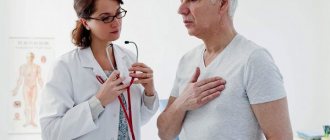
In modern medical practice, shortness of breath is a feeling of lack of air associated with a violation of the breathing rhythm. When our body lacks oxygen, it increases the frequency and rhythm of breathing, thereby eliminating its deficiency.
Depending on the various causes and factors that cause difficulty breathing, there are several types of shortness of breath, which, in turn, are divided into subtypes.
Types of shortness of breath:
- Due to the occurrence:
- Physiological – is the body’s natural reaction to physical or mental activity. It may occur when breathing adapts to certain conditions (with an increase in atmospheric pressure);
- Pathological - occurs as a result of disruption of the body by diseases (pneumonia, bronchitis, heart failure, myocardial infarction, hysteria) or poisons.
- By clinic:
- Objective – can be determined using a medical examination.
- Subjective - based on the patient’s sensations without changing the rhythm and frequency of breathing and is in no way confirmed by a medical examination. The occurrence of such shortness of breath can be observed in mental illness.
- Mixed – confirmed by objective studies and the patient’s feelings. Most diseases are accompanied by this type of shortness of breath.
- Depending on the respiratory phase disorder:
- Inspiratory dyspnea - occurs due to difficulty in inhaling (the cause may be a narrowing of the lumen of the larynx or a tumor of the trachea).
- Expiratory shortness of breath - occurs due to difficulty in exhalation (the cause may be sputum in the lumen of the bronchi or bronchospasm).
- Mixed shortness of breath - when breathing becomes difficult, both when inhaling and when exhaling (shortness of breath with pneumonia).
What is expiratory dyspnea?
As mentioned above, expiratory dyspnea is difficulty in exhaling during respiratory activity.
There are several degrees of severity of shortness of breath:
- Mild degree - occurs during long walking.
- Medium degree - the pace of walking slows down, it becomes necessary to stop to normalize breathing.
- Severe – stopping while walking becomes more frequent, every 5-10 minutes. Breathing is noisy and heavy.
- Very severe degree - difficulty in exhaling occurs even at rest, active movements are impossible due to increasing suffocation.
What diseases cause inspiratory dyspnea?
IO accompanies many DS diseases:
- pneumoconiosis;
- pneumonia;
- laryngotracheitis;
- ARVI.
Dyspnea manifests itself as a symptom:
- heart failure;
- myocardial infarction.
Chest injuries, severe intoxication, and pulmonary thromboembolism are accompanied by difficulty in breathing. With osteochondrosis, respiratory dysfunction occurs due to compression of blood vessels and nerve endings.
Causes
There are quite a lot of diseases, the symptom of which is expiratory shortness of breath. Most often these are diseases of the respiratory system (bronchial asthma, pneumosclerosis).
Let's consider the main ones:
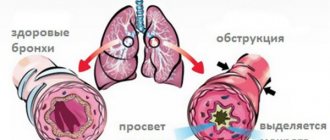
- Obstructive bronchitis . Due to inflammation of the small bronchi, their spasm develops and ventilation in the lungs is disrupted. This causes difficulty in exhaling.
- Bronchial asthma . Difficulty in exhalation develops due to chronic inflammatory processes in the lung tissue. Because of them, tissue hyperactivity occurs, which leads to the fact that upon contact with allergens or dust, bronchial obstruction begins and, as a result, shortness of breath and a feeling of suffocation develop. But shortness of breath in bronchial asthma is not constant, but appears only during attacks.
- Emphysema . In this case, difficulty in exhaling occurs due to the fact that the air space in the lungs increases.
- Pneumosclerosis of the lungs. Expiratory shortness of breath occurs in response to the replacement of pulmonary connective tissue. The elasticity of the lung decreases, and respiratory dysfunction begins. This disease is caused by various inflammatory diseases in the lungs.
- Tumors of the lungs or mediastinum can also cause expiratory dyspnea. They compress the bronchi and cause breathing problems.
