Ticks are small arachnids, the average size is only half a millimeter! They become more active during the warm seasons of spring and summer; dry and hot weather means an increased risk of being bitten. The danger of ticks is that they carry viruses that are deadly to humans. For example, Lyme disease, tick-borne encephalitis, tick-borne typhus, tularemia, ehrlichiosis. We have collected photographs of what tick bites look like on a person’s body so that you can recognize the enemy by sight. We will also give advice on how to protect yourself and your family, and how to remove the parasite from the victim’s skin after a bite.
What is the danger of ticks
Being the cause of infections dangerous to human health, they can cause serious diseases, one of which is tick-borne encephalitis, which affects the nervous system; it can lead to severe disability and even death.
However, not every insect is dangerous; only 10-15% of individuals are carriers of the virus. But no less dangerous are borreliosis, granulocytic anaplasmosis, and monocytic ehrlichiosis, which are also caused by ticks. In addition, in different regions, ticks are the cause of infectious diseases such as spotted fever, hemorrhagic fever, typhus, etc.
The causative agent of the disease is transmitted in the first minutes after suction along with saliva, which has an analgesic effect. By the way, as research by Belgian scientists from the Free University of Brussels has shown, the saliva of bloodsuckers has amazing properties: after fixing on the skin, anti-inflammatory substances enter the human body with saliva that can “deceive” the human immune system, substances that prevent clotting: the blood remains liquid. The tick can feed for hours and even days, while it is virtually invisible to the human defense system.
When do symptoms appear after a person is bitten by an infected tick?
The incubation period for many insect-borne infections can range from a few days to a month. For example, symptoms of borreliosis, erchiliosis, hemorrhagic fever can be noticed in the first 2 weeks after infection. And tularemia – after about 3 weeks.
In order to begin treatment on time, the tick is examined in laboratories, while the bitten person is under observation, body temperature is measured every day, and the skin is examined.
Where can you find a tick?
These small insects have an excellent sense of smell and can sense their prey from 10-30 meters away. They can wait for a person in tall grass or low bushes. Most often they concentrate on paths or forest paths, they are attracted by the smell of animals and animals that move along them. However, a walk even within the city will not protect you from an attack: often a person, after spending five minutes on the street, discovers an uninvited guest on him.
In addition, a person can become infected without even leaving home. The parasite can be carried by pets, as well as by people - on clothes, with flowers, etc. The existing opinion that ticks “jump” on humans is not true. In fact, a tick clinging to clothing crawls upward. It is found most often on the upper parts of the body; hence the impression that he fell from above.
Where is the bite usually located?
Favorite places on the body for ticks are areas with delicate skin and a developed capillary system: the groin and abdomen, lower back, chest, neck, armpits, ears. An attached tick can stay on the human body from several minutes to several days. Unfortunately, a person does not feel the moment of the bite, since the tick secretes a special substance that prevents pain. Some time after suction, the tick, which has already drunk blood, takes on a rounded shape and a grayish color, and has also significantly increased in size.
Features of ticks dangerous to humans
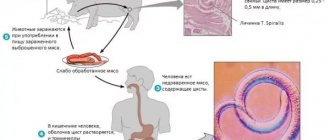
There are more than 40,000 species of ticks in nature. Among them, the most dangerous to humans are blood-sucking ixodid ticks. They resemble small brown bugs with four pairs of legs and a proboscis (the size of a hungry individual is about 5 mm; a saturated tick usually increases significantly). During a bite, pathogens of infectious diseases enter the human body along with the saliva of the tick.
However, not all ticks are carriers of infections. Many of them are sterile, that is, they do not contain viruses and bacteria dangerous to humans (the number of infectious and non-infectious ticks varies depending on the region). But since it is impossible to determine by the appearance of a tick whether it is infected or not, you must always remain vigilant.
Both female and male arthropods bite people. This usually happens after the end of a long autumn-winter hibernation - ticks wake up and need blood. Their food source can be both animals and humans.
