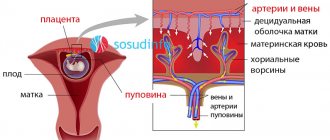
Fetal growth retardation syndrome (FGR), or malnutrition, is a pathology in which the development of a child in the womb slows down due to a number of unfavorable circumstances. As a result, the baby in all respects lags behind the normal indicators provided for a specific gestational age. Developmental delay affects the height, body weight, and level of mental maturity of the fetus. Most often, there are no specific signs of FGR. The only indications of deviation are the expectant mother’s unhurried weight gain, a miniature tummy, as well as unusual behavior of the baby in the form of too active or, conversely, rare movements. Read about the specifics of the pathology and ways to eliminate it in the article.
Intrauterine growth retardation is diagnosed when the fetus is low-weight - it lags behind the required weight by 10 percentiles or more. According to medical observations, FGR occurs in every tenth pregnant woman and, in fact, is a fertile ground for the development of concomitant diseases of the fetus and infant.
The statistics are disappointing: on average, 70-90% of cases of malnutrition overshadow the 3rd trimester (if the pregnant woman has health problems). 30% of babies suffering from FGR are born prematurely. The risk group includes young expectant mothers who became pregnant before their 18th birthday, and women over 30 years of age. Older primigravidas are especially prone to developing pathology.
obesity 1, 2, 3 degrees, treatment of obesity with folk remedies
Obesity is a metabolic disorder in the body , in which an excess amount of adipose tissue not only poisons life, but also provokes the onset of all sorts of diseases. Doctors say that overweight people are at risk of varicose veins, cholelithiasis, hypertension, atherosclerosis, diabetes, rheumatism...
With obesity, a high level of fat remains in the blood for a long time, which has a gradual destructive effect on the condition and functioning of the central nervous system, which ultimately leads to a serious disruption of fat metabolism throughout the body.
With obesity, the load on all organs and systems increases. The activity of the cardiovascular system is especially affected, causing cholesterol metabolism disorders and atherosclerotic changes in the aorta and coronary vessels of the heart. The more fat deposits, the more they interfere with the functioning of the heart. The supply of oxygen to tissues is also reduced, breathing is impaired and the lungs begin to suffer.
In addition, obese people are more likely to suffer from hypertension, angina, myocardial infarction and cerebral hemorrhages. Due to the deposition of fat in the abdominal cavity, the intestines are displaced, which, in turn, leads to disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
There is no need to talk about the appearance of an obese person. The saddest thing is probably that the human psyche is undergoing changes that are not for the better. He becomes inattentive, absent-minded, constantly tormented by weakness, drowsiness, emotional instability, irritability, dizziness and headaches.
With obesity, the body receives a number of kilocalories that exceed its needs. And carbohydrates in cells are intensively converted into fats. Excess body weight begins to accumulate. In general, it is generally accepted that obesity most often affects women who have crossed the forty-year mark. But how many overweight men do we see with funny beer bellies? Remember the joke? Two pregnant women met. One asks the other: “Who are you waiting for?” - A boy. And you? - And I’m a girl. The daughter of one of the women heard their conversation, then saw a man at a bus stop with a big belly and asked: “Uncle, who are you waiting for?” - Bus…
As the classic said, all this would be funny if it weren’t so sad. But the saddest thing is that recently a huge number of overfed children and adolescents suffering from obesity have appeared.
The causes of obesity are called very different. For example, hereditary constitutional predisposition, low physical activity, pregnancy, breastfeeding, menopause, hormonal changes caused by endocrine diseases, and banal gluttony, that is, systematic overeating.
Obesity can also be caused by prolonged depression, chronic stress and even small but daily troubles, family quarrels, conflicts at work and other hassle. Especially if a person is worried about his future, his social and material status, and at the same time eats up all his worries with an additional portion of high-calorie food.
For women, it is undesirable to exceed a waist circumference of 88 cm. For men, 100-102 cm is acceptable.
Already at the 2nd degree of obesity, a person begins to experience shortness of breath, a bitter taste in the mouth, swollen legs and joint pain. And with degree 4 obesity, a person practically turns into a disabled person. He is only interested in food. He can eat day and night. Men develop impotence, women develop frigidity and increased hair growth throughout the body. In addition, women's voices become rougher and menstruation may stop. Hence infertility and premature aging.
There is no way to treat obesity without diet. But you shouldn’t prescribe it to yourself. An experienced specialist is needed. In addition, a gradual increase in physical activity is necessary and sessions with a psychotherapist are advisable. There are special medications that reduce appetite.
Among the folk remedies for the treatment of obesity, it is recommended to drink a decoction of white cabbage leaves instead of water during the day: 250 g of cabbage are poured with 1.5 liters of water and brought to a boil. Boil over low heat for 10-15 minutes. Cool and filter. Bring the liquid to the original volume and drink in slow sips throughout the day - at least ¼ cup at a time. After each meal, you must get up from the table and walk around for at least 15 minutes.
In addition to official medicine, homeopathic doctors treat obesity.
We all want something tasty and it’s hard to deny ourselves. But the only way out of this situation is for everyone to monitor their body weight from their youth and not bring it to critical. It is always more difficult to treat than to prevent the development of the disease.
According to the latest statistics, 30% of the population of economically developed countries suffers from obesity.