- A foreign body in the bronchi or trachea leads to their blockage, and as a result, breathing problems. In these conditions, not only exhalation is difficult, but also inhalation.
- Poisoning by carbon monoxide , salts of heavy metals or fumes of poisons. Shortness of breath occurs in response to inhibition of respiratory function by these substances.
Kinds
Breathing disorder can occur in the presence of many diseases. There are three types of shortness of breath.
- Inspiratory. The problem occurs when inhaling. Most often, this symptom appears with heart failure and damage to the upper respiratory tract. Bronchial spasms, accumulation of secretions, tumors compressing the airways, swelling of the mucous membrane - all this is the cause of inspiratory dyspnea.
- Expiratory dyspnea. Characterized by slow exhalation with a slight whistle. It is diagnosed during swelling of the mucous membrane, the appearance and accumulation of secretions or other obstructions in the bronchi. The patency of the bronchi worsens, which causes shortness of breath.
- Mixed. This type of dyspnea is quite common. It appears in acute stage cardiac and respiratory failure, and in advanced lung pathology.
As you can see, inspiratory and expiratory shortness of breath are caused by different reasons. That is why the treatment should also be different.
Symptoms
It often happens that a person cannot immediately diagnose incipient shortness of breath. Problems associated with difficulty in exhaling can be associated with physical exertion or nervous tension.
Meanwhile, the pathology that causes breathing problems develops further and the patient’s condition worsens significantly.
Do not neglect such a symptom as shortness of breath. Contact a specialist if you have any doubts.
What symptoms are accompanied by expiratory shortness of breath?
What is characteristic of expiratory dyspnea:
- The very first symptom will be a significant prolongation of exhalation . The patient may notice that the exhalation has become 1.5-2 times longer than the inhalation.
- During auscultation (listening to the chest), crepitus and dry wheezing during exhalation . With severe shortness of breath, these wheezes can be heard at a distance.
- Respiratory failure such as expiratory shortness of breath may be accompanied by painful sensations during breathing movements .
- It is possible to develop cyanosis of the lips and nose, acrocyanosis , and general pallor of the skin.
- If the cause of expiratory shortness of breath is bronchial asthma, then a feeling of lack of air occurs some time after contact with an allergenic substance or object. With long-term asthma, a boxy sound in the lungs during shortness of breath.
- The pressure inside the chest cavity changes, as a result of which, when exhaling, the intercostal spaces protrude forward .
If, with frequent shortness of breath, you observe at least a few of these symptoms, then this is a serious reason to consult a specialist. You may be developing pulmonary pathology.
Classification of shortness of breath
There are many factors that provoke bronchial asthma. This can be due to an allergen entering the human body, too intense physical activity, or severe stress.
Very often an asthma attack is accompanied by shortness of breath. However, it can also occur in a state of remission, when other manifestations of the disease are absent. In this case, the patient is prescribed special treatment, the nature of which is determined based on the type of disorder.
The following forms of shortness of breath are distinguished:
- Inspiratory dyspnea. In this case, bronchial asthma is not always diagnosed. Such shortness of breath can occur due to swelling or swelling of the larynx and trachea, as well as when a foreign object enters the respiratory tract. In this case, the patient has difficulty breathing, which is not typical for asthma. However, only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis.
- Expiratory dyspnea. It is with shortness of breath of this type that the doctor preliminarily diagnoses bronchial asthma. It occurs when there is a significant narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi, which is typical for this pathology. Depending on the duration of shortness of breath, several subtypes are distinguished:
- temporary. Most often it occurs in a patient diagnosed with acute lobar pneumonia. It is typical for cases when the inflammatory process affects a large area of the lung. In this case, the affected area does not participate in breathing, which is dangerous for the patient’s life;
- constant. Observed in chronic lung diseases, for example, emphysema;
- obstructive. This disorder is associated with problems that occur when air enters the lungs. This type of shortness of breath can bother the patient even at rest. In this case, exhalation is difficult, which corresponds to the symptoms of bronchial asthma.
