In medical practice, there are various diseases of the bladder in women, the symptoms are both general and specific. With any inflammatory process in the genitourinary system, a slight increase in body temperature is possible. There is also an increased urge to urinate, pain and a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. With cystitis, urinary incontinence may develop without the urge to urinate. The color of the urine changes and a cloudy sediment appears.
Inflammatory processes in the bladder can develop for several reasons. Cystitis occurs when infection penetrates from the vagina into the urethra. In the vagina of a healthy woman there is a microflora consisting of lactobacilli, bifidobacteria and opportunistic microorganisms. Bladder inflammation is often caused by vaginosis, an imbalance in microflora.
Bladder pathologies
In women, the following bladder pathologies are identified:
- urethritis;
- cystitis;
- urolithiasis disease;
- neurogenic dysfunction (impaired innervation of the bladder);
- leukoplakia.
Less common: cystocele, tuberculosis or bladder cancer.
Urethritis
This pathology develops when an infection enters the urethra due to poor personal hygiene.
The following symptoms appear:
- frequent urination with a feeling of tingling, itching, burning;
- blue-green discharge from the urethra.
Cystitis
This disease of infectious origin is an inflammation of the urinary mucosa. May appear against the background of urethritis.
The symptoms of the disease are:
- frequent urination;
- pain in the form of cutting even at rest, which intensifies during urination;
- the organ feels full;
- Possible involuntary urination.
The color of the urine changes, and there is a cloudy sediment in it; there is a sharp and unpleasant odor. The general condition worsens - the temperature increases, symptoms of fever and general weakness occur.
Cystitis can occur with periods of remission for quite a long time, then we are talking about a chronic form of the disease. In chronic cystitis, relapses occur, the symptoms of which are similar to the acute form of the disease. The chronic form occurs against the background of an acute one, when the disease is not completely cured, or self-therapy was carried out without contacting a specialist.
Causes of bladder infection:
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- hypothermia;
- excessive consumption of hot, spicy, smoked foods and alcohol;
- anal sex;
- immune and hormonal imbalances in the body.
The culprit of the pathology is usually E. coli, which lives in the gastrointestinal tract. It penetrates the woman’s urethra and multiplies in the bladder, promoting inflammation. Provocateurs of cystitis are intestinal trichomonas and staphylococcus.
Video on the topic:
Cystalgia
This is a typical female disease. It occurs due to a failure in the regulation of bladder functions of an endocrine-nervous nature. The symptoms are very similar to those of acute cystitis, accompanied by an unstable psychological state. Most often, the disease affects unbalanced, vulnerable women who lead a sedentary lifestyle, aged 20-50 years.
Symptoms of cystalgia are associated with the process of urination:
- aching pain;
- muscle pain after bowel movement;
- slight urine discharge.
When examining the organ, no signs of inflammation are observed; vascular hyperemia is detected.
Since the disease is not infectious and is not characterized by an inflammatory process, treatment is advisory. Advise:
- physical activity (sports, walking, swimming);
- proper nutrition (spicy foods, alcoholic drinks, and foods that irritate the intestines are excluded);
- psychocorrection (sedatives, relaxation).
Urolithiasis disease
In women, this abnormality of the bladder can be caused by a metabolic failure or prolonged congestion in the urinary system, as well as the penetration of stones or sand through the ureters from the kidneys into the bladder. Stones are found in women of different ages and come in different sizes, shapes and structures. There are cases of asymptomatic development of pathology.
Signs of urolithiasis:
- a feeling of heaviness, bloating and pain in the abdomen (its lower part);
- burning during urination;
- the presence of blood streaks in the urine due to traumatization of the urinary tract mucosa by stones (blocking the urethra with a stone makes the stream of urine intermittent or absent altogether).
Symptoms may worsen after exercise.