What is it: Anemia 1st degree
The insidiousness of this disease lies in the fact that the mild form does not manifest itself at all and the symptoms characteristic of this disease are practically absent. Anemia can only be suspected if the skin becomes too pale. That is why timely diagnosis is of great importance to determine the presence or absence of anemia in a pregnant woman. It is very important to determine the presence of this disease in the body in a timely manner and carry out comprehensive treatment, since anemia can have very serious consequences for the development of the fetus, the condition of the mother, and also affect the course of the birth process.
That is why it is necessary to treat and prevent anemia from the first weeks of pregnancy.
There are three degrees of complexity of anemia. When anemia of the first severity occurs, the hemoglobin indicator is in the range of 90-110 g/l. Due to the fact that iron plays a very important role in the body's hematopoietic system, the blood helps transport useful and nutrient substances, as well as oxygen, to the fetus. Doctors recommend closely monitoring hemoglobin levels, and even a slight deviation from the norm should cause serious concern.
Anemia of the 1st degree often does not manifest itself at all during pregnancy and a woman may not even be aware of its presence until blood tests are taken. A pregnant woman may not feel dizziness, headaches and many other signs of anemia, but the fetus acutely feels this deficiency through oxygen starvation. Treatment of first degree anemia in pregnant women is carried out under the supervision of a doctor at home. In the presence of anemia of the second and third stages, iron deficiency should be eliminated only in a hospital setting.
Endometrial hyperplasia disease and pregnancy: 7 rules
The main causes of anemia in pregnant women are considered to be:
- Chronic diseases;
- Lack of normal nutritious nutrition;
- A short break between births;
- Miscarriages and heavy bleeding;
- Complication of pregnancy.
In this case, it is imperative to follow a special diet, which involves consuming foods containing a lot of iron, as well as leading a healthy lifestyle.
Where do fat reserves come from? Excess weight during pregnancy.
Obesity is not just excess fat in the body. This is a chronic relapsing (with exacerbations) disease that contributes to the manifestation and development of many other chronic diseases. This disease also affects the course of pregnancy.
Natalya Alexandrova: “The main sign of obesity is excessive accumulation of adipose tissue in the body. Adipose tissue is a depot (place of accumulation) of incoming energy. The more adipose tissue, the higher the amount of “extra” energy obtained from food and not spent.”
What to do
VZRP cannot be ignored. After identifying the pathology and finding out the possible causes of its occurrence, the woman is prescribed treatment. When choosing the direction of therapy, the degree of FGR is taken into account. The main method of treatment is the use of medications. The following types of medications are recommended for therapy:
- Improving blood flow in the placenta. For this purpose, droppers with Actovegin are used.
- Blood thinners (Curantil, Trental, Aspirin). Thinned blood moves faster through the vessels, which speeds up the delivery of oxygen to the fetus.
- Relieving spasms of blood vessels and uterus. When spasms occur, the blood vessels are compressed, so blood flow in the placenta is disrupted and the fetus does not receive enough oxygen and nutrients. Have a relaxing effect: Magnesia, Ginipral.
- Vasodilators (Theophylline).
The woman is also prescribed medications that reduce nervous tension and vitamin complexes. During treatment, it is recommended to go to the hospital. During the subsequent months of pregnancy, the expectant mother should eat a varied diet, often walk in the fresh air, refrain from physical overexertion and get plenty of rest.
During therapy, the condition of the fetus is constantly monitored. For this, additional ultrasound and cardiotocogram are performed. If the child’s condition worsens, doctors decide on urgent delivery by cesarean section.
Where do fat reserves come from?
The factors for the development of obesity are diverse and can act both jointly and separately. The most common of them are behavioral characteristics (physical inactivity - decreased physical activity, overeating), genetic predisposition, and endocrine system disorders. Numerous studies have found that obesity in childhood is a powerful predisposing factor for obesity in adulthood, especially when one or both parents are affected. Thus, with normal body weight of parents, obesity occurs only in 9% of children, with obesity of one parent - in 50%, and with obesity of both parents - in 70% of cases.
There is a special center in the brain, the hypothalamus, which is responsible for the feeling of hunger and satiety. Constant overeating leads to disruption of the hypothalamus, and the normal amount of food eaten can no longer suppress the feeling of hunger, so a person has to eat more and more. Excess food is stored as if in reserve in the fat depot, which leads to an increase in the amount of fat in the body, that is, to the development of obesity.
What is the danger
Inappropriate fetal development is considered a serious pathology. In most cases, it affects the physical parameters of the newborn. The baby is born with low weight. However, the main danger of FGR is that if the problem is ignored, the fetus develops pathologies that are expressed in congenital diseases or lead to intrauterine death.
IUGR is most dangerous at the beginning of pregnancy. During this period, the formation of all organs and systems occurs. Developmental disorders can have irreversible consequences and affect the further course of pregnancy. Most children with IUGR are born prematurely. READ ALSO: Ginipral: instructions for use during pregnancy
The risk of complications during childbirth increases. Babies suffer from hypoxia and asphyxia. After birth, children adapt to the external environment for a long time and slowly gain weight. Low birth weight newborns are more likely to suffer from jaundice. As children grow up, they often get sick and have an increased risk of developing the following pathologies:
- cardiovascular diseases;
- overweight;
- diabetes mellitus;
- hypertension;
- anemia.
Possible problems
Pregnancy.
