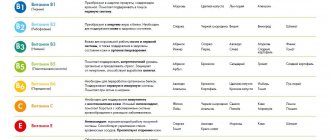
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin and is stored in the liver. Vitamin A is essential for your baby's embryonic development - including the development of the heart, lungs, kidneys, eyes and bones, as well as circulation, breathing and the central nervous system. It also helps the body fight infection and promotes normal metabolism.
Vitamin A is especially important for women who are about to give birth because it promotes postpartum tissue repair. It also helps maintain normal vision and protects against colds, flu and respiratory tract infections. Let's figure out what the dosage should be and what are the features of taking vitamin A during pregnancy.
What is vitamin A?
There are two types of nutrients:
- ready-made vitamin A (retinol);
- provitamin A (carotenoids).
Prepared vitamin A is used directly by the body and is found in animal products such as eggs, milk and liver. Provitamin A is found in fruits and vegetables, but your body must convert this type into retinol.
There are over 600 carotenoids found in nature, but only a few can be converted into retinol. Beta-carotene is the most common carotenoid.
The standard measurement of vitamin A is REA (retinol potency equivalent), which is based on the potency and source of vitamin A. One microgram (mcg) of retinol (formulated vitamin A) is equal to 1 mcg REA, and is also equal to 12 mcg beta-carotene or 24 mcg alpha-carotene. carotene.
An older standard of measurement that is still used (especially on food labels) is the use of International Units or IU. IU is quite difficult to convert to EAR because the conversion depends on the type of vitamin A, for example, EAR 900 mcg can be from 6,000 to 36,100 IU of vitamin A.
Why is it needed
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that is stored in the liver. Vitamin A is important for your baby's embryonic growth, including the development of the heart, lungs, kidneys, eyes and bones, as well as the circulatory, respiratory and central nervous systems.
Vitamin A is especially important for women who are about to give birth because it helps with the repair of postpartum tissue. It also helps maintain normal vision, fights infections, supports your immune system and helps in fat metabolism.
Retinol is an antioxidant that is essential for a healthy pregnancy. It is one of many nutrients that plays an important role in:
- helping the body maintain homeostasis;
- prevention of anemia;
- maintaining metabolism during pregnancy;
- maintenance and development of tissues (cell growth) during pregnancy;
- fetal development, especially bones, teeth, skin and vision.
How much vitamin A do you need (vitamin A dosage during pregnancy)?
Vitamin A norm during pregnancy:
- Pregnant women 18 years of age and younger : 750 mcg EAR per day.
- Pregnant women 19 years of age and older : 770 mcg EAR per day.
- Breastfeeding women 18 years of age and younger : 1,200 mcg EAR per day.
- Breastfeeding women 19 years of age and older : 1,300 mcg EAR per day.
- Non-pregnant women : 700 mcg EAR per day.
You do not need to get the recommended amount of vitamin A every day. Instead, try to use this recommended amount by averaging over several days or weeks.
Dosages and regimen
Preparations containing vitamin A are prescribed by specialists for therapeutic or preventive purposes.
Table. Vitamin A dosages.
| Patient category | Dosage, ME | |
| Adults | 5 000 | |
| Pregnant | 6 600 | |
| Nursing | 8 250 | |
| Pediatric patients | Up to a year | 1 650 |
| Preschoolers | 3 300 | |
| Pupils | 5 000 | |
| Therapeutic dosages for different degrees of vitamin deficiency | Adults | From 33,000 to 50,000–100,000 |
| Children | 1 000–20 000 | |
Can an overdose of vitamin A happen?
The normal human diet provides the body with large amounts of vitamin A. It is available in meat, dairy products, fish, eggs and fortified cereals as formulated vitamin A (retinol). It is also present in most fruits and vegetables, mainly in the form of carotenoids.
During pregnancy, it is important to avoid overdosing on prepared vitamin A, as it can cause birth defects and liver toxicity in high doses. However, you can get as many carotenoids as you want from fruits and vegetables.
Women age 19 and older (whether pregnant or breastfeeding) should get no more than 3,000 mcg EAR (or 10,000 IU) of prepared vitamin A from supplements, animal sources, and fortified foods each day. For women 18 years of age and younger, the upper intake limit is 2,800 mcg EAR (9,333 IU).
