Etiology and pathogenesis
During pregnancy, the production of anticoagulants decreases. An insufficient amount of these substances leads to increased blood viscosity. In this way, the woman’s body tries to protect itself from large blood losses during labor. A disruption in the defense mechanisms can cause the formation of blood clots. Sometimes thrombosis in pregnant women develops without the influence of pathogenic factors. The following processes can also cause the development of the disease:
- slowing blood flow;
- injuries or wear and tear of the vein walls;
- increased blood clotting;
- insufficient physical activity;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
Factors that increase the risk of deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities:
- woman's age is over 35 years;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs;
- number of pregnancies more than four;
- hemoglobinuria;
- excess body weight.
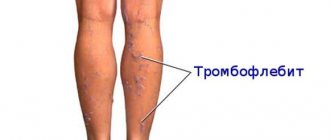
Clinical manifestations, diagnosis
The main signs of thrombophlebitis during pregnancy:
- The appearance of edema, an increase in the volume of the diseased limb;
- Painful discomfort upon palpation;
- The skin of the sore leg becomes red and hot to the touch;
- A bursting, severe pain appears at the site of the blood clot.
- Feeling of heaviness, increased fatigue of the legs;
- The skin becomes shiny, dense to the touch, the color changes to bluish or marbled;
- The venous pattern is enhanced due to the bulging of the saphenous veins on the lower limb or in the abdomen;
- A pulling, bursting pain appears on the inner surface of the lower leg and thigh, intensifying when walking;
- Increased heart rate;
- The temperature is rising.
Temperature during pregnancy
Thrombosis in the lumen of deep vessels manifests itself less clearly and requires additional diagnostic methods.
Diagnosis during pregnancy has limitations - X-ray contrast angiography is not possible. Ultrasound scanning and impedance plethysmography methods are used. These methods of instrumental research are recognized as safe, sensitive, and informative. Scintigraphy during pregnancy is contraindicated; it leads to the development of hypothyroidism in the baby.
Thrombosis in the deep veins of the thigh and pelvis develops slowly, without significant symptoms. When the localization of a blood clot cannot be detected immediately, examinations are carried out every five days. As an exception, venography is prescribed.
Examination and treatment are carried out by an angiosurgeon. The woman may need to be hospitalized in the vascular surgery department.
Symptoms of pathology
Deep vein thrombosis during pregnancy is manifested by the following symptoms:
With this disease, the expectant mother may experience headaches.
- swelling of the soft tissues of the affected limb;
- feeling of heaviness in the legs;
- clear pattern of saphenous veins;
- pain along the entire length of the vascular bundle;
- body aches;
- muscle weakness;
- headache;
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased pain after pressing on the location of the pathology;
- increase in skin temperature in the affected area.
Prevention
It is difficult to avoid the development of thrombosis during pregnancy, but it is quite possible, follow a few simple rules.
Methods for preventing thrombosis during pregnancy:
- eliminate salty and all junk foods from your diet, eat more seasonal vegetables and fruits;
- if there is no tendency to edema, drink at least 2 liters of fluid per day to avoid an increase in blood density;
- do gymnastics for pregnant women, swimming, but avoid excessive physical stress on your legs;
- wear compression garments;
- do a light foot massage every day;
- if heavy legs regularly bother you, throw them on the wall and lie in this position for 15-20 minutes;
- walk in the fresh air for at least an hour every day;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- Rest and sleep with your legs slightly elevated.
Start prevention from the first weeks of pregnancy, especially if you are over 35 years old, have two or more children, smoke, or have signs of varicose veins.
Varieties
Pathologies of the circulatory system, which are characterized by the formation of blood clots, are divided into the following types:
- Thrombophlebitis - usually affects superficial veins. Clots occur in deformed venous cavities that have been subject to pathological processes, such as damage. As a result, inflammation of blood vessels and soft tissues occurs.
- Phlebothrombosis - can affect completely healthy veins. The main location of the disease is the deep veins. The cause of the disease is a violation of the coagulation properties of blood.
Childbirth with thrombosis can occur naturally. Caesarean section is done in cases of pulmonary embolism.
Traditional and folk methods of treatment
During pregnancy, after thrombophlebitis is diagnosed, treatment is carried out with the following drugs:
- Indirect thrombin inhibitors (unfractionated and low molecular weight heparin), synthetic heparin pentasaccharides and factor Xa inhibitors (Rivaroxaban, Apixaban, Edoxaban).
- Direct thrombin inhibitors: Argatroban, Lepirudin, Bivalirudin, Dabigatran.