- Mixed. With this type of breathing disorder, it is difficult for the patient to both inhale and exhale.
It is important to remember that, in addition to bronchial asthma, shortness of breath can also occur with other pathologies, for example, with heart disease. You cannot diagnose yourself and prescribe treatment on your own. Only a doctor can do this.
Diagnostics
In order to diagnose expiratory shortness of breath, you need to see a doctor. Get examined by a therapist and possibly a cardiologist.
So, what methods are used to diagnose the development of expiratory dyspnea:
- Examination by a doctor . Some patients have such severe shortness of breath that the doctor can hear it from a distance and determine its frequency, rhythm and tempo.
- During auscultation, the specialist will hear dry wheezing (with the onset of an attack of bronchial asthma);
- Percussion detects a box sound in the chest cavity.
- Carrying out an ECG (if there is a suspicion that breathing problems occurred against the background of cardiovascular pathology);
- An x-ray helps determine the disease that caused shortness of breath (for example, pneumonia).
- If you determine the vital capacity of the lungs (VC), you can find out the degree of bronchial obstruction.
- An increase in body temperature against the background of expiratory shortness of breath indicates the development of obstructive bronchitis.
- For more information, your doctor may order a blood gas test.
All these methods together will help to obtain the most accurate data and identify the nature of shortness of breath, what pathology is causing it and what methods should be used to eliminate it.
Causes, symptoms and treatment of expiratory and inspiratory dyspnea
The reasons for the development of inspiratory dyspnea may be the following:
- Loss of lung tissue of its normal elasticity. A similar situation is observed with pneumosclerosis, fibrosis, and pleurisy of the lungs.
- Lung cancer can provoke the occurrence of inspiratory shortness of breath.
- Inspiratory dyspnea often plagues patients with advanced tuberculosis.
- Coarse pleural deposits and carcinomatosis can provoke the appearance of inspiratory dyspnea.
- Sometimes inspiratory dyspnea occurs in pregnant women. This pathological symptom is explained by the high position of the diaphragm.
- If a foreign body enters the respiratory tract, a person will develop inspiratory dyspnea.
- A tumor of the larynx is another cause of difficulty breathing.
- Laryngeal stenosis and swelling of the vocal cords is characterized by the appearance of inspiratory dyspnea. It often bothers children under one year old, which is due to the structural features of their throat. The lumen of the respiratory tract in children is narrower than in an adult. When pathogenic flora gets on the tonsils and larynx, edema develops faster in babies. This condition is called laryngitis.
Older people say that the first sign of aging is shortness of breath. You can agree with this opinion, but not completely. Sometimes this feeling is a sign of a serious illness, which is diagnosed in young people too. In the article we will talk about what expiratory shortness of breath is. But first, let’s find out what types of dyspnea exist.
Breathing disorder can occur in the presence of many diseases. There are three types of shortness of breath.
- Inspiratory. The problem occurs when inhaling. Most often, this symptom appears with heart failure and damage to the upper respiratory tract. Bronchial spasms, accumulation of secretions, tumors compressing the airways, swelling of the mucous membrane - all this is the cause of inspiratory dyspnea.
- Expiratory dyspnea. Characterized by slow exhalation with a slight whistle. It is diagnosed during swelling of the mucous membrane, the appearance and accumulation of secretions or other obstructions in the bronchi. The patency of the bronchi worsens, which causes shortness of breath.
- Mixed. This type of dyspnea is quite common. It appears in the cardiac, acute stage, with advanced lung pathology.
As you can see, inspiratory and expiratory shortness of breath are caused by different reasons. That is why the treatment should also be different.
Dyspnea degrees
There is not just one cause of expiratory shortness of breath; there are many factors that cause this disease. Let's talk about them now.
- Iron deficiency in the blood, anemia. Most often found in women.
- Excess weight.
- Blockage of the pulmonary artery by a blood clot.
- Insufficient oxygen supply to the heart muscle.
- Disruption of the left side of the heart and stagnation of blood in the pulmonary veins.
- Disruption of the functioning of large bronchi and tracheal membranes.
- Bronchial asthma.
In addition, expiratory shortness of breath can be caused by the entry of a foreign body into the bronchi.
Now let's talk about some of the reasons in more detail. Depending on the existing pathology, the problem may be caused by the following factors.
- Disturbance in the trunks of the respiratory department. Usually occurs with an overdose of sleeping pills, anesthetics, or drugs. The frequency and depth of breathing changes.
- Bronchial obstruction. The functioning of the bronchi deteriorates due to the fact that the elasticity of the tissue inside the lungs changes. Diseases that cause dyspnea for this reason: asthma, foreign body entry into the bronchial aorta, bronchopulmonary cancer, bronchial inflammation. Expiratory shortness of breath in asthma is expressed in the form of sudden attacks. This symptom applies to all diseases caused by bronchial obstruction.
More about the reasons
In addition to the above factors that cause the disease, the following can also be mentioned:
- Thoracic-diaphragmatic disorders of the thoracic aorta. Due to the large accumulation of fluid in the chest, spinal deformation occurs.
- Disruption of the cardiovascular system. Signs of expiratory shortness of breath occur with slow blood circulation in the small stomach and dysfunction of the left ventricular part of the brain, and as a consequence of such diseases: hypertension, coronary heart disease and others.
- Change in the amount of pH in the blood. The disease appears when there are disorders of the liver, kidneys, or problems with the endocrine system. In patients, the frequency and depth of breathing changes, appetite disappears, and the skin acquires a yellowish tint.
To summarize, there are four main causes of the disease:
- Heart failure.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Respiratory system dysfunction.
At the initial stage of the disease, no obvious symptoms are observed. But you should always pay attention to the slightest changes in breathing.
- One of the main points that indicates the presence of expiratory shortness of breath is the length of the exhalation. It increases, sometimes it can exceed twice the inhalation.
- Exhalation is accompanied by muscle tension.
- Intrathoracic pressure changes, protrusion and collapse of the spaces between the ribs occurs.
- As you exhale, the veins in your neck are visible.
In bronchial asthma, expiratory dyspnea is characterized by the presence of a box sound, which occurs due to the accumulation of excess air and limited movement of the diaphragm.
In addition, symptoms of dyspnea include:
- When exhaling there is a crunching sound or whistling sound.
- The person leans forward unnaturally.
- The patient often holds his throat or chest.
- The skin becomes paler.
- General weakness.
- Additional muscles are involved in the breathing process.
Diagnostics
In order for treatment to be prescribed on time, a correct diagnosis must be made. At the first symptoms of the disease, you should immediately consult a doctor. A complete examination of the patient will be carried out.
- The specialist examines the patient. If shortness of breath is severe, the doctor can determine its frequency, pace and rhythm.
- Listening. During an attack of bronchial asthma, dry wheezing is heard.
- Tapping will help detect box sounds in the chest.
- A chest x-ray is used to determine the disease causing expiratory shortness of breath.
- Electrocardiography is performed if a disorder of the cardiovascular system is suspected.
- Echocardiography.
- The degree of narrowing of the bronchi is determined.
- Body temperature is measured. An elevated level indicates the development of obstructive bronchitis.
- Additional examination includes blood gas analysis.
If there is a person next to you who is suffering from expiratory shortness of breath, then you need to know how to help him. We hope that these tips will tell you what to do.
- Place the patient in a seat.
- Try to calm him down. It's no secret that stress, excitement, and anxiety lead to an increase in heart rate. In this regard, the consumption of oxygen and nutrients becomes greater, and the person’s condition worsens.
- Well ventilate the room where the patient is.
- Be sure to control air humidity. If it is dry, then put a pan of water on the fire. Do not cover it with a lid. There is another way to make the air in the room more humid - hanging wet towels and sheets.
People who often suffer from bronchial asthma must have an inhaler. You need to make sure that it is filled. Having alleviated the patient’s condition, immediately call an ambulance.
Treatment
Getting rid of the problem should be started only after the reasons for its occurrence have been clarified and the doctor has outlined an action plan, where the first place is to relieve the symptoms of the disease.
