Description of the disease
Urticaria, or, as doctors also call it, nettle fever, is a dermatological disease of an allergic nature. The disease, which many also know as urticaria, is accompanied by the appearance of a vesicular rash on the skin, which occurs along with other unpleasant symptoms. It may be a full-fledged disease or a symptom of some other disease.
What is urticaria
Why does it occur
Since urticaria is allergic in nature, the main causative factor contributing to its development is an allergic reaction. The role of an allergen can be played by various irritants, including:
- Food;
- medications;
- ultraviolet radiation;
- severe stress;
- synthetic fibers;
- pet hair;
- pollen or road dust;
- chemicals.
Reasons for the development of urticaria
Sometimes urticaria develops against the background of other diseases or pathological conditions:
- chronic infection, such as infectious gastritis;
- dental caries or chronic tonsillitis;
- liver failure;
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract.
Etiology of urticaria
Note! If urticaria manifests itself as a concomitant symptom, it usually has a chronic course. The symptoms of the pathology are less pronounced, and periods of exacerbation practically do not occur.
Characteristic symptoms
Urticaria is usually accompanied by pronounced symptoms. A pink or red rash suddenly appears on the skin. The blisters have a round shape, and in some cases they merge into one large blurry formation. The affected areas of the skin are very itchy, but after a certain time the rash goes away and appears in another place.
Signs of hives
The transition of nettle fever to a chronic form leads to the fact that the patient’s condition can alternate between exacerbation and improvement. The duration of such periods is always different. When urticaria worsens, additional symptoms appear:
- Strong headache;
- general weakness;
- diarrhea;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- increase in body temperature.
On a note! The most complex form of the disease is Quincke's edema or giant urticaria. This is an acute allergic reaction, accompanied by massive swelling of the mucous membranes or skin. This condition requires immediate medical intervention.
Dangerous symptoms of urticaria
All of the above signs refer to the external manifestations of urticaria, but there are changes that occur inside the patient’s body.
Upon contact with an allergen, the cells of the body are gradually destroyed, resulting in the release of histamine (tissue hormone). It affects the body in such a way that liquid enters the cavity between the cells from small blood vessels. This leads to redness and swelling of the tissue.
Treatment options
The first thing to do to treat hives caused by an allergen is to eliminate exposure to it. For this, the patient is not only physically distanced from the allergen, but also undergoes manipulations aimed at removing the antigen from the body. These include: a cool shower, rinsing the nose and stomach, rinsing the eyes with saline. solution and others.
Treatment for food allergies is a strict diet. It excludes not only the allergenic product, but also all products containing substances that can cause a cross-reaction.
ASIT therapy is used to treat allergies. Its main task is to increase the development of resistance to the allergen. The patient receives small doses of a drug containing an allergen. Gradually the body gets used to its effects and stops reacting to it. The immune system response decreases and eventually stops. It makes sense to start therapy before direct contact with the allergen.
It is advisable for people who are allergic to pollen to undergo preventive therapy 2 months before the plants begin to bloom.
To eliminate other types of allergies, a complex of drugs is used that eliminate the symptomatic manifestations of the disease.
These include:
- immunosuppressants – reduce the immune system’s response to an allergen;
- antihistamines – relieve itching and swelling without depressing the patient’s central nervous system;
- immunoglobulins – strengthen the immune system;
- glucocorticoids – remove inflammation, normalize the functioning of the thyroid gland.
As an emergency treatment measure, blood purification from antigens is used using plasmaphresis.
Etiology and diagnosis
Another factor that raises doubts about whether urticaria is contagious or not is the lack of a general theory about the etiology of this disease. Unfortunately, even experts cannot name the exact cause of the development of urticaria and its origin. It is believed that some forms of nettle fever can be transmitted genetically. Therefore, within the family of the infected person there is a fear that the disease will spread to other members.
Differential diagnosis of urticaria
Despite the level of modern medicine, doctors cannot always find a connection with the patient’s pathology and the resulting skin rash. To clarify the etiology, it is necessary to carry out various diagnostic measures. But even this does not give a 100% result, so the origin of urticaria in some infected people cannot be determined.
Features of diagnosing urticaria
Is it possible to walk if you have hives?
So, we sorted out the question: “Is urticaria transmitted or not?” Is it possible to walk if you have hives? Considering that many people ask this question out of fear of spreading the disease, in cases where the exact diagnosis is known and the factor provoking the disease is discovered, walking is not prohibited. In general, walking with this disease is even beneficial.
But there are two types of urticaria, which are also not transmitted to other people, but walking with them can harm the patient:
- heat type of the disease;
- if the course of the disease is accompanied by Quincke's edema.