During pregnancy, favorable conditions are created for the development of fatty tissue, the biological meaning of which is to protect the unborn child. This is due to hormonal changes in a woman’s body, namely increased synthesis of progesterone and human chorionic gonadotropin (hormones that support pregnancy) and a deficiency of estradiol, produced by the ovaries mainly outside of pregnancy. The action of these hormones causes the deposition of adipose tissue mainly in the area of the mammary glands, buttocks, thighs, and abdomen.
In obese patients, pregnancy rarely proceeds without complications. The most common include gestational diabetes, or diabetes during pregnancy, arterial hypertension, hypercoagulation (increased blood clotting), cardiac dysfunction, toxicosis, preeclampsia (it is characterized by increased blood pressure, the appearance of edema, protein in the urine), urinary tract infections, miscarriage or post-term pregnancy. pregnancy (a condition in which pregnancy lasts more than 41-42 weeks), premature rupture of amniotic fluid, the birth of a child with a large body weight (more than 4000 g).
The most dangerous complication is preeclampsia - the most severe form of gestosis, the main symptoms of which are an increase in systolic pressure above 140 mmHg. Art., diastolic pressure above 80 mm Hg. Art., as well as proteinuria (loss of more than 3 g of protein per day in urine). In addition to the above symptoms, there may be signs of damage to other systems and organs: the appearance of headaches, abdominal pain, blurred vision. Laboratory tests reveal increased levels of liver enzymes and changes in the blood coagulation system.
Obesity also affects child development. As is known, folic acid plays a key role in the formation of the nervous system, and with obesity, its metabolism in the body of a pregnant woman changes, which can lead to the development of defects of the nervous system in the fetus.
Childbirth.
In obese women, not only pregnancy, but also childbirth itself occurs with a number of peculiarities, which is caused by hormonal changes. The internal system that triggers labor in such women remains imperfect by the end of pregnancy, and the lack of formation of a labor dominant (a focus of excitation in the brain) leads to post-term pregnancy, and subsequently to weakness of labor, the severity of which increases in proportion to the degree of obesity.
When labor is weak and cannot be corrected with medication, doctors are forced to resort to surgical delivery (caesarean section or forceps) to avoid acute oxygen deprivation in the newborn. But it is possible that the need for a cesarean section will be due to a discrepancy between the sizes of the pelvis of the mother and the fetus, since obese pregnant women, as mentioned above, are more likely to give birth to children with a large body weight.
In turn, surgical intervention is also associated with a large number of complications, since the severity of the subcutaneous fat layer impairs the healing of postoperative scars
You can purchase clever scales that analyze the mass of fat, muscles, and bones. During pregnancy, these scales can only be used for weighing, since they have not yet “learned” to take into account the weight of the fetus, placenta, and amniotic fluid.
In 6-30% of obese women in labor, bleeding occurs during childbirth, as well as in the postpartum period, the causes of which are both impaired contractility of the uterus and changes in the blood coagulation system.
It should also be remembered that obese women are at risk of developing carbohydrate metabolism disorders, that is, diabetes mellitus, therefore, 2 months after childbirth or after cessation of lactation, they need to be examined to determine blood glucose levels.
Pregnancy with stage 3 obesity
This option happens much less frequently, since the chance of conceiving in women with third degree obesity is very small. The chance of a successful birth also decreases. Without the help of specialists, everything often ends in miscarriage. When it comes to childbirth, doctors try to use a caesarean section. The natural birth of a child becomes difficult and in obese patients there may be no initiation of natural processes, such as contractions, etc.
Despite all the difficulties, there are many cases in modern practice when childbirth was successful.
How to reduce the risk?
Despite the presence of a large number of complications, obesity is not a contraindication to pregnancy. When preparing for conception, a woman needs to consult not only an obstetrician-gynecologist, but also an endocrinologist; Throughout pregnancy, it is mandatory to follow all doctor’s recommendations.
First of all, a woman should control her weight. In pregnant women with normal body weight, the increase in body weight during pregnancy should not exceed 10-12 kg, of which approximately 4 kg is due to an increase in the mass of adipose tissue, and in pregnant women with obesity, and especially with severe obesity, the increase in body weight should not be more than 5-6 kg.
Most obese pregnant women need to undergo a glucose tolerance (resistance) test at their first visit to an obstetrician-gynecologist. The test consists of determining the blood glucose level 1 hour after ingesting 50 g of glucose. If violations are detected, it is necessary to adhere to a special diet, and in some cases, the doctor may even prescribe insulin injections.
To reduce the excitability of the food center, frequent meals are recommended (8-6 times a day), while the food should be low in calories, but occupy a large volume in the stomach, which helps eliminate the feeling of hunger. It is necessary to exclude from the diet flavoring substances that increase the excitability of the food center and increase appetite (spicy, salty dishes, broths), as well as substances that are quickly absorbed and digested (confectionery, sweets, sweet fruits).
The protein content in a pregnant woman's diet should be sufficient, 20% of the daily diet. The recommended proportion of fats is approximately 30%, and carbohydrates - 50% of the daily diet. That is, nutrition should be rational, there is no need to focus only on meat or only dairy products, as well as only on vegetables and fruits, and, of course, there is no need to overuse sweets. A pregnant woman's menu should be varied: 6-11 parts are grains, 3-5 parts are vegetables, 2-4 parts are fruits, 3-5 parts are dairy products, 2-3 parts are meat products, legumes or nuts, Part 1 - sweets. The energy value of the diet depends on BMI, but on average it is 2500 kcal per day.
