What is prolactin?
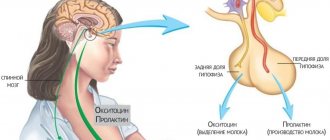
The lactogenic hormone (lactotropin, mammotropin), which is a single-chain polypeptide, is called prolactin. It is produced by the pituitary gland with the participation of the nervous system and hypothalamus.
The leading target organ for mammotropin is the mammary gland. It is extremely important for the normal lactation process, stimulates the production of colostrum and promotes its transformation into milk, stimulates milk production. Prolactin is the main stimulator of the growth of lobules and ducts of the mammary glands. In addition, he takes part in:
- in the formation of appropriate psychological and emotional reactions of a woman (“maternal instinct”);
- in maintaining high concentrations of progesterone;
- stimulates the production of androgens by the adrenal glands.
There are receptors sensitive to lactotropin in almost all organs and tissues (from the myocardium to the skin), but its effect on these organs has not yet been clarified. However, it is known that a violation of the content of mammotropin in the blood is important not only for the female body, but also for the male one, since it is involved in spermatogenesis.
Standards
Prolactin standards for women depend on the phase of the menstrual cycle, and they range from 4.5 to 50 ng/ml. The normal range for men is considered to be from 2.5 to 17 ng/ml. The figures shown may vary slightly for each specific laboratory. Typically, each clinic indicates its own reference values.
When planning pregnancy, the level of the hormone in the ovulatory phase is determined. The normal prolactin level is considered to be from 6.5 to 50 ng/ml. Hyperprolactinemia (increased levels of prolactin in the blood) is more often observed; less often this level is reduced.
Hormone functions
Prolactin performs many vital functions in the female body.
Prolactin: the norm in women depends on age and phase of the cycle
Main functions of the hormone:
- activates the synthesis of androgens and normalizes the functioning of the adrenal glands;
- in adolescence, participates in the development of secondary sexual characteristics;
- promotes lactation, prepares the mammary glands for milk production;
- a sufficient amount of prolactin blocks ovulation during pregnancy;
- maintains the amount of progesterone necessary for successful pregnancy.
In the male body, prolactin has the function of producing seminal fluid and prostate secretion. Therefore, it is not only a female, but also a male hormone.
There are 4 isoforms (fractions), which differ in their properties:
- Monomeric. Makes up 85% of the total amount of prolactin;
- Large – 10%;
- Macroprolactin – 5%;
- Glycolysed. Its quantity is not taken into account in the study.
All the main functions of prolactin in the body belong to its monomeric fraction.
Reasons for increased prolactin
People often ask what does increased prolactin mean in women and why does this happen, as well as why prolactin is increased in men, and what led to this? The reasons are basically the same for both sexes. With the exception of pregnancy, lactation, specific operations on the female genital organs and polycystic ovary syndrome - these factors can only be attributed to the female gender. Modern medicine usually divides all the causes of this phenomenon into 5 main groups:
- physiological;
- pathological (organic or functional);
- pharmacological reasons;
- postoperative conditions;
- idiopathic hyperprolactinemia.
Physiological causes are not associated with the disease, most often these are deep sleep, excessive emotional or physical stress, frequent flights (for women), sexual intercourse, pregnancy and lactation, excess protein foods.
The cause of organic hyperprolactinemia is tumors (pituitary or hypothalamic). A functional increase in prolactin levels is associated with serious diseases of internal organs (liver, thyroid, kidneys, ovaries) or with excess estrogen in the blood.
The level of mammotropin can be affected by some antihistamines, antipsychotic and antiemetic drugs, estrogens, hormonal contraceptives and a number of other medications. Hyperprolactinemia can be a consequence of curettage (if such operations are repeated regularly), medical abortions, or surgical interventions in the chest area.
In addition, there is an idiopathic form of increasing hormone levels, in which the number of pituitary cells is not subject to change, but their function is enhanced. The reasons for this phenomenon are unknown.
The main signs of excess lactotropin can be considered: decreased sexual activity, difficulty conceiving, increased volume of the mammary glands and weight gain not associated with changes in diet, weakened hair growth. They are characteristic of both sexes.
When the indicator is below normal
Hypoprolactinemia develops due to:
- neoplasms of the anterior or posterior pituitary gland;
- tuberculosis;
- poor nutrition, diets associated with starvation or carbohydrate deficiency;
- injuries or pathological processes in the brain;
- bleeding during pregnancy or childbirth;
- taking hormonal medications;
- dysfunction or inflammatory diseases of the ovaries;
- hereditary pathology of the endocrine system;
- menopause;
- diabetes insipidus;
- excessive physical and psycho-emotional stress;
- smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages and psychotropic substances.
Hypoprolactinemia manifests itself in the following:
- in a nursing woman, lactation decreases or completely stops;
- discharge from the mammary glands appears in women who do not have infants;
- periods are absent or come intermittently;
- a woman is rapidly gaining extra pounds, regardless of diet;
- inability to get pregnant;
- the appearance of hair in places of the body that are uncharacteristic for women;
- emotional lability.
Therapy for hypoprolactinemia is carried out depending on the causes that caused it and the presence of other pathological processes in the body. So, a decrease in prolactin levels against the background of other normal indicators indicates that a woman needs rest, a reduction in physical and psycho-emotional stress, and normalization of sleep and wakefulness.
What it should be at a given age - the attending physician will tell you.
Such patients are recommended to have a nutritious diet enriched with vitamins and minerals, sufficient sleep, an active lifestyle, giving up bad habits, walks in the fresh air and a positive attitude.
Stress is one of the main causes of hormonal disorders. To normalize the results of a prolactin test, sometimes it is enough to simply minimize the number of stressful situations in life.
Hyperprolactinemia due to other diseases requires treatment. Therapy is prescribed by the attending physician according to the patient’s age and depending on the pathology. May include taking sedatives, antibacterial or anti-inflammatory drugs. In some cases, surgery is required.
The effect of prolactin on pregnancy
During pregnancy, mammotropin is involved in the production of surfactant (a special “lubricant” of the lungs, a surfactant contained in the pulmonary secretion of a full-term fetus). This makes the first breath of a newly born baby possible. Modern research shows that this hormone is able to reduce the level of pain, so it is often produced in large quantities during pain.
During pregnancy, this hormone prepares the mammary glands for lactation. Milk is not produced only because the process is blocked by progesterone. Progesterone levels drop quickly after the placenta is delivered, and colostrum, then milk, begins to be actively produced.
Normal prolactin level during pregnancy
Normally, during gestation, the body maintains an increased level of mammotropin. The standards depend on the stage of pregnancy. Prolactin during pregnancy, unlike progesterone, is more convenient to normalize not by week, but by trimester:
- I trimester (8-12 weeks) - 3.2-43 ng/ml;
- II trimester (13-24 weeks) - 13-166 ng/ml
- III trimester (25 week - before birth) - 13-318 ng/ml.
The peak concentration of prolactin in the blood of a pregnant woman occurs in the period from 20 to 25 weeks of gestation. Before childbirth, the level of the hormone decreases slightly and increases when the baby begins to feed.
Is it possible to get pregnant with elevated prolactin?
It depends on the causes of hyperprolactinemia. If ovulatory processes are disrupted, conception will not take place; if ovulation is preserved, pregnancy is possible.
Relationship between hormones
A woman’s reproductive function is regulated not only by prolactin. Hormonal balance in the blood is important.
Progesterone is involved in preparing the uterus and the body as a whole for bearing a fetus. Its normal amount is the key to a successful pregnancy.
Thus, hyperprolactinemia leads to decreased progesterone production and lack of ovulation. There is a violation of the monthly cycle. Pregnancy occurs extremely rarely.
Hypoprolactinemia increases the amount of progesterone, which also negatively affects the functioning of the reproductive organs and makes conception impossible.
Estradiol is involved in preparing the egg for fertilization and the presence/absence of ovulation depends on its amount in the first phase of the cycle.
An increased level of prolactin leads to a decrease in the amount of estradiol produced by the ovarian follicular apparatus, which negatively affects the possibility of conception and is a common cause of infertility. Significantly exceeding the indicators is fraught with the development of amenorrhea, metabolic dysfunction, gaining extra pounds and even obesity.
The level of prolactin in the body depends on many factors: the patient’s age, cycle phase, conditions and lifestyle. If alarming symptoms appear that indicate a hormonal imbalance, you should immediately contact a specialist in the field of gynecology or endocrinology.
A blood test allows you to identify abnormalities that may be associated with physiological factors, and not pose a serious danger to life and health, or with pathological processes that require timely treatment and even surgical intervention.
The human body produces a large number of hormones, including those that ensure reproduction. One of these hormones is prolactin.
If a woman is planning a pregnancy with an increased level of prolactin, a number of questions immediately arise: why does this happen? Is conception possible in this case? And how can this level be brought back to normal?
Diagnostics
A blood test to determine prolactin is carried out from 9 to 11 am; it is recommended to abstain from sex before donating blood. If the level turns out to be too high, the tests are repeated twice more to verify the results. Diagnostic measures are not limited to stating the fact of hyperprolactinemia. In addition to taking blood for this hormone, the patient or patient may be prescribed:
- blood test for thyroid hormone levels;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland, liver, kidneys, adrenal glands, female genital organs;
- MRI or CT, craniography;
- tests with metoclopromide and thyrotropin-releasing hormone;
- examination of the organ of vision.
Consultations with narrow specialists are recommended who can contribute to the prescription of the necessary diagnostic procedures.
Treatment before pregnancy
Therapy most directly depends on the underlying disease. And treatment should begin by addressing the cause. However, there are medications that are prescribed in many cases to suppress prolactin production. For these purposes, drugs are used that are derivatives of ergot alkaloids and are antagonists of dopamine receptors (bromocriptine, cabergoline). Trade names for these drugs: Dostinex, Bergolak, Agalates, Abergin, Parlodel, Bromocriptine. When planning pregnancy, Dostinex and Bromocriptine are most often recommended.
We also invite you to watch a video on the topic: