Caesarean section at the 37th week of pregnancy is performed at the onset of labor for women with contraindications for natural childbirth; it may be prescribed earlier than planned (38-40 weeks) due to a threat to the life of the mother and fetus. By this time the child is quite viable, his lungs are sufficiently developed to begin breathing independently. However, it has been proven that such children are susceptible to respiratory diseases after birth.
For a woman, the risk of cesarean delivery at 37 weeks and at a later date is the same; infection, vascular thrombosis, and bleeding are possible. The surgical technique and preparation are no different from classical ones.
Caesarean section at 37 weeks: when can it be done?
A caesarean section at 37 weeks is indicated if it is impossible to further prolong pregnancy to 39-40 weeks. It can be prescribed routinely if there is a predicted threat to the life of the mother and/or fetus:
- severe course of late toxicosis - increasing edema, uncontrolled increase in blood pressure;
- decompensation of maternal diseases - heart and respiratory failure, decreased kidney and liver function, diabetes mellitus;
- risk of placental abruption;
- a thin suture on the uterus with a threat of rupture;
- insufficient oxygen supply to the fetus - intrauterine hypoxia, slow heartbeat.
An emergency caesarean section at 36 or 37 weeks of pregnancy is carried out when there are signs of the onset of labor, when labor cannot be carried out through the vagina:
- placenta previa;
- transverse, oblique position of the fetus;
- large fruit;
- narrow pelvis or pelvic bone deformities;
- multiple pregnancy with abnormal location of at least one fetus, common amniotic sac, connection of blood ducts;
- fibroids or other tumor of the cervix, scars;
- complicated myopia;
- transplanted kidney;
- developmental defects or diseases of the child in which passage through the natural birth canal is undesirable (for example, heart disease);
- genital (vaginal) herpes, condylomas, cervical polyps;
- HIV infection.
Urgent surgery at 37 weeks of pregnancy is needed to save the life of the fetus in case of prolapse, entanglement of the umbilical cord, placental abruption, or premature rupture of amniotic fluid.
What happens in the body, harbingers of childbirth
37 weeks is 9 obstetric months and 1 more week. Early full-term pregnancy - this is what the medical diagnosis will sound like from 37 weeks to 38 weeks 6 days. Mom’s hearing immediately picks up the treasured word “full-term.” Yes, the fears of giving birth to an “immature” baby, poorly adapted to life outside the mother’s belly, are behind us.
The concepts of “full term” and “maturity” of the fetus are different. “Maturity” implies the child’s full readiness for extrauterine life and is assessed by a combination of characteristics: the baby’s height and weight, head size, condition of the skin, hair, nails, genitals, umbilical cord, placenta, ossification nuclei. It also happens that a full-term baby is born with signs of immaturity.
So, the most important thing is that a 37-week fetus is absolutely viable, can breathe and suck, and screams loudly.
What sensations accompany the 37th week:
- The emotional state at the 37th week for most mothers is very labile, that is, unstable. But who is surprised? Some mothers are in a state of peace, others are in apathy, others are waiting - they can’t wait to finally see their baby. But what they all have in common is the “nesting” syndrome. Just a manic desire to arrange, “make comfortable”, wash, clean and decorate your home as best as possible.
- If the uterus has dropped (most often this happens at the 37th week) and its weight puts pressure on the bladder and intestines, urination becomes more frequent, and a tendency to constipation appears even in those mothers who have not yet encountered it. Immediately before childbirth, on the contrary, diarrhea may appear as a way to cleanse the body. Uterine pressure and constipation, unfortunately, often lead to another unpleasant “surprise” of the 37th week - hemorrhoids. When coughing or sneezing, droplets of urine may be released.
- The number and intensity of movements decreases at the 37th week, especially if the stomach has already dropped. This is explained by the fact that the baby becomes cramped in the uterus, he cannot “dance” as before, but is only able to move his arms and push his legs. But sometimes he can very sensitively kick mom in the ribs, in the bladder.
- A slight decrease in body weight is possible due to a decrease in edema and blood thickening. Don’t be alarmed if, at your next visit to the doctor, instead of the expected increase, you hear: “Minus 1.5 kg.” Your body's circulating blood volume is reduced and "concentrated" to minimize potential loss during childbirth. During the entire third trimester, weight loss should not exceed 3 kg; this may be a sign of fetal distress. Normal weight gain by week 37 is generally between 8.2 and 14 kg, depending on your body type and your pre-pregnancy weight. As a rule, thin mothers gain more.