The hunt for potential food occurs in the following way: the tick, using hooks on its legs, climbs onto blades of grass or sticks sticking up and waits for a victim, if one appears; the arthropod grabs it with its front legs and begins to look for a place suitable for a bite. Those people who think that a tick can fall on its head from a tree are mistaken; these animals cover no more than 10 m of distance in their entire lives and certainly do not climb trees. They can be found on the neck and head only because, once on the human body, they always move upward in search of an open and “juicy” area of skin.
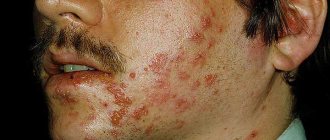
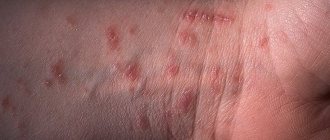
What does a tick bite look like?
And although the bite does not cause pain, a local allergic reaction develops; This is what a person pays attention to first of all. At the site of the bite, redness appears, having a round shape, its diameter does not exceed 1 cm. The color can vary from pinkish to dark red, depending on the intensity of the allergic reaction.
In addition to redness, the bite site can be easily recognized by swelling on the skin. Often a bloodsucker can be found attached to the spot on top of the spot. In addition, itching and burning appear - they can bother a person for a week. In some cases, local manifestations on the skin appear after a couple of days. However, with tick-borne typhus, the first sign of a bite will be a blister at the site of infection, which later turns dark red.
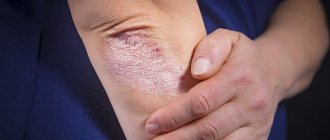
Borreliosis
The site of a tick bite that transmits borreliosis looks characteristic; There is also another name for the disease - Lyme disease. In this case, a spot-like erythema appears, the size of which can reach 10-20 cm, although there are cases when the spot in diameter reached 60 cm. After some time, a red border appears along the contour of a round, oval or irregular-shaped spot, the center of the erythema may be white or bluish in color.
Gradually the color becomes less intense and the stain becomes crusty. Then a scar is formed, which disappears without a trace after two weeks. However, after a month and a half, signs of damage to the nervous system, joints, and heart appear.
However, often there are no manifestations at all. Due to the fact that the bite is painless, a person may not notice the insect attack. If there are no pathogens of dangerous diseases in the tick’s saliva, then a person will never know about the incident, not attaching much importance to minor redness, itching or swelling.
Dangerous diseases after the bite of an infected tick in a person
About 20% of blood-sucking arthropods are carriers of infectious diseases. Ticks infect the following infections:
- encephalitis;
- borreliosis;
- erchiliosis;
- spotted fever;
- tularemia;
- tick-borne relapsing fever.
The most dangerous and most common of these diseases are encephalitis and borreliosis.
The symptoms of encephalitis are similar to the flu, so they often try to cure it on their own. But due to such treatment, which does not lead to improvement, encephalitis is recognized and diagnosed at the last stage, when the nervous system is affected.
Interesting! Encephalitis can be contracted not only from a tick, but also by consuming milk from an animal that carries the infection. In this case, the internal organs are affected first, and then the brain.
Borreliosis is not such a serious disease. Antibiotics are prescribed to treat it. Since this infection has a long incubation period, patients often do not remember the tick bite. To prevent the development of pathology, it is necessary to take it for examination immediately after removing a tick from the skin.
Immediately after the diagnosis of borreliosis is made, treatment begins, regardless of whether the patient has symptoms. Untreated borreliosis becomes chronic and leads to death.
The bite mark of a tick that carries borreliosis differs from an uninfected one in the following features - a painful donut-shaped lesion - erythema. Pressing the muscle causes pain.
The disease manifests itself at the initial stage with problems with the respiratory system, headache, and poor health. Treatment is carried out at home.
What determines the symptoms after a tick bite?
Each person's reaction to a bite is individual. Some won't even notice, others will experience discomfort for several days. How can you explain such different symptoms?