If there is an aggravated reaction to UV rays, then you should choose the right time to spend outside. A suitable time would be early morning or evening, when solar activity is weak. Otherwise, complications of the disease may occur.
When can you get hives?
Is urticaria contagious to others and is it transmitted by airborne droplets? These questions worry many people who have had to deal with itchy skin and rashes. As noted earlier, the disease can be triggered not only by infectious pathologies, but also by allergies to medications and various allergens, hormonal disorders and other disruptions in the body. But to encounter signs of urticaria, infection with an infectious pathology alone will not be enough.
Is hives contagious?
The causative factor against which the infectious form of urticaria develops is predominantly a viral disease. Such clinical cases are dangerous in terms of infection. But even here the key role is played by the state of immunity with the individual characteristics of the body.
Note! The process of producing special antibodies to allergens is not always activated in the body suffering from an infectious disease. Therefore, typical symptoms of urticaria in the form of a skin reaction will not develop.
Is it possible to get infected with urticaria?
The appearance of urticaria and, therefore, its contagiousness is influenced not by the infection itself, which can be contracted, but by the characteristics of the human body. The weaker its protective functions, the greater the chance of developing nettle fever.
Features of application
Non-hormonal ointments for urticaria
- Do not apply the product to healthy skin;
- avoid getting the ointment on the mucous membrane;
- Do not use antihistamine ointments on children under 2 years of age. This may cause side effects, for example, the child may show signs of intoxication;
- Be sure to follow the dosage when using ointments, creams or other forms of medicine;
- Apply the medicine to the affected skin carefully, avoiding intense scratching of the resulting rash.
How to use ointment for urticaria
In what cases is infection impossible?
Some internal factors that contribute to the development of urticaria provoke a non-contagious pathology. These factors include:
- formation of malignant tumors;
- hormonal imbalance;
- increased sensitivity of the patient's body to acetylcholine;
- consumption of certain foods;
- exposure to water, sunlight or cold;
- entry of various toxins into the body;
- consequences of taking certain medications.
When it is impossible to catch hives
If the causative factor is severe stress, then the blisters that appear on the skin will not be contagious. In such cases, the optimal method of therapy would be to maintain a calm lifestyle, avoid stressful situations and maintain a healthy diet. The appearance of skin symptoms under the influence of all of the above factors is nothing more than the reaction of the body, or rather the human dermis, to various negative processes.
Pathogenesis of urticaria
What is inducible urticaria?
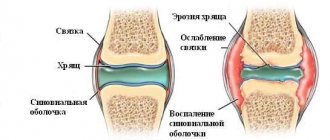
-Symptoms of inducible urticaria are red, itchy spots on the skin (Fig. 1). Inducible urticaria forms in response to physical irritation. For example, exposure to excess heat, cold or pressure. Inducible urticaria is known as “physical” urticaria.
The causes of induced urticaria are known:
Figure 3.
- Combing
. As a result of scratching, red, swollen stripes or scratches develop on the skin (Fig. 3). Doctors call this "dermatographism." This type is characterized by the fact that the skin reacts to the action of nails when scratching in areas of itching. - Cold
. In people who are sensitive to cold, hives appear after the skin begins to warm up again after cooling. - Increased body temperature or sweating
. People who are sensitive to heat or sweat develop many tiny spots when their skin cools after a hot shower or exercise. - Vibration.
Signs of hives appear on those parts of the body that touch vibrating objects. Skin irritation occurs on the palms. For example, among motorists when their palm comes into contact with the steering wheel of a car, or among a lawn mower. - Intense pressure.
Redness and swelling appear in the part of the body where pressure was applied. For example, after carrying a heavy bag, the palm suddenly swells and swells. Or the soles of your feet swell after a hike. - Physical exercise.
Hives that appear during exercise may be a sign of a dangerous problem called anaphylaxis. If symptoms appear after exercise, they are most likely caused by changes in body temperature or sweating. - Sunlight or water
. Hives caused by sunlight or water are rare.
Inducible urticaria is considered a chronic type of urticaria.
Urticaria and children
If we talk about preschool children, they rarely encounter signs of nettle fever. If the causative factor for the appearance of a red rash is an allergy, then the likelihood of infecting other people is minimal. But if parents identify blisters on their child’s skin, then they need to consult a doctor to determine the cause of such an allergic reaction.
Urticaria in children
Children are most often exposed to infectious diseases, including rubella, chickenpox, scarlet fever and others. All these pathologies do not pose any danger to adults, but for children whose bodies have not yet fully formed, they can lead to serious consequences.
Features of the development of urticaria in children
How to treat urticaria at home in adults
To answer the question of how to treat urticaria in adults at home, you must first go to a dermatologist’s office and find out what the doctor recommends. At the first signs of allergic reactions, you should call an ambulance or go to the hospital to see a dermatologist. Using an examination and laboratory tests, the doctor will determine the type of disease, make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. Indeed, in addition to acute and chronic urticaria, they distinguish: solar, cold, cholinergic, contact, idiopathic.
Can a child get infected from his mother?
During the process of passing through the birth canal, the child can become infected with certain types of pathologies from the mother. But if a pregnant woman suffers from allergic rashes, then infection cannot occur. During breastfeeding, the disease can pass to a small child through breast milk. If an endogenous irritant acts as an allergen, then it, being present in the circulatory system, can enter the mother’s breast milk.
Is urticaria transmitted from mother to child?
To determine the degree of danger of urticaria, you need to monitor how the disease manifests itself. In itself, it does not pose any threat to the patient’s life, but under certain factors anaphylactic shock or Quincke’s edema may occur. Such complications require emergency medical attention.
Quincke's edema is a dangerous complication of urticaria
How can I help myself?
Try to avoid taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and alcohol. Avoid taking excessively hot showers and wearing tight-fitting clothing. Provide yourself with adequate sleep.
Chronic hives are not caused by food allergies, but some people find that the condition gets worse after eating certain foods. If so, try to avoid these foods. But if the list of such products turns out to be too long, tell your doctor about it.
General recommendations
Regardless of the type of urticaria that occurs, experts recommend following the following recommendations:
Diet for urticaria
- carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene, especially if you suspect the development of an infectious disease. This is an excellent preventive method;
- subject all products to thorough heat treatment during cooking;
- Monitor the general condition of your body. If even the slightest violations are detected, you need to contact a specialist for examination. You also need to follow all the doctor’s recommendations, since incompletely cured urticaria can lead to complications;
- take vitamin complexes to protect the body from the possibility of developing an allergic reaction. A properly selected course of vitamin therapy will improve immune barriers;
- try to avoid stressful situations, since along with an existing rash that has arisen as a reaction of the body to an external irritant, a rash may appear due to severe stress.
Principles of treating urticaria
Try to explain to people around you that a skin rash that appears is not a sign that they are contagious.
Stages of development of urticaria
Doctors call the following forms of urticaria as stages:
- Immunological - its onset coincides with the first moment of contact of the skin or body with an allergen or irritant. As the allergen spreads through the bloodstream, the body produces and releases antibodies into the blood;
- Pathochemical – the formation and release of ready-made biologically active substances of allergy mediators occurs, which interact with the allergen;
- Pathophysiological is the body’s response to the produced mediators and after they increase in the blood composition, clinical symptoms of the pathological process appear.
Food triggers allergic urticaria in about half of all cases. In principle, allergies can be triggered by absolutely any food product, but most often it is fatty fish, sweets, honey, nuts, citrus fruits, artificial preservatives and dyes. Therefore, if you encounter an allergy, carefully analyze the menu for the last 24 hours.
- Pharmacological preparations
Allergic reactions caused by taking medications account for up to 30 percent of all cases. Most often, allergies are caused by antibacterial drugs, vitamin-mineral complexes and, by the way, birth control pills. If you suspect that medications are causing your allergy, stop taking them immediately and tell your doctor.
Allergies can be caused by pollen from almost any plant. True, most often the allergy in such cases makes itself felt a little differently - runny nose, lacrimation and itching of the eyes, cough and difficulty breathing. However, the possibility of allergic urticaria cannot be ruled out - everyone’s body is different. It is quite possible that yours decided to react to the allergen in exactly this way - with skin rashes.
Allergists very often diagnose people with an allergy to the saliva and/or fur of animals - cats, dogs, guinea pigs, hamsters. Moreover, there can be an allergy to any animal, or to just one. In some people, such an allergy may manifest itself as a cough, runny nose and other symptoms, and in others - by skin rashes.
But physical effects on the skin very rarely come under suspicion. Which, however, is not surprising - who would think of blaming the sun or frost for the development of hives? In fact, an allergic reaction to the sun's rays - as well as to high temperature and frost - is a phenomenon that occurs very, very often. And such an allergy can occur at any time, even if nothing like this has happened before.
- Cosmetics and household chemicals
It would seem that for modern housewives in our time it is practically paradise - there are no household chemicals that make life easier. Here you can find washing powders, detergents for washing dishes, glass, floors - you can’t list everything. But very often contact with this miracle of the chemical industry leads to the development of very severe allergic urticaria.
Moreover, all of the above is true not only for household chemicals, but also for cosmetics. Cleansing gel, cream, deodorant – is there not enough cosmetics in a woman’s handbag? And almost any of these drugs can trigger allergies.
How to get rid of hives
The key to successful treatment and quick recovery is a timely visit to a doctor and a correctly prescribed therapeutic course. Complex therapy for urticaria must include:
Preparations for urticaria
- correct diagnosis to identify and eliminate the causative factor;
- take antihistamines;
- the use of external agents that eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of nettle fever;
- desensitizing treatment;
- use of hormonal drugs (prescribed for severe disease);
- compliance with a therapeutic diet. A combination of drug treatment and diet therapy will speed up the recovery process.
Features of the treatment of nettle fever
On a note! Provided that all measures are taken in a timely manner, the symptoms of urticaria disappear literally after 1-2 days of treatment. But if adequate assistance is not provided to the patient, the pathology may accompany him for several weeks.
Basics of disease therapy
The patient has to constantly remember about his disease, and non-drug methods - elimination (cessation of contact with the provoking factor) and diet must be followed at all times. However, a course of therapy with pharmacological drugs, when it comes to allergies, is carried out only during exacerbation with the help of such groups of medications as:
- Antihistamines.
- Mast cell membrane stabilizers.
- Glucocorticosteroids.
They are used for external (local, topical) application to affected areas of the skin and systemic (general, internal) use. There are medications that are intended only for emergency care - in particular, Adrenaline (Epinephrine), which belongs to the group of sympathomimetics.
Patients are required to:
- Elimination. This is a set of measures aimed at stopping contact with the trigger (provocateur). For treatment to be effective, it is necessary to find out which substance (for allergies) or factor (for non-immune urticaria) causes the reaction. To do this, skin tests and laboratory tests are performed.
- Diet. Dietary restrictions can be permanent or temporary. Completely exclude from the diet those foods that cause urticaria symptoms. For several weeks, avoid potential allergens: citrus fruits, tomatoes, sausages, nuts, peanuts.
- Lifestyle modification. Urticaria is a serious reaction, so the patient should familiarize himself with information about this disease and, in consultation with a doctor, choose quick-acting medications that can be taken when symptoms occur. These are, as a rule, antihistamines in tablets - Cetrin, Zyrtec, Erius, etc. If contact with an allergen occurs at home or in the workplace, it is worth considering how to avoid it and develop an algorithm for restrictive measures.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Troxerutin Vramed instructions for using the ointment
After completing the course of medication, you should continue to follow the principles of elimination and diet.
This will avoid provoking the reaction and causing a recurrence of the urticaria episode. It is important to remember that no pharmacological agent will be 100% effective without stopping contact with the trigger. Therefore, a non-drug approach remains the mainstay of therapy.
Diet for urticaria
- identification of the causative factor and its subsequent elimination (for example, stopping the medication that caused the urticaria);
- adherence to a hypoallergenic diet (all potential allergens are excluded from the diet, for example, peanuts, citrus fruits or tomatoes);
- taking systemic medications (we are talking about potent drugs in the form of tablets or capsules).
Allergen products prohibited for urticaria
Ointments should be supplemented with systemic drugs, the selection of which should be carried out on an individual basis. First of all, such drugs should not cause increased drowsiness. Let's consider the main drugs used as an addition to ointments in the treatment of urticaria:
- Kestin;
- Telfast;
- Cetrin;
- Erius;
- Loratadine and others.
Systemic drugs for urticaria
These drugs need to be taken for several days (depending on the therapeutic course drawn up by the doctor). When treating urticaria in pregnant women, the best option would be medications based on loratadine. They are safer for the body and do not cause side effects.
Treatment of urticaria in children
Statistics show that children suffer from urticaria quite often. The disease is accompanied by white or red skin rashes, as well as severe itching. The rash can appear on different parts of the body; it often appears on the child’s face. But how to fight a disease when you can’t use potent drugs? To do this, you need to follow the instructions below.
Step 1. Use antihistamines at the first onset of hives symptoms, without waiting for the symptoms to go away on their own. But medications can only be given to a child as prescribed by a doctor.
Give antihistamines
Step 2. Relieve the unpleasant symptoms of hives with oat lotion. This will help relieve burning and itching. Parents should also ensure that their child does not scratch the affected area of skin.
Make lotions from oats
Step 3. Treat the rash with a special herbal-based ointment. Local products containing aloe vera cope well with skin irritation. You can also relieve swelling and itching with a cold compress. Just wrap a few ice cubes in a handkerchief and apply to the sore spot.
Use external remedies
Step 4. Dress a child infected with hives in clothes made from cotton fabric. This will help the body to breathe, which will prevent the disease from spreading. Tight clothing should be avoided.
Use clothes made from natural fabrics
Step 5. If swelling occurs on the child's face during therapy, stop taking the medications and take the child to the doctor. Often, bloating leads to swelling of the throat, which is very dangerous for the child’s health.
