
- Ultracaine;
- Ubestezin;
- Novocaine (in the absence of allergies).
Ultracaine is considered the most popular remedy in dentistry - it is effective and safe, but its disadvantage is the price. Replacing Ultracaine with Novocaine is possible if the woman tolerates it well.
It is forbidden to use products containing adrenaline - they can harm the baby. Lidocaine is also prohibited due to its effect on cardiac activity.
When deleting
When removing a tooth, the same medications are used as in its treatment. Most often, it is necessary to remove teeth with a higher dose, so it is advisable not to use the Novocaine injection and completely replace it with Ultracaine. Otherwise, the recommendations are similar.
Which anesthetic to choose
Currently, drugs with a minimal dosage of adrenaline are used, which allows them to be used to treat pregnant women. The most popular drug in this group is Ultracaine. "Ultracaine" does not penetrate the placental barrier, and therefore is absolutely safe for the fetus. Also, Ultracaine does not pass into breast milk, which means it can be used for dental treatment in nursing women. In each specific case, the doctor selects the required dosage, based on the individual characteristics of the woman and the duration of her pregnancy.
Thus, the expectant mother not only can, but also needs teeth, especially since at present it is absolutely safe for her health and the health of the child.
When and how is dental treatment performed?
Can pregnant women have their teeth pulled out under anesthesia? It is possible and even necessary, because tooth extraction without pain relief can cause shock. In general, any surgical treatment involving violation of the integrity of the gums should be carried out only in extreme cases, when there is no alternative.
The same applies to installing braces. If it is possible to postpone this to another period, it is better to do so. Because orthodontic appliances involve tooth movement, which can be painful. And then the expectant mother will be tempted to take painkillers. If pregnancy occurs while wearing braces, of course, you should not remove them. But you need to double or even triple your hygiene.
If there is a need for routine treatment of caries or other dental diseases at the beginning of pregnancy, then it should be postponed. In the early stages of pregnancy, the formation of the placenta is just beginning, and the fetus is not fully protected from the negative effects of medications. In the first trimester, the laying of all organs and systems takes place. Exposure to negative factors leads to changes in the genetic material of cells - mutations.
In the second trimester, the risk of negative effects of the drug on the fetus is lower. The formed placenta prevents toxins and medications from the mother’s blood from entering the body of the developing fetus. Treatment with anesthesia will no longer be so dangerous.
In later stages, the uterus and placenta are depleted, so the fetus’s body again becomes vulnerable to many medications. These features must be taken into account when prescribing any medications, including those intended for anesthesia in dentistry. Some medications may be more harmful in the third trimester than in the first weeks of pregnancy.
During pregnancy, the course of all physiological processes in a woman’s body changes. The need for minerals, vitamins, and nutritional compounds increases. Against the background of calcium deficiency, dental caries often develops, which is an indication for subsequent treatment by a dentist and the use of local anesthesia.
For prevention, you should follow a few simple recommendations:
- maintaining a diet with a sufficient content of calcium salts, phosphorus, vitamins;
- oral hygiene, brushing teeth at least 2 times a day;
- preventive visits to the dentist at least 2 times a year.
We suggest you read where you can get your dentures repaired
Thanks to timely detection, caries in the initial stages is treated without the use of local anesthesia. Following the recommendations will allow you to avoid medical procedures requiring the administration of an anesthetic.
Despite the emergence of fairly safe anesthetics, the use of any medications during pregnancy is recommended to be kept to a minimum. Before visiting the dentist, it is advisable to consult with a gynecologist regarding the possibility of using specific medications.
Ultracaine drug
What anesthesia is used during pregnancy
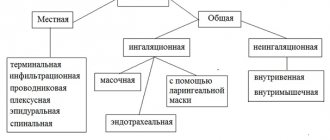
If possible, the expectant mother is given epidural (regional) anesthesia. If this type of anesthesia cannot be used, then multicomponent balanced anesthesia with artificial ventilation is performed. In this case, a special tube is used that is inserted into the trachea.
Epidural anesthesia is the safest method of pain relief for the expectant mother and fetus. To carry it out, a needle is inserted through an opening in the spinal canal. The injection area is called the epidural space. There are nerve roots that carry pain impulses from the uterus. Before inserting the needle, the skin at the injection site is numbed. A catheter (silicone tube) is inserted into the needle, through which the local anesthetic is injected. The medicine can be added if necessary, thus prolonging the effect of anesthesia up to 36 hours.
