Rabies: incubation period in humans, symptoms and diagnosis Rabies is an acute infectious disease caused by a virus that enters the human body when bitten by a sick animal or gets its saliva on the skin. Clinically characterized by severe damage to the nervous system. It is one of the most dangerous infectious diseases.
Without specific treatment - the introduction of a rabies vaccine - the disease is fatal. The sooner a person seeks medical help after a bite, the less likely they are to get sick. Let's get acquainted with the causes and signs of rabies in people, talk about the principles of its diagnosis and treatment, as well as how to avoid this dangerous disease.
Pathogenesis
The virus is unstable in the external environment - it dies when heated to 56 ° C in 15 minutes, when boiled - in 2 minutes. Sensitive to ultraviolet and direct sunlight, ethanol and many disinfectants. However, it is resistant to low temperatures and phenol.
The virus multiplies in the nerve cells of the body, forming Babes-Negri bodies. Viral copies are transported through neuronal axons at a rate of approximately 3 mm per hour. Reaching the spinal cord and brain, they cause meningoencephalitis. In the nervous system, the virus causes inflammatory, dystrophic and necrotic changes. Death of animals and humans occurs due to asphyxia and cardiac arrest. [adsense1]
Symptoms of rabies in humans
The incubation period of rabies ranges from 10 days to 3-4 (but more often 1-3) months, in some cases up to one year, that is, the virus can exist in the body without showing symptoms. In immunized people it lasts on average 77 days, in non-immunized people it lasts 54 days.
Isolated cases of extremely long incubation periods have been described. Thus, it was 4 and 6 years after immigration to the United States for two immigrants from Laos and the Philippines; The virus strains isolated from these patients were absent from animals in the United States, but were present in the regions of origin of the immigrants. In some cases of a long incubation period, rabies developed under the influence of some external factor: a fall from a tree 5 years after infection, an electric shock 444 days later.
The duration primarily depends on the location of the injury. The longer the virus has to get to the brain, the longer a person will remain outwardly healthy. In medicine, cases have been described in which the disease manifested itself even 4 years after the bite of an infected cow.
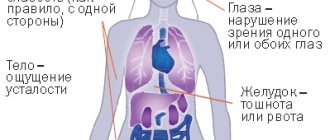
Rabies in humans goes through three stages of development, each of which manifests itself with different symptoms.
Main signs of ill health
The main problem is that although the incubation period usually lasts from 1 to 3 months, it can also be as short as 10 days or as long as one year. Symptoms of infection may be absent, and the full clinical picture appears already in the agony stage.
Special signs of rabies in humans, which appear at the very beginning of the disease:
- increased excitability,
- insomnia,
- redness and swelling of the healing scar,
- nagging pain, burning and itching at the site of injury,
- temperature increase,
- problems swallowing food.
Please note that signs of rabies in a person are a signal for immediate hospitalization. Every minute is precious! The development of “sores” in children occurs much more intensively than in adults. Also during this period, a person may be overcome by causeless fear, melancholy, and anxiety. This is the prodromal phase. The first signs are observed within 2-3 days, sometimes the phase drags on to 5-6 days.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is based on medical history: an animal bite or salivation of the skin. Then specific signs of rabies play a role: fear of hydrophobia, increased sensitivity to irritants (sounds, light, drafts), excessive salivation, attacks of psychomotor agitation with convulsions (even in response to the slightest movement of air).
Laboratory methods include the detection of rabies virus antigens in imprints from the surface of the cornea. A blood test reveals leukocytosis due to an increase in the content of lymphocytes. After the death of the patient, an autopsy reveals Babes-Negri bodies in the brain.
First signs
A person infected with rabies may experience cold-like symptoms in the early stages:
- the appearance of fever;
- headache;
- muscle pain;
- loss of appetite;
- nausea;
- prostration.
In the future, the symptoms will progress and you need to focus on the following signs:
- increased temperature after a bite (up to 40.5° C);
- delusional states;
- hallucinations;
- anxiety and agitation;
- cramps and tingling in the bite area.
If no changes are observed after the bite, you should consult a doctor : the animal could be a carrier of other infections and diseases.
How long does it take for them to appear?
Rabies has its own incubation period. Often, for the first signs of the disease to appear, it takes time - from 1 to 4 months . 10 days are enough for pathology to develop , and sometimes it takes a year to pass.
There is a known case where the period from the virus entering the body to the development of symptoms was 6 years. Such a long incubation period is explained by the fact that the virus moves through the body along nerve fibers and not through blood vessels, which significantly delays the manifestation of the clinical picture.
The timing of rabies manifestation also depends on the following factors:
- type of animal infected;
- amount of virus;
- immunity strength;
- localization of the bite (the most dangerous places are those with a wide network of nerve endings - hands, genitals, head).
Observations of the disease allowed us to identify 3 main phases of its course:
The development of the disease is not always unambiguous and does not always maintain exactly this sequence. There are cases when rabies debuted immediately from the third stage (paralytic rabies) or was limited to signs of only the second stage (furious rabies).
The prodromal stage (3 days) is characterized by a slight increase in body temperature (up to 37.3° C). The patient experiences inexplicable anxiety and sleep disturbances. The healed wound left by the bite begins to hurt.
In the peak stage (4 days), an increase in sensitivity is observed, and the muscles cramp. Hydrophobia and aerophobia arise. Patients are visited by a feeling of fear, they become irritable and aggressive.
At the final stage of paralysis (last days), the person is completely immobilized and asphyxia occurs.
Treatment of rabies in humans
Until 2005, there were no known effective treatments for rabies once clinical signs of the disease appeared. I had to limit myself to purely symptomatic means to alleviate the painful condition. Motor agitation was relieved with sedatives, and convulsions were eliminated with curare-like drugs. Respiratory disorders were compensated by tracheostomy and connecting the patient to an artificial respiration apparatus.