Contact your doctor if complications develop
If an allergic reaction occurs after taking a medicine prescribed by a doctor, parents should contact the doctor immediately. Similar reactions can also occur after eating.
Traditional methods
More than any other symptom, a patient with urticaria is concerned about itching. Sometimes it becomes so strong that a person cannot tolerate it. He scratches the skin until it bleeds, which causes the blisters to persist for a long time, and the wounds can become infected. Folk remedies help soothe itching and relieve external manifestations of the disease.
Potato compress. 2-3 peeled root vegetables should be grated, placed on a napkin and a compress applied to the face for 20-30 minutes. After completing the procedure, you need to wash your face with warm water to wash off the starch.- Flour cospress. From rye flour and warm water you need to knead a weak dough, which is enough to make a compress on all affected areas of the body. Roll out the dough, apply to the skin, hold for 30 minutes. Rinse off any stuck dough with cool water.
- Bath with herbal infusion. Take crushed chamomile, oak bark, juniper, and a string in equal proportions, pour a liter of boiling water. Leave for 30-40 minutes, pour into the bath. You can stay in the bath for up to 20 minutes; the water should be warm, but not too hot. You cannot wipe yourself after the procedure, as you may injure the skin. It is permissible to blot the water with a soft towel.
- Peppermint decoction. Take 3-4 tbsp. spoons of mint, pour boiling water and leave for 10 minutes. Strain the finished broth and drink as regular tea.
- Nettle decoction. This plant has a strong anti-inflammatory and strengthening effect. 4 tbsp. spoons of dry plant need to be poured with 200 ml of boiling water, leave for 20 minutes. Drink during the day.
To support the nervous system, it is recommended to take an infusion of valerian root: 10-15 drops per glass of water before bed. Valerian relieves nervous excitement and helps with insomnia.
Summing up
Urticaria is not a contagious disease, but this does not make it any less dangerous to the patient’s health. In addition, urticaria in some cases is inherited. But if the cause is an infectious disease, then healthy people may well become infected by airborne droplets. Therefore, when diagnosing urticaria, it is important to determine the causative factor.
Difficulties in treating urticaria
Skin rashes, which appear depending on the state of immunity, can lead to serious complications in the absence of timely medical care. The most dangerous of them is Quincke's edema. But to summarize, we can say with confidence that urticaria is not transmitted to healthy people, so there is no need to be afraid of a skin rash on your loved ones or friends, knowing that it is urticaria fever.
Preventing the development of urticaria
List of drugs
In dermatological practice, two types of ointments are used in the treatment of urticaria - hormonal and non-hormonal. The former contain hormones, due to which such drugs have a higher effect when compared with other types of drugs. Non-hormonal ointments, in turn, act more gently, so when treating an allergic rash, the result achieved is not as pronounced.
Types of ointments for urticaria
Both hormonal and non-hormonal ointments can be purchased at the pharmacy without a prescription, so many people, refusing medical help, decide to self-medicate. But this solution does not always give the desired result, so before starting therapy it is still recommended to consult a specialist.
Features of the treatment of urticaria
Hormonal ointments
They contain artificial analogues of hormones produced by the human adrenal glands, manufactured in laboratory conditions. Among all antipruritic and antiallergic drugs, hormonal ointments are considered the most effective. Below are the most popular ones.
Table. Hormonal ointments for urticaria.
| Name of the drug, photo | Description |
| Hydrocortisone | An effective anti-inflammatory and antiallergic agent containing hormones. It is used not only for urticaria, but also for other skin pathologies. For maximum effect, Hydrocortisone should be applied to the skin 2-3 times a day. |
| Lorinden S | An excellent medication containing substances such as livalate, flumethasone and clioquinol. Has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. The product should be used 2-3 times a day for 10 days. |
| Soderm | It is produced not only in ointment form, but also in the form of lotion and cream. The active substance is betamethasone. The product has an excellent anti-inflammatory effect. When treating urticaria, it is recommended to apply the ointment 2 times a day. |
| Elokom | It has anti-edematous, anti-inflammatory and antihistamine properties, due to which Elokom is actively used in diagnosing urticaria. Apply the product once a day in a thin layer. |
| Advantan | An excellent product containing a synthetic hormone that copes with such unpleasant symptoms of urticaria as itching, swelling and irritation. To obtain the optimal effect, it is enough to apply the ointment to the affected skin once a day. |
| Prednisolone | It is actively used for various dermatological diseases, including urticaria. The drug has anti-inflammatory and antiallergic properties and is able to relieve swelling of tissues. With daily use, improvement occurs within a few days. |
Hormonal drugs become addictive quite quickly, so the course of therapy should not be too long, since long-term use becomes useless. Possible complications of hormonal ointments include disruption of the cardiovascular system, kidney and liver damage, and skin atrophy (in rare cases).