Obese women should reduce the energy value of food, but no more than 10%, otherwise the incoming food will not ensure normal growth and development of the fetus. It should be noted that obese pregnant women should never fast, as this causes ketonemia, that is, metabolic products - ketones - are found in the woman’s blood, which have an adverse effect on the development of the fetus.
For obese pregnant women, fasting days are recommended 1-2 times a week. Here are some of them (the amount of food eaten should be divided into 5-6 meals).
Curd:
400 g of low-fat cottage cheese is eaten per day, additionally 2-3 glasses of tea without sugar (with lemon) or rosehip decoction are allowed.
Apple:
1.5 kg of raw or baked apples. 2 glasses of tea without sugar are allowed.
Cucumber:
1.5 kg of fresh cucumbers, 2 glasses of tea without sugar. The calorie content of cucumbers is extremely low (2 times less than cabbage and 3 times less than apples).
Consequences for the child: anemia during pregnancy
For a child who is completely dependent on the state of the mother’s body throughout pregnancy, anemia can have very serious consequences.
In particular, such as:
- Fetal growth restriction syndrome;
- Threat of miscarriage;
- Premature birth;
- Toxicosis.
In this case, the child will not receive the required amount of useful nutrients. This affects the fact that the child will be delayed in growth and development, and there is also a high risk of various types of pathologies.
If anemia occurs in the second half of pregnancy, there is a high risk of premature birth, as well as fetal death.
In addition, low hemoglobin provokes a decrease in immunity, which is why complex treatment is required.
General concepts
In the process of bearing a child, the body of the expectant mother faces a radical hormonal change. This circumstance entails active gain of excess weight, which is a variant of the physiological norm. Additional kilograms appear due to the growth of the placenta and an increase in the volume of amniotic fluid. In addition, the mammary glands of the expectant mother increase in volume due to the growth of adipose and glandular tissue. These physiological mechanisms are aimed at ensuring the life activity of the unborn child. If weight gain during pregnancy does not exceed the acceptable limits, then there is no reason to panic.
Normal weight gain for the entire period of bearing a child is from 8 to 12 kg. If before pregnancy a woman had a problem with extra pounds, then the permissible weight gain should be no more than 6 kg. If a woman experiences a sharp increase in weight, this may indicate fluid retention in the body associated with a severe form of toxicosis (preeclampsia). Very often, obesity during pregnancy occurs against the background of endocrine disorders such as diabetes mellitus and diencephalic pathology.
Before using all kinds of methods for correcting excess weight, every pregnant woman needs to make sure that excess weight is caused precisely by the accumulation of adipose tissue, and not by fluid retention in the body.
Factors leading to aggravated medical history during pregnancy
Among the reasons why a woman may be diagnosed with OHA are:
- Socio-biological disadvantage. The absence or insufficient amount of funds to purchase the necessary medicines, vitamins, quality food, clothing and much more often leads the expectant mother to stress, which negatively affects the pregnancy. This group includes women without education and without work (or with low-paid work), leading an immoral lifestyle, as well as pregnant women who are forced to earn money through hard physical labor. In this case, pregnancy most often occurs with pathologies, which poses a threat to the health and life of the unborn child.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions. The environmental conditions in which the expectant mother lives also make a certain contribution to the well-being of pregnancy. The release of harmful substances into the atmosphere from factories and industrial facilities, increased air pollution from vehicles, and poorly purified water negatively affect the quality of life of a pregnant woman, which accordingly leads to a deterioration in the health of the woman and her fetus.
- Diseases in future parents. Genetic diseases, alcohol abuse and smoking, as well as drug addiction of one of the parents can lead to serious problems with the baby’s health. Mother's diseases (asthma, diabetes, heart disease, vascular disease, kidney disease) can cause pathologies in the child.
- Age of the woman in labor. Complications that arise during pregnancy and childbirth are often caused by the too young (under 16 years old) or mature (over 35 years old) age of the first-time mother. This is explained by the physiological characteristics of the female body, which best copes with bearing and giving birth to children between the ages of 18 and 30.
- Complications of the current pregnancy. These include pelvic or transverse presentation of the fetus, infection of the fetus or internal genital organs of the mother, severe toxicosis, gestosis, premature placental abruption.
Most of the factors leading to OGA are controllable. Therefore, future parents are obliged to adequately analyze the situation and plan the pregnancy responsibly.
Late pregnancy is one of the factors leading to OGA
Obesity levels
In medical practice, there are 4 degrees of excess body weight. Moreover, the latter degree is characterized by the formation of so-called morbid obesity, which poses a great danger to human health and life.
- With the development of first-degree obesity during pregnancy, proper body weight increases by 30%, which creates favorable conditions for the formation of developmental pathologies in the fetus. If a pregnant woman notices suspicious weight gain, she is advised to seek medical advice as soon as possible. With a stage 1 increase in body weight, a pregnant woman may experience increased fatigue, shortness of breath when walking and climbing stairs, and also observe excess deposition of adipose tissue in the hips, buttocks and abdomen.
- With grade 2 obesity during pregnancy, the risk of developing characteristic complications is at least 70%. This progressive serious condition leads not only to a deterioration in the well-being of the pregnant woman and fetus, but also to a decrease in the quality of life in general. Being in the second stage, excess body weight begins to respond less and less well to corrective measures. We can talk about the transition of the disease to the second degree provided that the body weight increases from 35 to 50%.