Complex treatment includes:
- Use of inhalers. Thanks to them, you can quickly restore normal breathing. Only with the correct selection of bronchomimetics can you not only stop an attack, but also reduce the frequency of their occurrence.
- Therapy aimed at reducing the patient's sensitivity to allergens.
- Medicines that act throughout the day and include glucocorticoids with beta-2 antagonists.
- Oxygen treatment. To relieve severe attacks, opioids are used.
- a special diet and frequent walks in the fresh air.
For bronchitis, mucolytic drugs are used; for bacterial infections, antibiotics are used.
Do not give up folk remedies, but only in combination with traditional medicine and after consultation with a specialist.
Expiratory and inspiratory dyspnea is a disease that can cause many problems. In order to avoid frequent attacks, try to follow these rules:
- stop smoking;
- avoid rooms with a lot of tobacco smoke;
- try to reduce contact with allergens;
- harden yourself and take vitamin therapy;
- give preference to proper nutrition;
- monitor dyspnea.
In medicine, dyspnea is a disordered breathing rhythm. Usually shortness of breath appears unexpectedly and is characterized by difficulty breathing, darkening of the eyes and the threat of suffocation. Shortness of breath is not a disease - it is only a symptom of a more serious disease.
The appearance of difficulty breathing indicates the presence of diseases such as pathologies of the cardiovascular system, blood circulation, problems with the lungs and respiratory tract.
If threatening signs of shortness of breath appear, you should immediately consult a doctor to identify the causes of the disease.
Shortness of breath or dyspnea in medical terminology is a violation of the respiratory rhythm towards faster or slower. In medicine, there are three types of dyspnea:
- Inspiratory. Heavy breath. Difficulty in passing air through the upper parts of the lungs. A sign of inspiratory dyspnea is frequent inhalations when talking or speaking in public.
- Expiratory. Difficulty breathing. Narrowing or blockage of the lower parts of the lungs.
- Mixed. Both inhalation and exhalation are difficult. The respiratory surface of the lungs is reduced.
There are five degrees of severity of shortness of breath:
- 0 — shortness of breath appears with increased physical activity;
- 1 - difficulty breathing occurs after fast walking or climbing stairs;
- 2 — dyspnea begins due to minor exertion;
- 3 - a person needs rest even with minimal exertion;
- 4 - shortness of breath occurs at rest.
The fourth stage indicates the presence of a serious disease that requires careful examination.
Symptoms of dyspnea
Treatment
Treatment should always be selected by a specialist. The use of any means and medications without medical advice is undesirable, since their use can only aggravate the situation.
Here are the methods and medications your doctor may prescribe to treat shortness of breath:
- If expiratory shortness of breath occurs against the background of a spasm, it is worth using antispasmodic drugs , namely bronchodilators. They will relieve bronchospasm and make breathing easier.
- For bronchial asthma for
To prevent attacks, inhalers with salbutamol and aminophylline solution are used intravenously. - If the cause of shortness of breath is an allergen, then the use of antihistamines .
- The doctor may prescribe breathing exercises , which will improve blood supply to the muscles of the chest, as a result of which they will better cope with respiratory function.
- Symptomatic therapy is used to relieve an attack of shortness of breath.
- The main thing in the treatment of expiratory dyspnea will be the treatment of the underlying disease that led to the development of respiratory failure.
- For obstructive bronchitis, the doctor will prescribe the patient medicinal inhalations , bed rest and a minimum of physical activity.
- For shortness of breath due to pneumonia, it would be appropriate to prescribe antibiotic therapy .
- If necessary, it is possible to prescribe hormonal drugs . Do not be afraid of hormones and neglect this type of treatment. The doctor will prescribe adequate medications and doses, and refusal of treatment may worsen the condition.
Prevention
To prevent the development of expiratory dyspnea, the following recommendations must be followed:
Stop smoking.
Treat chronic infections promptly.
If you have an allergy, you need to identify the allergen and direct efforts to minimize contact with it.