- The vitamin K antagonist Warfarin also belongs to this class of drugs.
- "Acetylsalicylic acid" and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Heparin is the most popular injection drug for detecting phlebitis in pregnant women.
To relieve pain, trypsin-heparin complex and Ascorutin are prescribed. Anti-inflammatory drugs also reduce pain and swelling - Ranselex, Ortofen.
Additionally, the vasoconstrictor “Detralex” is prescribed, which affects the speed of blood flow. At home, external remedies are used to help restore veins: Troxevasin, Lyoton or ointment with heparin.
Women with severe varicose veins and phlebitis must be prescribed compression stockings.
Folk remedies are used only after prescribing medications to relieve local symptoms. You can use cabbage leaf compresses with sea buckthorn oil or honey with olive oil.
Prevention of thrombophlebitis should begin with healthy pregnancy planning, which involves an active lifestyle, giving up bad habits and taking hormonal contraceptives. A full drinking regime reduces the thickness of the blood. The prognosis of the disease depends on the size of the affected area and the presence of concomitant pathologies (obesity, heart disease).
How is it diagnosed?
An important event in this case is collecting anamnesis.
Diagnostic measures are carried out by a surgeon and a gynecologist. First, the specialist collects a primary medical history and performs visual and tactile examinations of the patient. Then the following procedures are prescribed:
- Coagulogram is a blood test that shows the degree of blood clotting.
- Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) is a test that determines the amount of anticoagulants.
- Platelet aggregation analysis - determines deviations in the process of blood clot gluing.
- Soluble complexes of fibrin monomers (SCMF) - the study is a marker for pathologies such as thromboembolism.
- Dopplerography - an ultrasound procedure shows the degree of patency of the veins and the location of blood clots.
ethnoscience
Traditional medicine for the treatment of thrombophlebitis during pregnancy is especially popular because it allows them to avoid harmful effects on the development of the fetus.
The following means are used:
- Bee Honey. This product contains many microelements that strengthen the immune system, and also tones the veins and promotes tissue regeneration. To prepare the medicine, add 5 drops of flaxseed oil to 3 tablespoons of honey. The mixture is used in the form of a compress made from gauze fabric soaked in it.
- White cabbage. This vegetable optimizes venous outflow, which reduces stasis as swelling decreases. Cabbage is used in compresses. To prepare a compress, the cabbage leaf is treated with warm water and lubricated with oil. A compress is applied to the affected area of the vein, after which the leg is bandaged.
- Sagebrush. The composition of wormwood is prepared by brewing the plant in boiling water. After the solution has infused, it is diluted with the same amount of sour cream and applied to the affected areas of the leg. The composition is applied three times a day - each time for half an hour.
- Aloe compress. To prepare the composition, use 3 tablespoons of honey, 10 drops of aloe and 5 drops of sea buckthorn oil. You can also add 5-10 drops of carrot juice. The compress is applied for 2-3 hours every day.
- Horse chestnut tincture. You will need 10 shelled fruits. Chestnuts are poured with 0.5 liters of alcohol and left for at least 7 days. The tincture is taken 2 tablespoons per day before meals.
Homeopathic medicines are also used to treat thrombophlebitis:
- Venoflegel. This drug is a homeopathic remedy that belongs to the group of phlebotonics. Venoflegel tones smooth venous muscles, increasing their functionality. The contents of the drug avoid blood stasis and increase its rheological characteristics.
- Edas 203. Homeopathic remedy that has a local effect on the venous wall. Improves wall tone and starts the process of repair of the venous endothelium. Available in the form of an ointment.
- Job-Venum. This drug is a systemic phlebotonic. It affects platelets, reducing their adhesive properties, and also optimizes blood flow in the veins. Available in granule form.
Treatment of pathology
Traditional therapy
For deep vein thrombosis in the acute period, hospitalization is necessary. Such thrombosis is life-threatening for the patient. Drug treatment is prescribed by a specialist. Thrombophlebitis in pregnant women is treated with the following drugs:
| Group | Name |
| Anticoagulants | "Heparin" |
| "Nadroparin calcium" | |
| Medicines to prevent blood clots | "Acetylsalicylic acid" |
| Means for dilating the lumen of blood vessels | "Pentoxifylline" |
| Phlebotonics | "Vazoket" |
| "Detralex" | |
| "Venoplant" | |
| Anti-inflammatory | "Ortofen" |
| "Ranselex" | |
| "Sinmeton" | |
| Atithrombotic | "Tiklid" |
| "Clopidogrel" | |
| Angioprotective | "Venoruton" |
Traditional treatment
During the recovery period, little sea buckthorn can be used for external procedures.
