What are follicles in the ovaries in women?
What are follicles in the ovaries in women?
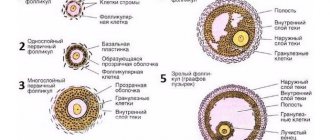
The female monthly cycle is divided into two phases - follicular and luteal. The formation of follicles occurs in the first phase. The follicle, consisting of epithelial cover and two-layer connective tissue, is the container of the egg, ensuring its development and preservation. The structure matures within a month. Inside, the reproductive cell is protected from the effects of negative factors. It matures to a certain stage, but maturation is completed after fertilization. The ovarian follicle is also a structure that provides estrogen synthesis. Follicular synthesis occurs continuously throughout a woman's life.
Each month, one follicle remains in the ovary, called the dominant one (less often two or three). The egg comes out of it. The dominant formation is larger than the others; before ovulation, its diameter can reach 2 cm. Under the influence of hormones, the walls rupture, the cell, ready for fertilization, enters the fallopian tube and moves towards the uterus.
If a dominant structure does not appear in the ovary, then the cycle is anovulatory, the corpus luteum is not formed, and conception is impossible. It happens that two or more dominant formations appear in the ovary in one month. This is a normal phenomenon, meaning that it is possible to fertilize two eggs and carry twins.
Complete absence of follicles
A complete absence of follicles in the ovaries can occur after early menopause or dysfunction. It is very difficult for doctors if it is even impossible to restore follicles in the body. Most often, in such a situation, the gynecologist prescribes hormone treatment.
A failure of the menstrual cycle will be the first signal that follicles are missing. A gynecologist is consulted if the menstrual cycle does not return to normal within 30-35 days.
Folliculosis is not always a problem, but the complete absence of follicles indicates that you should immediately undergo treatment.
Common deviations from the norm
The cyclical development of the dominant cell is determined by estrogenic influence. Estrogen prepares the uterus for the possible attachment of a fertilized egg and stimulates the thickening of the endometrium. The body responds to this by increasing the synthesis of luteinizing hormone in the pituitary gland. Under the influence of this hormone, the follicular membrane gradually becomes thinner and then bursts. The ovarian follicle changes by day as follows:
- On days 5–7 from the beginning of menstruation, the cell is 4–5 mm in diameter.
- On days 8–10, a cover of connective tissue appears. The dominant stands out among other formations.
- On days 11–13, the diameter of the dominant reaches 16–18 mm. The remaining follicles regress and gradually dissolve.
- On days 14–16, the next ovulatory cycle begins. The diameter of the remaining follicular cell, called the Graafian vesicle at this stage, is 20–22 mm.
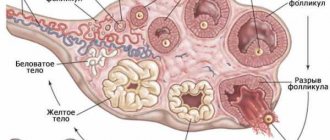
In place of the burst vesicle, a corpus luteum is formed, which synthesizes progesterone - a hormone that prepares the body for a possible pregnancy, regulates changes in the uterine endometrium for better attachment of the embryo, weakens the contractile activity of the uterus, and maintains the tone of the uterine cervix in the last months of gestation.
The number of follicles in the ovaries matters one way or another. During the formation of follicular cells, the following deviations may occur:
- Absence of a dominant, when the body produces insufficient follicle-stimulating hormone, but an excess of luteinizing hormone.
- Lack of follicles. Observed in diabetes, hyperthyroidism and other endocrine pathologies, it is a consequence of hormonal imbalance.
- Appearance of a persistent cell. During persistence, the follicular cell enlarges, but does not enter the rupture phase. There is no ovulation process. The pathological phenomenon is usually associated with an excess of male hormones in the female body. Without treatment, infertility develops.
- Multifollicular ovaries. At the preovulatory stage, there is an excess number of oocytes in the gonads. The pathological phenomenon occurs due to stress, chronic fatigue, mental and emotional disorders. With multiple follicles, therapy is not always required; after a couple of cycles, follicular synthesis may normalize.
- Luteinization is the appearance of the corpus luteum from an egg that has not left the membrane. Pathology is observed with hormonal imbalance, endometriosis, and inflammatory reaction in the reproductive system.
