Why is the TSH hormone so important when planning pregnancy? TSH is a pituitary hormone that takes an active part in regulating the basic function of the thyroid gland. Namely, in the processes of producing the hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These biologically active substances normalize the activity of the heart, digestive tract, and nervous system. They also affect the functioning of the reproductive glands. TSH is a specific indicator that allows us to judge the condition of the thyroid gland, which directly affects the conception of a child.
TSH norm in preparation for pregnancy
.jpg" />In a healthy woman, the TSH level should normally be from 0.4 to 4 mU/l, but during the preparation for conception the numbers should be from 0.4 to 2.5 mU/l. These values are due to the fact that after conception the indicators may differ slightly upward, depending on the trimester.
If a non-pregnant woman has a value above 3, it is very important to monitor the hormone level by an endocrinologist. A sharp increase in TSH threatens miscarriage or regression of pregnancy.
It should also be taken into account that reference values for hormones may differ in different laboratories; this is influenced by the test systems and analyzers used.
Low TSH level
Low levels of thyrotropin occur with:
- pituitary insufficiency;
- Plummer's disease;
- fasting;
- pituitary injury;
- thyroid neoplasms;
- an excess of thyroid hormones due to incorrect dosage of hormonal drugs;
- psychological diseases.
Low TSH when planning pregnancy often results in infertility. Replacement therapy allows a woman to restore her fertility, increasing her chances of conceiving.
High TSH level
A TSH level above normal can be triggered by:
- severe intoxication of the body;
- disruption of the central nervous system;
- intense physical activity;
- somatic or mental illnesses;
- recent surgery affecting the thyroid gland;
- cyst or tumor of the gland;
- adrenal insufficiency;
- overdose of drugs that affect TSH levels;
- thyroiditis – a chronic disease of the thyroid gland.
The presence of the above problems can affect conception, so it is important to undergo a full examination in order to find out the exact reason for the increase in TSH levels. Planning a pregnancy in such a situation should be approved by a gynecologist and endocrinologist, since during pregnancy, treatment drugs are limited.
In the first weeks of an interesting situation, when the expectant mother may not yet suspect her happiness, the level of TSH in the blood already decreases sharply. This in no way indicates a disease on the part of the mother’s body, but only confirms the fact of the presence of a small baby in the uterine cavity. That is why, based on changes in the quantitative indicators of TSH, one can conclude that pregnancy has occurred.
Too high a TSH level is not a barrier for a woman to become pregnant. Pregnancy with elevated TSH, as well as thyrotoxicosis and pregnancy, is a quite common occurrence in obstetric practice. But is it possible to get pregnant with hypothyroidism? It all depends on the severity of the disease and its complications in the sexual sphere.
In any case, the impact of the thyroid gland on conceiving and bearing a child is very great. Therefore, to plan a pregnancy, it is better to take time and undergo the necessary tests. Especially if the doctor suspects thyroid dysfunction and possible problems with future conception, as a result of which a small person should be born.
An endocrinologist diagnoses and treats the thyroid gland. It is to this doctor that your gynecologist or therapist will refer you if necessary.
Why is it so important to do the analysis?
When planning pregnancy, women should undergo hormonal testing to determine their thyroid status. If the concentration of T3 and T4 does not correspond to normal values, a thyrotropin test is taken. High or low levels of the hormone are grounds for treatment.
A TSH test is prescribed for symptoms of hypo- and hyperthyroidism:
- weight fluctuations;
- chronic fatigue;
- frequent constipation;
- emotional lability;
- irregular menstruation;
- swelling of the face;
- causeless anxiety;
- hand tremors;
- tachycardia;
- insensitivity to low temperatures;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- hair loss;
- neck deformity;
- hoarseness of voice;
- painful periods;
- protrusion of eyes, etc.
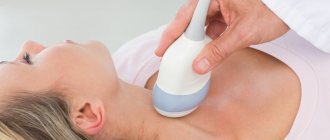
TSH in pregnant women with thyroid pathologies is determined every 3 months. For analysis, patients donate blood from the ulnar vein. Preliminary preparation for the examination eliminates errors in the results:
- Blood is drawn on an empty stomach between 8-00 and 11-00 am. During these hours, the content of thyrotropin in the blood is maximum.
- At least 8 hours must pass between the last meal and the test. Those planning a pregnancy can drink still water without dyes or flavors.
- 2 days before the examination, avoid fried and fatty foods, as they affect the level of thyroid hormones in the blood. It is prohibited to consume alcoholic beverages.
- For 1.5-2 hours before blood sampling, it is advisable to avoid physical activity and avoid stressful situations.
A month before the test, you should stop taking hormonal medications and iodine supplements.
Their use is fraught with false-positive or false-negative results. The concentration of thyrotropin during planning and during gestation is constantly changing. This is due to hormonal changes in the mother’s body against the background of intrauterine development of the fetus. In the first trimester, the membrane of the embryo begins to secrete human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), and at 16-18 weeks of gestation the fetus produces its own thyroxine. These hormones affect the activity of the pituitary gland, the synthesis of thyrotropin and its level in the mother's blood.
When planning pregnancy, the TSH hormone is normally in the range of 1.5-2.5 mU/l. Deviation from reference data signals thyroid dysfunction and endocrine disorders. Hormonal imbalance is fraught with:
- underdevelopment of eggs;
- anovulation (menstrual irregularities);
- pregnancy failure.
We suggest you read: Is it possible to do hair tinting during pregnancy
? If thyrotropin is high, the biosynthesis of thyroid hormones increases. They affect the production of female hormones. Because of this, the formation of the corpus luteum, a temporary gland that secretes progesterone after ovulation, slows down.
First trimester
After implantation into the wall of the uterus, the embryo begins to produce human chorionic gonadotropin. It stimulates thyroid function in the first trimester of pregnancy. Under the influence of hCG, the efficiency of the gland increases by 50%, so the T4 content in the blood increases.
There is an inverse relationship between TSH and free T4 fraction. If the level of thyroxine increases greatly, the secretory activity of the pituitary gland decreases. In this regard, the concentration of thyrotropin decreases. The TSH norm in women during pregnancy in the 1st trimester is 0.1-0.2 mU/l.
Second trimester
Gradually, the amount of hCG in the female body decreases. At 7-8 weeks of pregnancy, the level of human chorionic gonadotropin reaches 23100-151000 mIU/ml, and in the second trimester it drops to 4500-6500 mIU/ml. The thyroid gland is stimulated with less force, so the TSH concentration gradually increases. TSH normal values during pregnancy in the 2nd trimester remain within the range of 0.3-2.8 mU/l.
Third trimester
In the last trimester of gestation, thyrotropin levels approach the reference values before conception. An increase in thyrotropin is associated with:
- decrease in hCG level;
- the production of estrogens that bind free T4 in the blood;
- active development of the child’s skeleton.
Normally, the TSH level during late pregnancy is 0.4-3.5 mU/L.
If you feel worse, you should contact an endocrinologist. He will order a series of laboratory tests. One of the tests is a study of TSH levels.
It is recommended to donate blood for a TSH test in the following cases:
- Pregnancy planning.
- Infertility for a year.
- Frequent depression, apathy, irritability.
- Weight changes not related to diet or exercise.
- Frequent headaches.
- Paleness, dry skin.
- Increased heart rate, tremor.
- Hair loss.
The maximum concentration of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood is observed in the morning.
TSH synthesis is influenced by many factors, so before taking blood, you must follow the rules for 72 hours before the test:
- a woman should stop drinking alcohol, diuretics, and iodine-containing vitamin complexes;
- it is necessary to avoid any stressful situations, lack of sleep, strong physical activity;
- Severe hypothermia or, conversely, overheating must be excluded;
- 12 hours before blood sampling, a woman is prohibited from drinking or eating.
Doctors recommend that all women check their TSH levels at the preconception stage. If the pregnancy occurred unplanned, it is advisable to contact an endocrinologist and donate blood for TSH during the registration process. In some countries, this study has already been included in the list of mandatory tests for pregnant women, which has significantly reduced the number of miscarriages, as well as children born with mental retardation.
The TSH level when planning pregnancy is a very important indicator of the state of a woman’s reproductive function. Using this analysis, you can determine thyroid dysfunction, which is a serious cause for concern and requires medication (and sometimes surgical) correction.