- Stage 3 and 4 obesity is a severe pathological condition in which a pregnant woman’s body weight increases from 50 to 100%, and even more. Such conditions result in severe consequences on the part of the mother and child in 100% of cases. Expectant mothers who have problems with excess body weight, during registration at the antenatal clinic, undergo a laboratory test for glucose tolerance. This laboratory test is designed to detect disorders of carbohydrate metabolism with a view to their further correction.
For example, if a pregnant woman weighs 98 kg and height is 164 cm, then the proper body weight is increased by 54.6%, which is equivalent to grade 3 obesity. If such a situation arises, the expectant mother will need to consult a therapist, endocrinologist and other medical specialists.
Information: what is anemia and why is it dangerous?
Many pregnant women wonder what iron deficiency anemia is and why it is dangerous. Many doctors do not classify anemia as a separate disease, as they believe that anemia occurs as a result of another disease. Most women are diagnosed with anemia during pregnancy.
Human blood consists of:
- Red blood cells;
- platelets;
- Leukocytes.
Each of these cells performs a specific function. Hemoglobin is found in red blood cells, and it is these blood cells that give it its characteristic color. The main function of red blood cells is to saturate internal organs with oxygen and remove carbon dioxide. A low level of red blood cells leads to a drop in hemoglobin.
Anemia is very dangerous for pregnant women and often it begins to manifest itself when the situation becomes critical.
In this case, oxygen starvation and depletion of many organs and tissues are observed. Anemia is a very dangerous condition for a pregnant woman and child, which is why it is necessary to promptly diagnose and treat the existing disease. Important! The treatment method and medications are selected only by the attending doctor, taking into account all available indications and the general condition of the pregnant woman.
Consequences of excess weight in an expectant mother
If a pregnant woman suffers from second-degree obesity, then this condition can pose a serious threat to her condition, as well as to the body of the developing fetus. In addition, excess body weight can cause irreversible consequences for the process of bearing a child. An obese pregnant woman is at potential risk for the following complications:
- Spontaneous cessation of breathing during sleep (apnea). Considering that a developing child puts pressure on the diaphragm, thereby complicating the breathing process, the presence of excess body weight is an additional provoking factor leading to cessation of respiratory activity. This condition is extremely dangerous as it can be fatal;
- Gestational form of diabetes. Excessive accumulation of extra pounds in the body of the expectant mother leads to the formation of diabetes mellitus, which is difficult to correct;
- Post-term pregnancy. Very often, against the background of obesity of the 1st degree and above, women experience an increase in the period of bearing a child;
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary tract. In pregnant women with excess body weight, the risk of developing urogenital infectious and inflammatory diseases, which can cause spontaneous or premature termination of pregnancy, increases significantly;
- Problematic delivery. Often, obesity is an indication for induction of labor. In addition, overweight pregnant women are more likely to require painkillers to ease contractions;
- Preeclampsia. Due to the accumulation of excess adipose tissue in the body, women's blood pressure increases and protein particles are observed in a general urine test. This condition poses a threat to both mother and child;
- Impossibility of natural childbirth. A large number of extra pounds is an obstacle to standard childbirth. For such women, a caesarean section is more often recommended. It is important to consider that obese mothers are at high risk of intraoperative and postoperative scar suppuration. In case of repeated pregnancy, such patients do not have the opportunity to give birth naturally;
- Thrombosis of large vessels. Excess body weight during pregnancy leads to a deterioration in the rheological properties of blood, with the subsequent formation of blood clots in the lumen of blood vessels;
- Large fruit. An increase in the size of the fetus is usually caused by the development of diabetes mellitus in a pregnant woman. If the child’s weight exceeds 4 kg, then such a woman is recommended to undergo surgery such as a cesarean section;
- Frozen pregnancy. Excess body weight is one of the potential causes of intrauterine death of the ovum in early gestation;
- Spontaneous or premature termination of pregnancy.
Another extremely serious complication of obesity during pregnancy is the so-called perinatal mortality. The incidence of this complication in overweight mothers is at least 15%. The main cause of this complication is premature detachment of a normally located placenta. In addition, women with a similar diagnosis often experience postpartum hypotonic bleeding, which is caused by impaired blood clotting ability. Such situations most often affect pregnant women whose synthetic liver function is impaired due to excess body weight. Obese pregnancy itself is a risk. In addition, it is difficult for such women to become pregnant without additional medical care.
what is nzho during pregnancy on ultrasound
Monday is a hard day or the results of a trip to the residential complex
A little information about me: I am 24 years old, I have NEVER been thin, slim or underweight! I feel ideal, at my maximum weight I got pregnant MYSELF (without pills, treatment, etc.) at my maximum weight. Based on hormones, examinations, etc. before pregnancy, I am an IDEALLY healthy woman. But the truth is complete.
Now what I have on my hands and, in general, is the very story of my anger. I had an appointment with my doctor at the LC at 11 weeks with a severe toxicity, after which I was immediately sent to the hospital. There were 3 diagnoses in the referral: VSD of the hypertensive type (questionable), stage 2 VSD (just obesity, which I’m talking about I’ve known him since I was 13). Well, the tox went as the supplement went.
I also do an ultrasound at the Central Research Center with Evstigneeva. On the ultrasound, the doctor says that everything is fine, the placenta is not low (4 cm), that in general everything is fine and go enjoy your pregnancy!