- A follicular cyst is formed from an unruptured dominant. The bubble continues to grow, and on the ultrasound monitor it looks like a formation filled with liquid contents, with a diameter exceeding 25 mm. If there are several such blisters, then polycystic disease is diagnosed.
If more than 9 follicles are detected in the ovary, and this number does not change over the course of the cycle, then this is a pathology. Ultrasound reveals multiple small blisters. The doctor diagnoses polycystic disease, but not always. Sometimes multiple cysts exist for one cycle, provoked by stress, overwork and other negative factors, and disappear on their own at the next ovulation. If polycystic disease interferes with the formation of a dominant, then the ovulation process becomes impossible. In this case, hormonal therapy is prescribed.
When follicular formations do not appear in the ovaries every cycle, and then stop forming altogether, then we should talk about the early onset of menopause or a disruption in the functioning of the gonads. You can understand that there is a pathology by disrupting the cyclicity of menstruation. The patient is prescribed hormone therapy.
The number of all sleeping oocytes is laid down by nature at the stage of embryonic development. It is characteristic that before the onset of puberty it decreases significantly. One egg is released every month.
The number of capsules with oocytes is determined by the day of the cycle. There may be several of them just a few days after your period. On the fifth day there can be up to 10 of them, and this is also the norm. After all, only one follicle will be dominant.
Deviations
In the absence of a dominant follicle, the egg is not released. This happens as a result of hormonal imbalance and certain pathologies:
- decreased production of follicle-stimulating hormone and increased excretion of luteinizing hormone;
- regression due to hormonal disorders (including due to increased insulin levels);
- the presence of a persistent process;
- the presence of an overripe pouch;
- formation of a follicular cyst that grows in place of the dominant follicle (size exceeds 2.5 cm during ultrasound examination);
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- pathological luteinization, when without ovulation the corpus luteum grows at the site of dominance.
All ovarian development disorders require a thorough instrumental examination. Doctors prescribe tests of a woman’s hormonal levels, since the cause of deviations may be pituitary gland dysfunction and endocrine diseases.
If the ovaries have more than 10 follicles, they are called multifollicular. There is also polyfollicularity, that is, when an ultrasound reveals a significant number of vesicles. When their number increases several times, the diagnosis of “polycystic disease” is determined.
If the follicular elements are scattered throughout the periphery of the ovary, they become crowded. This interferes with dominance and all processes that promote conception.
This pathology develops due to stress and goes away after a short time. Treatment of the problem is carried out if:
- multifollicularity is caused by problems with the functioning of the endocrine glands;
- there is a sharp weight loss or weight gain;
- there were failures in the choice of oral contraceptives.
Follicular insufficiency is caused by hormonal problems. You can find out the problem with an ultrasound on the seventh day. If there are less than 6, then the probability of conception is negligible. Finally, if there are less than 4 of them, then pregnancy practically does not occur.
In some cases, women have no follicles at all. The occurrence of problems with the female body is signaled by the complete absence of menstruation. If they are absent for more than 3 weeks, you need to urgently visit a gynecologist.
It may not ripen due to the following reasons:
- dysfunction of the female reproductive glands;
- disorders of the functionality of the endocrine system;
- tumors of the pituitary gland, hypothalamus;
- inflammatory pathologies of the small pelvis;
- stress, nervous instability or depression;
- early onset of menopause.
In these situations, there may be no follicles in the ovaries at all. It often happens that it does not reach sufficient size for an egg to be released.
The pattern of its growth can be clearly presented in the form of a table.
| Cycle day | Quantity and characteristics |
| From 1 to 4 | Several follicles develop, each no larger than 4 mm in size. |
| 5 | Uniform development with atresia of several follicles. |
| 7 | The dominant follicle is determined. All others are completely reduced. |
| 8 | 12 mm |
| 9 | 14 mm |
| 10 | 16 mm |
| 11 | 18 mm |
| 12 | 20 mm |
| 13 | 22 mm |
| 14 | 24 mm. At this stage, ovulation occurs. |
Cells in the ovary that are deviated from the norm are when there are more than 10 of them. In medicine, several terms are used when diagnosing deviations from the norm, these are “multifollicular” and “follicular ovaries”. Before making this diagnosis, a woman must undergo an examination and an ultrasound scan.
Having heard such a diagnosis, you should not be upset and think that this is an indicator of infertility. Multifollicular ovaries can occur after nervous breakdowns, constant stress or overwork. In such a situation, there is no need to panic and you should not take any medications. Having eliminated the cause that caused this diagnosis, by the next period of ovulation we can expect normalization of the cells in the ovaries.
Factors that provoke deviations from the norm:
- incorrectly selected contraceptives;
- problems with the thyroid gland;
- after a period of feeding a baby (excess prolactin in the body);
- the endocrine system is not working properly.
Attention! What to do in such a situation? After examination by a specialist and confirmation of the diagnosis, a treatment method is prescribed and followed relentlessly. With improper treatment, infertility develops, so it should not be started.
There are two types of menstrual cycle and they occur depending on the number of dominant follicles.
Types of the menstrual cycle:
- normal;
- a cycle with deviations, in the absence of a mature dominant follicle.
With a large accumulation of hormones and multifolliculosis, infertility develops.
Video: how the follicle grows
The ovary is not a bottomless barrel, or How to calculate the onset of menopause
In the modern world, it is a rare woman who can afford to be truly weak and dependent. Most of us, especially in large cities, habitually rely only on ourselves. This means that they must first get a good education, then get a job, build a career, create a reliable rear in the form of an apartment, a car, a stable income (well, at least something from the list), and only then you can think about starting a family, and primarily about procreation. And all this is clear and logical. But, unfortunately, there is also a biological clock that goes very quickly, counting down the time when a woman can become a mother. As far as I know, the latest record in this area was set in India, where twins were born to a 70-year-old woman. However, it is necessary to understand that women who have accomplished such a “feat” are not in fact the genetic mothers of the children they born. In all cases of these late pregnancies, donor eggs from young women were used.
Memo
- a supply of follicles in the ovary that are capable of developing normally and ensuring the ovulation of a mature egg in response to natural stimuli or artificial stimulation by hormones.
With the modern level of development of medicine, it is possible to artificially restore the hormonal levels of almost any woman, which will allow her to carry a pregnancy to term. But nature wisely limited the time. It is believed that this is a protective mechanism that prevents the birth of children with serious genetic abnormalities in the first place. After all, throughout our lives we repeatedly encounter negative influences that change the structure of our genes. And the older a person is, the more likely he is to pass on defective genes to his offspring. And secondly, a child must not only be born, but also raised. There is a great risk that you will not have time to do this. The average age of cessation of menstruation in our region is 50 - 51 years
, early menopause is called, occurring at the age of 40 - 45 years. But there are cases when menopause occurs at 35 or even earlier (premature menopause). It should also be taken into account that a woman’s fertility, that is, the ability to conceive a child, is usually lost several years before the cessation of menstruation. According to statistics, women who stop menstruating at 50-51 years old lose their ability to conceive on average at 41 years old (so-called physiological infertility). And if the last menstruation should come at 40 years old, then at 30-something you can no longer count on pregnancy. Why do some people have to have an abortion at 50, while others cannot get pregnant by the age of 30, even with the use of modern reproductive technologies?
Methods for determining ovarian reserve
Ultrasound.
When conducting a transvaginal examination, the number of small (antral) follicles with a diameter of 2 - 8 mm in each ovary is counted.
This study is carried out on the 1st - 4th day of the menstrual cycle (from the first day of menstruation). The average value of antral follicles (AFC), which characterizes normal ovarian reserve, is 11 - 25. There is evidence that by the number of antral follicles one can determine the number of years when a woman can still conceive a child and the age of menopause. If there are 20 antral follicles in the ovary, it is assumed that a woman will remain fertile (able to conceive a child) for about 15 years and will stop menstruating after about 24 years. If there are 15 follicles in the ovary, then physiological infertility will occur after 9 years, and menopause will occur after 18 years. If 10 follicles are detected, pregnancy can be expected within 4 years, and menopause will occur after 13. If 5 or fewer follicles are detected in the ovary, the woman is most likely infertile, and her menstruation will stop in the next 6 - 7 years. Essential for assessing ovarian reserve and determining ovarian volume. A decrease in volume clearly indicates a decrease in reserves. Determination of the level of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) in the blood on the 2nd - 3rd day of the menstrual cycle.