More intense manifestations occur in children, the elderly, as well as in allergy sufferers or patients suffering from immunodeficiency conditions. By the way, parasites that are not carriers of infection can pose a danger. Tick suction can cause an allergic reaction, sometimes in the form of Quincke's edema. With rapidly developing swelling of the face, lips, and tongue, without the help of doctors, a person is in serious danger.
In addition, the manifestations are influenced by the state of health: in a weakened person the reaction will be more violent. However, the type of tick itself and the duration of its stay on the body are of no small importance. After being bitten by an insect that carries infectious diseases, even the absence of a local reaction on the body does not guarantee that infection has not occurred.
What should you pay attention to after a tick bite?
After infection, the first symptoms usually appear within two weeks. However, the latent period can vary from one day to two months. If up to this point a person has not consulted a doctor, then the presence of the following signs is a reason for an immediate visit to a specialist.
- Temperature increase
- Headache
- Decreased blood pressure and increased heart rate
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Skin rashes, itching, swelling
- Chills, aching joints
- Difficulty breathing, shortness of breath
- Drowsiness, muscle weakness, increased fatigue
- Lack of appetite, nausea, and even vomiting
- Photophobia
- Sensitivity disturbances in any part of the body, hallucinations, etc.
Thus, the manifestations can be very different, and the difficulty is that the above symptoms may resemble other diseases. Therefore, only a doctor can identify the cause of the ailment. In case of a tick bite, self-medication can lead to serious consequences; if the outcome is unfavorable, paralysis, paresis, speech impairment, etc. are possible.
Dangerous symptoms
The first symptoms may appear 2–4 hours after a tick bite:
- drowsiness;
- chills;
- muscle and joint pain;
- photophobia.
If the victim’s body reacts very strongly to the tick’s saliva, then the following signs are possible:
- fever;
- chills;
- headache, dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- swelling;
- lack of coordination.
If such symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a doctor.
One of the main signs of a tick bite is an increase in body temperature to 37–38 °C. This indicates that an infection has entered the human body. Most often, the temperature rises in the first hours after the bite, but this can also happen after 7-9 days.
One of the symptoms of a tick bite is an increase in temperature to 37–38 °C
Signs of a bite in children and pregnant women
Signs of a tick bite in children are somewhat different. The main indicators are:
- red spot (erythema) ranging in size from 7 mm to 1 cm;
- increase in body temperature to 37–37.5 °C.
Symptoms develop 5–6 hours after the bite:
- weakness;
- drowsiness;
- chills.
If such symptoms are detected in a child, you should immediately go to the hospital.
Symptoms in pregnant women are also somewhat different. Within 3–4 hours after the bite, the expectant mother may experience the following signs:
- temperature rise to 38 ° C;
- tachycardia;
- slight decrease in blood pressure;
- headache;
- weakness;
- photophobia.
What to do if you are bitten by a tick?
First of all, if you find an attached tick, remove it immediately. However, this must be done very carefully, without breaking the proboscis, with which the parasite is firmly and deeply strengthened for the entire time of suction. It is unacceptable to crush or pull out a tick with force. Otherwise, infection is inevitable. Today there are special devices on sale; if you live in a disadvantaged region, it makes sense to purchase this device in advance.
How to extract correctly
If it is not available, you can use manicure or medical tweezers. Holding it perpendicular to the bite site, you should carefully grab the body of the parasite, then carefully rotate the tweezers around the axis until the tick is removed. If you don’t have tweezers at hand, you can remove the tick using a regular thread: make a loop, put it around the proboscis near the skin, tighten or twist it in one direction and, using a rotating motion, slightly pulling it up, carefully pull the tick out.
Try not to crush the parasite, as this can infect the wound; meanwhile, the tick may not have had time to excrete anything yet. You can also use two matches; in extreme cases, you can remove the tick with your hands, wrapping it with a piece of bandage. Avoid using oil to remove ticks; even if he crawls out on his own, time will be lost, and such an individual may not be taken for analysis.