Quite often, when planning a pregnancy, a woman does not suspect that she has reproductive problems. A comprehensive examination allows not only to determine the presence of pathological changes in the body that negatively affect the conception of a baby. But also to confirm their possible causes, thanks to an extensive analysis of the hormonal background of the expectant mother.
According to statistical studies, in most cases, infertility in women is associated precisely with hormonal imbalance. In particular, with violations of the proportions of TSH, T3, T4.
Why is it necessary to do a prescribed TSH test when planning a pregnancy?
- The TSH level makes it possible to assess the condition of a woman’s reproductive system.
- Using the analysis, you can identify possible problems with the thyroid gland that negatively affect conception and pregnancy.
- The study allows us to confirm the suspected cause of female infertility.
So, the influence of the thyroid gland on conception is very great.
Elevated TSH when planning pregnancy
A condition that requires increased attention from an endocrinologist. TSH levels above the established norm can lead to ovarian dysfunction and lack of ovulation. And this is the impossibility of getting pregnant.
Causes
Among the main reasons for this condition:
- Insufficient iodine content. This is the most common culprit of elevated TSH.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Various tumors, including the pituitary gland.
- Increase in the size of the thyroid gland.
- Recent surgical interventions.
- Tissue necrosis.
- Intoxication of the body.
- Infectious diseases.
These are not all the reasons, but the main ones are those that most often cause an increase in TSH levels. If hormonal levels are not corrected, conception may not occur. But even if pregnancy occurs, the fetus can be rejected by the woman’s body. It is also important that certain pathologies can develop in the fetus - autoimmune thyroiditis, which provokes placental insufficiency.
Symptoms
You should pay attention to the following conditions:
- Increased body weight. Often, with an increased TSH compared to the norm, it is difficult to lose extra pounds.
- Slow heart rate.
- Dry skin that may begin to peel over time.
- Constant constipation or problems with bowel movements in general.
- Drowsiness or slow reactions.
- Swelling and swelling.
The effect of the hormone on conception
Problems with the thyroid gland affect a woman’s reproductive function, affecting the menstrual cycle:
- regularity is disrupted;
- progesterone production decreases;
- anovulatory cycles appear;
- amenorrhea develops - monthly bleeding stops altogether;
- infertility is noted.
As a result of a lack or excess of thyroid hormones, endocrine infertility can develop.
TSH deficiency when planning pregnancy
This is no less dangerous condition. An indicator less than 1.5 mU/l is considered reduced. if pregnancy is already a fait accompli, then the norm for women in an interesting position cannot fall below 0.4 mU/l. Diagnosis of such processes occurs in a disease such as thyrotoxicosis, which is considered a genetic disease.
Symptoms
Warning signs include:
- Nervous state.
- Constant increase in body temperature and tremors.
- Headaches that occur quite often.
- Elevated blood pressure levels.
- Tachycardia.
- Inability to gain weight.
This pathology is dangerous, it is difficult, but treatable and only under the supervision of a doctor. Some cases require surgery, but this is prohibited in the first trimester.
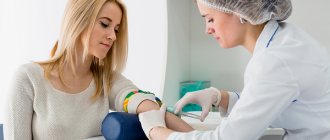
How to take the test: preparation and on what day
A blood test for thyroid hormones is taken in the morning on an empty stomach; before the test, you should adhere to certain recommendations:
- take a break after eating for 10-12 hours;
- exclude during the day: alcohol, cigarettes, fried and fatty foods;
- do not carry out diagnostics in the presence of infectious diseases;
- stop taking hormonal medications one month before;
- stop taking medications containing iodine 4 days before;
- provide physical and emotional comfort.
When planning conception, blood can be donated on any day of the month, regardless of the cycle. Doctors recommend that after 30 years of age, check the level of thyroid hormones annually, during a preventive medical examination. When treating hormonal imbalance, tests are taken twice a year, if such a need is confirmed by the attending physician.
Planning a pregnancy is a crucial period in a woman’s life.
In order to guarantee the conception of a healthy baby, the expectant mother is prescribed many examinations.
Among them are mandatory blood tests for hormones. If you have already been tested, then you have probably heard about the TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) test.
It and its role in pregnancy planning will be discussed in our article today.
Preparing for analysis
Proper preparation and delivery of the analysis affects the reliability of the result. Specialists at the AltraVita clinic recommend the following algorithm for preparing for the test:
- For three days, alcohol consumption and smoking are excluded.
- You can't physically overwork yourself.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- If you are taking any medications at the time of donating blood, you should inform your doctor. If possible, you should temporarily stop taking medications, especially vitamins, hormones, and iodine-containing medications. After antibiotic therapy, you can donate blood no earlier than a week later.
- On the day of blood sampling, you should not eat or drink, smoke or chew gum.
Psycho-emotional outbursts negatively affect hormonal levels, so you need to be in a calm state before and during tests. You cannot donate blood if you have an elevated temperature or an acute infectious process. Checking the concentration of thyrotropins over time requires donating blood within one hour.
Calculate dates suitable for taking tests
And have time to sign up for your first free appointment with a fertility specialist before 06/01/20
Results sent successfully. Please check your email.
Clear results
Elevated TSH when planning pregnancy
Reading time 4 minutes
Planning a pregnancy is not complete without undergoing many tests in order to avoid problems with the child’s health in the future and to ensure the normal development of all systems and organs. Mandatory procedures include monitoring TSH levels. For doctors, the conclusion of this analysis is of great importance. Small deviations from the given norms, for example, elevated TSH during pregnancy planning, can indicate a failed pregnancy and all sorts of pathologies.
Rules for taking analysis during planning
To exclude the influence of random factors on a reduced result, you need to properly prepare for the study. Substances that contribute to distortion of the result should not be ingested 72 hours before the analysis:
- do not take alcohol, vitamin complexes with iodine,
- exclude diuretics,
- avoid significant physical activity,
- eliminate stress, lack of sleep,
- avoid overheating or hypothermia,
- The last meal is around 19:00.
When testing is carried out correctly, the norm is 0.27-4.0 µIU/ml. Until 2012, the upper limit of normal was considered to be 2.5, then after a number of studies it was moved back to 4.
TSH norm when planning pregnancy
The hormone is produced by the pituitary gland. Since all organs and systems in the body work harmoniously, TSH interacts with T4 and T3 (thyroid hormones) according to the feedback principle. If the level of T4 is insufficient, then TSH is increased; if there is an excess of T4, TSH decreases.
Essentially, TSH analysis when planning pregnancy is an attempt to understand exactly how the thyroid gland and pituitary gland function. If there are deviations, hormonal therapy will be required to correct the condition. Donating blood to check the function is simply necessary, since one ultrasound examination does not provide a complete picture of what is happening.
The study is carried out using a proven method - ELISA, when the level of the hormone in the blood serum is checked, and the values revealed must be within the TSH normal range for pregnancy planning: 1.5–2.5 mU/l. after conception, the indicator may deviate in different directions, but should not go beyond 0.4–4 mU/l.
Serious deviations from the specified TSH norms when planning pregnancy and during pregnancy are fraught with complications. In the absence of hormonal adjustments, a child may be born with abnormalities in the thyroid gland. In the early stages, deviations are fraught with spontaneous miscarriages.
Normal TSH values
During pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes changes associated with the formation and growth of the fetus. The load on the organs of the endocrine system increases. In the first months of gestation, the mother's thyroid hormones participate in the formation of the child's organs.
In the last stages of pregnancy, the fetus develops its own thyroid gland, which begins to produce thyroid hormones. Therefore, closer to childbirth, TSH in pregnant women reaches almost normal values.
Norm TSH in women before pregnancy and during pregnancy
| Gestational period | Thyrotropin concentration, in honey/l |
| 1st trimester | 0.1-2.5 |
| 2nd trimester | 0.2-3.0 |
| 3rd trimester | 0.2-4.0 |
| outside of pregnancy | 0.4-4.0 |
In most women with multiple pregnancies, the level of thyrotropin in the blood decreases to zero. They are more susceptible to gestational thyrotoxicosis, so they should undergo prenatal screening at least once a trimester.
When testing blood, it is recommended to determine the level of not only thyrotropin, but also thyroid hormones (T3, T4).
