When visiting a reproductive medicine clinic, a couple who has problems conceiving may not be ready for the diagnosis announced by the doctors.
Reproductive dysfunction is detected even in cases where a woman has already had one pregnancy. Medicine distinguishes between 1st degree and 2nd degree infertility.
As experts explain, the characteristic assigned to reproductive dysfunction does not describe the diagnosis itself, its causes, or possible consequences. It only gives an idea of whether the woman had a previous pregnancy and how it ended.
Infertility of 1st degree and 2nd degree occurs in both men and women. The prerequisites for it may be various factors affecting the ability of both partners to conceive. Doctors give this diagnosis to a married couple after a year of unsuccessful independent attempts to conceive.
Female and male infertility of the 1st degree: what is it?
Problems with spontaneous conception are being discovered more and more often, and today almost every tenth married couple is forced to contact a reproductive medicine clinic to identify the causes of the problem and search for possible treatment options. Based on the results of the examinations, doctors can identify varying degrees of the disease.
To the question: “1st degree infertility, what is it?”, patients receive the following answer: it can be diagnosed in both partners and assumes the absence of pregnancy, if the woman has never given birth and the man could not carry out fertilization with either this one, nor with previous partners.
2nd degree infertility: what is it? Typically, this diagnosis is encountered when the process of conception has taken place, but for some reason has not resulted in the successful birth of a child.
Often among the prerequisites for pathology are surgical operations that affected the integrity of organs and the presence of scars and adhesions on them. This type of reproductive dysfunction is also called secondary infertility. Such a diagnosis can also be made in cases where there was a stillbirth or a miscarriage occurred, indicating the woman’s inability to bear a fetus.
As a rule, problems associated with the ovulatory process lead to the discovery of 1st degree infertility in women. It can be caused by various pathologies, including:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome;
- Problems in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- Unstable hormonal levels;
- Ovarian dysfunction;
- Incorrect functioning of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
Second degree infertility in women is caused by other factors. Primary reproductive dysfunction can be caused by the peculiarities of the immune system of each partner and their immunological incompatibility.
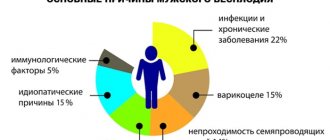
In the case of men, 1st degree of infertility is diagnosed with obstruction of the seminal ducts, problems with the development of germ cells, as well as their low quality. The cause may also be the independent production of antibodies against one’s own sperm. Varicocele disease can also lead to this diagnosis.
Causes of the problem
So, it becomes clear that secondary infertility or, as it is also called, second-degree infertility means the inability of a couple to conceive a child a second time, after a successful first pregnancy. Logically speaking, we can assume that the cause of the problem is acquired. What can become an obstacle to successful conception? Let's start with men. Their reasons are:
- Infections of the genitourinary system.
- Varicocele.
- Chronic diseases of internal organs.
- Head injuries.
- Diabetes.
- Taking anabolic drugs.
- Drug addiction, alcoholism.
Second degree infertility is more common in women. Their problems are caused by the following factors:
- Age. The favorable period for the birth of a baby is the age period from 18 to 35 years. Gynecologists recommend planning your first birth before age 28. As for the second, there are women who decide to give birth both after 18 years and at 45. But still, the thirty-year threshold is the beginning of the wear and tear of a woman’s reproductive system. It quickly fades away after 35.
- Disturbances in the endocrine system. Most often, these are hormonal imbalances, which can make themselves felt by disturbances in the menstrual cycle and irregular ovulation. The thyroid, putuitary, and adrenal glands often malfunction.
- Inflammation of the genitourinary system. This is a wide range of ailments, including endometriosis, chronic adnexitis, infectious inflammation as a result of abortion. Often women experience adhesions of the fallopian tubes. They interfere with patency and conception.
- Immunological reasons. Sometimes a woman’s body begins to synthesize antisperm substances. Such antibodies perceive male sperm as a foreign agent and suppress it. Therefore, conception does not occur.
- Lifestyle. The basis of reproductive health, as well as a woman’s appearance, is her lifestyle. If she is a heavy smoker, drinks often, eats fast food, and is obese, then what kind of reproductive health can we talk about?
More on the topic
1st degree infertility
Causes of female infertility and ways to solve the problem
Infertility after abortion
Treatment of infertility in women
Causes and signs of infertility in women and men
Female and male infertility 2nd degree: what is it?
Depending on the nature of the pathology and after a medical genetic examination, both partners may be diagnosed with reproductive dysfunction. But, depending on what caused it, primary infertility is distinguished and secondary - second degree.
As follows from the description of the factors influencing a woman’s ability to become pregnant, and a man, accordingly, to fertilize a partner’s reproductive cell, the prerequisites for the presence of dysfunction of one type or another differ.
1st degree infertility is characterized by congenital pathologies, while 2nd degree can be acquired after an incorrect surgical procedure or previous diseases:
- Abortion;
- Inflammatory processes;
- Infectious diseases.
These conditions often lead to obstruction of the fallopian tubes due to the formation of adhesions and can cause an ectopic pregnancy, in which doctors have no options and must interrupt the pregnancy.
The diagnosis of 1st degree infertility, as in the case of the second, can be made after identifying and treating endometriosis, as well as immune problems and endocrine pathologies, when the ovulatory process is disrupted.
Both degrees of infertility in women are detected when they are unable to bear a fetus and there are no necessary conditions for its growth and development. For example, due to the presence of neoplasms - polyps or fibroids, scars, cysts and inflammations. Pathologies of the uterine cervix also provoke a diagnosis of grade 2 infertility - in the case of erosion or disturbances in the composition of the cervical fluid.
In the case of second-degree male infertility, the cause is usually disturbances in the production of hormones, damage to the genitals, immune disorders and the effects of drug use. Inflammatory and systemic diseases can cause reproductive dysfunction.
Infertility Treatment Methods
Before starting treatment for female infertility, it is necessary to identify its cause. To do this, the woman undergoes a variety of examinations: ultrasound of the pelvic organs, salpingography, CT and TRI, as well as a general blood test and a study of hormone levels. The treatment algorithm for female infertility is as follows:
- elimination of pathological foci of inflammation in the woman’s reproductive organs;
- hormonal stabilization of the menstrual cycle;
- restoration of impaired or lost ovarian function;
- treatment of thyroid pathology;
- physiotherapeutic methods aimed at eliminating the causes that prevent a woman from becoming pregnant;
- plastic surgeries that restore normal anatomical relationships of the genital organs.
After determining the cause of male infertility, the doctor uses one of the methods for treatment that helps eliminate the problem:
- surgical intervention to eliminate minor defects of the genital organs;
- correction of nutrition and lifestyle;
- recommendations for giving up various bad habits;
- alignment of hormonal levels;
- antibiotics and antiseptics for the treatment of infectious diseases;
- methods aimed at improving seminal fluid expression and sperm quality.
In severe forms of male infertility, sperm can be collected, which is then used in assisted reproductive technologies, by puncture or testicular biopsy. For grade 2 infertility, the rehabilitation process lasts several years. It is successful only when both the man and the woman unconditionally follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Treatment of 2nd degree infertility begins with diagnostic measures. Men are prescribed antibacterial and antiviral drugs, as well as immunomodulators. Infertility of the 2nd degree is well treated using sanatorium-resort methods.
How to treat secondary infertility?
To determine reproductive dysfunction, doctors conduct a series of examinations and tests on the infertile couple, both women and men. Having found out what could have caused the problem, specialists offer treatment options depending on the diagnosis. First degree infertility requires a different approach than secondary. When a second degree is detected, doctors strive to eliminate the cause of the pathology. This may include restoring the functioning of the endocrine system, removing adhesions and restoring the normal structure of organs.
Causes
There are several reasons for secondary infertility in women.
- Age group. A woman's advanced age is a common cause of secondary infertility, because it determines the activity of the reproductive system of the female body. Statistics show that after 25 years, a woman’s chances of becoming a mother decrease, and after 35, the likelihood of pregnancy decreases even more. At this age, up to 7 menstrual cycles can occur without ovulation, while at 20-35 years old there can be only 1-2 cycles without ovulation during the year. Approximately 25% of all clinical cases of second degree infertility occur in this age group.
- Psycho-emotional status. A woman’s psychological state affects her hormonal levels. If she is exposed to stress or nervous tension, this can lead to disturbances in the functioning of the reproductive system. Sudden weight loss or obesity is a real stress for the body, which can also cause secondary infertility.
- Somatic diseases of the reproductive system. Inflammatory processes of an infectious nature in the female reproductive system can cause problems with conception. Second degree infertility may be associated with complications of other pathologies, for example, adhesions of the fallopian tubes or disruption of the ovaries. The presence of diseases of the reproductive system leads to a deterioration in the quality characteristics of natural lubricant (it can become too liquid or too viscous), which will interfere with the movement of sperm towards the egg. In addition, the following diseases are common causes of infertility: endometriosis, polyps, hyperplasia, uterine fibroids, polycystic ovaries, the presence of tumors in the uterus.
- Post-abortion. This operation can provoke infertility due to the development of the inflammatory process in the reproductive system.
- Thyroid gland dysfunction. All organs and systems in the body are interconnected. The production of sex hormones is influenced by the hormones synthesized by the thyroid gland. Among the main causes of second-degree infertility, experts identify hypothyroidism (decreased functional activity of the thyroid gland). This leads to suppression of ovulation and menstrual irregularities. Thyroid dysfunction can be caused by iodine deficiency.
- Lack of progesterone. This hormone ensures the onset and normal course of pregnancy. If it is deficient, a woman cannot become pregnant or will have frequent miscarriages in early gestation. You can determine the deficiency of this sex hormone by passing the appropriate test or measuring your basal temperature.
There are many reasons for the occurrence of secondary infertility in women, so this pathology requires a thorough diagnosis, based on the results of which the attending physician will be able to select treatment methods taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
How is primary infertility treated?
In the case of a woman, there is the following nuance: if the inability to get pregnant is caused by psychological factors, it is necessary to carry out therapy aimed at restoring the correct perception of motherhood. Most often, such treatment for the first degree of infertility brings the desired effect.
But, if the cause of the pathology is different, the couple is advised to consider options for artificial conception. The decision made in each specific situation is individual.
Diagnostics
If pregnancy does not occur in a couple who has not used contraceptives for a year, a diagnosis of “second degree infertility” is made. This is followed by a detailed examination of the couple.
The main study for a man is a spermogram (analysis of seminal fluid). This examination can determine possible causes of problems with conception or exclude them.
The list of diagnostic procedures for women is much wider.
- Gynecological examination. This is the initial stage of diagnosis. During the visit, the doctor will conduct a survey, collect an obstetric history and perform an examination of the patient. Based on the data obtained, the specialist will conduct a differential diagnosis and set the direction for further actions.
- Tests for the presence of infections. A comprehensive examination, including examination of the composition of a vaginal smear and a blood test, will help to identify their presence in the female body.
- Tests for hormone levels. A woman takes them if there is a menstrual cycle disorder, hair appears in unusual places, or a sudden weight gain occurs. In this case, the specialist prescribes a series of tests, which are taken on certain days of the cycle.
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvis. An examination of the pelvic organs is carried out several times during the cycle, which makes it possible to evaluate the functioning of the ovaries (determine whether ovulation is occurring), the activity of the uterine mucosa and the condition of the pelvic organs as a whole. Sometimes an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland is prescribed.
Signs of secondary infertility in women
The main sign of secondary infertility is the inability to become pregnant again. This condition is only a symptom of more complex and serious processes occurring in the body. They become an obstacle to reproductive function for the second time. The distinguishing criterion for primary and secondary infertility is only the presence of pregnancies in the past.
The time frame for diagnosis is the same in both cases. They may differ for patients of different age groups. The diagnosis is made to women under 30 years of age after a year of unsuccessful planning. Patients over 30 years of age should think about the problem after 6 months of failure, provided they have regular sex life without contraceptives.
Many women with secondary infertility already have children. When they were conceived, there may have been no problems at all. And the reason for failure the second time was age-related changes in the body. In patients over 35 years of age, pathologies of the reproductive system are diagnosed twice as often as in women under 30 years of age. However, many of them are asymptomatic and develop over years. Until a couple decides to get pregnant, no one knows that there will be problems with conception.
Secondary infertility can also develop in men. In this case, it will be more difficult to notice the problem. If a woman’s inability to get pregnant is often accompanied by cycle disorders, discharge, pain in the ovaries and changes in body weight, then in men all pathologies in the reproductive sphere occur hidden.
Unconventional treatment
Traditional medicine is widespread in the treatment of diseases of the reproductive organs. Herbs that are popular are: red brush, hogweed, and sage. It is important to know on what days of the cycle and for what disorders to take decoctions from them. However, traditional medicine should not replace traditional treatment, but complement it.
The prognosis of therapy for second degree infertility depends on the reasons that provoked the problem. Most often, the violations can be successfully corrected, after which the partners manage to conceive. If after treatment there is no chance of a natural pregnancy, doctors recommend resorting to IVF.