Alternative medicine methods are used during the recovery period. These procedures will help relieve swelling of soft tissues and reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process. Before starting therapy, consultation with a specialist is necessary. To relieve symptoms, the following recipes are used during pregnancy:
- Natural honey 2 tbsp. spoons are mixed with 10 drops of olive oil. The finished composition is applied in a thin layer to the localization of the pathology. A gauze bandage must be applied on top for 7 hours.
- The skin of the affected area is covered with sea buckthorn oil. Then you need to attach a leaf of white cabbage, securing it with elastic bandages. The compress is kept for 5 hours.
- Dry herbs of chamomile, strings of calendula, St. John's wort are poured with 1 liter of boiling water. The mixture is infused for 45 minutes. I use the prepared broth to make foot baths.
Surgery
The procedure is performed if a floating thrombus is detected. The specialist performs instrumental treatment by installing a vena cava filter. The instrument is shaped like an umbrella; it is placed into the vein cavity and removed after the blood clot gets inside the filter. Introduction occurs through the superior vena cava. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. Sometimes the following surgical interventions may be performed:
- thrombectomy;
- bypass;
- endovascular catheter thrombus extraction.
Treatment of thrombophilia in pregnant women
Complete elimination of thrombophilia caused by genetic abnormalities is impossible. If this disease is detected before conception, a set of measures is necessary to prevent increased thrombus formation. The list of comprehensive measures for the treatment of thrombophilia when planning pregnancy includes:
- taking anticoagulants (heparin, aspirin and their analogues);
- taking folic acid (up to 400 mcg per day);
- taking multivitamins with a high content of B vitamins and Omega-3;
- taking medications with progesterone derivatives.
In parallel with taking medications and dietary supplements, women are advised to follow a diet aimed at reducing blood viscosity and strengthening vascular walls. The diet includes a large amount of fresh fruits and vegetables containing vitamin C, seafood (as a source of Omega acids and iron), olive oil, dairy products and dietary meats containing B vitamins. Canned food and semi-finished products, alcohol, drinks with caffeine
Treatment of genetic thrombophilia during pregnancy requires constant use of anticoagulants and drugs based on nadroparin calcium to enhance microcirculation. To prevent cerebral edema and abnormalities in the development of the fetal neural tube, Magnitol and Dexamethasone are prescribed.
Throughout pregnancy, the patient is advised to undergo regular examinations:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and fetus (performed monthly);
- coagulogram (performed monthly);
- three-dimensional echography of the uteroplacental vessels (performed in the first trimester of pregnancy);
- fetometry and fetal Doppler (performed in the second and third trimester of gestation).
To reduce the risk of blood clots throughout pregnancy, a woman is advised to wear compression garments, moderate physical activity (walking, swimming), and special gymnastics. If necessary, a course of massage and electromagnetic therapy is prescribed.
Successful pregnancy and safe childbirth are common occurrences for patients with thrombophilia . Modern medicine has a lot of tools and techniques that can alleviate unpleasant symptoms and reduce the risk of complications to a minimum. Most women who are under the supervision of specialists and strictly follow their recommendations carry their pregnancies to term and give birth to healthy babies.
What are the dangers of thrombosis during pregnancy?
The disease is dangerous due to the formation of floating blood clots.
Thrombophlebitis during pregnancy without appropriate therapy can cause serious health problems. Deep vein thrombosis does not affect the condition of the fetus. An exception is the formation of clots in the vascular cavity of the placenta or umbilical cord. The formation of blood clots can lead to the following complications:
- acute venous insufficiency;
- inflammation of the venous network;
- thromboembolism;
- floating thrombus;
- septic processes;
- heart attack or stroke;
- venous gangrene.
Thrombophlebitis and pregnancy - is it possible to become pregnant and give birth with venous pathologies?
Thrombophlebitis is not a contraindication for natural childbirth, but only if the disease is at an early stage of development.
Natural childbirth is possible if the woman followed all the doctor’s recommendations - wore compression garments, took phlebotonics and anticoagulants. The day before giving birth, you should stop taking blood thinners to avoid heavy bleeding.
If there are several blood clots, a cesarean section is performed to avoid serious complications for mother and baby.
Pregnancy with thrombosis is quite possible; the disease does not affect conception in any way. But it is better to visit a doctor, undergo a full examination and treatment at the planning stage. Since there is a high probability of exacerbation of venous pathologies in expectant mothers, prepare yourself in advance for frequent visits to specialists; you may have to go to the hospital several times.