- At night, due to a deficiency of potassium, calcium, and magnesium, cramps in the calf muscles are possible. Paresthesia may also be a concern - tingling sensations, “pins and needles” in the hands. It is difficult for the fingers to hold small objects and bending is difficult. This occurs due to outwardly subtle swelling of the small joints of the fingers.
- At 37 weeks, you may notice droplets of colostrum when you squeeze your nipples slightly.
- Precursors of labor are likely to appear: The stomach drops. It becomes easier to breathe and eat, heartburn decreases or goes away completely. The timing of abdominal drooping is quite individual, in most cases it occurs at the 37th week, but quite possibly later. If at 36 weeks the height of the uterine fundus is on average 36–37 cm, then at the 37th week this figure is 1–2 cm less and is approximately 34–35 cm when measured from the symphysis pubis. Abdominal circumference 91–97 cm.
- If you have a jelly-like, egg white-like discharge, possibly streaked with blood—pinkish or brownish—you have a mucus plug coming out. There is no need to immediately get ready for the maternity hospital; it may well take 2 weeks before the birth.
- Braxton Hicks contractions. They prepare the uterus for future birth and are very similar to painful periods. Unlike true contractions, false contractions are irregular, their intensity and duration do not increase, moreover, if you lie down and drink soothing tea, the training contractions will stop. Just try not to miss the start of labor! If “false” contractions are repeated regularly, become more frequent and intensified, and amniotic fluid leaks, you are giving birth!
- The cervix is ripening. This harbinger can only be noticed by a doctor during examination and confirmed by ultrasound examination. The cervix softens and shortens under the influence of estrogens before childbirth.
My daughter used to have a “disco” late in the evening when I went to rest. It should be noted that sleep can also change in later stages - for example, I fell asleep easily, but woke up at 3-4 in the morning and could not fall asleep again. Someone, on the contrary, hibernates for whole days, accumulating strength before giving birth. So, my daughter waited until I had finished all my chores and lay down to read or watch TV, and she started kicking, trying to get into her bladder. Rarely missed...
The harbingers of labor are identical in both primiparous and multiparous women, but in the second case, the length of all periods of labor is significantly reduced.
Photo gallery: bellies at 37 weeks
In late pregnancy, the navel protrudes, the skin of the abdomen itches due to overextension
Don’t forget to take a photo of your belly, firstly, it’s beautiful, and secondly, it’s easier to notice changes from the photo
If you notice that your belly has dropped, you are anywhere from a few hours to 2-3 weeks away from giving birth
Caesarean section at 37 weeks of pregnancy: what is the fetus like at this stage?
Caesarean section at 37 weeks of pregnancy is not considered a threat to the survival of the fetus, since at this time all major organs are formed. If the 37th week has already ended, then the baby is considered full-term, at the turn of 36 and 37 - almost full-term, capable of independent breathing after birth.
On average, at this stage the child’s weight is 2800-2900 g, his height is 48 cm. A newborn can have:
- fairly dense skin, ear and nasal cartilage;
- nails reaching to the tips of the fingers;
- fluff on the shoulders and back;
- lubricant only in the folds of the body;
- the presence of surfactant in the lungs (prevents the alveoli from sticking together), which means the possibility of filling with air;
- actively working adrenal glands, producing stress hormones to adapt to new living conditions;
- a maturing nervous system, after birth there is a sucking and grasping reflex;
- the stomach and intestines may contract.
Possible consequences for the child
If a cesarean section is required before 39 weeks, the baby has an increased risk of breathing problems and a temporary increase in pressure in the pulmonary artery system (transient pulmonary hypertension).
This is explained by the fact that at this time fluid is still actively forming inside the pulmonary alveoli. Its production slows down only a few days before natural birth (at 39-40 weeks). If a caesarean section is started without signs of the onset of labor, then the newborn subsequently experiences respiratory failure. Such children may be prone to lung diseases and respiratory infections.
Are there any risks for mom?
For the mother, the risks of a cesarean section at 37 weeks of pregnancy and at a later stage do not differ significantly; complications are possible in the form of:
- uterine postpartum hemorrhage due to insufficient contractility of the uterus;
- infection - endometritis, pelvioperitonitis (inflammation of the pelvic peritoneum), wound suppuration;
- increased blood clotting with vascular thrombosis, blockage of the pulmonary artery;
- injury to neighboring organs (ureter, bladder, intestines);
- allergic reactions to painkillers;
- accumulation of blood (hematoma) under the skin, the membrane of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, inside the tissue of the uterus, bladder.