Today is the reception at the residential complex. First: I gained 2 kg in a month. The total gain is 5 kg, but minus 15 from the pre-pregnancy weight (now 21 weeks). The intimidation immediately began: if you give birth prematurely, you will give birth to a sick child, if you give birth at all. You yourself can die. Well, everything like that.
And she gives me a referral to the hospital at the CDC... for a consultation... with the same diagnoses that were taken in the hospital and were not confirmed now by the ECG and Echo!
I left there simply in hysterics... I don’t know why... either resentment or anger. I hate being scared. I hate it when people threaten me with my life or the life of my child. I don’t need to hammer home that I’m terminally ill and that it’s generally strange that I’m still alive...
Now I just don’t understand what to do next... I don’t care, plan to go to her, listen to her insanity? Change doctor in residential complex? Just look for a good paid doctor without signing a contract?
What does ultrasound visualization mean?
if one fetus freezes during a multiple pregnancy Statistics of frozen pregnancies with twins indicate that if one of the twins dies in the first trimester of pregnancy, the outcome Fetal death in the early stages of pregnancy with twins usually ends and
Obstetricians
Source
Tactics for managing pregnancy and childbirth with excess weight
Expectant mothers who are obese need not only specialized medical care, but also constant monitoring of the dynamics of the body's condition. The task of each medical specialist is to monitor the most important indicators of the health of the mother and developing fetus. The practice of managing pregnancy with obesity of varying degrees includes the following points:
- Regular echocardiographic examination of the fetus. In most cases, medical specialists recommend that a pregnant woman undergo an ultrasound examination of the baby’s heart. This type of medical diagnostic manipulation is available for implementation from 20 to 22 weeks of gestation. The purpose of this study is to exclude pathologies of the valvular apparatus of the baby’s heart;
- Performing a rapid test for gestational diabetes. During the period from 24 to 28 weeks of pregnancy, the patient is recommended to perform the so-called oral glucose tolerance test. For some overweight women, screening testing is recommended early in gestation;
- Regular visits to antenatal clinics. Frequent visits to this medical facility have a positive effect on the dynamic assessment of the condition of the mother and developing fetus. If necessary, obese pregnant women are prescribed additional ultrasound examinations to assess the baby's height and weight.
The management of pregnancy and childbirth in obese women directly depends on factors such as the degree of accumulation of extra pounds, the intensity of labor, the presence or absence of concomitant pathologies of the mother and fetus, as well as the nature of the presentation of the child in the pelvis. Based on the data obtained, medical specialists assess the patient’s ability to have a natural birth. If this is not possible, the woman undergoes surgery (caesarean section).
There is a widespread belief among medical specialists that a pregnant woman suffering from varying degrees of obesity should be hospitalized in a hospital 7-14 days before the expected due date.
This measure is caused by the need to implement measures aimed at preventing labor weakness and post-term pregnancy. Such support improves energy processes in the muscular lining of the uterus, thereby increasing the biopotential for physiological contraction.
To achieve a similar result, a 10% calcium chloride solution, estrogens, ascorbic acid and 40% glucose solution are used. If an obese woman in labor does not have indications for a cesarean section, then during labor she is recommended to administer painkillers and antispasmodics as often as possible. If there is a problem of weak labor, then along with drugs such as Oxytocin, the patient is administered Hydrocortisone and Insulin in small doses.
To achieve acid-base balance in the body and prevent pathological acidosis, medical specialists inject 5% sodium bicarbonate solution. In addition, drug prevention of intraoperative and postoperative bleeding is a prerequisite.
FGR 1st degree during pregnancy: methods of determination
Diagnosis of FGR has several objectives:
- determine the severity and type of delay;
- assess the state of placental blood flow;
- find the cause of the pathology.
To begin with, the pregnant woman undergoes a so-called external obstetric examination, during which the circumference of the abdomen and the height of the uterine fundus are measured. Next, the woman will undergo the following procedures:
- Ultrasound examination of a child's place. The method allows you to understand whether the placenta is mature enough, evaluate its qualitative parameters, location in the uterus, and detect areas of damage, if any. Ultrasound is often supplemented with Dopplerography of the uteroplacental blood flow to identify foci of disturbances and areas of infarction in the vascular bed.
- Fetal fetometry. During the ultrasound examination, the head, abdomen, chest, biparietal and fronto-occipital indicators of the head, and the length of the tubular bones of the fetus are measured. All measurements are analyzed in terms of standard indicators for each week of gestation.
- Fetal phonocardiography and cardiotocography . Thanks to these methods, it is possible to indirectly assess the quality of the blood supply to the fetus by analyzing the indicators of its cardiac activity. Arrhythmia, tachycardia and other variants of a child’s heart rhythm disturbance indicate fetoplacental insufficiency.
A general assessment of the results of ultrasound and cardiotocography allows us to draw up a biophysical “portrait” of the baby:
- adequacy of motor activity;
- quality of muscle tone;
- regularity of breathing movements;
- volume of amniotic fluid;
- maturity of a child's place.
A final score of 6-7 points indicates an unsatisfactory condition of the fetus, and a score of 4-5 indicates severe intrauterine hypoxia.
To find out the cause of FGR, as additional measures, the expectant mother is prescribed laboratory tests, which determine the amount of hemoglobin, red blood cells, hormones (for example, hCG, progesterone), and infectious agents. Methods of invasive prenatal diagnostics (amnioscopy, amniocentesis, cordocentesis) make it possible to detect various genetic abnormalities, structural and functional disorders of the fetal membranes.