Forecasts and preventive recommendations
After treatment it is necessary to undergo an ultrasound examination. Based on the diagnostic results, the attending physician makes a decision about the woman’s labor. If the result is positive, it is recommended to wear compression stockings during and after childbirth and bandage the affected limbs. Preventive measures include massage, walks in the fresh air, and diet for pregnant women. Sometimes a specialist will prescribe medications to maintain proper blood clotting. You can use relaxing baths based on medicinal herbs. The amount of water drunk should not exceed the established norm. Otherwise, severe swelling of the lower extremities will occur.
Emergency care and treatment of pulmonary embolism
If the development of pulmonary embolism is suspected, a pregnant woman is urgently injected into a vein with 10 thousand units of Heparin and fresh frozen plasma (at the rate of 15 ml/kg). These measures prevent a further increase in the volume of the embolized thrombus, the formation of blood clots and at the same time prevent the development of bleeding.
To provide cardiopulmonary resuscitation of the onset of cardiopulmonary shock, the following measures are taken:
- Transfer to a ventilator.
- Urgent catheterization of the subclavian vein.
- If ineffective blood circulation develops, artificial ventilation and chest compressions are performed.
- To eliminate spasm of the arteries and bronchi, the following are administered: Prostenon, Aspisol, Indomethacin, Fentanyl with Droperidol, Calcium chloride.
- If blood circulation is ineffective, Atropine and Adrenaline are administered. After this, a heart massage is performed.
- Trasylol or Contrical and Hydrocortisone are administered in combination with Prednisolone.
Thrombolytics are used to dissolve a blood clot:
- Streptokinase;
- Urokinase;
- Tissue plasminogen activator.
After this, the patient is prescribed anticoagulant therapy with low molecular weight heparins for 7-10 days. Discontinuation of these drugs is carried out only after complete stabilization of laboratory indicators of blood clotting. Anticoagulant therapy is not carried out in cases of planning surgery, a previous stroke, the presence of ulcers in the gastrointestinal tract or trauma.
In case of massive pulmonary embolism, all women who are allowed to continue pregnancy are advised to undergo surgery to implant a vena cava filter. This operation may be contraindicated in cases of septic embolization, obstructive thrombosis of the vein into which the filter will be implanted, and sepsis accompanied by the formation of abscesses in various tissues and organs. In such cases, the patient needs to perform ligation of the inferior vena cava.
Prognosis, complications and consequences
Complications of the disease are pulmonary embolism - blockage of the pulmonary artery by a blood clot, resulting in a heart attack. The patient is bothered by a cough, breathing becomes heavy and jerky.
A serious consequence of the illness is the underdevelopment or even death of the child due to oxygen starvation.
In a situation where the disease is neglected, there is a threat of death for both the pregnant woman and the fetus.
Thrombophlebitis is a dangerous pathology that can lead to serious consequences for the expectant mother and her child. Therefore, treatment should begin immediately after the first signs of an anomaly appear. With correctly selected and timely therapy, the prognosis is favorable.
What is cerebral venous thrombosis
Cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT) is a fairly rare disease. In fact, most cases of the disease remain unidentified.
With CVT, the outflow of venous blood in various parts of the brain is obstructed. Blood clots called thrombi form.
The disease causes ischemia, stroke, cerebral infarction and placental thrombosis.
Diagnosing CVP is difficult—symptoms vary depending on the individual characteristics of each case.
Most often women aged 20 to 35 years are affected.
At risk are:
- pregnant women;
- persons using psychotropic drugs;
- patients undergoing hormone replacement therapy;
- women taking oral hormonal contraceptives.
The disease has been known since ancient times; even ancient medical treatises described methods of treating it. The essence is the swelling, expansion, thinning and increase in size of the superficial vessels that carry blood to the heart. These vessels are veins. The muscle tissue in them is very thin, and the blood flows in the right direction thanks to the valves. So, the disease damages them, or with it they are completely absent. This valve failure is considered the trigger for the development of the disease.
Most often the disease manifests itself on the legs. Although often women (especially during pregnancy) are affected by varicose veins of the following localization: • vagina; • groin; • uterus, etc.
But even under such circumstances, childbirth with varicose veins is often carried out naturally.
What is acute thrombophlebitis
Thrombophlebitis is an inflammatory process in the veins, which is accompanied by the formation of blood clots, that is, blood clots themselves.