After removal, the wound should be treated with a disinfectant: iodine, alcohol, etc. If a black dot still remains, which means the head or proboscis is torn off, then treat the area with iodine. You should not pick at the wound, trying to remove fragments: this can worsen the situation.
After removal, wash your hands thoroughly with soap. Now all that remains is to place the culprit of the incident in a hermetically sealed container and submit it to the laboratory. Remember, a live tick must be delivered for examination within two days. To maintain its viability, you can place a damp cloth in the container. Some laboratories accept dead individuals and even fragments of their bodies for analysis, but the diagnostic accuracy in this case is much lower.
You can also remove a tick at a trauma center or at a clinic at your place of residence. However, when attacked by a tick, it is important to get rid of it quickly, and finding a suitable facility and traveling there may take some time.
What to do after a bite
You can submit the parasite to an accredited laboratory to identify infectious agents. To make sure whether a particular medical institution accepts ticks for analysis, it is better to first contact by phone. The list of institutions can be found on the Internet pages of the territorial administration of Rospotrebnadzor.
During the first two weeks, you should monitor your health status. If one of the above symptoms appears, you should immediately consult a doctor. By the way, today you can undergo examinations that allow you to detect tick-borne infections with high accuracy. For example, the ELISA method can detect specific immunoglobulins produced by the immune system in response to infection. Using PCR, fragments of the genetic material of the infectious agent can be detected in biological material.
If bitten by a tick: first aid and further actions
Stages of first aid for a parasite bite:
- Remove the tick.
- Wash the wound with soap and water.
- Treat the bite site with an antiseptic.
- Take an antihistamine (as needed).
- Seek qualified medical help.
Ticks are carriers of many diseases.
The sooner a tick is removed from the body, the less likely it is to become infected with dangerous diseases . Prompt action to remove the parasite increases the chance of avoiding its infected saliva from entering the body.
The more saliva of the pest penetrates the skin, the higher the likelihood of developing an infection.
Another reason why it is necessary to get rid of the parasite as soon as possible is the risk of an allergic reaction. It rarely appears, but can be severe.
It must be remembered that providing first aid will not help destroy the infection that has already entered the blood. Therefore, at the first opportunity, even if the parasite is successfully removed from the surface of the body, you must seek qualified medical help.
Removing the tick
When removing a tick, you should act extremely carefully and take your time. Movements should be smooth: rocking the pest with a slight upward pull of its body. Sudden movements are unacceptable, as they can lead to the parasite being torn and its head remaining in the wound. Under no circumstances should you squeeze the tick too hard to avoid crushing it. To date, cases of infection as a result of such actions are known. In this case, toxic substances from the insect’s body fill micro-wounds in the skin.
To remove the pest, you can use tweezers or thread, folding it into a loop. The parasite is captured close to the skin so as not to rupture it during the extraction process. There are also special devices for these purposes: a lasso handle, various twisters.
To remove a tick accurately, you must use the tools correctly.
Washing the wound
After removing the parasite, it is necessary to wash the wound in order to mitigate the body’s reaction to the bite at the site of injury. This action is necessary, but ineffective. Treatment of this kind will not completely eliminate the effects of the poison. However, in some cases, such measures can prevent the appearance of a blister.
Antiseptic treatment
The next mandatory procedure is antiseptic treatment. As such a tool you can use:
- alcohol or alcohol solutions;
- hydrogen peroxide;
- Miramistin;
- celandine juice.
The wound at the site of the bite is small and heals quickly, so a single treatment with this product is quite enough.
Taking antihistamines
An antihistamine should be taken if you notice that the bite area is red or a rash appears. Any drugs you have on hand will do:
- Suprastin;
- Ebastine;
- Loratadine.
Loratadine is one of the most popular antihistamines.
Although allergic reactions in this case are extremely rare, they pose the greatest danger at first. It is necessary to urgently call an ambulance if the rash grows and becomes similar to hives.