Treatment
Complex therapy for obesity during pregnancy consists of increasing the mobilization of fats from the so-called depots, as well as reducing the energy value of consumed foods. The practice of so-called therapeutic fasting is strictly prohibited during pregnancy, since these experiments lead to a deterioration in the general condition of the mother, the development of iron deficiency anemia, and the formation of fetal developmental abnormalities. Regardless of the degree of accumulation of extra pounds in a pregnant woman’s body, her diet should contain fermented milk products, chicken eggs, meat and fish. These food products have a supply of essential microelements that ensure the harmonious development and growth of the unborn child.
The key points of a healthy diet for obesity are rationality and balance. Meals should be taken in small portions 5-6 times a day. Following the correct dietary recommendations will allow you to restore impaired metabolic processes, as well as create a negative energy balance. The primary task for the expectant mother is to limit calories by reducing the consumption of carbohydrate foods. The optimal amount of calories for a pregnant woman is up to 2500 kcal. The carbohydrate component should be compensated by eating foods such as fresh berries, vegetables, wholemeal bread, and fruits (with the exception of highly allergenic ones). Restrictions include confectionery, berry and fruit jams, honey and fresh baked goods. Although overweight pregnant women need to limit carbohydrates, a sharp reduction in the amount of carbohydrate foods consumed can lead to the transformation of proteins into carbohydrate compounds. Such a process will not benefit the body of the expectant mother.
The fatty component of the diet should be compensated by consuming butter and vegetable oils. Products such as margarine, spreads, beef and pork fat should be completely excluded from the diet.
In addition, a pregnant woman’s body must receive the required amount of proteins, since these elements are not only building materials for the whole body, but are also a structural part of hemoglobin. Protein deficiency in the body is one of the main causes of anemia during pregnancy. It is recommended to get the protein component from products such as whole milk, low-fat fish and meat, as well as chicken or quail eggs. Particular attention should be paid to the amount of table salt consumed. Its excess leads to excessive accumulation of fluid in the body, with a subsequent increase in body weight. The daily allowable amount of salt is no more than 5 g.
If the expectant mother follows a balanced diet, her weight gain during the second half of pregnancy does not exceed 300 g every 7 days. For an expectant mother with excess body weight, so-called fasting days are useful, which include the consumption of fermented milk products, fruits and fruit juices. The frequency of fasting days should be no more than once every 7 days. During this day, it is permissible to consume no more than 600 g of low-fat cottage cheese, 1-2 glasses of low-fat kefir and tea without sugar. Eating fresh and baked apples without added sugar is beneficial.
In addition to the above-mentioned dietary recommendations, an obese pregnant woman is recommended to perform therapeutic exercises, the purpose of which is to activate metabolic processes in the body and increase fat utilization. The selection of appropriate exercises and their frequency is carried out on an individual basis, taking into account the advanced state of the pathological process and the presence of concomitant diseases in the pregnant woman. During complex therapy for obesity, every expectant mother is recommended to constantly monitor blood glucose levels.
Stage 1 FGR during pregnancy: treatment features
When determining treatment tactics, the doctor takes into account not only the degree of developmental delay, but also the severity of placental insufficiency and the general condition of the fetus.
Typically, an expectant mother with diagnosed FGR is prescribed:
- medicines that stimulate the child's blood supply. Improving blood flow in the mother-placenta-fetus ligament is achieved thanks to the therapeutic effect of angioprotectors and agents that affect the rheological properties of blood. In addition to these drugs, tocolytics are prescribed to reduce uterine tone and activate blood flow in the vascular bed;
- drugs with antihypoxic and membrane-stabilizing effects . Thanks to the action of actovegin, instenon, antioxidants and membrane stabilizers, the fetus can more easily tolerate a lack of oxygen. General strengthening agents are always added to the therapy program to stimulate plastic processes.
Treatment is always accompanied by weekly monitoring of fetal fetal parameters, Doppler blood flow in the placenta (once every 4-5 days) and daily assessment of the fetus’s well-being using CTG.
Timely treatment for stage 1 FGR due to compensated fetoplacental insufficiency with a satisfactory rate of fetal “ripening” allows you to extend pregnancy until 37-38 weeks (i.e., until the lung tissue is fully functional). If the process of fetal development could not be established within 10-14 days or its condition has worsened (for example, disturbances in cardiac activity have appeared), the expectant mother will have an early birth, regardless of the stage of pregnancy.
In case of grade 2 and 3 FGR with decompensation of fetoplacental insufficiency, in most cases a decision is made on emergency delivery by cesarean section.
If the pathology was detected immediately after its appearance, the prognosis for treatment is favorable. This is greatly facilitated by the correct tactics of treatment and management of pregnancy, the good health of the expectant mother, and the absence of gross deviations in the development of the fetus itself.
Prevention
If the expectant mother does not want to face the problem of obesity, then she is advised to follow simple rules that are aimed at maintaining metabolic processes in the body. These rules include:
- In the case of a hereditary predisposition to gaining excess body weight, every pregnant woman is recommended to follow a rational and balanced diet. This diet involves eating fresh fruits and vegetables, as well as limiting pasta, bakery and confectionery products. In addition, meals should be divided into 5-6 times;
- Therapeutic gymnastics classes selected by the attending physician on an individual basis;
- Timely medical registration in the antenatal clinic. This procedure must be implemented before the 12th week of gestation;
- Constant observation by a specialist obstetrician-gynecologist;
- Introduction of a categorical ban on the consumption of alcoholic beverages and smoking.
