Causes of streptococcal infection in pregnant women
Streptococcal infection during pregnancy is detected quite often in a smear. In some regions this figure is significantly higher than the statistical average of 30%. This is explained by the transmission of the disease. Streptococcus isolated in smears of a pregnant woman could enter the woman’s body through one of the following routes:
- From person to person, for example, when shaking hands, kissing.
- Sexually.
- Use of personal hygiene items by several people, one of whom is a carrier of a bacterial infection. This applies not only to towels, but even soap.
During pregnancy, women's immunity is significantly reduced. This is due to certain changes in the body.
Infection can occur both at the beginning of pregnancy and in the last weeks. Therefore, significant attention should be paid to the safety of the expectant mother. In some cases, it is even useful to limit your social circle.
At risk are women who have addictions that further suppress the functioning of the immune system. Also, negative consequences are more often recorded in those who suffer from diabetes.
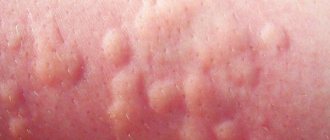
In addition to its unsystematic occurrence in a latent form, detected streptococcus in the urine of a pregnant woman can lead to the development of various skin rashes. We are talking about the following diseases:
- Superficial streptoderma. They come in the following varieties - Tilbury Fox, folds, annular, periungual, slit-like, bullous, lips, mucous membranes, including the oral cavity and throat.
- Deep streptoderma has one form. The disease is called ecthyma.
- Atypical streptoderma is lichen simplex, acute diffuse streptoderma. Papular syphiloid impetigo occurs only in children under 1 year of age in the absence of proper hygienic care. Its second name is diaper dermatitis.
Often, pregnant women confuse the first manifestations of streptococcal infection with other ailments. Therefore, it is important to know what symptoms are characteristic of this disease.
Streptococcus in pregnant women and children
During pregnancy, such an infection is diagnosed in a large number of women. The following can provoke the appearance of such a disease:
- Unprotected sexual intercourse (can cause fecal streptococcus).
- Failure to maintain intimate hygiene.
- Tight synthetic underwear.
Pregnant women are the main category of people who are exposed to this type of infection. The immune forces of the expectant mother are weakened during this period, which allows the infection to freely penetrate into the exhausted body and spread within it.
Experts recommend that women undergo tests and examinations throughout pregnancy to identify the causative agents of this disease. If it is detected, its treatment must be taken seriously. Untreated streptococcus can develop into purulent otitis media, sepsis, allergies, or problems with the cardiovascular and genitourinary systems.
- Streptococcus in urine - causes of appearance, routes and conditions of infection, diagnosis, treatment methods
In order for urine tests to give the correct result, it is necessary to carefully prepare for such a laboratory analysis. To do this, before donating urine, a woman needs to rinse her genitals thoroughly and cover her vagina with a sterile tampon. Urine is best placed in a sterile container from a pharmacy. If bacteria are detected, the pregnant woman will be prescribed a course of antibiotic therapy. In addition, the specialist will monitor her health even more carefully.
The most dangerous type of streptococcus in newly born children is agalactia. It can be fatal due to the infection's effect on the nervous system. In the mother's womb, such an infection is dangerous due to premature rupture of the membranes and other pathological conditions.
Without proper therapeutic measures, transmission of this bacterium to a child may result in meningitis, sepsis or pneumonia. Therefore, it is important to identify the presence of such a disease in a mother or her unborn baby as early as possible, and immediately begin a course of treatment. Antibiotics are used for this.
Diagnostics
Streptococcus and pregnancy are by no means a rare combination. According to statistics, 30% of pregnant women have this microorganism detected in a vaginal smear. This study must be carried out in a antenatal clinic.
The material is taken with a sterile cotton swab. Immediately before this, you should not perform hygiene procedures, wash yourself, or urinate. This may distort the validity of the analysis.