What to do with a tick
Remember that the tick must be preserved and delivered to the laboratory (preferably alive). To do this, after removing the parasite, you need to place it in a sealed glass container and close it tightly with a lid. Some people recommend burning it right away or pouring boiling water over it, but in the laboratory, using polymerase chain reaction, they can determine whether the pest is infected with any virus. You will receive a response from the center within a short time: from a couple of hours to two days.
After removing the tick, it must be taken to the laboratory
Is it possible to prevent a tick bite?
The likelihood of a tick attack depends on the epidemiological well-being of the region. Every year, Rospotrebnadzor publishes lists of areas endemic for tick-borne encephalitis; unfortunately, such information is not provided for other infections. People whose work involves being in a field or forest, as well as in cases where they will be in places where ticks accumulate, need to be careful.
Rule #1 – clothing
When going for a walk, choose appropriate clothing. The shirt or jacket must have long sleeves, and the trousers must be tucked into socks. Don't forget about the hood or scarf, which serves to protect your head. It is better if the items of clothing are light in color: this way the parasite can be easily detected. By the way, it is better to choose clothes with a smooth texture: when a potential victim approaches, the tick climbs to a height of no more than half a meter and waits. His reaction is lightning fast: with paws equipped with suction cups and claws, he reliably clings to clothes.
The tick does not dig into the victim’s body with lightning speed; it travels for several minutes in search of a suitable place. While on a walk, make it a rule to inspect your outer clothing every hour to detect insects in a timely manner. When you return home, also do not forget to examine yourself and your loved ones.
What can't you do?
When following the sequence of first aid for tick bites, it is important not to take actions that could harm the victim. If you are bitten, do not do the following:
- drip oil or alcohol onto the insect. These tick removal methods are rarely effective;
- try to burn the body with fire. You can burn the insect, but the head will remain in the wound;
- grab the tick with your fingers, trying to tear it away from the skin. In this way you will either tear the head off the body or crush it;
- leave the parasite in place, ignoring the bite. The longer the duration of contact of saliva with the skin, the higher the risk of contracting an infection.
Rule No. 2 – repellents
The range of tick control products available today is incredibly wide. Depending on the active substance they can be divided into:
- deterrents - repellents,
- acaricidal - destroying,
- insecticidal and repellent - with a combined effect.
The protective repellent can be applied to areas of the body or clothing. Avoiding contact, the tick will try to crawl away. The drugs are available in the form of aerosols, creams, lotions: Raptor, OFF, DEET, Ultraton and many others. etc. There are also less toxic products for children: Fthalar, OFF-children, Kamarant, etc.
Acaricides are based on a drug that has a nerve-paralytic effect on ticks; upon contact with treated clothing, the tick simply disappears. However, these products are not intended for use on the skin as they are toxic. By the way, clothing processing is not carried out on humans. It is laid out, processed and only after drying is put on. As a rule, the protective properties last up to two weeks.
There are also preparations intended for treating areas or premises. If you are planning a picnic in nature, then you can take care of your safety in advance by spraying a pre-planned place.
Rule No. 3 – vaccination
Preventative vaccines are available for some infections (but not all). Primary vaccination is possible from the first year of a baby’s life, then at any age in the absence of contraindications. You can get vaccinated by visiting a medical facility. However, it should be noted that the vaccination course should be completed 2 weeks before a possible encounter with ticks.
If you have been vaccinated against tick-borne encephalitis, does this mean that ticks are no longer dangerous? Vaccination against encephalitis protects 95%, but only against this infection, but in no case against all diseases carried by parasites. Therefore, even if vaccinated, precautions should be taken.
What should you do if you are bitten by a tick, but there is no vaccination? For unvaccinated patients, immunoglobulin administration is recommended, but this must be done in the first three days after the bite. If it is impossible to use immunoglobulin (lost time, contraindications, cost), antiviral agents may be recommended, but their effectiveness is not one hundred percent.