The 6th month of pregnancy marks the beginning of the 21st week of gestation and the end of the second trimester. At this moment, the mother's appearance changes dramatically. The abdomen becomes many times larger, fetal movements are regular. It is by the tremors that you can determine the condition of the child - the more intense and painful they are, the higher the risk of intrauterine oxygen starvation.
From the second half of the 6th month, a pregnant woman may experience late toxicosis or gestosis. A condition with characteristic disorders in the form of arterial hypertension and nephropathy.
Symptoms
With the beginning of the 21st week of gestation, the pregnant woman begins to experience various signs and symptoms, sometimes of an unpleasant nature:
- Reflux esophagitis - heartburn. The uterus puts pressure on all internal organs and puts pressure on the stomach. Its acidic contents sometimes flow into the lower esophagus. In some women, heartburn continues for a long time, and as the period increases, the condition worsens. Acid entering the esophagus causes discomfort and makes it difficult to swallow food. To get rid of heartburn, you need to review your diet and identify foods that provoke the development of reflux.
- Constipation is another “fate” of pregnant women. A difficult act of defecation not only brings discomfort and pain, it can cause the development of hypertension or cause premature discharge of amniotic fluid. Constipation is complicated by hemorrhoids. You can get rid of this unpleasant illness by adding fiber-rich foods and lactic acid products to your daily diet. In severe situations, rectal glycerin suppositories are used.
- Edema. No pregnant woman is protected from edema. The appearance of edema is associated with an increase in the volume of circulating blood. Lymphatic fluid leaks through the blood vessels and into the surrounding tissue. Edema is a rather dangerous phenomenon, indicating the inability of the kidneys to filter and remove metabolic end products.
- Increased urination and pain in the lumbar region due to pressure on the spine.
- Dyspnea. The symptom is associated with impaired respiratory function due to pressure on the lung tissue. At 6 months of pregnancy, shortness of breath develops after long walks or excessive physical activity. At 24 weeks, the fetus may change its position and rest against the lower part of the lungs with its legs or back. The more closely it adheres to the lungs, the more pronounced the symptoms of shortness of breath.
- Dizziness is associated with anemia, which is a common companion of gestation.
- Chronic fatigue. It may be a consequence of lack of sleep due to snoring and difficulty in nasal breathing.
- The most unpleasant symptom is excess weight. A woman in an interesting position should not gain a large number of kilograms. By 23-24 weeks, her weight should increase by no more than 5-6 kg, however, most pregnant women complain of increased appetite and do not adhere to the principle of proper nutrition. The way out of the situation is to include fasting days and follow a “pregnant” diet.
- Skin irritation. Increased sensitivity of the skin causes dryness and cracks. Sometimes a pregnant woman cannot wear certain clothes, which make her body itch and itch.
Symptoms may not bother the woman, but may be accompanied by other signs.
Despite a calmer hormonal background, women are concerned about the endocrine system, pancreas and nervousness.
How does the expectant mother feel?
The changes in the body not only of the fetus, but also of the mother are very significant. A woman at six months of pregnancy begins to experience new sensations that appear in connection with physiological processes. Changes in the body include the following:
the size of the tummy increases, it looks more rounded, in accordance with the size of the uterus;- movements become constant and usually intensify while the baby is awake;
- there is leucorrhoea - discharge from the female genital tract;
- the ligamentous apparatus becomes more strained, because it supports the enlarging uterus. This may manifest itself as nagging pain in the lower abdomen and simply not very pleasant sensations;
- dyspeptic symptoms occur . They are associated with the pressure of the uterus on nearby internal organs. Intestinal motility is often impaired and, as a result, constipation may occur;
- the amount of circulating blood increases, which is necessary for transporting nutrients and oxygen to the fetus. This is done through the vascular system of the placenta. An increase in this volume can lead to nosebleeds or bleeding gums;
- hormonal changes lead to changes in the functioning of the sweat glands, and sweating often increases even with a slight increase in air temperature;
- The skin also changes, especially in the abdominal area. Pigmentation may appear, itching and flaking may be present, and stretch marks may form. Usually everything returns to normal after childbirth, but to prevent stretch marks you should use special creams that moisturize the skin well;
- the breasts fill up and become a little larger in size. The shape of the nipple may also change;
- Swelling of the lower extremities may occur, especially in the ankle area, so it is very important to monitor the amount of fluid consumed;
- A woman's emotions can also change. Often the mood does not change, but anxiety, fear of childbirth, etc. may appear. The expectant mother begins to worry about how the baby is developing, about his health, and listens to his every move.