This is one important reason why it is not recommended to double your prenatal vitamin intake or take any supplements not recommended by your doctor. Most prenatal vitamins contain at least some vitamin A in the form of beta-carotene, but some multivitamins and fortified foods contain significant amounts of prepared vitamin A. Always check the product label or show all supplements to your doctor before taking them.
One more point . The risk of birth defects from consuming too much vitamin A is why pregnant women and those trying to get pregnant need to stay away from taking a drug called Isotretinoin and other retinol-related medications, including a topical product called Tretinoin. which is used to treat skin diseases.
Recommendations
We would like to give you some recommendations for the use of vitamin A during early pregnancy:
- be safe. It's best to avoid prenatal vitamins that contain any retinol form of vitamin A.
- Try to ensure that your daily vitamin A intake does not exceed 6,000 IU in early pregnancy (during the first 2 months).
- Avoid daily consumption of foods high in retinol, especially beef liver (43,900 IU/100 grams) and veal liver (22,500 IU/100 grams).
- Make sure your prenatal contains at least 3,500 IU of beta-carotene.
- Aim to get 4,000-5,000 IU of carotenes and carotenoids from your diet. You can do this by eating colorful vegetables such as carrots and green leafy vegetables.
- Eat brightly colored fruits.
- If you can't eat enough colored vegetables, find a good tasting vegetable powder that can provide you with 4000-5000 IU.
- Do your best to get enough vitamins and try not to worry.
Food Sources of Vitamin A
Beta-carotene-rich fruits and vegetables (especially orange and yellow ones, and leafy greens) are the best sources of vitamin A. You can also get enough prepared vitamin A from fortified milk and cereals.
Liver (from beef, veal or chicken, including pates and liverwurst) contains the highest amounts of ready-made vitamin A - so much so that you should limit your intake to one or two servings per month during pregnancy to ensure you don't get too much straightaway. An 85-gram serving of beef liver can provide more than eight times the recommended daily amount of vitamin A during pregnancy, thereby exceeding more than twice the safe daily intake!
Here are some good food sources of vitamin A:
- One medium yam (sweet potato): 961 mcg EAR (19,218 IU).
- 115 g canned pumpkin: 953 mcg EAR (19,065 IU).
- 100 g pumpkin, cooked: 572 mcg EAR (11,434 IU).
- 60 g raw carrots, chopped: 534 mcg EAR (10,692 IU).
- 75 g spinach, cooked: 472 mcg EAR (9.433 IU).
- 80 g cantaloupe: 466 mcg EAR (9.334 IU).
- 50 g kale, cooked: 443 mcg EAR (8,854 IU).
- 50 g kale, cooked: 361 mcg EAR (7.220 IU).
- 30 g fortified oatmeal: 215 mcg EAR (721 IU).
- One mango: 181 mcg EAR (3.636 IU).
- 240 ml skim milk (fortified with vitamin A): 149 mcg EAR (500 IU).
- 240 ml 2% fat milk (fortified with vitamin A): 134 mcg EAR (464 IU).
- 240 ml whole milk: 110 mcg EAR (395 IU).
- 1 tablespoon butter: 95 mcg EAR (355 IU).
- One large egg: 80 mcg EAR (270 IU).
- 90 g broccoli, cooked: 60 mcg EAR (1.207 IU).
Grinding, slicing or juicing, as well as heat treatment, allow carotenoids (provitamin A) to be more easily absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. You may also be able to absorb more if you eat a small amount of the oil (about a teaspoon) along with your fruits and vegetables.
Read more: 20 Foods Rich in Vitamin A: List of Vitamin A Foods.
Retinol in food
To provide a pregnant woman’s body with all the necessary substances, it is not necessary to take pills. Nutrients from natural foods are the most beneficial and are best absorbed. At the same time, many dishes on our usual table are sources of vitamin A.
- Food of animal origin. These are eggs and dairy products, fish oil. Particularly worth highlighting is whole milk. This also includes the kidneys and liver.