The analgesic effect after the administration of the anesthetic occurs within 10-20 minutes. It is worth noting that a woman may feel a shooting sensation in her leg when the catheter is inserted.
The following complications occur after epidural anesthesia:
- Headache. It can occur in a pregnant woman a day after the use of anesthesia.
- Skin itching. It occurs purely at the site of needle insertion. Treat it if necessary with antihistamines.
- Difficulty breathing. This complication develops due to the patient being on her back for a long time. In this case, oxygen is supplied through a special mask.
- Dizziness, rapid heartbeat, numbness of the tongue, metallic taste in the mouth. These signs may occur at the time of administration of the anesthetic. To avoid such sensations, a test dose is given to the woman before the full volume of the medicine is administered.
There are a number of contraindications for epidural anesthesia. These are bleeding disorders, sepsis, bleeding, skin infection at the site of catheter insertion, neurological diseases, and patient refusal.
If we are talking about simple surgical interventions in the third trimester, then it is possible to use mask anesthesia. In this case, the anesthetic enters the pregnant woman’s body through the respiratory system.
Another type of pain relief is nitrous oxide, used by inhalation. That is, again, a mask is used. It is worth noting that this type of anesthesia can harm the development of the baby. But in low concentrations (the ratio of oxygen and nitrogen is 1:1) and for a short time, this type of anesthesia is still used. A low nitrogen concentration does not have a negative effect. It induces deep sleep and relaxes muscles.
Increased accuracy
It turns out that local anesthesia for dental treatment during pregnancy is quite acceptable. Pregnant women can also have their teeth removed, but only if there is an urgent need for it. Doctors will still always look at each case individually to assess the risks and determine what to do next.
During dental treatment during pregnancy with local anesthesia, it is important not only to choose the drugs correctly, but also to follow the technique of their administration. The doctor should ensure that the woman’s blood pressure does not drop sharply. During dental treatment, pregnant women should not disturb the doctor and inform him about changes in their health.
A large belly has added to the difficulties in dental treatment in recent months. Firstly, it will disturb her, because not everyone can sit still for 30-40 minutes while the treatment lasts. Secondly, the dentist will also have to choose a position for the chair so that he and the patient feel comfortable, and the tummy does not interfere with the manipulations.
Concerns of doctors and patients
A survey of 702 private dentists in Germany showed that only 61% of them treat pregnant patients, 35.5% postpone treatment until the postpartum period, and 3.5% refer them to other clinics. Only 10% of dentists perform all necessary types of treatment, 14% refuse local anesthesia. Almost half of the dentists indicated that they would not treat in the first trimester, and 8.5% - in the second. 1
Read also: You can treat your teeth while breastfeeding
In a survey of 116 dentists in Connecticut, USA, 97% of dentists said they had treated pregnant women, but only 45% felt comfortable doing so. 2
Seeking a consultation with a gynecologist does not clarify the situation much. A survey of 138 obstetricians in North Carolina, USA, found that 49% rarely or never recommend dental examinations to patients. 3
Women themselves have little idea of the risks of refusing treatment during pregnancy. In a 2012 survey, two-thirds of Australian women said they did not seek dental care during pregnancy, even if they had problems. 4
Is it possible to have anesthesia during pregnancy?
You can't stand the pain. This is stressful for both the expectant mother and the child. You simply cannot do without anesthesia when performing the following procedures:
- dental treatment, including endodontic – the dental nerve reacts to the slightest mechanical impact, causing acute pain;
- tooth extraction - when a tooth is removed from the alveoli, the nerve endings are damaged, and, of course, unbearable pain occurs. And if you do not use an anesthetic, painful shock may occur;
- prosthetics – installation of a prosthesis requires preparation (grinding) of the enamel; this is a rather unpleasant and painful procedure.
However, any type of anesthesia is potentially dangerous during pregnancy. The use of various medications, including anesthetics, can negatively affect the development of the fetus.
Therefore, at the dentist’s appointment, the patient is obliged to warn the doctor about her pregnancy, and also indicate the exact date. Then the doctor will be able to select special anesthetics, the active substances of which do not cross the placental barrier and do not harm the baby.
You can't stand the pain. This is stressful for both the expectant mother and the child. You simply cannot do without anesthesia when performing the following procedures:
- dental treatment, including endodontic – the dental nerve reacts to the slightest mechanical impact, causing acute pain;
- tooth extraction - when a tooth is removed from the alveoli, the nerve endings are damaged, and, of course, unbearable pain occurs. And if you do not use an anesthetic, painful shock may occur;
- prosthetics – installation of a prosthesis requires preparation (grinding) of the enamel; this is a rather unpleasant and painful procedure.
However, any type of anesthesia is potentially dangerous during pregnancy. The use of various medications, including anesthetics, can negatively affect the development of the fetus.
Therefore, at the dentist’s appointment, the patient is obliged to warn the doctor about her pregnancy, and also indicate the exact date. Then the doctor will be able to select special anesthetics, the active substances of which do not cross the placental barrier and do not harm the baby.
Contraindications to the use of Lidocaine (spray, injection) during pregnancy
Before using any drug, the doctor should check with the woman for possible contraindications. For Lidocaine, this list is as follows:
- Individual hypersensitivity reaction.
- Low blood pressure.
- Pathologies of the liver and/or kidneys.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Despite the restrictions on the use of Lidocaine during pregnancy, many doctors still use this drug for anesthesia during various medical procedures. The experience of most women who have already given birth is based on a single administration of the drug. No negative phenomena were noted, the children were born on time and without developmental deviations.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpolicyandsafetyru
To summarize, it is worth noting that despite the warnings of the drug manufacturers, the drug still finds use in such a category of patients as pregnant women. It is difficult to answer for sure whether Lidocaine is harmful during pregnancy. While there are potential risks from exposure of the drug to the baby in the womb, there is no statistical data regarding a higher number of complicated pregnancies after a single use of Lidocaine.
Is it possible to take the anesthetic “Lidocaine” during pregnancy? To give the correct answer, it is enough to carefully read the instructions for use for this product. Upon careful study of the annotation, one of the contraindications is the gestation period. True, use in exceptional cases is still possible.
True, the doctor should be aware of the possible risks and side effects of such a procedure using Lidocaine. The prescription of an anesthetic drug often depends on the age of the fetus in the womb, which may affect whether the drug can be used or avoided entirely.
Oral care
Once pregnant, a woman should observe hygiene even more carefully and in no case neglect it. If she follows the basic rules, she will not have to visit the dentist either during pregnancy or during breastfeeding, which is also not recommended.
- If possible, limit your consumption of sweets.
- After each meal, brush your teeth or rinse your mouth.
- If toothpaste causes nausea, you can switch to tooth powder.
- You should also use dental floss, especially after eating food containing poppy seeds, strawberries and other foods with small seeds.
- Instead of juices, it is better to eat fruits.
- It is recommended to exclude soda, because... it also contributes to the erosion of enamel.
It would be ideal if every woman planned a pregnancy and underwent a full medical examination before conception, incl. dental. Sanitation of the oral cavity is the key to a smooth pregnancy, because the likelihood of dental problems occurring within 9 months is minimized.
It is recommended that pregnant women avoid dental treatment due to not only the harm of anesthesia to the fetus, but also the anxiety that the woman experiences. Pressure surges, rapid heartbeat - all these are harmful factors that harm the child. Therefore, a preventive examination by a dentist is the best option.
What types of pain relief and drugs are used for anesthesia in pregnant women?
As a rule, during pregnancy, doctors try not to perform any medical procedures using any medications, including anesthetics. Therefore, if the operation can be postponed indefinitely, then wait-and-see tactics are used - until the baby is born. The exceptions are:
emergency surgical interventions for conditions that threaten the life of the mother (most often these are operations to remove ovarian cysts, breast tumors, appendicitis, gall bladder);- application of retaining sutures to the cervix for isthmic-cervical insufficiency;
- acute dental problems (pulpitis, need for tooth extraction, etc.).
The frequency of use of painkillers in pregnant women averages about 1-2%.
Recent studies show that most painkillers have an adequate level of safety for mother and fetus. Experts also believe that it is not the anesthetic itself that plays a huge role in the subsequent development of abnormalities, but the anesthesia technique - it is very important to prevent a sharp decrease in the pregnant woman’s blood pressure and oxygen level in the blood.
Various drugs are used for anesthesia in pregnant women. Thus, in minimal doses, Morphine, Glycopyrolate, and Promedol do not harm the mother and fetus. Ketamine is also used in small doses in combination with other drugs for intravenous anesthesia; with prolonged use, it increases the tone of the uterus. Lidocaine is used for local anesthesia, which penetrates the placenta, but is quickly eliminated from the baby’s body.
In extremely rare cases, nitrous oxide and diazepam are used for pain relief, which can adversely affect the fetus, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy. In addition, some experts argue that local anesthetics containing adrenaline (for example, ultracaine, used in dentistry) should also not be used in pregnant women - there is a possibility of a sharp narrowing of blood vessels and disruption of blood flow to the placenta.
Regional (epidural) and local anesthesia during pregnancy are the safest methods of pain relief. If their use is impossible (in the presence of contraindications or in complex surgical cases), then they resort to multicomponent anesthesia using artificial ventilation.
Thus, surgery during pregnancy using anesthesia can harm the unborn baby, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy. Therefore, in order to avoid problems, it is necessary to eliminate all chronic sources of infection before planning (for example, cure carious teeth so that dental anesthesia is not required during pregnancy) and be fully examined.
If, during pregnancy, intervention is still required, but it is possible to postpone it until a later date (there is no acute pain and no obvious threat to the mother’s health), it is best to perform the operation in the second trimester of pregnancy.
And most importantly, expectant mothers should remember that our health largely depends on ourselves. Therefore, during this wonderful period you need to be especially careful.
If the expectant mother has a special sensitivity to the active ingredient “Lidocaine”, then taking the drug is impossible.
The list of contraindications includes the following:
- active heart failure;
- high blood pressure;
- breastfeeding and early pregnancy;
- renal and hepatic pathologies;
- history of bradycardia and the like.
Doctors do not recommend that a pregnant woman use an anesthetic in the form of a spray if there is a maximum likelihood that the patient will have an epileptic seizure. At the time of using Lidocaine, the woman’s condition should be regularly checked.
If the recommended doses are exceeded and lidocaine is used inadequately, reactions may occur in the form of:
- the appearance of itching and rash on the skin;
- impaired blood pressure and shortness of breath;
- sleep disorders and migraines;
- state of weakness and dizziness;
- vomiting, nausea and disorders of the digestive system;
- disturbances in the functioning of the heart up to the complete cessation of its work.
If there is even a minimal chance of one of these conditions occurring, treatment should be started immediately. Sometimes emergency delivery and hospitalization of the pregnant woman in a medical facility may be required. These options are possible when using the drug “Lidocaine”, which belongs to the group of anesthetics.
In any case, before treatment with any medications during gestation, you need to carefully study the instructions for the medications, since the use of many of them can cause irreparable harm to the expectant mother and her baby.
Preparations for anesthesia
H-2 histamine receptor blockers (ranitidine)1 are used to reduce gastric secretion. The drugs are administered intramuscularly. These drugs are used without fail in preoperative preparation to prevent vomiting. In the later stages, an overdose of drugs from this group can have a negative effect on the maturation of the nervous system.
Antihistamine (antiallergic) drugs (Suprastin, Tavegil, Diphenhydramine) have the same disadvantages as H-2 receptor blockers, since their mechanism of action is similar. However, with the correct dosage and when used only as indicated, the risk of complications for the child is minimal. These drugs are auxiliary, i.e. They themselves do not have an analgesic effect.
| 1H-2 histamine receptors control the production of digestive juices, including in the stomach. |
Preparations for inhalation anesthesia
These drugs are introduced into the body by inhalation in a mixture with oxygen through an endotracheal tube or, in some cases, an anesthesia mask - at the discretion of the anesthesiologist.
Ftorotan, Isoblurane, Halothane are included in this group of drugs. In Russia, Ftorotan is used more often. This drug has the ability to dilate the bronchi, which is good if the patient has bronchial asthma, but can cause disruption in the uteroplacental blood flow due to vasodilation. Therefore, it is most often used as one of the components of combined anesthesia (when several drugs are used). During such anesthesia, the woman does not feel anything.
Nitrous oxide is sometimes used, short-term and in reduced doses, as one of the components of combined anesthesia during cesarean section. In this mode, it does not have time to have a negative effect, causes good sleep, relaxes the muscles and the uterus. During combined anesthesia, the patient also does not feel anything.