Based on the results obtained, the correct functioning of the endocrine system is assessed. If necessary, women are further examined and appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Association between TSH and future pregnancy
As you know, planning a pregnancy is a very important moment in the life of any woman who wants to become the mother of a healthy baby. During this period, you need to do a huge number of tests, including determining the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone of the pituitary gland. Why is TSH so important when planning pregnancy? Let's try to understand how the thyroid-stimulating hormone of the pituitary gland, the thyroid gland and infertility are related to each other.
It is very important during pregnancy planning to undergo a special test to determine the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone. This is necessary to prevent possible problems with conception and exclude causes of infertility associated with deficiency or, conversely, with hypersecretion (excess) of TSH.
Thyroid hormones affect almost all internal human organs. They play a special role in regulating reproductive function, preparing a woman’s body for conception and successful childbearing. Elevated or low levels of the hormone can cause profound disruption of metabolic processes in the ovaries. In practice, this manifests itself as scleropolycystic disease, anovulatory cycle, and the like. The result of such pathological processes is endocrine infertility. And if pregnancy does occur in such women, in most cases it is spontaneously terminated in the early stages.
By the amount of TSH, the doctor can judge whether a woman has hyper- or hypothyroidism (increased or decreased synthesis of thyroid hormones). This level of neuroendocrine regulation is characterized by the “feedback” principle. That is, with high titers of T3 and T4, there is a tendency to decrease TSH, and with reduced concentrations of thyroid hormones, it tends to increase. That is, a TSH test is a sure way to determine whether a woman has thyroid dysfunction. This makes it possible to assess the role of such disorders in the process of conception, correct the functioning of the gonads and increase the ability to reproduce.
What is TSH: role for the body
TSH is an abbreviation for thyroid-stimulating hormone. It is produced under the influence of thyroid hormone-releasing hormone, and its synthesis is inhibited under the influence of the somatostatin fraction in the hypothalamus.
Thyrotropin itself is secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. It is responsible for stimulating TSH centers in the thyroid gland. Thyrotropin promotes the activation of thyroxine and triiodothyronine.
These hormones are designated T4 and T3, respectively. They are responsible for the growth process, for protein, fat and carbohydrate metabolism, and affect mental health and mood. The proper functioning of the digestion, heart and reproductive system depends on them.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone is in close relationship with T3 and T4. It promotes their production. When the concentration of thyroxine and triiodothyronine in the blood increases, these hormones, in turn, begin to suppress the production of thyrotropin by the pituitary gland.
It is because of this inverse relationship that an analysis of thyrotropin levels is also mandatory when examining the thyroid gland.
TSH hormone and pregnancy planning: normal
The level of thyroid-stimulating hormone can indicate the presence of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism - increased or decreased production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland.
TSH produced by the pituitary gland interacts with it according to the feedback principle - if the thyroid gland produces too many hormones, then the level of TSH in the blood is reduced, if it is low, then it is increased.
In fact, a TSH test is performed in order to accurately identify the presence or absence of thyroid dysfunction. Since even an ultrasound examination of this organ and specific tests for general hormones do not provide a complete clinical picture.
The study of TSH levels is carried out using the ELISA method - that is, the method of determining the concentration of the hormone in the blood serum using an enzyme immunoassay.
How to normalize TSH levels?
If there are deviations from the norm, you need to undergo examination by an endocrinologist. It is necessary to take a blood test for hormone levels and undergo an ultrasound of the thyroid gland.
Then the doctor selects drug treatment. If TSH is elevated, iodine supplements are usually prescribed. If the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone is low, the endocrinologist selects drugs that inhibit the activity of the thyroid gland.
Nutrition is also subject to correction. If the TSH level is high, it is recommended to eat seaweed, seafood, and iodized salt, but if the TSH level is low, foods high in iodine should be excluded from the diet.
Only an endocrinologist can tell you how to bring TSH levels back to normal during pregnancy after a thorough examination of the patient and identifying the cause of the deviation.
Low TSH
A decrease in the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone occurs in a number of pathological conditions:
- destruction of the pituitary gland, death of gland cells;
- polycystic thyroid gland with manifestations of hyperthyroidism;
- consequences of long-term use of hormonal contraceptives;
- intoxications affecting the female body;
- low TSH with thyrotoxicosis;
- chronic stress or depression.