FSH is a pituitary hormone that stimulates the growth and maturation of follicles until ovulation.
It is known that the levels of FSH and estradiol (a hormone produced by the ovary in the first phase of the cycle) are inversely related. Therefore, FSH above 30 IU/l indicates the onset of menopause and cessation of ovarian function. The FSH level, indicating good ovarian reserve, is 3 - 8 IU/l. With a normal FSH level, mainly in women over 35 years of age, various tests can be used to clarify the assessment of ovarian reserve: using clostilbegite (clomiphene citrate) - clomiphene citrate challenge test, FSH analogues - EFORT (exogenous FSH ovarian reserve test) and others. These tests are carried out to predict the response of the ovaries to hormonal stimulation and determine the advisability of ovulation stimulation in a natural cycle or as part of IVF. Determination of inhibin B in the blood on the 2nd - 3rd day of the cycle.
Inhibin B is produced directly in the follicles and reduces the production of FSH. A decrease in the level of inhibin B below 45 pg/ml is a sign of a decrease in the number of follicles, which predicts the low effectiveness of hormonal stimulation.
Descending
Relatively recently, it was established that the time allotted to us in order to acquire offspring and the time of menopause directly depend on the supply of eggs in our ovaries. It is different for every woman. Currently, the term ovarian reserve is used, which we will talk about. In a female embryo, eggs are detected in the ovaries from the 16th week of pregnancy. By the fifth month, the number of germ cells in the ovaries is at its maximum - about 7 million. From this time, during the further development of the girl, the number of follicles (vesicles containing eggs) will only decrease. By the time of birth, there will be about 1 million of them left. By the age of the first menstruation, the ovaries contain no more than 500,000 follicles. Before the first menstruation appears, a decrease in the number of follicles occurs due to atresia. In this case, the egg dies, and the follicle is gradually overgrown with connective tissue, forming a microscopic scar. After puberty, ovulation occurs in a healthy ovary - the release into the abdominal cavity of a mature egg capable of fertilization. On average, during the life of a modern woman, about 400 eggs are consumed in this way. And all the rest undergo reverse development - atresia. This process occurs constantly: during pregnancy, breastfeeding, when taking hormonal contraceptives, despite the absence of ovulation. It has now been established that after an average of 37.5 years, the rate of follicular atresia increases. This milestone is considered critical, after which the ovarian reserve and the likelihood of pregnancy sharply decrease. Menopause occurs as a result of depletion of the ovarian follicular reserve.
Method for determining ovarian reserve Determination of anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) in the blood.
It is believed that the AMH level depends little on hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle, so it can be taken on any day, but it has been established that the maximum value of the indicator is observed 4 days before ovulation, and the minimum 4 days after it. AMH is produced in the ovary only in follicles with a diameter of no more than 8 mm. Therefore, this hormone is considered the most accurate marker of ovarian reserve. A decrease in AMH levels clearly indicates a decrease in the number of follicles in the ovary. Currently, there is no consensus regarding the standards for the value of AMH. The following gradation is proposed: less than 0.3 pg/ml – very low level; from 0.3 to 0.6 – low; 0.7-0.9 – normal reduced; 1-3 pg/ml – normal good; more than 3 pg/ml – high, may indicate the presence of polycystic ovaries; more than 11 pg/ml - a very high AMH value may indicate the presence of a granulosa cell tumor of the ovary. Currently, the study of AMH is given great importance. It is assumed that the level of this hormone can not only predict the likelihood of pregnancy and the effectiveness of hormonal stimulation, but also predict quite accurately the age of menopause. Studies have found that with an AMH level of more than 0.39 pg/ml, it is possible to predict that menopause will not occur within the next 6 years with 90% accuracy. And an AMH level of less than 0.086 pg/ml clearly corresponds to the beginning of the premenopausal period, which usually lasts about 4 to 5 years, after which menstruation stops. There are also attempts to compile tables with the use of which you can correlate your age and AMH level and calculate your individual age at menopause. However, I would like to warn those who have already completed their reproductive function and are not interested in becoming pregnant against trying to use this information as a method of contraception. Even if all the data suggests that you will never be able to get pregnant again, I still advise you to use reliable contraception until you reach menopause. Even in women with single follicles in the ovary, spontaneous ovulation and pregnancy are possible. Miracles do happen, and if you don't need them, you need to take care of your safety.