If possible, they try not to use this drug in the early stages, because NITRIC OXIDE is toxic to young growing cells and disrupts DNA synthesis, that is, it can lead to the formation of mutations and developmental defects, so with prolonged use it can cause a miscarriage or harm the development of the child (one one of the main reasons for the high percentage of spontaneous abortions among anesthesiologists and nurse anesthetists).
Drugs for intravenous anesthesia (injected into a vein)
Ketamine (Kalilsol) is used, as a rule, in the third trimester, in reduced doses, in the absence of contraindications from the mother (hypertension, increased intracranial pressure, epilepsy, extreme forms of gestosis in pregnant women, which are accompanied by convulsions). Most often, it is used after the baby has been removed, if it is necessary to manually examine the uterus, suturing ruptures and incisions of the perineum.
Ketamine (Calipsol) in the first and second trimester is used only for special indications and only in small doses in combination with other drugs, as it increases the tone of the uterus. In the third trimester, this negative effect decreases. The uniqueness of this drug is that in addition to sleep, it also causes quite strong pain relief. When using KETAMINE, complete anesthesia is achieved, however, its administration and especially recovery from anesthesia may be accompanied by hallucinations.
Barbiturate drugs2 - Hexenal, Sodium Thiopental - are used to maintain sleep during surgery, as one of the components of balanced anesthesia, are administered intravenously, and can cause temporary respiratory depression in a newborn. Such children should be under special close supervision in the first hours after birth.
Sodium hydroxybutyrate is most often used in obstetrics for medicinal sleep. It is administered intramuscularly or with drink. Contraindicated in case of gestosis in pregnant women (a condition manifested by increased blood pressure, the appearance of protein in the urine, edema), accompanied by increased blood pressure, and epilepsy.
| 2Barbiturates are a group of drugs derived from barbituric acid that have hypnotic, anticonvulsant and narcotic effects due to their inhibitory effect on the central nervous system. |
Diprivan is a drug for short-term anesthesia. It is used as one of the components of general anesthesia at the beginning or end of anesthesia. Diprivan contains egg and soy protein, so the drug is contraindicated in patients who are allergic to them. The mechanism of action of Diprivan on fetal development is not fully understood, so they try to use the drug during cesarean section or during surgical interventions during or after childbirth.
Contraindications to anesthesia during pregnancy
Main contraindications to local anesthesia:
- neurological diseases;
- blood clotting disorder;
- acute inflammation of the mucous membrane in the injection area.
It is not recommended to administer pain relief between 2 and 8 weeks of pregnancy, when all the baby’s organs are forming. Therefore, it is better to postpone treatment to a later date.
The third trimester is also a dangerous period for dental procedures. It is especially not recommended to carry out any operations in the 9th month, since there is a high risk of increased uterine tone and premature birth.
Main contraindications to local anesthesia:
- neurological diseases;
- blood clotting disorder;
- acute inflammation of the mucous membrane in the injection area.
It is not recommended to administer pain relief between 2 and 8 weeks of pregnancy, when all the baby’s organs are forming. Therefore, it is better to postpone treatment to a later date.
The third trimester is also a dangerous period for dental procedures. It is especially not recommended to carry out any operations in the 9th month, since there is a high risk of increased uterine tone and premature birth.
Anesthesia during pregnancy - consequences for the fetus and mother
Today, when pain management is used almost everywhere, many are interested in the question of whether general anesthesia affects early pregnancy? Anesthesia and other medications can have a negative impact on the development of the baby. Moreover, harm is caused to the body at different times. This may be due to several factors:
- Certain anesthetics can cause increased uterine tone. At this point, the embryo experiences severe discomfort as the uterus changes shape. The embryo does not receive the required amount of oxygen, and this leads to hypoxia. Uterine tone can develop for many reasons, so taking anesthetics is not the only provoking factor.
- Medicines can cause disruption of body functions.
- The mother may develop hypoxia, which often causes termination of pregnancy due to fetal death.
The period between two and eight weeks is considered the most dangerous.
Caution in choosing a technique and medications must also be exercised in the last stages, since the woman’s body bears the maximum load. Incorrect technique, incorrect technique can lead to premature birth