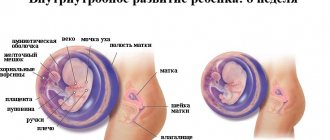
How the fetus develops
By the beginning of the 6th month of gestation, the organs and systems of the fetus are working at full capacity. The baby provides itself with oxygen and necessary elements supplied with the blood.
He is able to blink, touch his face and umbilical cord with his hands. The hearing organs are fully formed, so future humans can hear and respond to external sounds.
Movements become more thoughtful and meaningful.
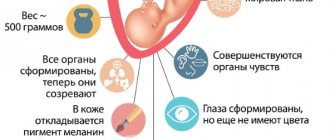
The weight of the fetus at 23-24 weeks of gestation averages 700 g, height reaches 28-30 cm.
Motor activity is recorded by the mother. At this stage, the baby is already able to identify voices and external touches.
Congenital reflexes become more perfect, the baby can swallow amniotic fluid, suck fingers and hiccup.
The nervous system and brain are actively developing. The formation of convolutions and gray matter occurs. Brain activity is recorded on the monitor screen of ultrasound equipment.
At this stage, the heart muscle is also clearly visible.
The baby is quite thin, but only because there is no fat layer, which appears a little later.
Despite a large number of skills, a child will not be able to survive in extrauterine conditions. His pulmonary system is underdeveloped. The lungs are not included in the breathing process.
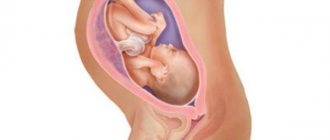
Belly at 6 months pregnant
The figure of the expectant mother has changed significantly since the beginning of her pregnancy. The waist has smoothed out somewhat, movements have become smoother. Now you can't hide your belly. It began to resemble a soccer ball. Urgently update your wardrobe, don’t constrain yourself and your baby. Choose loose dresses made from natural fabrics (cotton, linen, wool). After all, when, if not now, can one show all the femininity and beauty of the situation.
We recommend 1 month of pregnancy
From now on, you will really gain weight, and rapidly. On average - 500 g every week. There is not only active growth of the fetus, but also the muscle mass of the uterus. Don't worry about how quickly your size increases; the weight will be distributed evenly. Over the entire period of pregnancy, the total gain at this stage will be 5-8 kg. If it is more, it is better to tell the doctor about it, because in the future, excess weight can lead to gestosis (excessive swelling) and complications during labor. The doctor will select the right diet. But under no circumstances go on a diet on your own; do not risk your child’s health.
Photo
photo: babycenter.com
- If it is a boy, his testicles will soon begin to descend into the scrotum, a process that will take 2-3 months.
- The baby inhales and exhales amniotic fluid, preparing the lungs for the first breath of air.
- It is more sensitive to sound. The nerve endings in the baby’s ears are already much better developed than before.
- Does your back hurt? Thank your shifting center of gravity and the hormones that weaken your joints and ligaments.
Ultrasound
If the expectant mother has not yet undergone a 5 month ultrasound, the time to do it is now. It's better to do it before 22 weeks. The purpose of the examination at this time is to identify abnormalities in the development of the fetus (if any), to assess the condition of the amniotic fluid, placenta and uterus. And find out the gender of the child.
Changes in a woman's body
Compared to the modification of a baby, the female body undergoes fewer changes.
The uterus, increasing in size, occupies a third of the free space. At the 6th month, the abdomen becomes rounded and rises towards the solar plexus.
Sometimes a pigmented strip appears. Increases hair growth in unwanted places.
Skin pigmentation continues. Sometimes, at 21-22 weeks of gestation, condylomas and papillomas form on the genitals and the backs of the hands. A pregnant woman is often bothered by itching of the mucous membranes, and in the presence of chronic diseases, a period of their exacerbation is observed.
The female body consumes large amounts of calcium, which is used to build and strengthen the skeletal system of the fetus. Externally, this manifests itself as the destruction of tooth enamel, the development of caries and lamination of the nail plates.