Treatment of FGR
Treatment for FGR is prescribed by a doctor based on the severity of FGR and the reasons that caused it. Most often, treatment for FGR includes:
— treatment of chronic diseases of a pregnant woman and treatment of infections, correction of hemostasiogram;
- treatment aimed at normalizing the uteroplacental blood flow system. To do this, the doctor prescribes drugs that improve uteroplacental blood flow (Actovegin, Kurantil), and also have a relaxing effect on the muscles of the uterus (Ginipral, No-Spa).
During treatment, it is mandatory to monitor the baby’s condition in order to assess the effectiveness of the therapy:
- ultrasound examination (fetometry). It is carried out every 7–14 days to take measurements and assess the baby’s growth rate;
- Doppler examination. Performed every three to five days to monitor uteroplacental blood flow;
— cardiotocography. It is carried out every other day or daily to assess the state of the child’s cardiovascular system.
To assess the effectiveness of therapy, data from all three diagnostic methods in combination are required.
Based on these results, the doctor makes a decision about continuing the pregnancy or the need for urgent delivery, as well as about the method of delivery itself (naturally or surgically).
What should the expectant mother do to increase the effectiveness of treatment?
- try not to worry, as emotional tension and stress only harm the baby;
- eat well, rest, sleep;
- be more outdoors;
- Follow doctors’ recommendations for taking medications and diagnostic procedures.
Narrow pelvis and pregnancy
Anatomically narrow pelvis of 1-2 degrees in a woman has practically no effect on the course of pregnancy and the intrauterine development of the child. Data from numerous medical studies have revealed only minor features of the course of pregnancy in such patients:
- The gestation period in 90% of cases is 39 weeks . Post-term pregnancy is extremely rare;
- The frequency of pregnancy complications is 75-80% , which is associated with an increase in the number of hormonal and extragenital pathologies in such pregnant women;
- Much more often, pregnant patients with a narrow pelvis suffer from symphysiopathy and sacroileopathy - excessive mobility and relaxation of the bones and joints of the pelvis, accompanied by pain and gait disturbances;
- The shape of the abdomen in primiparous pregnant women with a narrowing of the pelvis is pointed , in multiparous women it is drooping;
- Often pregnancy is complicated by premature release of water and abnormal position of the fetus (pelvic, oblique and transverse presentation), associated with an unusually high position of the fetal head before birth;
- Pathological shortness of breath in the third trimester is also caused by the fetus being too high in the mother’s abdomen.
The algorithm for managing pregnancy in a patient with a narrow pelvis involves the following mandatory measures:
- The method of delivery should be determined taking into account the degree of pelvic narrowing and the expected height and weight parameters of the infant. In most cases, doctors prefer to perform a caesarean section.
- Since women with a narrow pelvis often do not carry their pregnancy to term until 40 weeks, such a young lady must be hospitalized in the maternity hospital a couple of weeks before the expected birth.
How to determine
From the point of view of an obstetrician, a narrow pelvis and a fragile physique of a female figure are not the same thing . Sometimes a wide-hipped pregnant lady is surprised to learn from her doctor that she has a narrow pelvis. And vice versa, a thin and narrow-hipped girl in appearance has anatomically normal pelvic parameters.
It is impossible to diagnose a narrowing of the pelvic bones in a pregnant woman based only on external signs. Therefore, obstetricians-gynecologists determine this pathology based on the following diagnostic measures:
Visual inspection
The doctor studies the woman’s constitution as a whole and conducts a survey to identify risk factors for the presence of pelvic narrowing. Indirect signs of this pathology are:
Height is less than 160 cm;
- Foot size less than 36;
- The length of the index finger on the hand is less than 8 cm, and the length of the entire hand is less than 16 cm;
- Hip circumference less than 85 cm;
- Injuries and fractures of the pelvic bones;
- Late development of menstrual function, delayed puberty;
- Androgenic signs: narrow hips, lack of expression of secondary sexual characteristics, excess hair growth.
Feeling and external measurement of the distance between the pelvic bones
For external manual measurement, a special device is used - a compass-like pelvisometer , with which the approximate parameters of the female pelvis are measured.
External measurements of the pelvic bones provide only an approximate idea of the size of the small pelvis. To clarify the data obtained, you need to measure your wrist circumference.
If the wrist is less than 14 cm, then the woman’s bones are thin, which means a slight decrease in the parameters of the pelvis is allowed. If the wrist girth is more than 14 cm, this is a sign of massive bones, including the pelvic bones. In this case, pelvic narrowing is diagnosed even if its dimensions correspond to the lower limit of standard indicators.
Gynecological examination and measurement of the small pelvis from the inside
The internal measurement of the so-called true conjugate - the segment between the pubis and the sacrum - gives the most accurate idea of the size of the pregnant woman's pelvis.
Instrumental research methods
Examination of pelvic dimensions using ultrasound and radiography is rarely used in obstetric practice..
These diagnostic procedures are theoretically unsafe for the fetus - and therefore they are used only in cases where the most accurate determination of the degree of pelvic narrowing is vital for the mother and her unborn child.
The results obtained, indicating the type and degree of pelvic narrowing, are entered into the pregnant woman’s exchange card.