- Plant food . These are carrots, tomatoes, sweet peppers of orange and red colors, all types of cabbage, pumpkin. Various legumes also contain large amounts of beta-carotene. If we single out the leaders among fruits, they will be peaches, apples, and apricots. Seasonal fruits such as melon and watermelon also contain this vitamin. Sea buckthorn, rose hips, and cherries are also useful.
- Greenery . If pregnancy occurs in the summer, then you can add “greens” to your diet. This includes sorrel, nettle, fennel, and horsetail. However, these products can only be used on the menu without fanaticism.
The table below analyzes in detail the quantitative content of retinol in popular food products and the percentage of coverage of a pregnant woman’s daily requirement for vitamin A. The calculation is based on the content of the substance in 100 g of a particular product.
Table - Foods high in vitamin A
| Product | Vitamin A content, mcg | Percentage of daily allowance coverage for pregnant women over 19 years of age |
| Fish fat | 25000 mcg | 35714% |
| Turkey liver | 8000 mcg | 1038% |
| Beef liver | 8367 mcg | 1086% |
| Chicken liver | 3300 mcg | 428% |
| Sweet red pepper | 250 mcg | 32% |
| Carrot | 2000 mcg | 259% |
| Acne | 1200 mcg | 155% |
| Sweet potato | 1000 mcg | 129% |
| Broccoli | 386 mcg | 50% |
| Celery | 750 mcg | 97% |
| Spinach | 750 mcg | 97% |
| Butter | 450 mcg | 58% |
| Dried apricots | 583 mcg | 75% |
| Black granular caviar | 550 mcg | 71% |
| Green salad | 550 mcg | 71% |
| Quail eggs | 483 mcg | 62% |
| Red granular caviar | 450 mcg | 58% |
| Pumpkin | 250 mcg | 32% |
| Green onion | 333 mcg | 43% |
| Camembert cheese | 303 mcg | 39% |
| Cream 35% | 270 mcg | 35% |
| Cheddar cheese | 277 mcg | 35% |
| Basil | 264 mcg | 34% |
| Chicken eggs | 260 mcg | 33% |
Remember that a contraindication is taking a synthetic form of retinol combined with a vitamin diet. There is no doubt that vitamin A is necessary for the body during pregnancy and in everyday life, like many other substances. But is it worth taking chemicals when there are natural products that can meet the body’s needs?
Signs of Vitamin A Deficiency
Due to the fact that the required amount of vitamin A is quite easy to obtain from the food consumed, its deficiency in residents of developed countries is rare, with the exception of cases of certain diseases. Signs of deficiency include poor night vision and a weakened immune system. People with a deficiency may also develop a condition called xerophthalmia, which causes the cornea of the eye to dry and thicken. You can learn more about the signs and symptoms of vitamin A deficiency here - Vitamin A deficiency: symptoms in adults and children, treatment, prognosis.
Recommended norms of vitamins and minerals for pregnant women. Very good signs.
Multivitamins and vitamin-mineral complexes for pregnant women.
Recommended norms of vitamins and minerals for pregnant women.
A brief description of the most popular vitamin and mineral complexes.
Content of vitamins and minerals in vitamin-mineral complexes.
Pregnancy is an amazing period in a woman’s life.
At this time, the woman provides not only for herself, but also for the rapidly growing body of the unborn child. In addition, the pregnant woman’s own body changes radically. Metabolic processes go faster, new substances circulate in the blood, even the structure of some organs and tissues changes. Naturally, in such a situation, the female body requires significantly more nutrients. The need for vitamins and microelements during pregnancy literally doubles. Today, there are various multivitamins and vitamin-mineral complexes specially adapted for the body of a pregnant woman. How can pregnant women navigate the huge number of multivitamin preparations? Vitamin complexes for pregnant women can be roughly divided into three classes: economical, medium and premium.
The economy class includes such multivitamin complexes as: COMPLIVIT MAMA , ALPHABET MOTHER'S HEALTH . But some doctors believe that these vitamins are not enough. The complex should have, if possible, a complete set of vitamins and minerals. The middle class includes VITRUM PRENATAL , PREGNAVIT , MULTI-TABS PERINATAL , LADY'S FORMULA PRENATAL . The premium class is represented by VITRUM PRENATAL FORTE , MATERNA , ELEVIT PRONATAL .