The result of a cytological examination is ready a few days after taking it. The presence and type of microflora and sensitivity to antibiotics are determined.
You can do a rapid test for streptococcus yourself. Thanks to this, only the presence or absence of bacteria is determined.
In order to clarify the diagnosis, a polymerase chain reaction blood test, screening for GBS Ag using latex agglutination, coagglutination and enzyme immunoassay are prescribed.
Ways of infection with streptococcus
A certain percentage of women are carriers of streptococcal infection, without having any alarming symptoms until the bacterium becomes active due to reduced immunity.
GBS bacteria are able to live and develop naturally in the body. The microorganism is not transmitted through food, household items or water. The cause of infection is unprotected sexual contact and lack of genital hygiene.
If this streptococcus was detected in the urine during pregnancy, the reasons can only be a weakened immune system and a change in the vaginal microflora. Streptococcus is transmitted to a child from an infected mother in utero or during childbirth.
Factors contributing to the development of infection in a child:
- More than 18 hours passed after the amniotic fluid broke and before the baby was born.
- At the time of birth, the woman had a body temperature of more than 37.5 degrees.
- The age of the woman giving birth is up to 20 years.
- Childbirth before 37 weeks.
It is worth noting that streptococcus agalactia is a common cause of death in newborns . Typically, signs of infection appear immediately after birth. Children have pale skin, uneven breathing, fever, vomiting and neurological pathologies.
Despite the fact that the risk of infection of babies is quite low, about 2 cases per 100 infected mothers, you should not refuse diagnostics for streptococci.
- Blood in urine during pregnancy: causes, treatment, tips and reviews
How to treat streptococcus before and during pregnancy
The treatment regimen for streptococcus agalactia is selected depending on the patient’s condition. If the disease is latent and the woman does not plan to have children, local therapy can be limited. When a patient is planning a pregnancy, treatment for streptococcus begins only after symptoms appear.
Pregnant women who do not have significant symptoms should be seen by a doctor and re-examined at 35 weeks. During lactation, local treatment is prescribed until symptoms disappear. Oral antibiotics are not prescribed because they pass into breast milk.
Treatment tactics:
- A woman is planning a pregnancy. Therapy is prescribed only for vaginal discomfort. If there are no obvious symptoms of infection, conception and pregnancy are not prohibited.
- The woman is not planning a pregnancy and has symptoms. If urine culture does not contain pathogens, local treatment is prescribed to eliminate symptoms.
- A pregnant woman with streptococcus detected in a smear or bacterial culture. If streptococcus is detected early and there are no signs of inflammation, a re-examination is prescribed at 34-35 weeks. Therapy is carried out before labor or during labor (at least 4 hours before delivery). The woman is given penicillin antibiotics, cephalosporins or macrolides. It is not advisable to carry out therapy several weeks before birth: streptococcus will colonize the vaginal mucosa after treatment is completed.
- Lactation period. During feeding, treatment with antibiotics can be dangerous for the child, so local effects are preferred. Typically, Hexicon suppositories with chlorhexidine are used, 1-2 per day for a week. After some vaginal preparation with lactobacilli to restore the microflora.
Symptoms of the disease
As a rule, there are no exact symptoms for this disease. Everything will depend on how large the affected area is on the patient’s body. During its life, this pathogen releases toxins harmful to the body, which lead to unpleasant sensations in the patient. The most typical signs are:
- Increase or decrease in temperature level.
- Skin rashes.
- Blood pressure surges.
- Problems with urination.
- Rashes on the skin.
- Painful sensations in the kidney area.
First, the patient develops redness in areas of the skin, which develops into a purulent infection. If you apply light pressure to the affected area, you may feel pain. This condition indicates that the disease has entered an acute stage.
Patients with streptococcus should remember that if they do not consult a doctor promptly, toxins may enter their blood, which can provoke a state of shock. Therefore, experts recommend that at the first symptoms of such a disease, immediately contact a medical facility for diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of appearance and possible complications
The disease appears due to weakened immunity, infection occurs through airborne droplets. In addition, the routes of transmission of streptococcal infection can be as follows:
- During dental procedures.