What we have, we don’t store
This is how things normally happen. But many diseases, toxic effects, and medical interventions can accelerate the process of follicular atresia and reduce ovarian reserve. There is the concept of “premature ovarian depletion syndrome”, when at any age (sometimes at a very early age) a woman practically stops menstruation, blood hormone levels become the same as in women in menopause (the level of FSH - follicle-stimulating hormone, and LH - increases significantly luteinizing hormone, estradiol levels decrease). This is an extreme degree of decreased ovarian reserve, possibly associated with genetic abnormalities. There is often a hereditary predisposition to the development of such disorders. On the female side: mother, grandmother, sisters. Such women often experience early or premature menopause, various menstrual irregularities, problems with conception and pregnancy. During severe pregnancy (toxicosis, fetal hypoxia, viral infections), the development of follicles in the ovaries may be disrupted in a female fetus, which will cause a decrease in the initial ovarian reserve. It is also possible that the follicular apparatus decreases under the influence of autoimmune processes, when the body begins to produce specific antibodies to its own tissues (autoantibodies). These antibodies destroy the follicles, also impoverishing the ovary.
During life, the ovarian reserve is exposed to various harmful effects.
Inflammatory diseases of the ovaries (adnexitis, inflammation of the uterine appendages, salpinogovophoritis) contribute to the development of connective tissue in the ovaries, decreased blood supply and mass death of the follicular apparatus. The foods we eat, the air we breathe, and the water we drink contain many chemical compounds that inevitably affect the body. I'll give just one example. Diethylstilbestrol (DES), a growth stimulant in cattle, has been used in livestock production for a long time. Subsequently, it turned out that eating meat containing DES during pregnancy leads to the development of various oncological diseases in the born child. In girls - breast cancer, vaginal cancer, as well as reproductive disorders - infertility, miscarriage. Smoking contributes to a decrease in ovarian reserve and an earlier onset of menopause. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) contained in tobacco smoke trigger the process of egg death through the activation of a specific gene. Surgeries on the pelvic organs significantly reduce the ovarian reserve.
And the maximum damage is caused when the ovary is removed or resected.
Until the thunder strikes
When may it be necessary to determine ovarian reserve? Firstly, it is necessary for women who are undergoing infertility treatment. If the ovarian reserve decreases, there is no point in spending years on long-term examination and treatment, because every year the chances of pregnancy decrease and it may happen that in a couple of years it will be impossible even with the use of high technologies. Therefore, it is better to immediately tune in to IVF (in vitro fertilization). Secondly, a study of the ovarian reserve is necessary before using ovarian stimulation to assess its prospects and select the most effective stimulation scheme.
Women with menstrual irregularities (shortening, irregularity, spotting between menstrual bleeding) undergo such a study before surgery on the uterus and appendages to select the extent of the operation (with low ovarian reserve, removal of even one ovary or extensive resection, as a rule, leads to premature menopause ). A study of the ovarian reserve can, in my opinion, be useful for healthy women who, for various reasons, are postponing the birth of children indefinitely.
Stages of development
The dominant develops in the ovary on average for 2 weeks, the remaining follicles are suppressed at the initial stage of formation. The dominant formation, under the influence of estrogen and luteinizing hormone, bursts in the middle of the month. An ultrasound shows that the bubble in the gonad has disappeared, leaving a small amount of fluid in its place. Next, the corpus luteum will form in this place. In its formation, the ovarian follicle goes through the 4 stages described below.
At the primordial stage of connective tissue. It is small and flattened. During one cycle, 5–20 such structures are formed in the gonad.
Secondary follicle
On days 8–10 of the cycle, secondary structures are formed. The thickened follicular epithelium produces fluid, which is a source of estrogen, gradually filling the resulting bladder, the diameter of which is 10 - 12 mm. The formation can be single-cavity or consisting of several chambers. At this stage, there are about 10 formations left.