Positive effects of nutrients in foods for pregnant women
Why is it important to include dietary foods containing calcium? This will help form the baby’s bone skeleton and prevent calcium deficiency in the mother’s body. The healthiest food is low-fat dairy food, broccoli. Due to the pressure of the enlarged uterus on the digestive organs of the abdominal cavity, heartburn or constipation may occur. These conditions cause discomfort in pregnant women. A proper diet can relieve these symptoms.
To counteract heartburn, you can use it in food: jelly, potato juice, oatmeal. They have a protective effect on the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract and prevent the aggressive effect of hydrochloric acid on the walls of the esophagus. For heartburn, it is advisable to use these products at every meal. This will lead to a reduction in abdominal discomfort.
Constipation is caused by impaired mobility of the digestive tract. You can improve your mobility by eating fiber-rich foods. These are, first of all, vegetables and fruits. To preserve their beneficial properties, you need to consume them raw. In addition to fiber, pregnant moms will get vitamins and minerals.
Analyzes and research
Mandatory research parameters remain unchanged:
- measuring the weight of the expectant mother;
- size and volume of the abdomen;
- detection of edema in the lower extremities;
- blood pressure measurement.
The patient is not examined on a gynecological chair, but if there are grounds, a smear is taken without the use of vaginal speculum.
The heartbeat is determined with a stethoscope. CTG is performed rarely, and only from 24 weeks.
A routine ultrasound is performed to identify malformations and determine external parameters (height, weight, size of limbs).
In addition to general diagnostics, uteroplacental blood flow is assessed using Dopplerography, and measurement of the uterine isthmus.
Laboratory tests are mandatory:
- detailed blood test;
- general urine analysis, and in case of increased urination, analysis according to Zimnitsky;
- blood biochemistry: urea, creatinine, glucose, total protein;
- transaminases and blood diastase;
- serum iron and ferritin;
- blood test for hemolysins and Rh antibodies (if indicated);
- hemostasiogram with determination of D-dimer.
If necessary, hormonal studies and determination of thyroid hormone levels are added.
When primary signs of a threatened miscarriage appear, the patient is admitted to a hospital for prolongation of gestation.
What you can do
With the beginning of the 6th month of gestation, some bans on daily activities are introduced.
The following remain permitted:
- walking in the fresh air;
- wearing compression garments if there is a predisposition to varicose veins;
- additional intake of vitamins and iron.
From 23 weeks you can wear a prenatal bandage to support the abdomen and relieve stress on the spine.
At home, perform pregnancy exercises, train the vaginal muscles, or do yoga.
Visiting the pool is welcome, but you need to be careful not to get too cold and not “pick up” an infection in a public place.
Baby six months pregnant
By the sixth month, the child actually looks the way he will when he arrives in the outside world: all the systems and organs of the small body are functioning, the baby can already hear and distinguish sounds, makes sucking movements, holding a finger in his mouth, clenches and unclenches his fists.
In the sixth month, the baby’s brain continues to improve: grooves and convolutions are already visible on it, which continue to deepen and “draw out” more clearly. By the end of the month, the baby’s brain weight will reach 100 g.
The only organ that is not yet mature enough is the lungs: alveoli are still forming on them. But, at the same time, a surfactant is already being formed in the lungs - a substance that prevents them from sticking together when breathing, and the child himself is already beginning to make some kind of breathing movements. By the way, if it suddenly happens that the baby, for one reason or another, is born prematurely, at 6 months, doctors give more than 50% that the baby will survive - precisely thanks to sufficiently developed lungs.
Although the child’s eyes at this stage are still covered with film, he knows how to react to light and opens his eyes slightly. The baby's facial expressions are well developed: on an ultrasound you can see how the baby frowns, wrinkles his face, squints and moves his eyebrows.
The fetal body is still thin, but from this month the active accumulation of subcutaneous fat begins. By the way, the active period of growth during the month of pregnancy is replaced by intensive weight gain by the baby: every day he will gain about 10-12 g in weight, so in a month his weight will double, and sometimes even more.