- Due to bronchitis, which is chronic.
- Through the placenta.
Such bacteria enter the urine through the urethra, passing from the skin. It is not uncommon for the pathogen to enter the urethra through the anus from the colon. This route of transmission is typical for women due to the structure of their genital organs. If left untreated, streptococcus can cause serious complications.
The most common of these is urethritis, which appears only if the patient's bladder is in a weakened state. Signs of this disease are burning and severe itching in the urinary canal. As well as discharge and pain when urinating.
In addition, prostatitis, cystitis, vesiculitis, balanitis may appear, or the microflora in the vagina may be disrupted. They can occur after a prolonged sore throat, which was provoked by the appearance of streptococcal pathogens in the respiratory tract. Also, bacteria can enter the kidneys from the urinary system and cause glomerulonephritis.
- Staphylococcus in urine: causes, diagnosis and what to do
Why is streptococcus in urine dangerous during pregnancy?
If streptococcus agalactia is detected in the urine during the gestational period, the woman needs urgent treatment. In the absence of timely treatment, the bacterium increases the risk of pathological conditions of the mother and fetus:
- premature rupture of membranes, chorioamnionitis;
- diseases of sepsis, meningitis, pneumonia in a newborn;
- premature birth;
- intrauterine fetal death;
- the appearance of a child with cerebral palsy (CP);
- problems with learning, hearing and other pathologies in the child.
Treatment of the disease
If streptococcus is detected in the urine during pregnancy, then treatment should be started immediately. It consists of several stages:
- Antibacterial therapy.
- Strengthening the immune system.
- Bringing intestinal microflora back to normal after antibiotic treatment.
- Detoxification of the body.
- Symptomatic therapy.
To restore intestinal microflora, the following are additionally prescribed:
During the treatment period, excessive physical activity should not be allowed. In case of high intoxication, bed rest is required.
Treatment using folk remedies is possible, but only with the permission of a specialist.
If a staphylococcal infection is not treated, a pregnant woman may experience rupture of the membranes, premature birth, or intrauterine fetal death. Prevention of streptococcus is very simple: maintaining personal hygiene, preventing colds, strengthening the immune system. With timely treatment, you can get a normal outcome and avoid unwanted complications.
What is streptococcus
Microorganisms of the streptococcal family belong to anaerobic bacteria, have a spherical or ovoid shape, and are parasites of animals and humans. Bacteria multiply and live in the respiratory system, gastrointestinal tract, skin, and genitourinary system. A large number of streptococci settle in the mouth, nasal cavity, throat, and large intestine. The pathogen is found in the urethra in men and in the vagina in women. In nature, streptococci are common on the surface of mushrooms, plants, and in the ground.
Streptococcal bacteria belong to the opportunistic microflora and are constantly present inside the human body. The microorganism does not cause harm at low concentrations; its quantity is controlled by the immune system. When the body's defenses weaken, streptococci begin to actively reproduce, releasing toxins that poison a person, leading to inflammation and infectious diseases.
Groups
Today, more than 100 species of streptococci are known, which differ in their pathogenicity. Depending on the effect on red blood cells, there are 3 main groups of these bacteria:
- Viridans or alpha streptococci - provoke incomplete hemolysis.
- Beta-hemolytic streptococci - cause complete destruction of red blood cells and are the most dangerous for humans.
- Gamma streptococci are non-hemolytic bacteria. Pathogens do not cause destruction of red blood cells.
Mechanism of action on the body
The pathological effect on the human body is due to the ability of streptococci to produce toxins during their life processes:
- erythrogenin - under its influence, vasodilation occurs;
- streptolysin – promotes the destruction of heart tissue and blood cells;
- enzymes (hyaluronidase, amylase, streptokinase, proteinase) - help streptococcus quickly spread throughout the body;
- lethal toxin, necrotoxin – cause tissue necrosis;
- leukocidin - harms the immune system, negatively affecting white blood cells.