Clots begin to grow near the vein and gradually spread throughout the vessel. If the vein is of small diameter, a tributary of the main trunk, then it can be completely closed by a blood clot, but this does not pose a serious threat to health and life. If clots form in large veins in the legs, then it is dangerous for them to spread into the inferior vena cava system or break off a blood clot.
Thrombophlebitis develops against the background of slow venous blood flow, which occurs with varicose veins. If an injury to the venous wall is added to this (and a distended vein is also damage), then this is an additional factor that contributes to the onset of blood clot formation.
The disease is characterized by an inflammatory process occurring in the internal walls of the bloodstream with the simultaneous formation of blood clots.
The disease is accompanied by fever and pain in the affected limb. The main danger is possible thromboembolism of the lungs or heart.
Often the disease is triggered by pregnancy. In women during this period, intra-abdominal pressure increases and the blood becomes more viscous.
Delivery is carried out by caesarean section, but a natural process is also possible.
Before giving birth, compression stockings or compression bandages are worn.
At the beginning of labor, heparin is administered, 5000 units.
Childbirth with different types of varicose veins
There are several types of diseases that affect labor and the characteristics of childbirth.
1. Varicose veins of the lower extremities. It has already been mentioned. This is the most common form. With a normal course and compliance with all necessary measures, a woman can give birth on her own. With such a pathology, you cannot do without special equipment. That is, the expectant mother should wear anti-varicose stockings during childbirth or her legs should be wrapped with an elastic bandage (this is done for any location of the disease). This is necessary in order to avoid blood reflux through the veins during the pushing stage.
2. Varicose veins in the groin. In this case, natural delivery is also not prohibited. Of course, this depends on the degree of development of the pathology and its severity. If the manifestations are severe (there are serious difficulties in the movement of blood through the vessels), then the doctor will most likely insist on surgery. For childbirth with varicose veins in the groin, in order for it to go smoothly, a woman needs to prepare seriously and thoroughly, not forgetting to follow all the doctor’s recommendations and preventive measures during pregnancy.
3. Varicose veins of the uterus. It may not manifest itself at all, appearing in all its glory during pregnancy. The disease occurs: • due to inflammatory processes of the reproductive organ, • abortion, • irregular cycle; • uncontrolled use of contraceptives, • genetic failure; • hormonal disorders and other factors.
Varicose veins that appear in the uterus when carrying a baby are a natural process, since they (the baby) compress the uterine veins in the later stages. But if the disease was present initially, that is, before pregnancy, then, of course, an interesting situation can only aggravate the situation and lead to various complications.
Childbirth for varicose veins of the uterus is recommended only surgically. Natural ones cause such tension in the organ that this force can rupture a vein. The same can be said about cervical varicose veins. In addition, impaired blood flow will not allow the uterus to open normally. Therefore, surgical delivery for cervical varicose veins is also recommended.
4. Vaginal varicose veins. There are quite a few reasons for the appearance of pathological vasodilation in this place, most of them are associated with pregnancy. Childbirth with vaginal varicose veins depends on the severity of the disease. Natural delivery takes place under the full supervision of a doctor, because without pushing, the eruption of the baby’s head can cause a rupture of the vein.
At the moment of pushing, the doctor squeezes the affected area, protecting it from overflowing with blood. To prevent varicose veins (both large and invisible) from rupturing, perineotomy and episiotomy of the perineum are performed.
Varicose veins sometimes go away after the birth of a child, as the main factor in the development of the disease, pregnancy, disappears.
And yet childbirth and varicose veins of the small pelvis are compatible. And even natural delivery is possible, if the condition of the blood vessels allows it and does not threaten the life and health of the mother and baby.
Types of disease
Thrombophlebitis is divided into several groups, depending on the origin, location of the inflammatory process, and area of damage.
By affected area:
- deep vein thrombophlebitis - inflammation most often occurs in the femoral vein, or in the internal organs;
- superficial thrombophlebitis - the vessels that are located near the skin become inflamed.
- local inflammation - the pathological process occurs at the site of attachment of the blood clot;
- migrating inflammatory process - subsides in one place, moves to another area, the disease quickly progresses.
Depending on the reasons:
- varicothrombophlebitis;
- post-injection thrombophlebitis;
- septic or infectious;
- aseptic.
Depending on the size of the blood clot:
- occlusive - against the background of blockage of the vessel, blood flow slows down significantly;
- ischemic - severe swelling and thrombus leads to complete blockage of the lumen of the vein, blood does not flow to the tissues, necrosis develops;
- non-occlusive - the thrombus does not interfere with normal blood flow.
Inflammation of the veins occurs in acute or chronic form.