Visual stage of follicle development
At the final stage, the development of one oocyte continues, for the remaining formations the process of oppression begins - atresia. The remaining dominant reaches 2 cm, protrudes into the abdominal cavity on one side, and attaches to the connective layer of the ovary on the other. Inside is an egg ready for fertilization.
During its development, the follicle goes through several stages (phases).
Early phase
Several follicles are growing. After one of them (dominant) reaches 24 mm in diameter, ovulation occurs.
Luteal phase
The period between ovulation and the start of a new cycle is called the luteal phase (or corpus luteum phase). After the graafian bubble bursts, it begins to accumulate fats and pigments. This is how the corpus luteum develops. It produces progesterone, androgens, esradiol.
These substances activate the maturation of the endometrium. The uterus is preparing for the implantation of a fertilized oocyte. If pregnancy occurs, the corpus luteum continues to secrete progesterone until the placenta reaches a certain size and begins to produce it itself.
If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum is destroyed. The levels of estrogen and progesterone gradually decrease, which contributes to the start of a new monthly cycle.
Double ovulation in one or different ovaries
Every month, about eight follicles begin to grow in the female body. Most of them do not fully develop; only one or two continue to grow.
Double fertilization occurs due to natural causes and medication. Moreover, naturally, the maturation of two dominant elements occurs much less frequently.
In a healthy female body, one dominant follicle regularly matures, but sometimes multiple ovulations occur: the release of two or three eggs. That is, a multiple pregnancy - expectant mothers are prepared for the birth of fraternal twins: twins, triplets.
There is a high probability that the children will not be too similar to each other. And they won't necessarily be the same gender. Twins appear in a different way: during the division of one egg.
This is interesting! In world practice, there are eleven “double” conceptions with a difference of several days.
Cases of double ovulation in one and two ovaries have been recorded, occurring simultaneously or with an interval of several minutes to several days. The first embryo becomes the eldest, the other the youngest. Twins' fathers are sometimes different: if the mother had more than one partner during this time period.
Dominant follicle in the left ovary
In practice, the follicle of the right ovary is often dominant. This is possible due to better blood supply to the organ and a greater number of vessels than in the left appendage.
In rare cases, the right ovary may contain 2 dominant follicles at once. This will result in the conception of identical twins.
If the female reproductive system is in order and healthy, then both organs of the reproductive system can alternately produce eggs ready for fertilization. If in most cases a dominant follicle appears on ultrasound in the left ovary, this may indicate pathological abnormalities in the right, such as:
- Inflammatory processes;
- Cystic formations;
- Abnormal structure;
- Change in the shape of an organ as a result of surgery or injury.
A mature and large enough follicle that provides complete protection for an egg ready for fertilization is called dominant. Its size can reach a couple of centimeters just before ovulation. Most often it is located in the right ovary.
The process of ovulation occurs during the period when, under the influence of hormones, the dominant cell reaches its maximum size and ruptures. The finished egg is sent to the uterine tubes. Ovulation does not occur if the dominant cell remains immature.
Attention! It also happens that dominant follicles mature in both ovaries at once. Such cases are very rare. This should not be a cause for concern. The simultaneous maturation of dominant formations suggests that during the period of ovulation a woman has every chance of conceiving two embryos.
How many follicles should there be for conception?
In order for a woman to become pregnant, the egg must mature completely. How many follicles should there be to conceive? At the stage before fertilization, it is necessary to have one - high-quality dominant development. He should be ready to ovulate. If an ultrasound examination reveals two such formations, and they both undergo fertilization, twins will be born.
- Nail painting for beginners step by step with photos
- Meatballs in the oven: recipes with photos
- Baker's cyst disease of the knee joint
What are antral glands
Antral follicles are vesicles about 8 mm in size in which the maturation of eggs occurs. The ability to get pregnant is directly related to functional activity and the number of formations. Women play a major role in determining fertility. In case of infertility, the number of antral follicles is usually counted. Their number determines the probability of successful conception of a child.
| Quantity | Result |
| Up to 5 | The worst indicator. Infertility, in which stimulation will not bring any results. |
| 6 — 10 | Indicates disorders in the woman’s reproductive system |
| 10 — 15 | Low chance of conception |
| 15 — 26 | High chance of pregnancy |
| More than 26 | There is a possibility of developing polycystic disease |
These are glands that are highly likely to develop into a primordial follicle. In the future, it has the potential to evolve into a dominant one, from which an egg will then be released.