High levels of streptococcus in the urine indicate the presence of diseases of various organs and systems. The pathogen can cause the following pathologies:
- sore throat, scarlet fever, tonsillitis, pharyngitis;
- urethritis, cervicitis;
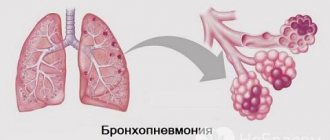
- bronchitis, pneumonia;
- prostatitis, balanitis;
- meningitis;
- cystitis;
- sepsis;
- periodontitis;
- pyelonephritis.
Treatment
If a high concentration of streptococci is detected in the urine, complex therapy is prescribed. Treatment is carried out in the following areas:
- antibacterial therapy (preliminary testing is carried out to determine the sensitivity of bacteria to various types of drugs);
- strengthening the body's immune defense;
- restoration of intestinal microflora disturbed by taking antibiotics;
- detoxification therapy;
- symptomatic treatment;
- prescription of antihistamines (necessary for children if they are allergic to antibiotics).
Each direction of treatment involves the use of medications. The following groups of drugs are used:
- antibacterial drugs for internal use (Penicillin, Augmentin, Levofloxacin, Ceftriaxone, Erythromycin);
- local antibiotics (Bioparox, Tonzilgon N, Chlorhexidine);
- immunomodulatory agents (Immunal, Imunorix, Imudon, Lizobakt);
- probiotics (Bifidumbacterin, Linex, Bifiform, Acipol);
- detoxification (Enterosgel, Albumin, Atoxil);
- antihistamines (Suprastin, Claritin, Cetrin);
- anti-inflammatory (Paracetamol, Ibuprofen);
- vasoconstrictors (Farmazolin, Noxprey);
- antiemetics (Cerucal, Motilium).
Symptoms of an increased concentration of streptococcus in the urine
The presence of increased levels of bacteria in the urine causes negative manifestations in organs and systems. When infected with streptococcus, the following symptoms are characteristic:
- frequent urge to urinate;
- increase or decrease in body temperature;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the groin area;
- rash in the form of spots on the skin;
- painful sensations, burning sensation when urinating;
- acute pain in the lower abdomen;
- discharge of cloudy urine;
- redness at the affected areas;
- pain in the throat, pharynx;
- the formation of a whitish coating in the form of flakes on the mucous membranes of the cheeks, pharynx, and tongue;
- nausea, vomiting;
- increase or decrease in blood pressure;
- aching pain in the lumbar region.
Patients develop an allergic reaction to the waste products of the pathogen. It manifests itself as a spotty rash that is covered with yellow crusts and contains pus. Infection with streptococcus often provokes autoimmune processes that cause destruction of joints, heart, and kidneys. Impaired functioning of the filtering organ leads to an increase in the level of creatinine in the patient’s blood.
In the absence of timely treatment, infection with streptococci can develop endometritis, urethritis, vaginal candidiasis, chronic inflammation of the bladder and prostate gland. Purulent discharge appears from the urethra, patients experience severe pain in the lower abdomen, lumbar region, itching, and swelling. The autoimmune disease glomerulonephritis is a late complication of infection caused by streptococcus. In the kidneys, healthy connective tissue is replaced, and the functioning of the organ is disrupted.
Children may experience symptoms of early and late infection. In the first case, the onset of the disease occurs in the first week of the baby’s life and can lead to pneumonia, sepsis, and meningitis. The disease is accompanied by increased drowsiness, fever, and problems with the respiratory system. Late infection occurs from 7 days to 3 months after the birth of a child and provokes sepsis and meningitis. The disease occurs with high body temperature, cough, nasal congestion, drowsiness, convulsions, and problems with eating.