Woman 36 weeks pregnant
At the thirty-sixth week, the fundus of a woman’s uterus is already directly under the sternum. It becomes difficult to breathe, sometimes the child kicks his legs literally under your heart. We hope you are attending birthing classes. Your whole life now passes under the sign of the birth of a child. You have already decided where and how you will give birth and whether you will use pain relief. Pregnancy is accompanied by the following annoying phenomenon. Hormones lead to synchronous hair growth of the skin. In normal conditions, some hair grows and others fall out. For pregnant women, everything is different. Dont be upset. After childbirth, synchronous hair growth will stop.
There are only 4-5 weeks left until the birth. You may be nervous that your baby might be born prematurely. Among your friends or relatives there are probably those who went into labor a little earlier than expected, and everything went well.
You're already 36 weeks pregnant and you might already be tired of it. But there is no need to ask the doctor to speed up labor.
You have now gained from 11 to 13.5 kg, and there is still a month before giving birth. It will not be unusual for your weight to remain the same until you give birth.
Now your baby is surrounded by the maximum amount of amniotic fluid. The baby will continue to grow in the following weeks. At the same time, your body will absorb some amniotic fluid, thereby reducing the volume around the baby and giving him less opportunity to move. You will notice that the baby begins to move less and is not as active. Some women are afraid that he has stopped moving altogether or that he is moving differently than usual.
Starting this week, you should see your doctor weekly. Most fetuses by this time are located head down in the uterus. However, 4% of babies are in a butt-down position. This is called a breech or breech presentation. In this case, some problems during childbirth are possible, although not necessarily. Quite often, obstetricians warn the expectant mother that delivery by cesarean section should be considered as one of the real options for her.
Is it better to have a planned caesarean at 38 weeks?
The closer the cesarean section is to the date of natural birth, the better the baby is developed, so at 38 weeks a planned cesarean section will have a better prognosis than at 37.
Since shifting the operation to an earlier date does not depend on the wishes of the doctor and the woman in labor, it is only important for the woman to strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations. In each case, an individual action plan is drawn up. It is determined by the condition of the woman and child.
Emergency caesarean section
There are a number of cases when, while preparing for a natural birth, there is a need for an emergency cesarean section. There could be many reasons for this. There is no point in talking about what week an emergency caesarean section will be required. This may be 38 weeks or earlier if any pathologies were discovered that threaten the life of the mother and child. Let us note that a second caesarean section can also be an emergency and at what time it will have to be done is not always known.
This operation is performed with the consent of the woman, with the exception of the incapacity of the woman in labor. Then the consent of her close relatives will be required.
A planned caesarean section differs from an emergency one in the type of anesthesia used. Emergency caesarean section requires quick action, so general anesthesia is used. This type of anesthesia allows you to be completely unconscious.
However, recently, spinal anesthesia is being used more and more often.
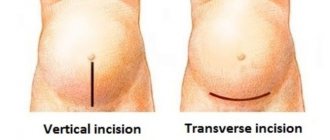
It is carried out using anesthesia between the lumbar vertebrae into the spinal canal, the effect of the drug begins within 5 minutes. This allows you to proceed to an emergency caesarean section as soon as possible. This anesthesia only numbs the lower part of the body, so the woman is conscious and can observe the progress of the operation. Note that in this case the incision will be made from the navel area to the pubic part, i.e. longitudinal. In case of emergency cesarean section, such an incision best provides access to the pelvic organs.
The danger of an emergency cesarean section is the risk of infection. Therefore, during the operation and after it, the woman in labor must take antibiotics, which will be prescribed by the attending physician.
The psychological side of emergency caesarean section should also be noted. After all, what is planned is discussed in advance, thereby the woman is ready for it and does not consider it as a disaster. When an emergency caesarean section causes anxiety and fear, since the woman in labor was ready for a natural birth. For many, such childbirth is a shock, which requires additional attention to the woman from medical personnel.
Doctors advise that someone close to you be in this situation: husband, sister, mother, perhaps even a psychologist. A woman, being in a state of anxiety and fear, cannot always adequately assess situations. Therefore, a close person nearby is simply necessary, in particular, to remind you that this operation is important for the baby’s health, and worries here are unnecessary.
How is a planned caesarean section performed at 37 weeks?