Potentially, all antral glands have a chance to mature into a full-fledged oocyte. But there can be no more than 500 of these in a woman’s entire life. By the age of 50, a woman’s monthly cycle gradually fades away and reproductive function ceases.
Eggs began to be carefully studied after artificial insemination became widespread. Thanks to research, leading gynecologists were able to figure out why some women can easily give birth to a child, while others suffer from infertility. That's why scientists took control of antral follicles. What is it?
Follicles reaching a size of 8 mm are called antral. An ultrasound can show how many reserve eggs have collected for further fertilization. With small antral follicles, the probability of positive fertilization is very low. If the size of the antral formation reaches 5 mm, then stimulation by a gynecologist is required for conception. If the size is greater than 5 mm, the woman does not need stimulation. During pregnancy, follicular development stops.
What parameters do follicles have before ovulation?
A dominant follicle is a follicle whose size exceeds the diameter of other cells by at least 1.5-2 times . Gynecologists determine the normal course of a woman’s menstrual cycle using generally accepted indicators that illustrate changes in the size of the follicles, as well as their growth rate.
By the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle, gynecologists mean the period from the first day of bloody vaginal discharge until the onset of ovulation. With an average cycle length of 28 days, the follicular phase lasts the first 2 weeks.
| Period of the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle | Condition of follicles considered normal |
| 1 day from the start of bleeding | The ovaries contain at least 20 minimum-sized follicles with an immature egg inside each. The diameter of the follicles during this period does not exceed 0.5 mm. Due to the increase in the concentration of hormones, in particular LH and FSH, the follicles begin to increase in size. |
| 4–5 days from the start of bleeding | In one of the ovaries a dominant follicle is found - preantral, the size of which is at least 2 mm. Menstruation ends or the discharge becomes scarce, due to which the endometrium begins to actively increase. |
| One week from the start of bleeding | The dominant follicle in one of the ovaries matures to a size of 5 mm, after which a cavity is formed inside it for the subsequent accumulation of follicular fluid and other changes that occur in the body as ovulation approaches. |
| 13-14 days from the start of bleeding | The dominant follicle increases to 20 mm in diameter, which is why its walls rupture, thus releasing the egg that has matured by this time. The egg is “sucked” into the opening of the fallopian tube with the help of fimbriae (special tissue processes located in the fallopian tubes). |
What does an ultrasound show?
Capsules with eggs can be easily detected on the screen during ultrasound diagnostics from the fifth day of the cycle. In the future, their dimensions increase. On the 7th day of the cycle, you can see which of them is dominant.
Upon examination, empty follicle syndrome can be detected. This means that the ovary is not able to provide the release of the sex gland. Such a woman needs to get rid of infertility.
Ultrasound is completely safe for the body.
FAQ
This process lasts only 9 days (plus or minus one). Provided that the woman’s hormonal levels are stable, ovulation occurs on the 14th day of the cycle.
With a hormonal disorder, there may be too many follicles in the ovary or, conversely, too few. Sometimes there is no sex gland at all.
All these phenomena negatively affect a woman’s reproductive function.
The shrinkage of the follicle on the day of ovulation leads to the fact that the egg cannot be released from it. The woman will not be able to get pregnant. An increase in the Graafian vesicle indicates a high probability of a cystic process. It also has a negative effect on conception.
In this case, they talk about its persistence. This phenomenon is considered pathological and requires correction.
Fraternal twins occur when not one, but two eggs are released from the ovary.
The follicle is the most important structural element of the ovary. The likelihood of an egg being released and a woman’s chances of becoming pregnant depend on their number and development. The discrepancy between its size and quantity and the norm is a pathology. Such women should be treated for infertility.
Bottom line
Follicles are a structural unit of the ovaries, their quality and normal quantity determine the ability to procreate. Monitoring folliculogenesis helps track ovulation, assess ovarian reserve and detect possible pathologies of folliculogenesis.
The normal number for self-conception of a baby is 16-26 follicles in the appendages; if there are less than 15 vesicles, fertilization is possible using auxiliary methods. If there are less than 4 germ cells, then infertility is diagnosed.