Non-hormonal ointments
If the patient has been diagnosed with a mild form of urticaria, which is not accompanied by pronounced symptoms, then he is prescribed drugs that do not contain hormones. They have a gentle effect on the human body, so side effects occur extremely rarely.
Table. Non-hormonal ointments for urticaria.
| Name of the drug, photo | Description |
| Zinc ointment | A widely known drug with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. The ointment also has a drying effect, which is very important in the treatment of urticaria. It has virtually no contraindications. |
| Fenistil-gel | An effective anti-inflammatory and pain reliever, which is prescribed not only to adult patients, but also to children. Fenistil-gel is able to eliminate itching, burning and other symptoms of urticaria in the shortest possible time. |
| Nezulin | It is made on a plant basis, so this drug has no side effects. The combination of natural ingredients copes with the inflammatory process, irritation and itching. Prescribed for all patients, regardless of gender or age. |
| Psilo-balm | Another non-hormonal remedy for urticaria. The active ingredient is diphenhydramine. The drug has antipruritic and analgesic properties and has a systemic effect on the patient's body. |
| La Cree | The drug contains vegetable oils, extracts and other natural ingredients, thanks to which La-Cri successfully copes with various skin problems. Prescribed to patients of different age groups. |
| Gistan | An antiallergic product consisting exclusively of natural ingredients. Thanks to its complex effect on the body, Gistan promotes the rapid restoration of affected skin areas. |
First aid for urticaria at home is determined by the symptoms, the nature of the urticaria rash, and other manifestations of allergies. Traditional treatment consists of the following:
- Antihistamine (anti-allergic), sedative (calming nerves) drugs: Diazolin, Tavegil, Tazepam, Fenkarol, Pipolfen.
- What helps with hives “for a long time”? The best remedy is strong immunity and isolation from the allergen. Vitamins, drugs to support immunity: multivitamins, riboflavin, nicotinic and ascorbic acid, calcium, pyridoxine and other supporting drugs.
- Corticosteroid drugs (for prolonged form, persistent itching): Prednisolone, Prednisone.
- Anabolic steroids: Nerobol, Retabolil.
- How to cure hives at home? It is also important to strengthen blood vessels by taking calcium gluconate or chloride, calcium glycerophosphate with rutin, salicylates, and iron.
- External agents (ointments). How to treat urticaria (namely urticaria rash)? These are such popular drugs as Prednisolone ointment, Elokom, Advantan, Flucinar, Deperzolon, Fluorocort, Lorinden S.
How to treat urticaria at home is determined by an allergist or dermatologist.
The mainstay of treatment for urticaria is the use of antihistamines. They act directly on histamines. These substances are produced in response to an allergen and provoke severe symptoms of urticaria.
- Tavegil is one of the most popular drugs for urticaria. Relieves itching, swelling and quickly eliminates lacrimation. The main component in the composition is clemastine. The substance has an antihistamine effect, but does not cause drowsiness. You can take the drug for 2-3 weeks, 1 tablet 2 times a day.
- Zyrtec is an antihistamine based on cetirizine. It has a pronounced effect, quickly eliminates general and local symptoms of urticaria. The medication is easy to use, since to achieve a therapeutic effect it is enough to take 1 tablet per day. Duration of therapy is 10-14 days.
- Erius is an antihistamine that has an effect due to the content of desloratadine. It is considered quite effective, helping to quickly eliminate the signs of urticaria and prevent complications. The patient needs to take 1 tablet of the drug per day. The course duration ranges from 7-14 days.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Severe wrinkles on the forehead at 30 years old folk remedies
How to treat urticaria with medication?
Urticaria is a fairly common and dangerous disease that is allergic in nature. When this disease appears, quite unpleasant symptoms are diagnosed in the form of itching, rash, digestive system disorders, etc.
To treat the pathological process, appropriate drugs are most often used.
Urticaria is a specific disease that occurs due to exposure to an allergen. That is why, when it appears, it is necessary to adhere to the general principles of treatment.
He should stay indoors or in shaded conditions as much as possible. Urticaria is accompanied by corresponding rashes. The patient should wear light and loose clothing during this period.
Experts do not recommend traveling long distances. If the cause of urticaria is stressful situations, then patients are recommended to take antidepressants.
During the course of the disease, drinking alcoholic beverages is strictly prohibited. The patient must adhere to a dietary diet. He is not recommended to eat coffee, wine, preservatives and foods that contain allergens.
The human diet should include mainly plant and dairy foods. If you follow the basic principles of treating urticaria, you will be able to get rid of this disease as soon as possible.
To ensure effective control of urticaria, medications are most often prescribed.
They are used not only externally, but also prescribed internally, which provides them with the highest possible effect. There are a large number of medications used to combat the disease.
The selection of a specific medication should be carried out only by a doctor in accordance with the individual characteristics of the patient and the severity of the disease.
Antihistamines eliminate free histamine and also remove it from the body. This substance negatively affects the immune system, which leads to rashes and itching.
If the drugs are taken for a long time, this will lead to a decrease in their effectiveness. In this case, it is recommended to change the drug every 14 days. A negative factor in taking medications is the presence of sedation.
Urticaria usually occurs in people prone to individual immune sensitivity reactions; Pathological variants not related to allergies are rare.
The treatment regimen includes different groups of pharmacological drugs for planned and emergency care.
Let's try to understand what they are and how to choose the right medicine for urticaria for an adult patient.
Diagnostics
Not every episode of rash requires immediate medical attention. The following information can help you decide whether you need to see a doctor and what to expect when you see your doctor.
Warning signs
Some symptoms and characteristics are cause for concern:
- Swelling of the face, lips, throat, tongue or airways (Quincke's edema);
- Difficulty breathing, including wheezing;
- An allergic rash that is intensely colored, forms open sores, or lasts more than 48 hours;
- Fever, swollen lymph nodes, jaundice, weight loss and other symptoms of a general (systemic) disease
When should you immediately consult a doctor?
It is necessary to call an ambulance at home if:
- the person has difficulty breathing or wheezing;
- the person feels as if his throat is closing.
You should go to an emergency room or primary care provider as soon as possible if:
- symptoms are severe;
- the person feels increasing weakness or dizziness, or experiences severe fever or chills;
- vomiting or abdominal pain or diarrhea develops.
You should consult a doctor if:
- a rash appears on the skin after a bee sting (for advice on treatment if another bee sting occurs);
- other symptoms are observed, such as fever, joint pain, weight loss, swollen lymph nodes, or excessive sweating during sleep;
- the rash recurs without exposure to a provoking factor;
- symptoms last more than 2 days.
If an adult has urticaria that appears suddenly, disappears quickly and does not recur, then a medical examination is usually not required. The cause is usually a viral infection.
What does a doctor do when examining a patient?
Doctors first ask questions about symptoms and medical history. They then perform a physical examination. Typically, a medical history and physical examination will reveal the possible cause of the disease and determine what tests are needed.
Doctors ask the person to describe in detail each episode of the rash and any other symptoms that occurred (such as itching, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the face and tongue). They ask about the person's activities before and during the episode and about possible exposure to substances that may cause allergic reactions, including medications they are taking. The person is also asked about specific symptoms that might indicate a cause, previous allergic reactions and recent travel.
The trigger for hives cannot always be determined based on medical history (often because the trigger is something that may have been previously experienced).
During a physical examination, doctors first check to see if the patient has swelling of the lips, tongue, throat, or airways. If swelling is present, treatment is started immediately. Doctors then pay attention to what the rash looks like, determine which parts of the body are affected, and check for other symptoms that can help confirm the diagnosis. Doctors may use various physical stimuli to see if they can trigger a skin rash. For example, they may apply light pressure, heat and cold, or strokes to the skin.
People should not try to trigger hives themselves as a severe reaction may develop.
Carrying out analyzes
Typically, testing is not required for a single episode of urticaria unless symptoms indicate a specific condition that requires treatment (eg, certain infections). However, if the rash has unusual characteristics, recurs, or persists, investigations are usually performed.
Typically, tests include a complete blood count and blood tests to measure levels of electrolytes, sugar (glucose), and thyroid-stimulating hormone and determine how well your kidneys and liver are functioning.
Allergy skin tests, such as the skin needle test, are performed by an allergist (a doctor who specializes in allergy pathologies) to identify specific allergens. Imaging studies and other blood tests are performed based on the results of your medical history and physical examination. If the results suggest that the cause is a disease affecting the entire body, then a thorough examination is necessary to identify it.
A skin biopsy is performed if the diagnosis is unclear or if the hives persist for more than 48 hours.
Some causes and distinctive features of urticaria (urticaria).
