Causes of inguinal hernia in men
Due to the structure of the canal, hernias in men are much more common. Inside the inguinal canal there is a spermatic cord, through which the testicles from the abdominal cavity are lowered into the scrotum from early childhood. Therefore, the entrance to the canal is widened and the canal process does not overgrow. With the further growth of the child and in the presence of a provoking factor, the abdominal organs move into free space.
In older men, the canal remains a weak spot for the same reasons. The congenital risk factor is joined by an acquired one, in which the muscles of the abdominal wall weaken, forming a protruding hernia.
An inguinal hernia can be congenital or acquired. Congenital is formed when the testicle descends from the abdominal cavity into the scrotum in boys. Acquired appears when the muscle and tendon layer of the abdominal wall of the inguinal canal is weak.
Predisposing factors for the development of the disease: destruction of connective tissue (age-related), defective muscles provoked by systemic and frequent diseases, increased intra-abdominal pressure - with chronic cough, constipation, heavy lifting, obesity, etc. These factors gradually lead to a defect - the formation of a hernial orifice in the groin canal and further to the formation of pathology in a man.
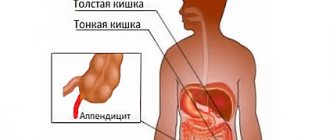
Sometimes pathology can develop after surgery performed in the abdominal cavity: resection of the duodenum, gastric resection, gall removal, hysterectomy, removal of appendicitis, adnexectomy, etc.
Diagnostics
To identify an inguinal hernia, the patient is examined in vertical and horizontal positions, a straining test and a cough test are performed.
To clarify the localization of the pathology and the condition of the inguinal canal, an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity, pelvic organs, and scrotum is performed. Ultrasound allows you to find out which internal organs are involved in the pathological process. For the same purpose, irrigoscopy (possible intestinal involvement is determined) and contrast-enhanced cystoscopy (bladder involvement) are performed.
In men, inguinal hernia occurs 9 times more often than in women, most often in children under 10 years of age.
If an ultrasound examination does not detect a hernia, an X-ray examination with a contrast agent is performed to clarify the diagnosis.
Differential diagnosis of inguinal hernia with hydrocele of the testicular membranes (hydrocele), varicose veins of the spermatic cord (varicocele), lymphadenitis, spermatic cord lipoma, and femoral hernia is necessary. The inguinal-scrotal form of the disease in children must be differentiated from undescended testicle into the scrotum (cryptorchidism).
Classification of inguinal hernias
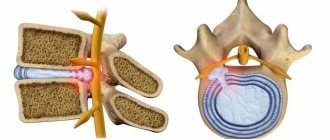
Anatomical features distinguish the following types of hernias: oblique, combined and direct. Oblique can be either congenital or acquired. In this case, all the elements that make up the hernial contents exit through the inguinal ring into the canal and are located along it among the structures of the spermatic cord.
Congenital - develops if the abdominal process in childhood, located in the groin canal, does not heal and its cavity freely communicates with the abdominal cavity.
Acquired - appears in adults and is divided into the following types:
- Direct and internal - the stroke is short, not connected with the male reproductive system, always an acquired form. It has a characteristic protrusion of the peritoneum through the inguinal space, bypassing the spermatic cord, into the inguinal canal.
- Oblique or external - the hernial sac is connected to the spermatic cord, to the membrane of the testicle, which leads to complications of the male genital organs.
Inguinal oblique hernias are divided into several types:
- Beginning - the hernial sac can be palpated only at the entrance to the groin canal; this type cannot be identified independently.
- Canal - in which the bottom of the hernial sac is located at the level of the external opening of the canal and the sac located in the inguinal canal does not affect the abdominal wall and is detected when it is under strong tension.
- Funicular - the bottom of the sac is located in the canal at different levels of the spermatic cord and the hernial sac descends along the spermatic cord towards the scrotum.
- Inguinal-scrotal hernia is one of the most severe types of indirect hernia, but it occurs quite often. The hernial sac with its contents (intestinal loops, internal organs and peritoneum) descends into the scrotum area and increases its size several times.
The following types of hernias also occur:
- Combined - complex formations that consist of several sacs, and the hernial sacs do not communicate with each other and exit through different hernial openings. A combined hernia may consist of several direct inguinal or oblique hernias, or a combination of them,
- Irreversible - the adhesion of the hernial sac and hernial contents makes it impossible for it to disappear and eliminate on its own,
- Sliding inguinal – formation of a hernial sac by the parietal peritoneum and its visceral layer,
- Recurrent – appears again after surgery. There are repeatedly recurrent hernias, provoked by the wrong choice of hernioplasty method, as well as a technical error in the operation,
- Reducible,
- Uncomplicated inguinal
- Complicated pathology.
Inguinal rings
As you know, the inguinal canal has walls on which rings are located. The superficial inguinal ring in appearance resembles a depression that lies exactly in the middle of the inguinal ligament. It should also be noted that it is located clearly opposite the hole and never moves from this place.
But the deep inguinal ring lies directly above the pubic bone. On the outside are the oblique abdominal muscles (abdominals), and they are the ones that limit the deep ring. There is a medial edge above it, and a lateral edge is located clearly parallel to it on the other side.
Symptoms of an inguinal hernia in a man
At an early stage, the disease can go undetected for a long time due to the absence of symptoms. Only after heavy exertion, severe coughing, and abdominal tension do patients begin to notice a protrusion. An inguinal hernia can develop suddenly, gradually and acutely.
An inguinal hernia in men is caused by the following symptoms:
- Tumor-like protrusion in the groin - the swelling has different sizes, increasing with physical exertion, severe coughing and decreasing, also disappearing in a lying position. Tumor-like formations cause constant or periodic dull pain of varying intensity and are localized in the groin and lower abdomen, also radiating to the lumbosacral region.
A large inguinal hernia creates inconvenience during physical activity and walking. When the cecum enters the hernial sac, intestinal pain and constipation appear.
Sliding hernias in the bladder provoke physical disorders: pain in the urethra, frequent urination, urinary retention (in elderly patients), pain above the pubis. In acute appendicitis - inflammation of the appendix, which is a hernial content, pain in the abdomen, nausea, vomiting, fever and tachycardia.
- Enlargement of the side of the scrotum - with a scrotal inguinal hernia, the corresponding side increases.
- Incarceration of a hernia - compression of the hernial contents in the inguinal gate develops incarceration. In this case, nausea, vomiting, increasing groin pain appear, gases do not pass and the hernia acquires a tense, irreducible state.
- The strangulated form causes certain complications: coprostasis, inflammation of a section of the intestine, necrosis of a section or other element of the contents of the hernia, ischemic orchitis.
- Painful pulling sensation in the groin.
- Discomfort while walking - increases with increasing load.
- Diarrhea, constipation, false urge - if there is an intestinal disorder.
- Impaired urination - occurs rarely, in case of entry through the inguinal ring into the hernial sac of the bladder.
Symptoms
In men, the symptoms of an acquired inguinal hernia (see photo) are as follows:
- The formation can be straightened with regular pressure, and a characteristic rumbling sound can be heard.
- In a lying position, the protrusion usually either levels out or greatly decreases in size, and vice versa, in an upright position it increases and appears again.
- In the reduced state of the hernia, you can easily feel the enlarged inguinal ring through the skin.
- When the hernial sac descends into the scrotum, the corresponding half of the scrotum increases in size.
- With strong coughing, straining, or sneezing, the hernia increases in size and becomes tense; if you put your hand on it, you can easily feel it.
With a small inguinal hernia, there are no longer any symptoms that bother the patient. But with a significant increase in protrusion, the following ailments may appear:
- Pain in the lower back, lower abdomen - this occurs due to compression of other organs and intestines.
- Aching, prolonged pain in the area of the hernial formation.
- Other signs of indigestion, such as bloating, loud rumbling.
- Constipation, this is also caused by compression of the intestinal loops in the hernial sac.
- In rare cases, if part of the bladder gets into a hernial formation, problems with urination may occur.
The symptoms of an inguinal hernia are quite obvious upon visual examination; the formation has a dense elastic consistency and is easily palpable on its own. It can be round, and if the hernial sac descends into the scrotum, then the protrusion has an elongated shape. As a rule, with a genetic predisposition, the body’s tendency to develop a hernia, a hernial protrusion may occur after lifting weights and intense physical activity. [adsense2]
Provoking factors
Factors contributing to the appearance of anterior abdominal hernia:
- Heavy physical activity - sports, professional,
- Diseases that provoke increased pressure in the abdominal area - bronchial asthma, cirrhosis of the liver, chronic lung disease, acute bronchitis, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and pneumonia,
- Alcoholism,
- Smoking – causing an unproductive and prolonged cough,
- Obesity increases the load on the anterior wall of the peritoneum and prevents the hernia from appearing for a long time.
Surgery against pelvic pathologies
Now surgery to remove an inguinal hernia in men is one of the most effective ways to relieve such a pathology. There are a number of basic techniques that have proven to be effective:
- planned;
- emergency in case of infringement;
- laparoscopy.
Different methods have similar steps:
- Anesthesia. Either general or conduction anesthesia is used, which is injected into the spinal cord and makes the nerves insensitive in a certain area of the body.
- Providing access to education. During a standard operation, a person's soft tissues are opened. During laparoscopic surgery, manipulations are performed through small punctures.
- Truncation of the hernial sac. This is the main stage of the procedure. It consists of repositioning an organ that has protruded beyond the cavity, removing part of the peritoneum and suturing the gate.
- Strengthening the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity. To avoid recurrence of the disease, a special mesh is installed on the shell protecting the insides.
Before the intervention, the doctor carries out preparatory measures. The operation itself does not last long; the period of returning to your normal lifestyle takes much longer.
Recovery after inguinal hernia surgery in men
Despite the effectiveness of the surgical method, many are afraid to take this step. This treatment technique is not classified as complex. But since the formation is in close proximity to other organs, and also interacts with thin membranes, the implementation of any manipulation requires high-quality training and skill of the doctor. Therefore, it is necessary to choose only experienced and trusted specialists. After all, an operation to eliminate an inguinal hernia in men has some negative consequences that appear immediately or some time after it is performed. These include:
- Relapse of the disease. The most common symptom that occurs when the abdominal wall is insufficiently strengthened. The organs exit into the same hole.
- Infection. When tissue is cut, infection may enter the internal cavities. The instruments must be sterile, and the intervention itself must take place in a specially designed room. This requirement should be taken into account when receiving treatment in commercial clinics.
- Mistakes and errors in technology. Due to the inexperience of the doctor, a violation of the integrity of the bladder, spermatic cord, as well as damage to the hip joint may occur.
The percentage of unsuccessful interventions is lower than the number of successful procedures. But in any case, such treatment must be followed. Often, after a negligently performed operation to remove a hernia in men, not only rehabilitation, but also repeated surgical care is required.
Restoration measures include a whole range of measures:
- bed rest for 5-7 days;
- reduction of load up to 1.5 months;
- prohibition on lifting heavy objects (this rule also applies to the post-rehabilitation period);
- adjusting the daily diet with the exclusion of products that cause gas formation (legumes, fermented milk);
- eliminating the possibility of a cold.
The nature of these measures and the timing of their observance are prescribed by the doctor. Consult your doctor about all important aspects, from diagnostic methods, therapy to rules of daily life after recovery.
Diagnosis of the disease
At the first suspicion, a man must consult a surgeon who will conduct the following diagnostics of the patient:
- Study of patient complaints,
- Examination of the groin area,
- Palpation of the area - to assess the size and shape of the protrusion both in a vertical and horizontal position and the reducibility of the hernia,
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity - allows you to examine the contents of the sac, the structure that forms its contents,
- Ultrasound of the scrotum - with a muscular hernia, it becomes large and resembles testicular hydrocele; the examination is used to effectively differentiate the two diseases,
- Irrigoscopy,
- Cystography,
- Cystoscopy,
- Ultrasound of the bladder,
- Blood and urine tests are prescribed immediately before surgery to determine the functions of organs and systems and identify relative contraindications.
Examination of the inguinal canal by a doctor
To examine the inguinal canal, no special procedures are required. The doctor examines the patient, then finds out his exact complaints, after which he can establish a diagnosis and identify the presence of abnormalities. In some cases, the presence of a hernia is visually visible.
In order to draw a conclusion about a person’s health status, the doctor examines the inguinal canal. The scheme is as follows: he inserts his little finger into the outer ring. If this organ is in order, only the tip of the finger can go there. When the little finger is inside the ring, the doctor can perform a cough test. This allows him to feel the shocks.
Sometimes, in order to study the inguinal hernia in more detail, the patient will need to undergo an ultrasound. Mostly they do without it. This study is used only in complicated cases.
Surgery
Treatment of the disease includes surgical removal and strengthening of abdominal wall defects. It is possible to close the hernial defect and restore the integrity of the wall using local tissues - aponeurosis (hernioplasty is performed using one’s own tissues) and synthetic prostheses (hernioplasty involves the installation of a mesh prosthesis).
In modern medicine, surgeons use a plastic method using a mesh graft - the hernial orifice is strengthened from the inside with a polypropylene mesh, which subsequently serves as a frame for the germination of connective tissues. The mesh prevents the exit of internal organs. The tension method reduces the risk of disease relapse; treatment is also carried out laparoscopically.
Strangulated and large protrusions recur in 50% of cases. The strangulated species is operated on urgently, causing multiple complications of the genitourinary and gastrointestinal systems. A long period makes the patient incapacitated; prolonged infringement sometimes leads to death.
Only a surgeon can decide how to treat the pathology, based on the individual characteristics of the patient and his condition. The surgeon also determines the duration of treatment.
In medicine, the gold standard for surgical treatment of inguinal hernia is hernioplasty according to Liechtenstein. The operation is used for all types of protrusion. During the operation, plastic surgery of the inguinal canal is performed, strengthening it with a special mesh made of polymer material, which prevents the development of relapses.
Some cases involve the use of other modifications of plastic surgery:
- Hornioplasty according to Girard-Spasokukotsky - used for oblique types of pathology of small sizes, especially in young patients,
- Bassini or Kukudzhanov method - for direct, recurrent pathologies, large indirect hernias,
- In case of a strangulated hernia, if the operation was carried out in a timely manner and the strangulated organ was not removed, the operation is practically no different from hernioplasty using the Kukudzhanov method.
Previously, the only method of getting rid of the pathology was tension repair - the hernial orifice was tightened with tissue of the abdominal wall. But modern technologies and innovative acquisitions have made it possible to use effective and painless methods, which include:
Tension-free plastic surgery using the Lichtenstein method - after local anesthesia, the surgeon makes an incision in the groin area and the spermatic cord compartments. The hernia is excised or simply reduced. Next, the hernial orifice is repaired; in its place, the doctor places a polymer mesh with a hole for the spermatic cord and sews the mesh to the surrounding tissue. Since the material used is synthetic, it is not rejected by the body. Gradually, the mesh becomes overgrown with human tissue and will act as a supporting material. A few hours after the operation, the patient can leave the hospital. The disadvantage of this technique is the small scar at the incision site.
Laparoscopic surgery - after general anesthesia, three punctures are made in the anterior abdominal wall. Instruments penetrate through them and carbon dioxide is pumped into the abdominal cavity. Gas and maximum wall tension force the hernial sac back into the cavity. Using the inserted instruments, the surgeon places a patch in the form of a mesh on the inside of the hernial orifice and sutures the error. If the hernia is of an impressive size, the technique is ineffective. The laparoscopic method is more expensive than standard surgery.
Endoscopic surgery is considered safer and more effective. Local anesthesia is used. No scars remain on the body, internal tissue damage is minimal, the operation is performed in the preperitoneal space, and the patch is applied not from the inside of the abdominal cavity, but between the layers of its wall. This method does not require suturing the wall, because it is held in place by pressure inside the cavity.
Causes of inguinal lymphadenitis
The most important reason is an infection that has somehow penetrated to the inguinal lymph nodes. A common pathogen is E. coli. And besides it, other pests of the human body can also contribute to the appearance of problems: staphylococcus, diplococcus, and also Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
In addition, there is another, no less important reason - the accumulation of inflammatory cells in the area where the microorganism is detected. Most often, microscopic organisms reach the lymph nodes using vessels with lymph flow from a certain area of the body that has recently been infected.
Postoperative complications
Frequent complications after surgery are:
- Hematomas - to avoid them, ice is applied after surgery,
- Seams coming apart
- Infection of the wound and its suppuration - to avoid the inflammatory process, a course of antibiotics is prescribed,
- Hydrocele of the testicles - when the membrane of the testicle is damaged, the size of the scrotum increases on one side or both. The pathology is treated surgically,
- Damage to the spermatic cord occurs due to the negligence of the surgeon and is associated with the individual structure of the groin canal. The cord is located next to the hernial sac and its damage is fraught with male infertility,
- Damage to the hip joint - occurs due to rough sutures,
- Relapse - if the regimen is not followed, a secondary appearance of protrusion occurs,
- Damage to a blood vessel provokes testicular atrophy.
Any operation, even an easy and safe one, can cause complications. Sometimes they appear due to the fault of the patient who violates the restrictions of the rehabilitation period, sometimes due to the fault of the doctor. Complications can also arise due to the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
2Conservative treatment of inguinal hernia
The only method of conservative treatment recognized by doctors is wearing a bandage, which reduces the load on the groin muscles and alleviates the patient’s condition. In certain cases, a special bandage not only does not give positive results, but also aggravates the situation, leading to complications.
The use of a bandage is allowed only with a reducible type or with contraindications to surgical intervention:
- For elderly patients,
- For problems with blood clotting - anemia and leukemia,
- For heart diseases - acute stage of heart attack, stroke, heart failure, hypertension,
- Pulmonary diseases - pulmonary ephymesis, severe bronchial asthma,
- Exacerbation of chronic pyelonephritis, with acute hepatitis and liver cirrhosis,
- Diabetes mellitus - surgical hospitals allow patients with a sugar level of 9-10 mmol/l to undergo surgery,
- Immunodeficiency,
- Infectious process of the acute phase.
Visceral therapy is the mechanical reduction of the sac into the cavity, after which the patient experiences relief. But such therapy is not a panacea for pathology and only an experienced manualist can perform these actions. It is not recommended to straighten the protrusion yourself. This leads to serious consequences.
Pain in the inguinal rings
Many professional doctors accurately claim that the inguinal rings themselves cannot hurt, because the ring is only an opening. Also, pain in that area does not guarantee the presence of a hernia. Its appearance has nothing to do with inguinal rings.
The two most common problems that can be accompanied by pain around the rings are inguinal lymphadenitis and inguinal sprain. But still, instead of drawing conclusions on your own, you should contact a specialist.
Medications
Medicines used for inguinal hernias:
- Antacids - Maalox and Phosphalugel, Almagel - prevent damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive system,
- Antispasmodics – Papaverine and No-Shpa – eliminate discomfort and increased peristalsis.
For hernias of the anterior abdominal wall, anti-inflammatory drugs are not used, since they also eliminate pain. When taking these drugs, there is a risk of missing the pathology, which is fraught with mortal danger.
Is it possible to cure
If an “inguinal hernia” has been diagnosed, then most often it is proposed to remove it surgically. At the initial stage, the doctor may recommend a course of therapy. Along with it, each patient can start wearing a suspensor. Moreover, the patient makes this decision independently. Surgery is not the only way to treat an inguinal hernia. If the patient has no pain and the disease is at an early stage of development, a specially designed therapy may be offered.
If, nevertheless, the decision was made to operate, then it is necessary to undergo a full examination by a therapist, urologist and cardiologist. Naturally, a number of analyzes and studies will be required. But still, before deciding to surgically remove an inguinal hernia, you can try treatment without surgery.
Treatment of the disease without surgery
Treatment of the disease without surgery is impossible, given the pathogenesis. The bandage also does not cure, but helps to retain the protrusion in the abdominal cavity. According to doctors, physical exercise is also not able to cure the disease. But experts still advise using exercises to increase the muscle strength of the abdominal wall, but only in a sitting position or lying on your back:
- A load weighing from one to two kilograms is placed on the abdominal wall and breathing is performed with the stomach,
- With a horizontal body position - lift the legs in a straight position at an angle of 30 degrees,
- In a horizontal position, lift the shoulder girdle and shoulder blades, with your hands behind your head,
- In a horizontal position with your knees bent, you need to squeeze the ball placed between your legs.
Treatment
If lymphadenitis appears as a result of an infection or a sexually transmitted disease, the main task of treatment in the hospital will be to eliminate them. A quick solution to the problem is quite possible if, after eliminating the infection, the lymph nodes return to normal on their own soon.
In other cases, the main source of the disease cannot be accurately determined, so general radiotherapy is prescribed. This is followed by standard therapy, aimed mainly at strengthening the lymph node system.
More recently, people considered surgery to be the best treatment. Although recently a number of studies have been carried out showing that the removal of affected lymph nodes often contributes to the formation of not entirely correct lymph outflow.
ethnoscience
The traditional medicine health resort offers patients to get rid of their illness with cold. Patients are allowed to apply a cold compress to the protrusion site, wipe the protrusion with ice, or swallow ice cubes for pain relief. Doctors deny such therapy, because cooling leads to muscle contraction and pinching of the hernia.
Popular lotions, compresses and ointments:
- Place two teaspoons of oak bark in half a liter of boiling water and boil for 15-20 minutes. Cool the broth and use for compresses. Keep the compress for three hours.
- Sauerkraut juice – used for compresses.
- Apple cider vinegar - 500 gr. Dilute four tablespoons of apple cider vinegar with water and use for lotions.
- Golden mustache, onions, plantain leaves are passed through a meat grinder, pork fat is added to the chopped greens. The resulting ointment is applied to the site of the protrusion.
If you have an inguinal hernia, you should not self-medicate. Only timely and qualified help is the best way to get rid of this disease.
Complications
All complications arising from an inguinal hernia can be divided into 3 categories. The first includes conditions that arise as a result of disruption of the functioning of organs trapped in the sac. The second includes disorders caused by compression of intestinal loops that protrude into the resulting cavity. The third includes conditions that arise as a result of pressure from the hernial sac on surrounding organs. In the absence of targeted treatment, the patient may experience several types of complications at once.
Inflammation
The most common consequence of hernia progression is the activation of the inflammatory process. Such damage to the contents of the hernial sac can occur due to the influence of a number of unfavorable factors. This condition is accompanied by the appearance of severe symptoms. Patients complain of the following symptoms:
- local soreness;
- redness;
- swelling of the scrotum.
The patient may exhibit signs of general intoxication of the body. Body temperature often rises, complaints of nausea, general weakness and headaches appear.
Infringement
The most dangerous complication of a hernia is strangulation of its contents. Not only the intestines, but also parts of the greater omentum, which often penetrate into such defects, can be subjected to compression. Clamping of organs occurs in the area of the inguinal ring. This leads to the fact that blood circulation in the tissues is disrupted and the ischemic process starts. This pathological condition is accompanied by an increase in acute symptoms, including:
- intense pain syndrome;
- bloating;
- vomiting;
- nausea;
- the appearance of blood in vomit and feces;
- increase in body temperature.
A complication of a hernia is strangulation, which is accompanied by the appearance of blood.
If measures are not taken in a timely manner to release organs, necrosis develops. The affected area may rupture, which leads to the release of its contents into the abdominal cavity and the development of peritonitis. If the appendix is compressed in the inguinal ring, acute appendicitis develops.
Damage
With increased intra-abdominal pressure, sudden movements and injuries, there is a high probability of damage to the organs located in the sac, the hernial orifice and the inguinal ring. In most cases, tissue stretching is observed. This disorder is accompanied by the appearance of severe pain. In the future, an inflammatory process and tissue swelling may occur.
Complete ruptures are extremely rare. In most cases, the formation of an opening and the release of intestinal contents are observed in the presence of ischemic tissue damage.
Irreversibility
Common consequences of the lack of targeted treatment include irreducibility of the defect.
This condition is characterized by the fusion of the walls of the internal organs caught in the defect with the walls of the hernial sac. The appearance of such a defect is caused by improper use of the bandage. This pathological condition is often accompanied by a slight dull pain. This disorder causes constipation. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, adhesive disease may occur. With this pathology, the risk of strangulation of the contents of the hernial cavity increases.
Intestinal obstruction
Often, intestinal obstruction occurs when the hernia is strangulated and irreducible.
This condition is accompanied by a violation of the passage of feces through the intestinal loops, which are located in the hernial sac. This condition is often observed in people who, in the presence of an inguinal hernia, suffer from chronic constipation. The disorder leads to symptoms such as:
- flatulence;
- stomach ache;
- bloating;
- vomit;
- headache.
In the absence of targeted treatment, decay and fermentation of feces may occur. This leads to severe intoxication of the body.
Coprostasis
This pathological condition is often the result of intestinal obstruction. Coprostasis is often observed in men with irreducible hernia. This condition develops slowly and is accompanied by dull abdominal pain, constipation and general malaise. By palpation, you can determine the place where feces stagnate and become compacted. The disorder can be eliminated by conservative methods, but in severe cases, surgical interventions are used to remove stool that has stagnated in the intestines.
Coprostasis develops slowly and is accompanied by constipation.
Hypogonadism
A rare complication of an inguinal hernia is hypogonadism, which is the result of an enlarged sac that descends further into the scrotum. Pressure is put on the testicles, as well as the blood vessels that supply them. Due to these processes, the androgen-secreting function of the testicles is reduced. Due to a decrease in hormone production, a man has problems with spermatogenesis, erection and ejaculation. In the absence of targeted surgical treatment, hypogonadism leads to irreversible impairment of reproductive function.
Recommended diet after inguinal hernia repair
To speed up rehabilitation, it is advisable to maintain your diet and consume liquid, pureed food in small portions during the first days. After four to five days, you need to gradually switch to a normal diet: eat foods containing fiber and proteins. The diet should include:
- Boiled, but not fatty meat (chicken or beef),
- Vegetables – steamed or raw,
- Cottage cheese,
- Berries, fruits,
- Porridge – buckwheat, millet, pearl barley and oatmeal,
- Fish, seafood,
- Dried fruits, nuts.
Eliminate alcohol and coffee. It is recommended to quit smoking.
Conservative methods of therapy
As a rule, they are ineffective. If the hernial sac is reduced, that is, there is no infringement, or there are contraindications to the operation, wearing a medical bandage is indicated. The size of the product is determined by the doctor. Bandages can be either single- or double-sided.
It is important for patients to understand that the use of this medical product does not cure an inguinal hernia. This is only a means of preventing strangulation and prolapse of the intestines and other organs into the hernial sac. You can completely get rid of the disease only through surgical methods.
Disease prevention
To prevent the disease, it is necessary to avoid excessive physical activity and lift heavy objects. You should promptly take care of the stable function of the gastrointestinal tract, since constipation is a provocateur of an inguinal hernia. It is also recommended to lose excess weight and exercise, strengthen the abdominal wall with exercises and not neglect therapeutic exercises.
It is important to follow a proper diet, eat little and not drink alcoholic beverages. You should reduce your intake of fatty and spicy foods, flour and confectionery products, and consume more meat, fish and vegetables.
Causes
An inguinal hernia is formed under the influence of the following provoking factors:
- Premature pregnancy. If the process of delivery occurred earlier, some internal organs and the “pocket” itself did not complete the full cycle of their development. As a result, the latter remained open.
- Hereditary predisposition. If close relatives have been diagnosed with an inguinal hernia, the likelihood of its development increases significantly.
- Weakness of the muscle tissue located in the abdominal wall.
- Excess body weight. With obesity, the abdominal organs experience increased stress.
- Various types of groin injuries. As a rule, after receiving them, there is a significant weakening of the ligaments and muscles.
- A sharp decrease in body weight. If there is no fat layer in the area of the inguinal canal, intestinal loops and other internal organs easily penetrate into the empty volumes.
- A lifestyle that does not involve frequent physical activity. Against the background of physical inactivity, muscles atrophy and become flabby. They cannot fully perform their functions, as a result of which the organs pass into the canal without resistance.
- Frequent and high-intensity physical activity. Against the background of overexertion, the level of intra-abdominal pressure increases.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which are accompanied by frequent constipation.
- Chronic cough.
Thus, the disease can develop under the influence of many provoking factors. Information regarding how to treat an inguinal hernia should be provided by a doctor, but every patient should understand that even surgery will not be as effective as possible unless they make lifestyle adjustments.
Treatment with folk remedies
Traditional methods of treatment will help neutralize inflammatory processes and relieve pain, but this does not mean that the problem can be completely solved. All the same, sooner or later, you will have to seek treatment from a doctor. The following traditional medicine recipes are often used:
- The hernia herb should be collected, washed and steamed for 10 minutes, the resulting mixture is applied to the sore spot, this method is recommended to be carried out once a day, a compress is applied to the place and held for 40 minutes, this therapy can be carried out for 35 days;
- To prevent the development of a hernia, you can use three cabbage leaves, which must be chopped (meat grinder), the resulting mixture is applied to the affected area overnight;
- To make a compress from oak bark, you need to take crushed dried bark, pour boiling water, boil over a fire for 10 minutes, leave, cool, then moisten gauze and apply to the affected area, wrap in a cloth and wear for 3 hours;
- Take an aloe leaf, peel off the skin, sprinkle with soda and apply to the sore spot, previously treated with an alcohol solution;
- Take 500 grams of melted pork fat, mix with 100 ml of vinegar essence and add a raw chicken egg, leave the resulting solution for 5 days, then melt the mixture, add a spoonful of badger fat and 2 quail eggs. The result is an ointment that must be used morning and evening for 30 days. Such activities will help relieve pain.
For the treatment of inguinal hernia, waxweed, Russian gorichnik, fragrant spikelet, jaundice, calistegia zaborina, wormwood, Scots pine, elecampane, willowherb, calamus, and gulyavnik are used. Decoctions are prepared very simply; to do this, you need to take a pinch of any herb from the above list, pour a glass of boiling water and leave in a thermos; you should consume a quarter of a glass three times a day.
It must be remembered that medicinal plants cannot replace surgical intervention, so monitor your health and avoid complications. The above recipes will help prevent pain and inflammation, thereby reducing the risk of relapses. Listen to your body and be healthy!