Neurogenic bladder dysfunction or innervation disorder
In this case, there is no ability to control urinary function, and this is associated with neurological, psychological or traumatic disorders. The cause of such disorders can be both congenital and acquired diseases of the nervous system or stressful situations. Disorders of this kind in old age can be observed in both women and men.
The following reasons can be noted for the occurrence of such pathology of the bladder:
- tumor or inflammatory processes affecting areas of the spinal cord or brain (stroke, encephalitis, intervertebral hernia);
- prolonged stress;
- spinal cord or brain injury (concussion, spinal fracture).
The disease may affect:
- brain and spinal cord;
- peripheral nerves.
Characteristic is complete or partial loss of urinary control. The severity of symptoms depends on the degree of damage to the nervous system.
The symptoms are:
- frequent urge to empty the bladder or, conversely, their almost complete absence;
- little or no discharge;
- intense sensations of pain in the lower abdomen;
- frequent night urination (more than 2 times per night);
- incontinence from bladder overflow.
There are 3 types of neurogenic bladder dysfunction (impaired urine flow):
- atonic type (hypotension). This type is characterized by low organ tone and lack of urge to urinate. An increase in the volume of urine causes the sphincter to relax and urine cannot be retained;
- autonomous type (non-reflexive). With this type, the patient experiences urge only after the bladder is full. This anomaly occurs when the central nervous system is damaged.
- spastic type (hyper-reflex bladder). It is characterized by involuntary urination when fluid first enters the body. There is a constant leakage of urine, an intermittent stream is observed when urinating, and frequent urination is typical, mainly at night.
Leukoplakia of the bladder
It forms in patients against the background of the presence of a chronic infection in the genitourinary system, as well as due to hormonal changes (menopause, long-term use of oral contraceptives). This pathology is quite rare.
The disease is characterized by pathological changes in the bladder, during which the transitional epithelial cells of the mucous membrane are replaced by keratinized (flat) epithelial cells that do not have protective functions.
Causes of the disease:
- intestinal infections (Trichomonas);
- sexually transmitted infections (gonococcus, mycoplasma, chlamydia, ureaplasma);
- herpes virus.
The source of the disease can be:
- intrauterine contraceptives;
- chronic pathologies of the genitourinary system;
- promiscuous sex life without the use of contraception;
- disruption of the endocrine system.
Leukoplakia is often accompanied by female diseases, like cervical erosion and others.
There are 2 types of leukoplakia:
- bladder body;
- bladder neck (much more common).
The symptoms of this pathology are very similar to the symptoms of chronic cystitis.
The general symptoms of the disease are:
- cramping pain in the lower abdomen;
- increasing discomfort when urinating;
- a burning sensation occurs in the lower abdomen;
- disturbance of the process of urination with an intermittent stream;
- general malaise.
Pyelonephritis
The entry of microbes into the kidney through the ureters and urethra provokes in a woman the most dangerous pathology of the urinary system among ascending infections - inflammation of the renal pelvis (pyelonephritis). The occurrence of this disease is facilitated by a failure of the process of urine outflow from the kidney, problems in neuromuscular conduction, constant overflow of the bladder, weakness of the smooth muscles of the organ, and cystitis.
The first symptoms of acute pyelonephritis are fever, lower back pain and painful urination.
Bladder neoplasms
Bladder cysts are often congenital. This benign neoplasm can be diagnosed at any age. The presence of a cyst can be checked by palpation of the lower abdomen. The cyst is located between the navel and pubis. It may not show itself for a long time. When the cyst develops to a large size, an acute inflammatory process occurs, which is accompanied by suppuration.
The cavity may contain particles of serous fluid and mucus inside; when they leave the capsule, infection of the surrounding tissues occurs and an increase in temperature is observed, acute pain occurs, which becomes more intense in a standing position. When the contents of the cyst enter the bladder, the urine becomes cloudy and has an unpleasant odor. When contents leak into the abdominal cavity, peritonitis develops.
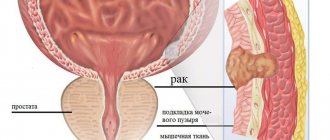
Bladder cancer is rare in women .
Its symptoms are similar to those of urolithiasis or cystitis. A clear clinical picture is possible when the tumor is located near the urethra. The development of a malignant tumor is characterized by the appearance of bloody impurities in the urine. Symptoms of irritation of the walls of the bladder may be observed - frequent, often false, urges to empty the bladder, a feeling of incomplete emptying, pain in the lower abdomen, and difficulties with urine excretion.
Cystitis
Cystitis takes the lead among bladder diseases in women. This is due to the fact that the female urethra is short and is located next to the exit of the rectum, therefore it is easily accessible for pathogenic microbes to enter the bladder. The culprit of the pathology in most cases is Escherichia coli, which normally lives in the gastrointestinal tract. It enters the short and wide urethra of a woman and multiplies in the bladder, promoting inflammation. The causative agents of cystitis can be intestinal trichomonas and staphylococcus.
According to the course of the disease, acute and chronic cystitis are distinguished. The chronic form develops against the background of an acute form in cases of an incompletely cured disease, or self-therapy without contacting a specialist.
Diagnosis and treatment
Urinary tract inflammations are treated comprehensively. Depending on the type of disease, different drugs are prescribed.
Urethritis
Therapy for urethritis includes antimicrobial drugs. To prescribe adequate treatment, urine culture is prescribed to determine the causative agent of the pathology.
Cystitis
For cystitis, antibacterial treatment is carried out using antibiotics, antifungals, antispasmodics and other drugs. To relieve pain at home, you can place a bag of heated cereal or a bottle of warm water on the lower abdomen.
You should drink a weak solution of baking soda several times a day. This helps reduce the acidity of urine and relieve discomfort. It is advised to follow a special diet and drinking regime: you need to consume about 2-2.5 liters of water per day, exclude coffee and alcoholic drinks from your diet, and reduce the consumption of foods high in calcium.
Neurogenic pathology of the bladder
Therapy for neurogenic pathology of the bladder begins with determining the cause of the pathology. There are 2 options: medicinal and surgical. When the cause of bladder dysfunction is neoplasms, mechanical damage, or pathologies of the brain or spinal cord, surgical intervention is performed. In case of emotional shock or prolonged stress, the use of medications is accompanied by psychological correction.
It is also recommended to douche with antiseptic agents, receive thermal procedures, and in the diet - exclude spicy and smoked foods from the diet, drink more water.
If diagnostic methods have confirmed the absence of inflammation in the organ, then the use of sedatives, psychotherapeutic sessions, and complex physical exercises are assumed.
Leukoplakia
When treating leukoplakia, the reason for using surgical or conservative techniques is the stage of development of the disease.
Drug therapy is carried out after tests are taken and the pathogen is detected. Anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial therapy is prescribed, as well as physiotherapy of the bladder structures (where laser, electrophoresis, microwave treatment and magnetic therapy are used).
In the early stages of the disease, traditional methods are effective, for example, herbal teas:
- common yarrow;
- calendula;
- cinquefoil;
- horsetail;
- oats.
Surgery is used if a malignant tumor is suspected. Using a cytoscope, tissue affected by cancer cells is removed while maintaining the integrity of the organ.
Another modern surgical method is laser surgery, which is minimally invasive and non-contact. The foci of the disease are burned out without bleeding. After surgery, hormonal therapy is administered to prevent relapse.
Self-medication of leukoplakia of the bladder is unacceptable, since this pathology is very serious, and its treatment requires supervision by a doctor.
Tasks of the body
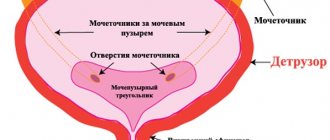
Anatomy describes the bladder as a hollow organ, the main function of which is to collect, accumulate and expel urine (another name for the organ is vesica urinaria). This organ has a unique structure for the human body: the description of the bladder says that it has great extensibility and elasticity, and a round shape.