In 2005, there were reports that a 15-year-old girl from the United States, Gina Gies, was able to recover from infection with the rabies virus without vaccination, when treatment was started after the appearance of clinical symptoms. During treatment, Gis was put into an artificial coma, and then she was given drugs that stimulate the body's immune activity. The method was based on the assumption that the rabies virus does not cause irreversible damage to the central nervous system, but causes only a temporary disruption of its functions, and thus, if you temporarily “turn off” most of the brain functions, the body will gradually be able to produce enough antibodies to defeat virus. After a week of being in a coma and subsequent treatment, Gis was discharged from the hospital several months later without signs of being affected by the rabies virus.
However, rabies is incurable in its final stages. The probability of death if infected is 99.9%. [adsense3]
How to prevent the disease
Doctors never tire of repeating that prevention is the best protection against all illnesses. Within three days after the accident, an anti-rabies vaccination is extremely necessary for a person - side effects are rare, accounting for only 3%. Later administered immunoglobulin has no effect.
Important: For six months after vaccination, you should not visit the sauna or bathhouse, overwork, overheat in the hot sun, or drink strong drinks. Failure to comply with the regimen can provoke an imbalance of the immune system, further development of the disease, and lead to death.
When sending your children on vacation to a camp or to their grandmothers for fresh milk, be sure to teach them what to do if they are bitten by a tick or any other insect. Pay special attention to bites from unfamiliar dogs and cats.
To ensure that your beloved pet avoids negative consequences from unexpected contacts with other animals, do not ignore annual vaccination.
We wish you to be reasonably careful on vacation, and do not forget that even the cutest and most affectionate animals can be sick. It is better to admire them from afar, without trying to caress, stroke or pick them up. If contact with an animal does occur, contact a doctor immediately. Remember that signs of rabies in humans do not appear immediately. The rabies vaccine is the only way to stop the virus from progressing. Let your four-legged friends bring only joy!
Rabies (from Latin rabies; obsolete hydrophobia or fear of water) is the name of a deadly infectious disease caused by the rabies virus entering the human body.
Its carriers are animal carriers , which infect a person by biting, scratching or salivating (the infection is contained in saliva). In the old days, it was believed that a sick person was possessed by evil spirits, demons. This is where the name “rabies” comes from.
50,000 worldwide die from infection with the rabies virus .
Wild animals that can become carriers of rabies:
Pets can also become carriers of the virus:
- dogs;
- cats;
- agricultural animals.
There is a theoretical possibility of transmission of the virus from person to person through a bite (not confirmed).
Features of vaccination
Since treatment of rabies at the stage when symptoms appear is no longer effective, to prevent the spread of the virus, prevention of the disease is required by administering a special vaccine.
Rabies vaccinations are prescribed to humans in the following cases:
- if he was injured by objects on which there was saliva of an infected person;
- if he was attacked by an obviously unhealthy animal and received open injuries to the skin;
- if he has been bitten by wild rodents;
- if he was exposed to the saliva of a patient with a pathology such as rabies, a person, and in other cases when the saliva of the alleged carrier could get into an open wound;
- if he has scratches on his body resulting from contact with an animal, which died soon after they were inflicted for an unknown reason.
Rabies vaccinations are prescribed immediately, at regular intervals. They are carried out both on an outpatient and inpatient basis - depending on the patient’s wishes and the severity of the bites.
It should be remembered that vaccination can cause side effects, such as redness of the injection site, increased body temperature, dyspeptic disorders, and general condition. There are special instructions regarding rabies vaccination and alcohol intake - to prevent the development of post-vaccination complications, people are prohibited from drinking alcohol during the vaccination period and six months after it.
Let's start with history
From clay tablets to modern times
The first mention of a dog bite disease, very similar to rabies, is found on cuneiform clay tablets of Ancient Mesopotamia in the third millennium BC. [1].
The ancient Greek philosopher Democritus described dog rabies in the 5th century BC, and Aristotle did the same, but he believed that humans do not get rabies. Cornelius Celsus, ancient Roman scientist, in the 1st century AD. However, he noticed a similar disease in people and called it hydrophobia [2].
Starting from the 13th century, we have information about large epizootics of rabies in Europe. They probably broke out on other continents, since this disease is almost ubiquitous in the modern world.
Epizootic is an epidemic among animals.
And if you think that all this was a long time ago, and now the virus does not pose any danger, you are greatly mistaken: according to WHO data in 2007, it annually claimed the lives of 55 thousand people around the world [3]. That's about 151 deaths per day! Such a constantly high indicator speaks of human vulnerability; epizootics break out every year, putting the life of every person at risk. At the moment, cases of rabies infection are regular in more than 150 countries of the world, including Russia [4] (Fig. 1 and 2).
Figure 1. Global rabies risk assessment
WHO website
Figure 2. Rabies-prone regions of Russia, 2014 data signature
"World Rabies Day"
Prevention
Specific prevention is carried out by conducting a course of combined administration of rabies vaccine and rabies immunoglobulin after being bitten or salivated by an animal. After a bite, you should treat the wound and consult a surgeon.
Wound treatment is carried out as follows:
- wash the wound generously with boiled soapy water or hydrogen peroxide;
- treat the wound with iodine or 70° alcohol;
- suturing the wound, as well as excision of its edges, is contraindicated;
- Anti-rabies immunoglobulin is injected around the wound and into the wound itself;
- after 24 hours, anti-rabies serum is injected.
The first two points of treatment should be carried out at home, even before visiting the doctor; the rest is carried out by the surgeon.