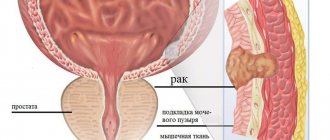
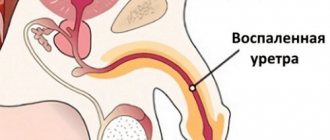
Cystoscopy is an endoscopic examination of the walls of the bladder using an optical system. Cystoscopy is usually combined with urethroscopy (urethrocystoscopy), since on the way to the bladder the device allows you to examine the walls of the urethra along its entire length. In this way, the most complete picture of the condition of the urinary tract is compiled. Previously, these types of diagnostics were considered separately, since different devices were used for them; today their functionality is combined. There is no equivalent replacement for cystoscopy. Neither X-ray nor ultrasound will give such an accurate picture of the condition of the internal lining of the urethra and the walls of the bladder.
Cystoscope
Modern cystoscopes perform all the functions of urethroscopes. The main element of a viewing cystourethroscope is a long thin tube in which the visual (optical system), lighting, and irrigation (irrigation) channels are combined. The tube can be rigid or flexible.
Rigid cystourethroscope
The tube diameter ranges from 1.9 to 4 mm. A rigid cystoscope provides a greater overview.
Flexible cystourethroscope (fiber ureteroscope)
Video ureteroscope
Purpose of the procedure
Urethroscopy helps to identify the following pathologies:
- Chronic cystitis;
- Neoplasms and stones in the bladder, wall defects (diverticula - protrusions);
- Prostate enlargement (this changes the shape of the bladder);
- Ulcers and damage to mucous membranes;
- Strictures (narrowings, fusions) of the lumen of the urethra, as well as papillomas and condylomas.
The absolute indications for urethrocystoscopy are blood in the urine, renal colic, and urinary disorders that cannot be diagnosed by other methods.
There is a special toolkit for cystourethroscopes, so with the help of these devices the doctor can perform not only diagnostic, but also therapeutic manipulations:
- Remove small stones.
- Take material for a biopsy if suspicious areas are detected.
- Rinse your bladder.
- Dissect urethral strictures.
- Remove condylomas and other benign tumors.
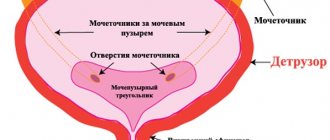
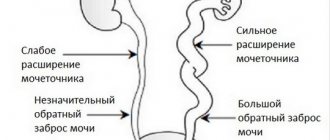
Cystoscopy is necessary for catheterization of the ureters in cases where the outflow of urine from the kidneys is difficult, as well as for relieving renal colic.
Catheterization of the left ureter
During cystoscopy, the doctor can also assess the condition of the seminal tubercle, the prostatic part of the urethra (how free its lumen is).
Features of conducting and evaluating chromocystoscopy
Before cystoscopy, 2-3 ml of 0.4% indigo carmine solution is injected intravenously or intramuscularly, the onset and severity of dye release into the bladder with urine from the ureters is observed and recorded. With intravenous administration, the expected time for the contrast to appear in the bladder is 3-5 minutes, with intramuscular administration - 15-20. Delay indicates a malfunction of the kidneys or obstructions in the ureters.
The absence of contrast in the bladder 12-15 minutes after injection into the vein indicates blockage of the lumen of the ureter:
- stone;
- with the development of stricture (fusion of walls due to inflammation);
- tumor.
The reason for the slow release of the dye into the bladder, in addition to damage to the ureters, is a sharp violation of the excretory function of the kidney.
Preparation and progress of the procedure
1-2 hours before cystoscopy, it is advisable to do a cleansing enema (the doctor may consider it necessary to conduct a rectal examination of the prostate for hyperplasia). On the day of the procedure, it is advisable not to consume food or irritating drinks. To exclude contraindications, before cystoscopy you need to undergo a general and biochemical blood test, a coagulogram, and it is advisable to perform an x-ray of the urethra (the study will show its shape and width of the lumen).
In case of acute inflammation of the genitourinary system, the procedure is not performed, and to prevent exacerbation of chronic pathologies, the patient is pre-administered a broad-spectrum antibiotic. As an alternative, you can take Monural at 10 pm on the eve of cystoscopy.
Immediately before cystoscopy, it is necessary to empty the bladder . Then the patient is placed on a urological chair (legs are spread apart and fixed on holders). Externally, the genitals are treated with an antiseptic solution.
For each patient, the diameter of the cystoscope tube is selected individually. Before insertion, it is lubricated with lubricant to facilitate insertion. This is usually medical glycerin, which does not impair the quality of the review. An anesthetic (2% warm solution of novocaine, gel with lidocaine or xylocaine) is poured into the urethra using a syringe with a rubber tip and manually massaged to the posterior urethra (inner part). If the patient has an unstable nervous system or there are painful changes in the mucous membrane of the urethra and bladder, then cystoscopy is performed under general or epidural anesthesia.
Stages of introducing a cystoscope into the bladder
In order not to injure the urethral mucosa during insertion, the tip of the cystoscope is protected by a special cover - an obturator, which is then removed, and its place is taken by the optical system. During the advancement of the device, the urethra may spasm (the sphincter in the bulbous part of the urethra will close), then the patient is asked to breathe deeply (with general anesthesia this is impossible, so doctors try not to use it). After passing through the urethra, the optics at the end of the device are replaced with cystoscopic ones.
With benign hyperplasia, the process of inserting a cystoscope is complicated because the prostatic part of the urethra becomes longer and its course changes.
To examine the walls of the bladder, you need to smooth them out as much as possible. Two methods are used for this:
- Dry, in which the bladder fills with air.
- Irrigation, when a special liquid (approximately 200 ml) acts as an expander.
Animation of bladder cystoscopy in men
Urine is not suitable as a filler, as it will significantly degrade image quality and can damage optical parts. After inserting the device, its remains are removed (suctioned off), and the bladder is washed with a warm solution of furatsilin. To take material for a biopsy, a special instrument is inserted that pinches off a piece of tissue (the process is painless). Cystoscopy lasts from 15 to 40 minutes. The conclusion is prepared within 15-20 minutes.
How to prepare for cystoscopy
To ensure that the examination is completed as quickly as possible and without complications, you should adhere to the following rules.
- Wash your genitals thoroughly. Hair in the pubic and perineal area must be removed.
- The diagnostic study is carried out under general anesthesia, and therefore you should not eat 8 hours before the test. The fullness of the bladder does not play a special role.
- Take a general blood and urine test first. This data complements the clinical picture and will help the doctor make a diagnosis.
- A blood coagulogram is mandatory.
- It would not hurt to conduct a preliminary x-ray and ultrasound diagnosis of the bladder.
It is also worth telling your doctor information about taking medications and previous therapy. Many drugs can distort the reliability of the examination and also cause undesirable consequences.
2 days before the study you should stop taking anticoagulants and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Whenever possible, people with diabetes should avoid using insulin.
Many people are interested in the question of whether cystoscopy is painful. The examination is accompanied by psychological and physical discomfort; the insertion of the device occurs painlessly, due to the fact that the patient is injected with an anesthetic substance. After completing the procedure, there may be some discomfort when going to the toilet, but it will go away the next day.
results
The healthy mucous membrane of the urethra is gray-red in color, blood vessels are visible through it. The color is uniform along the entire length. The shell is folded. There are no protrusions, ulcers, hemorrhages, ulcers, or protrusions on it.
In acute urethritis, the epithelium becomes bright red and swollen. Purulent effusion and loose growths may appear. Atrophic urethritis (changes in the structure of the walls due to hormonal imbalance) is characterized by the appearance of bluish tubercles - caruncles. If they do not cause concern, then treatment is not required.
In cases of chronic urethral infection, a diverticulum (pouch-like thickening) may be detected during cystoscopy. When squeezed or expanded, pus oozes out. Such formations are often found in patients with complaints of painful sexual intercourse.
In case of bladder injuries, cystoscopy will identify sites of vascular ruptures and hemorrhages. This diagnostic method also makes it possible to detect asymptomatic cystic cystitis (cysts in this case are small formations with fluid that arise at the sites of chronic inflammatory foci).
Picture of cystic cystitis Bladder tumor in the field of view of the cystoscope
Complications
The doctor will never forcefully advance the cystoscope ; he always strives to open the urinary canal, but in the first two days after cystoscopy, most patients still report discomfort when urinating and even bleeding. This is due to the fact that the mucous membrane of the posterior urethra is loose and easily damaged. Symptoms should subside with each passing hour. To relieve discomfort, you can use the urethral gel "Kategel". If the burning sensation does not go away, a dull pain appears in the lower abdomen, and the urine becomes cloudy, this means the development of cystitis. That is, during cystoscopy, an infection entered the bladder or an old, dormant infection became active. In rare cases, acute prostatitis, epididymitis, and urethritis may develop.
Urethral gel "Katedzhel" is a drug with local anesthetic and antiseptic effects for local use. Price in pharmacies from 197 rubles.
The most severe consequences of cystoscopy are a puncture of the bladder or ureter. This happens extremely rarely, usually during a biopsy. The reason is usually the doctor's inexperience. In such cases, acute pain immediately occurs, which does not go away after the procedure, and then the temperature rises. Surgery is necessary to correct the problem.
During the procedure, there is a low probability of developing so-called resorptive fever. This condition occurs immediately, usually during irrigation cystourethroscopy against the background of increased intraurethral pressure. The condition requires urgent intervention.
Rules for preparing for the examination
Preparation for cystoscopy depends on how the procedure will be performed. This is a method of pain relief; local anesthesia is most often used. But in rare cases, general anesthesia may be offered. A few days before the procedure, the urologist or diagnostician will prescribe the necessary tests and studies:
- Ultrasound;
- CT or MRI;
- X-ray;
- urine and blood tests;
- consultation of related specialists: therapist, neurologist, diagnostician, etc.
After this, the doctor will tell the patient what pain relief will be like and how the procedure goes. If you are undergoing general anesthesia, you should refuse food the evening before and on the day of the procedure. Drugs that reduce blood clotting are also prohibited. The doctor needs to be told about all medications that were taken over the past two days. Before the diagnosis itself, the person being examined empties the bladder. After the procedure, the patient is prohibited from driving, so assistance from loved ones may be required. Also, when packing, you need to remember to remember documents related to the disease: reports of previous studies, results of analyzes and tests.
Clinics and prices
Examples of clinics where cystoscopy can be performed:
- "Euromed" (St. Petersburg): 8800 rubles;
- “SM-clinic” (Moscow): dry urethroscopy – 4500 rubles, irrigation – 6000 rubles, cystoscopy – from 8500 rubles;
- “Unified Center for Spermograms and Problem Reproduction” (St. Petersburg): cystourethroscopy – 4400 rubles, cystoscopy with video recording – 3500 rubles.
The pain of the procedure itself and its consequences depend on the type of device, training and professionalism of the doctor.
Answers to frequently asked questions
- MRI or cystoscopy? Cystoscopy is a primary diagnostic examination of the mucous membrane with the possibility of simultaneous removal of a number of neoplasms, making it possible to accurately assess the condition of the organ. MRI of the bladder is mainly prescribed when cancer is diagnosed to determine its stage and determine the extent of spread.
- Is there an alternative to cystoscopy? If there are contraindications to cystoscopy, the doctor will prescribe an MRI or CT scan of the pelvis with contrast.
- Is it possible to have sex after cystoscopy? Protected sex and masturbation can be practiced after 7 days. Unprotected - no earlier than after 2 weeks (all microtraumas of the urethra must heal).
What does cystoscopy show?
When examining the bladder, the doctor pays attention to the condition, structure and color of the mucous membranes. By their appearance, he can judge the presence of certain pathologies. Depending on the condition of the internal walls of the organ, a diagnosis is made:
- the presence of atypical folding indicates hypertrophic processes;
- hyperemia, bleeding of mucous membranes, increased vascular pattern indicates an inflammatory process;
- pallor, absence of a vascular pattern on the mucosa, its thinning indicate atrophic processes.
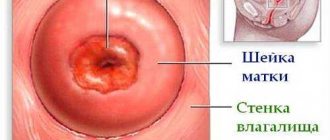
In addition, cystoscopy in women can detect diverticula, scars and strictures in the urethra and ureters, polyps and cancerous tumors. By examining the inside of the bladder, the doctor may also detect foreign objects: stones and sand.
Reviews from men
Pavel, 38 years old: “I’ve been “ripe” for a cystoscopy for a long time (I suffered from cystitis of unknown origin). In the end, I decided to have the procedure and realized that I was afraid in vain: the room was quiet, warm, the staff was calm, the doctor told me not to think about anything and to breathe evenly. The sensations are unpleasant, but with painkillers they are quite tolerable. There was no blood in the toilet, discomfort when urinating bothered me until the evening.”
Yaroslav, 29 years old: “Cystoscopy for me personally was torture, not so much physical as moral. The doctor said that without it nothing is clear, and an ultrasound showed a suspicion of a tumor. Out of fear he agreed. Cystoscopy put everything in its place - the formation is benign.”