The child’s bone tissue continues to strengthen, his nails are almost formed, and eyebrows and eyelashes have appeared. The baby has already chosen and follows a sleep-wake schedule, and in moments of special activity he is able to quite noticeably kick his mother from the inside. The child reacts with particularly strong movements to loud and sharp
sounds, his movements can become more active against the background of the mother’s excitement - due to the increased amount of adrenaline in the female body in this case.
The baby is now curled up, he is reliably protected by the placenta and amniotic fluid. Amniotic fluid is renewed every 4 hours, it keeps the baby afloat, creates a barrier to negative factors and smooths out possible tremors, maintaining a comfortable temperature. From time to time, the child swallows amniotic fluid, draws it in, “developing” the lungs.
By the end of the month, the baby’s height will be about 30-35 cm, and the weight can even reach 600-700 g.
What is prohibited and restricted
The “equator” of pregnancy is characterized by an increase in time restrictions and prohibitions.
Weak immunity can fail and a pregnant woman increases the risk of contracting colds or flu infections. If the epidemiological situation worsens, you should not visit crowded places, or you should use personal protective equipment - a medical mask.
After visiting the street, wash your hands with soap, wash your face and rinse your nasopharynx with saline solution.
The consumption of alcohol and nicotine is an absolute prohibition. As well as taking medications without consulting an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Also not recommended:
- lift weights more than 5 kg;
- engage in active sports;
- ride a bike;
- overwork;
- disrupt nutrition and drinking regime.
Studies have shown that following recommended restrictions reduces the risks of placental previa and placental abruption.
Nutrition
A woman in an interesting position at 24 weeks of gestation needs more natural microelements and vitamins.
Her diet should contain the following products:
- low-fat varieties of fish for the development of the baby’s central nervous system;
- dairy products, especially cottage cheese, to replenish calcium loss;
- fruits with vitamin C and ascorbic acid to support immunity;
- beef – baked or boiled.
Prohibited foods: flour, chocolate, coffee, smoked products. Restrictions remain on salt and liquid.
The daily calorie requirement increases to 4000.
Sex
Sexual intimacy is possible only if there are no contraindications to it. For example, the threat of miscarriage, uterine tone and fetal presentation are contraindications to intimacy.
If there are no restrictions, it is important to choose a comfortable position for both partners and reduce the intensity.
Sex does not harm the health and development of the fetus, but if unpleasant symptoms and painful sensations appear during sexual intercourse, it is a reason to stop intimacy.
Dangers
A complication of pregnancy is associated with a violation of the isthmic-cervical blood supply. The child lacks oxygen and his development is disrupted. This condition is diagnosed by external signs and ultrasound results.
At six months of gestation, fetal fading or late miscarriage may develop.
Intrauterine death or genetic disorders incompatible with life are eliminated by stimulating artificial labor.
Changes in the nature of the discharge are the primary signs of pathology.
Various infectious processes and the presence of intrauterine infection worsen the course of pregnancy. A woman needs to be attentive to the well-being and condition of her own body.
Signs of an ectopic pregnancy
At 6-7 weeks, an ectopic pregnancy may become apparent. The name itself suggests that this is a pregnancy when the fertilized egg is not in the uterus. It may be in the fallopian tube, abdominal cavity, or cervix. Tubal ectopic pregnancy is the most common of them.
The main signs of the likelihood of an ectopic pregnancy are severe pain in the lower abdomen. Usually they are localized on one side, depending on which tube the fertilized egg is located in. Such pain is always accompanied by bleeding. They are not always abundant, it all depends on the size of the embryo and its location in the tube (its wide or narrow part).
Regular test strips can also indicate an ectopic pregnancy. When the embryo attaches outside the uterus, the hCG hubbub is released in smaller quantities than during a progressive uterine pregnancy. A regular pregnancy test, even at 6 weeks, may show a pale second line, which indicates a low hCG level. A more accurate result can be obtained by donating blood for hCG. Normally, at the 6th week of pregnancy, this figure should be in the range of 10,000-30,000 mIU/ml.
The most accurate way to diagnose an ectopic is an ultrasound examination. Using an ultrasound machine, a specialist can easily determine the location of the fertilized egg, be it the abdominal cavity or the fallopian tube.
If a woman has bleeding or brown discharge, even in small quantities, accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, it is imperative to rule out an ectopic pregnancy by undergoing an ultrasound.