Causes
Until now, experts cannot name the exact causes of the pathology. However, there is an opinion that cardiospasm of the esophagus develops as a result of disturbances in the functioning of the muscular and nervous tissue of the organ.
That is why factors that provoke the disease include frequent stressful situations and depressive states.
Among the possible causes of achalasia, doctors identify:
- pathologies of infectious etiology;
- viral diseases;
- lack of B vitamins in the body;
- poor and unhealthy diet;
- violation of the innervation of the organ.
Pathology can develop due to congenital nerve plexus defects.
The disease is also considered a complication of oncological processes occurring in the body. The disease is provoked by lupus erythematosus and polymyositis.
Disease prevention
The course of the disease is slow and progressive. If treatment is not timely, this can lead to internal bleeding, exhaustion and perforation of the walls of the esophagus, as well as stomach pain. Achalasia can also cause stomach cancer.
The simplest method of preventing the disease is proper nutrition. Doctors recommend chewing food thoroughly and slowly. Mandatory and constant monitoring of the patient by the attending physician is also provided.
Stressful and shock situations should be excluded. They harm not only the esophagus, but can also affect the health of the stomach. If you experience constant stress and depression, you need to turn to taking sedatives.
Symptoms of the condition
The main signs of the disease include:
- impaired swallowing (dysphagia);
- night cough;
- nausea;
- suffocation;
- heartburn;
- bad odor from the mouth;
- belching;
- increased salivation;
- loss of appetite;
- sleep disorder;
- reflux of food from the esophagus into the pharynx (regurgitation).
Often patients with this diagnosis complain of chest pain. Such sensations can radiate to the shoulder blade, shoulder, jaw or neck. In pathological conditions, gastric juice can be released into the upper esophagus .
If such symptoms are observed, it is important to contact a gastroenterologist who will confirm or refute this diagnosis.
This disease should not be confused with chalazia. The difference between these pathologies is that in the first case there is a violation of the opening of the cardia (sphincter), in the second there is a failure in its closure.
With chalazia, prolonged vomiting, heartburn and aching pain in the pit of the stomach or in the solar plexus area usually occur.
Signs and symptoms of gastric cardia insufficiency - when to consult a doctor?
At the initial stages of its development, the pathology in question may not manifest itself in any way.
Sometimes patients experience discomfort in the stomach after eating, or slight pain in the indicated area.
As degenerative processes progress, the following symptoms become apparent:
- Dysphagia . Difficulties with swallowing food can be selective: problems arise specifically with a specific type of food. The patient feels as if something is stuck in his throat, and the process of moving chewed food from the esophagus to the stomach is almost completely felt by him. At stages I and II of the disease, such complaints are of an episodic nature, but over time they become regular. In addition, swallowing liquid food often causes more difficulties - solid food puts more pressure on the walls of the esophagus, causing mechanical opening of the lower sphincter. This point has important diagnostic significance: with inflammatory phenomena and cancer, patients cope with liquid food much easier, while solid food causes severe pain.
- Regurgitation . Due to contraction of the esophagus, chewed food is thrown back into the oral cavity. At the initial stages of the disease, the symptom in question is represented by slight regurgitation almost immediately after eating. At stages III and IV of achalasia cardia, the situation is more complicated: instead of regurgitation, esophageal vomiting occurs. It can occur a couple of hours after eating, or during sleep ("wet pillow" syndrome). In the latter case, the development of pulmonary exacerbations cannot be ruled out: vomit can penetrate the respiratory tract, causing coughing and sometimes aspiration. Signs and symptoms of reflux esophagitis - diagnosis of reflux esophagitis, consequences of the disease
- Pain syndrome . At the beginning of the disease, when the pathological changes are not so pronounced, the pain is localized in the stomach area and makes itself felt immediately after swallowing chewed food. Subsequently, in the later stages of the disease, pain radiates to the chest area, neck, and sometimes even to the lower jaw. The whole picture described is accompanied by nausea and vomiting. After vomiting, short-term relief occurs. In advanced stages of the disease, pain is paroxysmal in nature: it can last several minutes or bother the patient for an hour. Physical activity, excessive anxiety or other factors can provoke another attack. The pain does not always go away on its own - in some cases, antispasmodics are required.
- Signs of asthenia . Due to the insufficient amount of useful microelements entering the body, a person begins to lose body weight over time. Among other things, discomfort after each meal negatively affects the psycho-emotional state, which affects appetite. The patient, for fear of developing another attack, is simply afraid to eat.
Rate
—
Features of the disease at a young age
The disease develops extremely rarely in children. Usually the pathology occurs after the age of five. Manifested by vomiting during or after eating.
Children often suffer from bronchitis and pneumonia if they have this disease. There is a cough, which is observed at night, and regurgitation.
The disease in childhood is characterized by dysphagia. Anemia often develops against the background of pathology, and physical development may be delayed as a result of poor nutrition.
Esophageal achalasia is also possible in infancy. When sick, newborns begin vomiting during breastfeeding and the frequency of regurgitation increases. Vomit has the appearance of uncurdled milk with the absence of gastric juice.