With a planned caesarean section at 37 weeks, the woman in labor should be admitted to the maternity hospital at 35 weeks. In the morning, the intestines are first cleaned, the woman takes a shower, then enters the operating room. There, a urinary catheter is placed and an anesthetic is injected into the spinal canal; general anesthesia is less commonly used.
After loss of sensitivity, an incision is made in the skin and uterus, and the baby is removed. After this, the doctor manually separates the baby's place, examines the uterine cavity, and sutures the tissue layer by layer. The woman is then given a cold pack on her lower abdomen and transferred to the intensive care unit or intensive care unit. There they control:
- blood circulation (pressure, pulse);
- kidney function (measure the amount of urine);
- breathing;
- contraction of the uterus;
- the condition of the seam;
- discharge from the genital tract.
The next morning after the examination, the woman in labor is transferred to a regular ward, and if there are no complications, she is discharged to her place of residence for 7-10 days.
How the fetus develops
Outwardly, a baby at 37 weeks is, of course, not such a plump, rosy-cheeked little one as in the diaper advertisement, but he is also quite cute. The skin turns pink while still covered with a cheese-like lubricant, but its amount decreases. Subcutaneous fat accumulates, which will later provide energy for extrauterine life. There are hairs, their length is about 1 centimeter. But it is quite possible that even at 40 weeks you will meet a bald son or daughter. The nails on the hands reach the end of the phalanx of small fingers. The facial features have already been completely defined, and there is no need to guess whether the baby will look like mom or dad. The cartilages of the nose and ears have become dense.
As for the internal organs and systems, the work continues:
- the cardiovascular system is actively working, the small heart beats at a frequency of 140–160 beats per minute;
- the brain and spinal cord are already fully formed, movements are coordinated, the processes of nerve cells “mature”, becoming covered with an insulating myelin sheath in order to conduct nerve impulses as accurately as possible;
- the lungs are also formed, the alveoli (small bubbles in which gas exchange will occur after the baby is born) are covered with surfactant - an important substance that prevents them from “collapsing”;
- the organs of the digestive system learn to work, digesting particles of swallowed amniotic fluid, forming meconium - original feces;
- kidneys work, urine replenishes amniotic fluid;
- Ossification of the epiphyses of bones continues. The skull does not completely ossify for the longest time, this is what nature intended for the non-traumatic passage of the child’s head through the birth canal.
- little eyes are able to see light, ears are able to hear mother’s voice.
The child’s lifestyle can be characterized by a quote from the mole from the cartoon about Thumbelina: “We’ve slept, now we can eat. We’ve eaten, now we can sleep...” Only in our case, we replace “eat” with “suck a finger.”
Who needs surgery?
Surgical birth, named after the Roman Emperor Gaius Julius Caesar, does not involve the baby passing through the mother's birth canal. The child is born as a result of laparotomy and hysterotomy - incisions in the abdominal wall and uterine wall.
This method of delivery is sometimes life-saving. It is carried out urgently to save the lives of a woman and her baby if something goes wrong during the process of physiological childbirth or as a result of injury. Emergency caesarean section accounts for no more than 7-9% of all surgical births. The remaining share is allocated for planned operations.
A planned caesarean section always involves careful preparation, as a result of which the risks of complications are significantly reduced.
Indications for elective surgery may appear from the very beginning of pregnancy, or may become obvious only at the end of the gestation period. Therefore, the decision on the timing of the operation is made at different times.
For an emergency caesarean section, the issue of timing is irrelevant. It is carried out when there is an urgent vital need for it. The planned operation is carried out according to the indications provided for in the list of clinical recommendations of the Russian Ministry of Health. This list is regularly reviewed and adjustments are made to it.
Today it provides for the following situations:
- The pathological location of the placenta is low placentation with incomplete overlap of the internal os or complete placenta previa.
- Postoperative scars on the reproductive organ from cesarean section or other surgical manipulations on the uterus. Caesarean section is also recommended as the only delivery option if there is a history of two or more cesarean sections.
- Clinical narrowness of the pelvis, pathologies of the bones and joints of the pelvis, trauma and deformation, tumors of the pelvic organs, polyps.
- Pathological discrepancy of the bones of the pubic symphysis - symphysitis.
- Pathological position of the fetus. By the 36th week of pregnancy - pelvic, oblique, transverse. Also pathological include some types of presentation, for example, breech presentation.