So, what should be the amount of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood for the doctor to declare a decrease in its level? In modern medical practice, a TSH level that does not exceed 1.5 mU/l is considered low. In pregnant women, this figure should not fall below 0.4 mU/l. It is important to note that TSH, which affects reproduction, may also decrease in healthy women. This is typical for representatives of the fairer sex who have been using hormonal contraceptives for a long time, smoking, and often going on starvation diets.
Most often, low TSH is determined in thyrotoxicosis. Thyrotoxicosis and pregnancy are a rare combination that occurs in two pregnant women out of a thousand registered at the antenatal clinic. In almost all clinical cases, thyrotoxicosis during pregnancy is associated with diffuse damage to the thyroid gland and is a complication of hyperthyroidism.
Thyrotoxicosis and pregnancy planning is a complex process, which, with the right approach, can be crowned with success if the sick woman strictly follows all the doctor’s prescriptions. The possible risk of such a pregnancy is the high risk of early miscarriages, as well as the likelihood of having a child with mental and physical disabilities.
So, infertility and thyroid diseases are closely related. Unfortunately, the pathological process does not always occur before the moment of conception, and doctors diagnose thyrotoxicosis already during pregnancy. In this case, the expectant mother is offered a course of hormonal medications that will calm the hormonal storm.
Elevated TSH
In medical language this phenomenon is called hypothyroidism. This condition has a bad effect on the functioning of the ovaries, as well as the formation of eggs. Ovulation can either occur with constant disturbances, or stop altogether. Elevated TSH during pregnancy planning will most likely lead to infertility.
Causes
For what reasons does TSH increase? This phenomenon is quite often transmitted genetically. Basically, the main reason why tests show elevated TSH when planning pregnancy is precisely genetic pathologies.
Very often, internal deviations of the body or negative actions from the outside contribute to the increase.
The main reasons why TSH increases:
- weakened immune system
- increased levels of iodine,
- thyroid cancer,
- mental state disorder,
- imbalance of emotional state,
- use of medications without supervision,
- consequences after suffering from various diseases.
Is it possible to get pregnant with elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone?
Elevated TSH during pregnancy planning can directly indicate infertility. Even if the female body still managed to conceive, then in the end, it will perceive the fetus as a foreign body and begin to reject it. The result is a miscarriage. If you save a fetus with high TSH, then most likely it will be impossible to avoid pathologies in the future.
Elevated TSH during pregnancy planning can give rise to autoimmune type thyroiditis. During pregnancy, this disease causes placental insufficiency. Sadly, the consequences can be all sorts of pathologies or miscarriage.
Low TSH
In medicine, this is usually not a very common occurrence, but this condition occurs in short periods and it is quite normal, however, to be wary of this indicator. It is imperative to find out why TSH is low.
Causes
The hormone thyrotropin indicates the functioning of the thyroid gland. A low rate most often indicates thyrotoxicosis.
This disease is transmitted genetically, and can also occur under the influence of other diseases directly related to the functioning of the endocrine system.
- diffuse toxic goiter;
- overdose of medications;
- tumors;
- consequences after suffering from chronic diseases;
- outcome after brain surgery or traumatic brain injury;
- pituitary necrosis;
- ovarian dysfunction.
And yet, can elevated TSH when planning a pregnancy ruin the dream of many women to become mothers? Very often this question is asked in the doctor’s office by women who dream of becoming mothers. Infertility and elevated TSH levels are a fairly common occurrence in the practice of a gynecologist. But this does not mean that a high TSH level will necessarily indicate the impossibility of conception. Today, medicine keeps up with the times and copes well with this disease with the help of a special course consisting of certain hormonal drugs. One of the most prescribed drugs in this case is Eutirox.
According to the results of a study by many specialists, many women who previously had elevated TSH when planning pregnancy after taking the drug immediately returned to normal TSH levels, and some of them immediately conceived a child. Remember that the drug is hormonal and you cannot drink it on your own. Before you start using it, you must definitely visit the office of an endocrinologist or obstetrician-gynecologist.