Over-the-counter medications for sunburn
Specific treatment for pain and fever can be achieved using special medications that should be in your first aid kit. First aid for sunburn can be provided by:
- acetylsalicylic acid in the form of 1 tablet;
- NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs): ibuprofen, ketoprofen, ortofen.
It is recommended to put panthenol spray in your travel bag. This medicine quickly relieves inflammation in the burn area and helps cope with other unpleasant symptoms.
Before using any medicines:
- carefully read the information on the packaging and instructions;
- follow the recommended dosage;
- Avoid taking medications to which the affected person has a history of allergies;
- Avoid using aspirin for people over 20 years of age, especially if they have gastrointestinal pathologies;
- Pregnant women should avoid taking medications unless specifically advised.
Diagnostic methods
Signs of the disease can be confused with symptoms of other pathologies of the digestive system. That is why the patient is required to undergo mandatory examination. The following diagnostic methods are prescribed for diagnosis:
- X-ray. Radiological signs of the disease can be determined using a contrast agent (barium).
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy. The esophagus and stomach are examined using an endoscope.
- Manometry. This method allows you to determine the state of various parts of the esophagus during swallowing.
In addition, a chest x-ray is taken. Laboratory methods for testing blood and urine are also shown.
Classification of pathology
There are 2 types of achalasia depending on the main reason for its development:
- Idiopathic (primary). It occurs as an independent disease.
- Symptomatic (secondary). Develops as a symptom of various diseases.
Experts distinguish four stages of the disease according to their characteristic features:
- First. The lower esophageal sphincter relaxes during swallowing, and its basal tone increases to a moderate extent. As a result, food does not pass well through the esophagus.
- Second. There is a constant increase in the basal tone of the esophageal sphincter, and the organ itself expands.
- Third. The distal region of the esophagus begins to scar, which causes stenosis and expansion of the parts of the organ that are located above this zone.
- Fourth. The narrowing in combination with expansion and scars is more pronounced. At this stage, complications of esophageal achalasia develop.
Depending on the degree of the disease, appropriate treatment is prescribed. It can be conservative or surgical. The main goal is to normalize the motor function of the esophagus.
Negative effects of sunburn
Sunburn of the skin is a trophic disorder caused by the sun and excessive sunbathing. It is necessary to exclude failure to take measures to protect against ultraviolet radiation. Most of these burns are clinically manifested by pain of moderate intensity, occurring against the background of intensely erythematous areas of the lesion with altered sensitivity.
Second degree sunburns are deeper injuries and therefore more painful and require more time to heal as well as complex treatment. The skin, in this case, is very hyperemic, swollen and covered with blisters (vesicles or pustules). The pain is also more intense. This confirms a serious injury involving nerve endings.
It is worth knowing that prolonged exposure to open sunlight can also provoke:
- heatstroke or other problems caused by excessive temperature;
- allergic reactions to UV radiation as well as some sunscreens;
- vision problems: decreased visual acuity, damage to the retina, up to partial or complete loss of vision.
Long-term dangers of sunburn include:
- increased risk of developing skin cancer;
- exacerbation of diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis;
- the appearance of cataracts (direct harmful effects of intense sun over a long period of time), this, in turn, is one of the reasons for the development of blindness;
- pigmentation and structural changes in the skin - the appearance of brown spots and premature wrinkles.
The severity of these problems depends largely on each individual skin type. Thus, people with fair skin, freckled blondes, or redheads with blue eyes are more sensitive to radiation. Age also plays an important role. People are most prone to burns under the age of 6 and over 60 years of age.
Drug treatment
In the initial stages of the disease, if symptoms are not expressed, treatment with medications is prescribed. For the disease, the following groups of drugs are used:
- Nitrates (Isosorbide dinitrate, Nitroglycerin). These drugs help improve esophageal motility.
- Calcium channel blockers (Nifedipine, Verapamil). They are prescribed more often. Drugs in this group help relax the muscles of the organ.
- Antispasmodics (Halidor, No-shpa, Papaverine). Help relieve cardiospasm and reduce pain.
- Prokinetics. Used for normal motor function. These include medications such as Ganaton and Motilium.
Also in some cases, antacids and sulfates are used.
Tablets help temporarily eliminate symptoms. If medications do not help, then surgical treatment is prescribed.
Surgical method
In the first and second stages, bougienage of the esophagus using an endoscope is usually prescribed. This treatment is quite effective, but sometimes complications develop, for example, organ perforation.
In the final stages, surgical intervention is used - laparoscopic cardiomyotomy. If such an operation is ineffective (as a result of atony or deformation of the organ), then extirpation is performed, in which the esophagus is removed. In this case, esophagoplasty of the organ is performed.
Dilatation is often prescribed, in which the cardia is stretched using a special balloon. This procedure is performed several times at intervals of five or six days.
Balloon dilation may have side effects. A dangerous complication during this procedure is rupture of the esophagus.