- The estimated weight of the child is more than 3.6 kg and its position in the uterus is incorrect.
- Multiple pregnancy, in which the fetus closest to the exit is located in the breech position.
- Monozygotic twins (twins are inside the same fetal sac).
- IVF pregnancy with twins, triplets, and often singletons.
- Incompetent cervix, with scars, deformation, scars in the vagina left after a difficult previous birth, which took place with tears above the third degree of severity.
- Significant developmental delay in the baby.
- Lack of effect from conservative stimulation of labor during post-term pregnancy – after 41-42 weeks.
- Severe form and degree of gestosis, preeclampsia.
- The inability to push due to a ban on such an action in case of myopia, retinal detachment of a woman’s eyes, certain heart diseases, as well as in the presence of a kidney transplant.
- Long-term compensated fetal hypoxia.
- A bleeding disorder in the mother or baby.
- Genital herpes, maternal HIV infection.
- Fetal developmental anomalies (hydrocephalus, gastroschisis, etc.).
Relative indications for caesarean section
Obstetric conditions in which operative delivery is preferable:
- Scar on the uterus.
- Presentation of umbilical cord loops.
- Progressive fetal hypoxia.
- Somatic diseases of the woman excluding the period of pushing.
Diseases of the cardiovascular and pulmonary systems in the stage of decompensation, high myopia, minor hemorrhages in the retinal vessels, epileptic seizures, etc.
- Large uterine fibroids.
- Bicornuate uterus, transverse septum in the uterine cavity and other developmental anomalies.
- 41-42 weeks of pregnancy in combination with the unpreparedness of the birth canal for childbirth (lack of effect from induction of labor).
- Pregnancy resulting from the use of high reproductive technologies in combination with a long history of infertility.
- Aged primigravida.
- Regional placenta previa.
- The estimated fetal weight is more than 4000 g according to examination data in combination with the first degree of pelvic narrowing and intrauterine hypoxia.
- Multiple pregnancy with incorrect position of one of the fetuses, with a combination of breech presentation in the first fetus and cephalic presentation in the second, conjoined twins, three or more fetuses.
- Combination of breech presentation of the fetus with:
- extension of the head (difficulties may arise when passing the fetal head);
- fetal weight exceeding 3500g;
- the location of the placenta in the fundus (normally, the pacemaker in the uterus is located in the fundus, so fundal placentation can reduce the impulse of the rhythm, which can lead to the development of weak labor);
- intrauterine fetal hypoxia;
- male sex of the fetus (the development of a birth tumor on the boy’s genitals cannot be ruled out. In addition, with excessive stimulation of the reflexogenic zones of the perineum, reflex activation of the fetal respiratory center can occur. This condition is dangerous due to intrauterine aspiration (swallowing) of amniotic fluid and the development of fetal asphyxia during the pushing period of labor ).
Absolute indications for elective surgery
Conditions for which only surgical delivery is indicated:
- complete placenta previa;
- oblique and transverse position of the fetus;
- narrowing of the pelvis 3, 4 degrees;
- pelvic tumors that interfere with the birth process;
- some fetal anomalies (gastroschisis, hydrocephalus and others);
- reconstructive operations on the perineum with the installation of mesh implants;
- varicose veins in the perineal area;
- gross cicatricial deformation of the cervix after operations (for example, after electroconization);
- developmental anomalies of the pelvic ring;
- removal of a large number of myomatous nodes in the anamnesis (for multiple uterine fibroids);
- signs of scar failure according to ultrasound (thinning of scar tissue, appearance of niches more than 3 mm deep);
- history of suturing 3-4 degree perineal tears;
- elimination of fistulas of the genitourinary system before pregnancy;
- technique of corporal cesarean section (longitudinal incision on the uterus) in previous surgical births;
- rotation of the placenta, diagnosed according to ultrasound diagnostics.
Caesarean and natural childbirth: differences between children
Children born by caesarean section are no different from children born through normal childbirth. Neither in development nor in appearance, such children will differ from each other. However, there is still a small nuance. During natural childbirth, the child gradually adapts to his new life and condition. And children born through Caesarean section were deprived of this opportunity. It is for this reason that such children are more likely to suffer from colds and are more susceptible to allergic reactions. Therefore, if there are no contraindications, then it is better to give birth naturally.
Note that a caesarean section can be performed at any stage, depending on the condition of the mother and fetus. But, nevertheless, there are a number of indications that cannot be ignored. These include the following: