Hidden blood detected directly in a woman’s stool usually indicates the development of serious pathologies.
The problem equally often occurs in girls after 14 years of age and in adults. The presence of the disease is indicated by persistent discharge from the anus for a long time. In no case should you leave everything to chance, much less try to be treated at home. At the first signs, you should consult a doctor and begin therapy.
Causes
The factors that contribute to the passage of blood into the stool in women are often different from those that lead to similar manifestations in men. This is connected, first of all, with reproductive function.
Such symptoms are practically the norm for pregnant women, and they usually disappear quickly after childbirth. However, this does not mean that there is no danger and treatment is not required. Representatives of the fairer sex encounter this problem most often in the last week. During this period, the grown uterus actively puts pressure on the pelvis, which leads to loss of elasticity of the rectum. The latter becomes very vulnerable to any mechanical damage.
Diagnostics
If blood is detected in the stool, you should immediately contact a specialist. A proctologist deals with these problems. The main diagnostic methods include:
- Visual inspection and palpation. In case of hemorrhoids or anal fissure, the problem will be clear already at this stage of diagnosis.
- Microscopy for helminth eggs. The material for the study is feces.
- Coprogram. This stool examination is necessary to diagnose the digestive system. This test can identify some helminths.
- Occult blood test. It is also called the Gregersen reaction or benzidine test. Blood pigments accelerate the oxidative process, which is the basis for such diagnostics.
- Digital examination of the rectum. It allows you to assess the condition of the tissues, mucous membrane and sphincter.
- Sigmoidoscopy. The need for implementation is determined by digital examination. This diagnosis is instrumental. A sigmoidoscope is a tube with a lighting device and a device that supplies air. This allows the intestinal cavity to be inflated and visual inspection through the eyepiece. Sigmoidoscopy allows you to simultaneously take a biopsy.
Basic methods of laboratory and instrumental diagnostics may not be enough to make an accurate diagnosis. In this case, resort to additional research:
- X-ray of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Ultrasound of the intestines or entire abdominal organs;
- colonoscopy (endoscopic diagnosis, similar to sigmoidoscopy).
If pathology in the upper parts of the digestive system is suspected, consultation with a gastroenterologist is necessary. For diagnosis, he resorts to palpation, ultrasound examination and FGDS.
Preparing for research
Some diagnostic methods require preparation. The specialist will definitely inform the patient about the necessary measures.
If you need to do a test for occult blood, preparation consists of adjusting your diet. The main principle of the diet is to reduce the content of iron-containing foods. For 3 days you need to give up the following foods:
- fish;
- meat;
- buckwheat;
- green vegetables;
- milk;
- tomatoes.
If these foods are not excluded or iron supplements are taken before the analysis, the result may be false positive. The rules must be followed: the patient needs reliable information.
Nutritional adjustments are also required before examinations such as sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy, FGDS and ultrasound diagnostics. Each option has its own special preparation - a specialist will tell you its principles.
About bleeding
Based on the appearance of the blood, it is not difficult to guess what pathology was the cause. The less it is mixed with feces, the lower its source is located. The shade is directly affected by intestinal enzymes. Minor damage usually gives the poop a glossy black appearance. Their shape is preserved. Serious, extensive wounds turn stool into a cherry-like jelly-like mass.
Pathologies formed in the rectum are characterized by the appearance of unchanged blood. These include in particular:
- haemorrhoids;
- various tumors;
- erosive damage.
To detect occult blood, the Gregersen method is used.
Signs of other diseases
Cancer formed in the colon is always accompanied by bloody discharge if the disease has reached advanced stages. Here, the feces are still excreted with mucus, often pus, and in general the consistency resembles raspberry jelly. The problem is that the disease is very rarely detected at the initial stage, since it has no obvious signs.
Benign neoplasms lead to fairly frequent, not too profuse, and sometimes continuous bleeding.
Crohn's disease almost never signals itself with the symptom in question. Its main symptoms:
- temperature;
- stomach ache.
Extremely severe forms of the disease provoke ulceration of the intestinal walls.
Diverticulosis is a pathology of older people. In women in particular, thickenings (or “pouches”) almost always form on the left side of the colon. Their destruction is accompanied by acute pain and profuse stool with a characteristic burgundy hue.
The most common problem among young women is ulcerative colitis. Its first symptom is bloody diarrhea. Subsequently, other manifestations make themselves felt:
- decrease in hemoglobin;
- quite severe pain;
- heat.
Reasons for the presence of blood in feces
To roughly understand what you are faced with, you need to correlate all the symptoms with blood in the stool. Often other signs come first. But you should tell your doctor about all these manifestations, and not treat yourself, because this can lead to bad consequences!!!
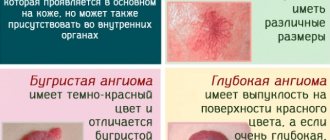
For hemorrhoids
In case of hemorrhoids, blood is released in drops after defecation, without mixing with feces. In addition to these signs, there are also characteristic symptoms of hemorrhoids:
- itching and burning of the anus;
- palpable bulging of the hemorrhoid;
- when a node is pinched - severe and sharp pain;
- pain during bowel movements.
This disease is characterized by stages; symptoms develop gradually, starting with a burning sensation and ending with prolapse of the node. Heavy bleeding from the rectum is possible if hemorrhoids have been mechanically damaged.
Anal fissure
With an anal fissure, a defect occurs in the mucous, submucosal, and sometimes the muscular layer of the anal sphincter. This problem occurs in people who move little and suffer from constipation.
Read also: Causes of heavy periods in teenagers
Blood can be seen on the surface of the stool; it remains on the napkin in the form of a scarlet stain, as well as on the underwear after defecation. There is no blood inside the stool, which indicates a superficial location of the source. Itching and burning are also present.
Only a doctor can differentiate an anal fissure from hemorrhoids after a digital examination. With early treatment, it is possible to prevent the chronicity of the crack, when the edges of the wound are covered with scar tissue and treatment will be problematic and prolonged. Therefore, it is important to immediately go to the doctor if blood appears after a bowel movement.
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum
An ulcer in the upper digestive tract can cause significant bleeding. In this case, the blood ferments, turns black and the feces become “tarry.” Peptic ulcer disease has its characteristic symptoms:
- pain associated with eating (hunger pain) in the pit of the stomach, in the epigastrium;
- heartburn;
- belching of air or stomach contents;
- nausea;
- sour vomiting followed by relief.
Intestinal thrombosis
This is an acute pathology of the abdomen, which begins suddenly and is characterized by vivid symptoms, and blood in the stool appears against its background. With thrombosis of intestinal vessels, ischemia and necrosis of the wall occurs. If you do not provide urgent surgical assistance, the disease will end fatally. Main symptoms of the pathology:
- sharp, very severe pain in the abdomen;
- nausea, vomiting;
- bloating;
- palpation of the anterior abdominal wall is sharply painful;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- blood in the stool;
- lack of peristalsis.
For cancer
Colon cancer may not manifest itself for a long time, gradually destroying the body. When the tumor grows significantly into the lumen, an obstacle to the movement of feces occurs. As a result, damage to the surface of the neoplasm occurs, which is manifested by the release of blood, which is mixed with the feces.
After defecation, a person finds stool streaked with blood, and it is possible to even notice clots. If the tumor is located in the upper gastrointestinal tract, the stool is black, and with underlying cancer, the stool is scarlet.
Other symptoms common to bowel cancer include:
- weight loss;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- the presence of mucus and blood in the stool, possibly purulent discharge;
- stomach ache;
- lack of appetite;
- elevated temperature;
- sweating, weakness, general feeling unwell.
Infectious diseases
Gastrointestinal infections of bacterial origin often affect the intestinal mucosa and can penetrate into deeper tissues. Ulceration of the surface leads to the appearance of blood in the stool. It does not always have time to ferment, which is why a person sees red colored stool after going to the toilet.
With intestinal infections, other symptoms bring more discomfort to the patient:
- nausea and vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- spasmodic abdominal pain;
- frequent urge to defecate;
- there is mucus and blood in the stool;
- feces are foul-smelling, liquid, and sometimes greenish;
- dehydration and impaired consciousness in connection with this;
- elevated body temperature.
Salmonellosis and dysentery can lead to the release of feces with blood streaks. Single-celled parasites (amoebas) and helminths (schistosomes) provoke the appearance of blood in the stool.
Tuberculosis of the intestines stands apart, which leads to the appearance of blood in the feces, both visible to the eye and hidden. Intestinal tuberculosis occurs both against the background of the pulmonary form and independently. This infection has no special features:
- abdominal pain mainly in the ileocecal region;
- diarrhea alternates with constipation;
- weight loss;
- loss of appetite;
- if the lesion breaks into the intestinal lumen - diarrhea with blood;
- if there is also a pulmonary form - symptoms of lung damage.
Angiodysplasia
This pathology is characterized by abnormal development and structure of intestinal blood vessels, which leads to their constant injury and bleeding from the intestine.
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis
The disease is of an immune nature and is associated with genetic predisposition. After the age of 20, they begin to appear.
Ulcerative colitis affects the large intestine to varying extents, which is accepted in the classification according to the distribution of the pathological process. Highlight:
- proctitis – only the rectum is damaged;
- left-sided colitis – the descending colon is involved up to the left flexure;
- total colitis - inflammation extends proximal to the left flexure.
Read also Stomach bleeding in newborns
The main signs of UC are frequent stools containing blood and mucus. In addition, patients note:
- false urges “for the most part” - tenesmus, including at night;
- Frequent bowel movements in mild cases may not exceed 4 times a day, in severe cases - more than 6 times, in extremely severe cases - up to 10-15 times;
- feeling of fullness in the intestines;
- Half of the patients experience severe abdominal pain;
- increased body temperature in moderate and severe forms;
- drop in hemoglobin;
- weakness in severe cases;
- weight loss;
- extraintestinal lesions - joints, skin, eyes, liver.
In accordance with the scale of inflammation and the duration of the exacerbation, the general condition of the patient changes. In severe cases, more blood, mucus and pus appear in the stool, and hemoglobin decreases.
One of the complications of UC is intestinal bleeding, which leads to significant blood loss. Without specific treatment, these complications cannot be avoided.
Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is autoimmune in nature and has a chronic wavy course. In this case, all layers of the intestinal wall are affected with the formation of granulomas. More proximal parts of the intestine are affected.
Damage to the intestine in Crohn's disease has several specific locations:
- terminal ileitis – inflammation of the ileum; damage to the upper gastrointestinal tract can “connect” to it;
- colitis - inflammation of the large intestine, can be combined with damage to the upper parts of the digestive system;
- ileocolitis is a combination of pathology of the terminal ileum and colon, combined with inflammation of the anorectal zone.
The symptoms of Crohn's disease are somewhat different from those of UC. Blood in the stool is less typical with this disease, but it appears with the development of complications - anal fissures, paraproctitis. In addition, there are the following signs:
- chronic diarrhea – more than 6 months:
- abdominal pain;
- anemia of unknown origin;
- fever;
- symptoms of intestinal obstruction;
- complications are frequent - rectal fistulas, paraproctitis, anal fissures;
- extraintestinal manifestations - arthritis, erythema nodosum, eye damage, sacroiliitis, psoriasis.
Intestinal polyposis
A polyp is a glandular growth on a stalk or broad base that is directed into the intestinal lumen. This formation is benign, but its growth leads to obstruction of the passage of feces and the formation of intestinal obstruction.
When the surface of the polyp is damaged, bleeding occurs. But more often the tumor has no symptoms. With adenomatous polyps, there is a lot of mucus in the stool.
Diverticulum
The cause of blood after bowel movements may be a diverticulum - a pouch-like protrusion of the intestinal wall. Symptoms of pathology:
- abdominal pain;
- chronic diarrhea alternating with constipation;
- clots or streaks of blood in the stool;
- flatulence, bloating.
Appendicitis
With appendicitis, streaks of blood mixed with feces are found, when inflammation of a section of the intestine occurs, attracting nearby tissues. But this symptom does not occur often, while the following come to the fore:
- pain in the stomach, which gradually disappears, giving way to pain in the lower abdomen;
- nausea and vomiting 1-2 times;
- severe pain in the right iliac region;
- when turning on the right side, the pain decreases somewhat;
- palpation of the abdomen is very painful;
- temperature increase;
- deterioration of general condition.
Peritonitis
Inflammation of the peritoneum, or peritonitis, occurs as a complication of untreated abdominal pathology - appendicitis, cholecystitis, endometritis, adnexitis, colitis and others. The first place is given to pain syndrome.
Defecation during peritonitis is difficult, and dynamic intestinal obstruction often occurs. In this case, the intestinal wall becomes inflamed, blood, mucus, and stagnant contents are released from the anus. Without proper help, a person can die.
Treatment
Even if the blood has stopped flowing, you still have to go to the doctor. If the condition suddenly worsens, it is advisable to call an ambulance. Full therapy begins only after a specialist makes a diagnosis.
To narrow the blood vessels located in the anus, apply a heating pad with very cold water or an ice pack to it. This method is not recommended for pregnant women.
For her part, the patient (when it comes to fissures in the anus or gastrointestinal pathologies) should definitely adjust her diet. All dishes are prohibited:
- sour;
- salty;
- fat;
- spicy.
What kind of blood is there in stool?
It is immediately necessary to make a reservation that some food products can color feces. Everyone knows that beets, tomatoes, spices, and also dishes with gelatin do this. Therefore, when you see the unusual color of excrement, you don’t need to be scared right away, but you should remember your previous diet.
There are two “incarnations” of the presence of blood in stool. There may be occult blood, but people are understandably concerned about the red marks they notice in the feces. Visible blood can have different appearances:
- streaks of blood, or stripes;
- a scarlet drop that falls on feces after defecation;
- mushy dark or black stools, “tarry”;
- solid bright liquid blood;
- mucus and/or pus together with a small amount of blood;
- blood clots in stool.
If there is one of these options, then it is necessary to describe it to the doctor, because this makes it easier to differentiate the pathology that you will have to deal with.
If after defecation the blood on the paper is bright, red, then this indicates that there was no influence from the enzymes of the digestive tract or bacteria of the large intestine. This means that it originates from the sigmoid colon, rectum or anus. The reason for this is:
- anal fissure;
- cancer of the named parts of the intestine;
- haemorrhoids;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis UC.
Unchanged blood can also be passed out in the stool in case of diseases of the higher sections of the intestine, when diarrhea occurs and red blood cells simply do not have time to ferment. Liquid stool with bright blood occurs with Crohn's disease and infections.
Dark, or tarry, stools are most often unformed, mushy, and occur when bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract - the esophagus, stomach, duodenum and small intestine. Red blood cells, passing through the stomach and intestines, are destroyed, turning the stool black.
If the blood appears in the form of a drop only after bowel movement or remains on the paper, then we are talking about a source located close to the anus, and most likely it becomes hemorrhoids or a fissure.
Completely bright blood indicates serious intestinal bleeding, the source of which can be any part of the colon.
If blood is detected in the stool, it is necessary to compare it with other symptoms and test results.
Alcohol is also strictly contraindicated.
Hemorrhoids in the initial stages can be easily cured with medications. As a rule, local medications are used in the form of suppositories or ointments. If constipation is the cause, a laxative is also prescribed. To minimize the risk of complications, it is necessary to carefully observe the rules of intimate hygiene. An enema with a decoction makes the situation easier:
- chamomile;
- sage;
- calendula;
- thyme.
Ulcerative colitis responds very well to treatment with conservative methods. Hormonal medications and diet are usually prescribed here. If bleeding is caused by infections, then the use of antibiotics, both local and oral, is indicated.
Benign tumors, including polyps, are removed using a colonoscope (if they are small) or a scalpel. The extracted material is checked, and if no cancer is found, then after the procedure the patient is sent home.