Risk factors for sunburn
To date, it is not reliably known what exactly provokes the development of the pathological condition in question.
However, there are many theories regarding the factors contributing to the dysfunction of the cardia muscles:
- Frequent exposure to stressful situations. Stress negatively affects the condition of all internal organs, but first of all it affects the gastrointestinal tract.
- Defects in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, which may be congenital or acquired.
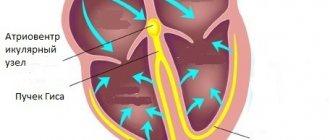
- Degenerative changes in the area of the esophageal wall, which negatively affect the structure of the Auerbach plexus. Thanks to this plexus, the muscles of the esophagus contract.
The intensity of skin damage depends on several factors, among which both the time chosen for tanning and diet are important.
- There is a higher risk of developing sunburn if exposure to ultraviolet rays occurs between 10 am and 4 pm. At this time, peaks in radiation intensity occur. You need to know that ultraviolet rays can easily pass through clouds.
- Positioning a person near surfaces that can reflect sunlight, such as water, white sand, snow or ice. UV rays reflected from them have double the harmful effects.
- Time of year (season) - the risk is higher during the summer due to the position of the sun.
- Altitude: At higher altitudes, due to the low level of filtration of radiation through the layers of the atmosphere, the intensity and severity of sunburn is higher.
- Latitude (relative to the equator): the closer to the equator, the greater the volume of direct rays passing through the atmosphere.
But sunburn can be prevented by taking protective measures before and after sun exposure. Basic preventative measures include:
- reducing time spent in the sun;
- choosing the right time for tanning;
- use of sunscreens;
- using clothing that does not allow ultraviolet rays to pass through.
Alternative remedies
Traditional treatment is used as an auxiliary method. It is usually recommended to use restorative medications based on medicinal plants such as:
- aloe;
- Eleutherococcus;
- marshmallow;
- ginseng;
- Rhodiola rosea;
- lemongrass
Folk remedies are used to relieve symptoms such as heartburn and pain. For this, a decoction of oregano and calamus is used. Efficiency is observed when taking products based on St. John's wort, motherwort, valerian and sage.
For achalasia of the esophagus, it is recommended to drink 20 drops of alcoholic infusion of Manchurian aralia roots. The product must be taken three times a day.
Medicines that reduce the symptoms of the disease and improve motility of the esophagus include a decoction of alder cones and an infusion of quince seeds.
Proper nutrition
One of the important nuances of treatment is diet. Proper nutrition during illness involves avoiding eating fried, fatty and spicy foods. Alcoholic and carbonated drinks are not allowed.
It is recommended to consume juices and drinking yoghurts more often. For the diet, soups and low-fat broths, liquid porridge, vegetable purees, fresh vegetables and fruits will be optimal. It is better to eat dishes that are pureed, not too cold and not too hot .
Food intake for this disease should be in small portions, but the frequency of eating increases - up to five to six times a day.
Proper nutrition involves chewing food thoroughly. Meals should be washed down with warm liquid. Plain water or tea is suitable for this.
Clinical recommendations from experts also include drinking mineral waters.
Complications
As a result of the disease, esophagitis (an inflammatory process in the organ) usually occurs. A hiatal hernia is a common complication of this pathological condition. If the disease is not treated in a timely manner, other serious complications may develop in the final stages.
These include:
- esophageal diverticula;
- pneumocarditis;
- pericarditis with purulent course;
- Barrett's syndrome;
- organ bezoars;
- oncological diseases;
- esophageal ulcers;
- pericardial-esophageal fistula.
Also, the pathology often affects the lungs, formations appear on the neck, and the mucous layer of the esophagus may peel off.
Esophageal achalasia is a fairly rare pathology. It significantly worsens the patient’s quality of life and leads to various complications. The disease's symptoms are similar to other ailments. Therefore, it is important to diagnose it in time and begin treatment, which consists of taking medications and folk remedies. At some stages, surgery is also indicated.
Stages of achalasia of the esophageal cardia
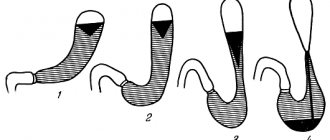
In its development, the pathology in question goes through several stages:
I - episodic disruptions in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract . The walls of the esophagus retain their elasticity, but spasms of the lower esophageal sphincter occasionally occur.
II - stable cardial dysfunction . Due to the slow movement of the food bolus, the walls of the esophagus lose their original shape - they stretch.
The first two stages of the pathology can last several months. Without treatment, the condition worsens and the disease progresses to the next stages of development.
III - stage of scarring of cardial stenosis. The esophagus expands to 6-8 cm, not only water, but also liquid is retained in it. Peristalsis is impaired.
IV - depletion of the walls of the esophagus and its acquisition of an S-shape . All this leads to the development of exacerbations: ulcerative defects, inflammatory reactions, extensive scarring, etc.
It may take several years for complications to become apparent. In general, insufficiency of the gastric cardia is characterized by periodicity: exacerbations are replaced by remissions.