Lead a healthy lifestyle.
Monitor your body weight. All diseases will be more severe in obese people.
Expiratory shortness of breath can develop with serious pathologies. It rarely occurs in healthy people, so if such a symptom appears, you should consult a doctor.
Education: Diploma in Cardiology received from Perm State Medical University named after. I. M. Sechenova (2015). Here I completed my postgraduate studies and received a diploma in Cardiology.
7 mistakes that cause the tonometer to overestimate blood pressure readings
Flax seeds - what do they cure and why does everyone eat them?
Shortness of breath is a feeling of lack of air, accompanied by pressure in the chest and increased breathing. A person with shortness of breath tries to take a deep breath. Shortness of breath can be acute or chronic. This condition is also called dyspnea. Normally, when a person is resting, he does not pay attention to his breathing. As it increases.
Heart failure is a series of disorders that are based on low contractility of the heart muscle. There is a misconception that heart failure is a heart disease, but it is not. Heart failure is a condition of the body in which contractility.
Asthma is a chronic disease, the basis of this disease is non-infectious inflammation in the airways. The development of bronchial asthma is promoted by both external and internal irritant factors. A number of external factors include various.
Myocardial infarction is a focus of ischemic necrosis of the heart muscle, which is formed due to an acute violation of the coronary circulation. This condition is a direct threat to life, and therefore requires emergency hospitalization of the person in the intensive care unit of the cardiology department.
Shortness of breath is a protective reaction of the body aimed at normalizing the gas composition of the blood. According to the definition of clinicians and pathophysiologists, shortness of breath is a condition that is characterized by a severe subjective feeling of lack of air against the background of disturbances in the frequency, rhythm, depth of respiratory movements, and the duration of inhalation or exhalation. The Yusupov Hospital has created all the conditions for the treatment of patients who have inspiratory dyspnea:
- Chambers with European level of comfort;
- The latest diagnostic equipment, which allows you to determine the type and severity of shortness of breath, identify diseases that have led to impaired respiratory function;
- The use of modern drugs that are highly effective and have a minimal range of side effects is registered in the Russian Federation;
- Attentive attitude of the staff to the wishes of patients and their relatives.
Severe cases of diseases manifested by inspiratory dyspnea are discussed at a meeting of the Expert Council. Professors, doctors of medical sciences, and doctors of the highest category take part in its work. Patients of the therapy clinic are advised by pulmonologists and cardiologists. With severe inspiratory dyspnea, patients are transferred to the intensive care unit, which is equipped with expert-class breathing equipment.
Preventing shortness of breath
As you know, it is better to carry out high-quality prevention of shortness of breath and the diseases that cause it than to fight it for the rest of your life. By following the recommendations below, you can prevent those ailments that cause difficulty breathing.
Here are the methods by which you will ensure yourself a life without shortness of breath:
- Firstly, if you smoke, then get rid of this bad habit. Smoking affects our lungs and bronchi, disrupting not only the respiratory system, but also all other systems of our body.
- Secondly , exercise. Skip the elevator, go one stop from the place you need, walk in the fresh air for at least half an hour every day.
- Adjust your weight. Everyone knows that excess weight is an additional burden on the heart and blood vessels.
Don't overexert your heart if you want to avoid shortness of breath. If you are overweight, then go in for sports and start eating right. A combination of physical activity and weight loss will help ensure that shortness of breath will stop bothering you. - Consult with specialists in a timely manner regarding alarming symptoms and conditions. Don't ignore your body's warning signs.
- Treat the underlying condition that is causing the shortness of breath.
- and salt caves will be useful The air there has amazing purity and healing properties.
- Every year it is worth visiting specialists , taking tests and doing fluorography. This will help to identify diseases that cause breathing problems in a timely manner.
- Avoid nervous tension and mental shock.
- Ask your doctor to prescribe you a course of breathing exercises if you feel it is necessary.
Types and symptoms of difficulty breathing
Normally, the frequency of inhalations and exhalations is 14-15 times per minute. Dyspnea is a condition in which the respiratory rate (RR) increases to 18 or more, and breathing itself becomes heavy and harsh. This happens for a number of reasons, which are based on insufficient oxygen supply to the blood. A healthy body can also experience hypoxia - for example, against the background of physical activity, the need for oxygen in muscle tissue increases significantly, heart rate and breathing increase. Physiological shortness of breath (in a healthy person) differs from pathological shortness of breath (in a patient) in that it always has a visible cause and goes away fairly quickly. If problems occur during sleep, at rest or with light exertion, dyspnea is a symptom of the disease.
Doctors distinguish several types of shortness of breath depending on how difficult it is to breathe:
- Inspiratory - difficulty breathing.
- Expiratory - difficulty in exhaling.
- Mixed type.
Shortness of breath is often accompanied by other symptoms indicating a lack of oxygen. So, against the background of heavy breathing, the following may be observed:
- Fatigue.
- Dizziness.
- Darkening in the eyes.
- Discomfort in the chest area.
Emergency assistance for a sudden attack of shortness of breath
All measures will be aimed at maintaining the patient’s condition until the ambulance arrives:
- Have the person sit on a hard surface;
- Calm him down, as an attack of shortness of breath is accompanied by panic and fear of death;
- Unbutton the shirt collar and remove tight clothing from the patient;
- Indoors, open the windows and let in fresh air;
- If possible, increase the humidity in the room. You can hang wet rags and towels on the radiators and use a spray bottle to humidify the air.
- The room in which the person is located must be warm. Warm the patient if possible with heating pads or blankets.
- Call an ambulance.
All these measures will help improve the condition of a person with a sudden attack of shortness of breath and will help him hold out until qualified medical care begins.
Shortness of breath due to heart disease
The second most common cause of dyspnea is heart disease. In this case, hypoxia occurs not because the blood is not sufficiently saturated with oxygen in the lungs, but because the myocardium cannot cope with its functions, and hemodynamics are disrupted. Most often, shortness of breath occurs due to the following heart diseases:
- Arrhythmias of various kinds, including bradycardia (decreased heart rate).
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Heart failure.
- Cardiac asthma (breathing problems occur at night).
- Inflammatory diseases - myocarditis, endocarditis, pericarditis.
- Congenital and acquired heart defects.
- Cardiosclerosis.
- Arterial hypertension.
Circulatory disorders that cause shortness of breath are accompanied by other symptoms. Thus, the most common symptoms of heart disease are:
- Swelling that occurs in the evening and is localized in the ankle area.
- Fatigue.
- Pain in the heart area.
- Cold extremities.
Dangerous accompanying symptoms
These symptoms include pain in the intercostal muscles when breathing. Sometimes the pain can be so severe that it leads to the development of pain syndrome. It, in turn, increases the patient’s nervous excitement and increases shortness of breath. It turns out to be a vicious circle.
Possible complications and consequences of shortness of breath:
- Oxygen starvation , as a consequence of insufficient saturation of the body with oxygen. The brain suffers, and fainting may develop.
- If you do not contact a specialist when shortness of breath appears, then there is a possibility of missing the development of such serious diseases as pleurisy, pneumonia, bronchial asthma and others.
Do not wait for complications to arise and the disease to progress. Contact your physician, cardiologist or pulmonologist if you consider your shortness of breath to be pathological. It’s better to protect yourself once again and not miss the moment for treatment.
Factors causing the problem
- Disturbance in the trunks of the medulla oblongata of the respiratory department. Usually occurs with an overdose of sleeping pills, anesthetics, or drugs. The frequency and depth of breathing changes.
- Bronchial obstruction. The functioning of the bronchi deteriorates due to the fact that the elasticity of the tissue inside the lungs changes. Diseases that cause dyspnea for this reason: asthma, foreign body entry into the bronchial aorta, bronchopulmonary cancer, bronchial inflammation. Expiratory shortness of breath in asthma is expressed in the form of sudden attacks. This symptom applies to all diseases caused by bronchial obstruction.