| Cause | Common signs | Surveys |
| Acute urticaria (lasting less than 6 weeks). | ||
Medicines such as:
| There is a skin rash that begins within 48 hours after using the drug. | Examination by a doctor. |
Emotional and physical stimuli
| For most stimuli, a rash that usually begins within seconds to minutes of exposure to the stimulus. For skin pressure, a rash that begins within 4–6 hours and affects only the area of skin where pressure was applied. For sunlight, a rash that affects only the area of skin exposed to sunlight. | Examination by a doctor. Exposure to a suspected physical stimulus to see if it causes symptoms. |
| Foods that cause an allergic reaction (food allergens) such as peanuts, tree nuts, fish, shellfish, wheat, eggs, milk and soy. | Skin rash that appears within minutes to hours after consumption. | Medical examination, especially medical history. Sometimes allergic skin needle test. |
Infections (rare causes):
| Symptoms:
| Investigations depending on the suspected infection (suggested based on the results of the medical history and examination). The diagnosis is confirmed if the rash disappears after the infection is eliminated. |
| Insect bites or burns. | A rash that begins within seconds or minutes of an insect bite or burn | Medical examination, especially medical history. |
| Serum sickness. | A rash that begins within 7 to 10 days after the injection. It may also be accompanied by fever, joint pain, inflammation of the lymph nodes, and abdominal pain. | Medical examination. |
| Substances that cause an allergic reaction upon contact (contact allergens), such as latex, animal saliva or dander, dust, pollen, or mold. | Skin rash that begins within minutes to hours of exposure. | Medical examination, especially medical history. Sometimes allergy tests. |
| Transfusion reactions. | Hives that usually begin within minutes of a blood product transfusion | Medical examination, especially medical history. |
| Chronic urticaria (lasts more than 6 weeks). | ||
Autoimmune diseases:
| Varying symptoms depending on the autoimmune disease. With systemic lupus erythematosus, symptoms may include fever, fatigue, headache, joint pain and swelling, pain when breathing, and mouth ulcers. Sjögren's syndrome - dry eyes and dry mouth With urticarial vasculitis - an allergic rash that:
| For all autoimmune diseases, blood tests are done to check for abnormal antibodies. Sometimes a skin biopsy. For Sjögren's syndrome, a study is performed to evaluate the amount of tear fluid produced. For urticarial vasculitis, a skin biopsy is performed. |
| Oncological disease (usually cancer of the digestive organs or lungs, or Hodgkin's lymphoma). | You may experience weight loss, night sweats, abdominal pain, cough (sometimes with blood), jaundice, swollen lymph nodes, or a combination of these symptoms. | Various studies are carried out depending on the suspected cancer. |
| Chronic idiopathic urticaria (diagnosed when no specific cause is identified). | Presents with a skin rash that occurs daily (or almost daily) and itching that lasts for at least 6 weeks, with no obvious cause. | Doctor's examination Blood tests and sometimes other tests, such as a skin needle test and exposure to various triggers, to rule out other causes. |
| Medicines (the same as for acute urticaria). | A urticarial rash that occurs in a person who takes prescription, over-the-counter, or herbal medications for a long time when there is no other explanation. | Examination by a doctor. Sometimes allergy tests. An avoidance study to see if the allergic rash goes away when the drug is stopped. |
| Emotional and physical stimuli (same as for acute rash). | For most stimuli, a rash usually occurs within seconds to minutes of exposure to the stimulus. For skin pressure, a rash that begins within 4–6 hours and affects only the area of skin where pressure was applied. For sunlight - a rash that affects only the area of skin exposed to sunlight | Examination by a doctor Exposure to a suspected stimulus to see if it causes symptoms |
| Endocrine disorders such as thyroid disease or increased levels of progesterone (a female hormone). | Signs of thyroid disease:
Occurs in women who take birth control pills (oral contraceptives) or undergo progesterone-based hormone therapy, or whose rash appears before the start of their menstrual cycle and goes away after it ends. | Examination by a doctor. If thyroid disease is suspected, a blood test is performed to measure thyroid-stimulating hormone levels. |
| Mastocytosis. | Small red bumps. Sometimes abdominal pain, mild hot flashes, and recurring headaches | Biopsy of skin and sometimes bone marrow. Sometimes blood tests to measure levels of substances released when certain immune cells (called mast cells) are activated. |
| Please note: The symptoms listed in the table are typical, but are not always present. | ||
Why does hives occur?
This is a systemic disease, the occurrence of which can be contributed by a variety of factors. People who are prone to allergic reactions or have a family history of this disease often suffer from urticaria.
The following factors can lead to the appearance of nettle rash:
- medications, most often antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- insect bites (bees, wasps);
- viral and chronic infectious diseases;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- products, including various spices and food additives;
- problems with the immune system;
- stressful situations;
- the presence of helminths or other parasites in the body;
- external physical phenomena (cold, pressure, water, sun, vibration).
The list of causes of chronic urticaria is headed by drugs and food, and the acute form of the disease in most cases occurs against the background of viral infections and gastrointestinal diseases.
Hormonal imbalance in the body can provoke the disease in women. This may be due to menstrual irregularities, taking hormonal medications, pregnancy or menopause.
Nettle rash is not always an independent diagnosis. Often it acts as a symptom of other pathologies. For example, such rashes are characteristic of autoinflammatory diseases, angioedema and mastocytosis (blood disease).