If we talk about the functions of the bladder, then its main role is that it is a temporary storage of urine . A section of the bladder shows that its walls are covered with folded epithelial tissue. The average thickness of the bladder wall is 2 mm; when stretched, it reaches 1.5 mm. The folds of the bladder mucosa are stretchable enough to accommodate an average of 600 mm of fluid.
From the point of view of evolutionary anatomy, the bladder consists of remnants of the epigastrium present in embryos. This is related to the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the organ, as well as the peculiarities of the control of its activity by the nervous system. According to Chinese medicine, the bladder meridian is the longest. The Bladder Meridian has 67 points, runs along the entire back of the body and is used to treat most organs of the body.
Preventive measures for bladder pathologies in women
Bladder pathologies can be prevented. To do this, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- following the rules of personal hygiene;
- timely detection and treatment of foci of chronic infections in the genitourinary system;
- avoiding hypothermia;
- maintaining a high level of immunity;
- timely emptying of the bladder;
- proper and healthy nutrition, drinking enough water.
An effective means of preventing cystitis is cranberry juice. The components of cranberry juice create a barrier against microbial flora and prevent the development of harmful colonies on the wall of the organ.
How does urination occur?
There is also a concept called “stretch reflex vesica urinaria”. This is a primitive reflex with centers located in the spinal cord. This stimulates urination in response to stretching of the vesica urinaria. This reflex acts like the knee-jerk reflex when the neurologist taps the kneecap with a hammer. When babies are trained to go to the toilet, this reflex is canceled by the higher nerve centers in order to establish voluntary control over urination.
During bowel movements, the muscles of the organ contract, and the sphincters relax and release urine. Therefore, the way the bladder works helps push urine out. This process occurs as follows:
- Vesica urinaria fills with urine and the walls expand. Sensory nerves sense stretch receptors and send signals to the spinal cord.
- Interneurons of the spinal cord switch the signal to the parasympathetic efferent (motor) fibers of the pelvic nerve.
- The pelvic nerve contracts the detrusor muscle, stimulating urination.
Despite the fact that after childhood this reflex is suppressed by higher nerve centers, its action should be taken into account in cases of spinal cord injuries, as well as in neurodegenerative diseases, when the brain is not able to send an inhibitory command.
Prevention
Diseases of the internal organ are easier to prevent than to treat. For this purpose, regular prevention is used, including proper nutrition and a normal daily routine. It is recommended to perform light physical activity daily and take vitamin complexes that strengthen the immune system. Hypothermia of the pelvic organs should be avoided. Stress and anxiety have a negative impact on the body, so you should protect yourself from them. It is necessary to ensure the cleanliness of the genitals so that the infection does not spread to the organs of the urinary system.
Spinal cord injuries
In clinical practice, the connection between vesica urinaria and spinal cord injuries is particularly important. There are two main clinical syndromes that occur depending on where the spinal cord is damaged.
The first is neurogenic or autonomic vesica urinaria with spinal cord injury above the T2 level. In this case, afferent signals from the walls of the organ are unable to reach the brain, and the patient cannot realize that the bladder is full. There is also no conscious control over descending signals to the external sphincter. As a result, the vesica urinaria is constantly in a relaxed state.
But at the same time, the spinal reflex remains involved, responding to the stretching of the organ. Therefore, the parasympathetic nervous system includes contractions of the detrusor muscle in response to the filling of the bladder with urine and stretching of its walls. As a result, the vesica urinaria itself empties as it fills (neurogenic vesica urinaria).
When flaccid vesica urinaria is observed, it means that the spinal cord is damaged below the T12 level. As a result, the transmission of commands from the parasympathetic nervous system to the bladder is disrupted. In this case, the detrusor muscle is paralyzed and its contractions become impossible. The spinal reflex also does not work. In this case, the hollow organ can fill to its limit, stretching much more than it would normally. This happens until involuntary urination begins.