Why does my left eye hurt?
Pain occurs in the left organ of vision for many reasons:
- Migraine. This is severe pain in the head that occurs due to a neurological disorder. An aura appears, painful sensations are transmitted to one of the organs of vision, the temples.
- Unilateral glaucoma. The pressure inside the chambers of the apple increases due to the uncontrolled influx of secreted fluid, which is not excreted, but accumulates.
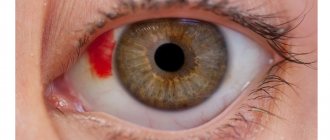
- Conjunctivitis of bacterial or viral nature. The infection may spread to only one eye. The disease is accompanied by symptoms: redness, inflammation, irritation. With bacterial conjunctivitis, purulent exudate is released.
- Increased intracranial blood pressure. If the pathology affects only the microcirculation vessels of the left eye, it is he who hurts.
- Neuritis. Inflammation of the nervous tissue causes acute pain on the side where the disease occurs. For example, if the left oculomotor nerve is inflamed, the eye will hurt only on this side.
- Blepharitis is an inflammatory condition of the eyelid. They are formed due to the spread of bacterial, viral, fungal, and parasitic infections. The patient's eyelids swell greatly, and fluid appears under the skin.
- Keratitis is inflammation of the cornea. The disease develops on one or both eyeballs. If left untreated, the cornea becomes cloudy and vision decreases. As an inflammatory reaction occurs, the patient experiences discomfort and pain.
- Systemic diseases affecting microcirculation vessels. Such pathologies include atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, and ischemic disease. Defeat is possible only on one side.
- Penetration of a foreign body. It comes in small and large sizes. In the first case, the patient can cope on his own. A large foreign object creates extensive damage and severe pain.
- Unilateral myopia. If there is no treatment, the brain gradually turns off the affected eye from function.
The disease can occur suddenly. Unpleasant sensations in the eyes are a reason to consult an ophthalmologist. Only in rare cases will the patient cope on his own.
Prevention
To prevent the progression of pain in the eyes, you must:
- Normalize your work and rest schedule.
- Reduce time spent using the computer.
- Drink enough water – up to 2 liters per day.
- Avoid smoky places.
- Use contact lenses correctly.
Proper hygiene will help you avoid bacterial and viral infections. You can prevent the entry of foreign bodies by wearing safety glasses during operation.
Pain in the eyes is a symptom of a certain damage to the visual analyzer. For effective treatment, you must first consult a doctor. You should not buy eye drops on your own.
Author: Denis Volynsky, doctor, especially for Okulist.pro
How to treat unbearably severe pain
If a person has unbearable pain, and there is a lot of time before seeing a doctor, you can improve the condition using the following methods:
- taking an anesthetic drug (Ketorol, Nise, Nimesil) that relieves a pain attack;
- washing the eyes with Furacilin solution to disinfect and eliminate possible foreign bodies;
- if the patient suffers from a systemic disease, take medications prescribed by the doctor (for example, for hypertension, use antihypertensive medications);
- If there is suppuration in the eye, you can use drops containing an antibiotic.
Other drugs are used only after examination by a doctor. Self-medication will lead to the development of side effects and complications.
What to remember
- Pain in the eyes can occur against the background of various diseases and disorders of the visual apparatus.
- If eye pain and headache are added to the pain, then you should immediately consult a specialist.
- To eliminate pain in the eyes and relieve pain, drops or ointments are prescribed. You can make compresses, lotions and homemade eye drops yourself.
- You should not put off visiting a doctor if the pain in your eyes bothers you for a long time. A specialist will help determine the cause and prescribe the correct treatment.
Urine lotions for ophthalmic diseases
If the patient uses urine therapy, follow the rules:
- It is not recommended to use the first portion, only the middle one will do;
- during treatment, adhere to a balanced diet so that useful substances are collected in the urine;
- the most useful liquid is collected early in the morning, after waking up;
- ban on drinking alcoholic beverages.
Before use, urine is boiled until the liquid evaporates by half. Add 2 teaspoons of honey. It has a bactericidal effect, so it will prevent or cure infection. After the liquid has completely cooled, it is applied to gauze and applied to the eyes. Keep the lotion for 10-15 minutes.
Useful video
From this video you will learn what a headache may mean:
With proper treatment and preventive methods, it is possible to permanently get rid of pain in the left side of the head and left eye.
Throughout life, every person encounters one or another unpleasant symptomatology.
Some signs are really worth noting and serious pathologies are identified in a timely manner.
But it often happens that unpleasant sensations only indicate that a person needs to change his job, position, or start leading a healthy lifestyle.
If your left eye and left side of your head hurt, then this is not a reason to panic. This symptom occurs both in serious pathologies and in mild ailments. Let's look at the most common causes of pain.
What diseases cause eye pain?
Many people have eye pain due to ophthalmological and systemic diseases. The reason may be in the organs of vision or in other disorders. The choice of specialist and treatment depends on the cause of the pain; in order to identify it, laboratory and instrumental examination methods are prescribed.
There are a number of ophthalmological diseases and conditions that can affect soft tissues, blood vessels, and nerves located in the organs of vision.
They cause acute and chronic pain:
- Increased eye strain. It occurs in people who spend a long time in front of a computer, phone, TV, or tablet. Pain occurs when reading books frequently in poor conditions, for example, in low light.
- Entry of a foreign body. It can penetrate the cornea due to strong winds, sparks from a welding machine, or for other reasons. Acute pain, redness, photophobia, increased sensitivity, and spasm of the eyelids occur.
- Conjunctivitis. It can be of an allergic, bacterial, viral nature. This is a disease in which the conjunctiva of the eye becomes inflamed. Redness, swelling, pain, and photophobia appear. With bacterial conjunctivitis, purulent exudate is released.
- Blepharitis is inflammation of the eyelids. It can develop due to the proliferation of fungi, viruses, bacteria, parasites (eyelash mites). The eyelids swell and an abscess filled with fluid may form under the skin.
- Keratitis is inflammation of the cornea. The inflammatory process begins as a result of mechanical damage, burns, and the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. If the disease lasts a long time, the cornea becomes cloudy and visual acuity decreases.
- Glaucoma is an increase in intraocular pressure due to impaired outflow of secreted fluid. There are anterior and posterior chambers in the eyeball, and fluid constantly circulates inside them. If it accumulates but does not come out, the pressure increases. This can lead to damage to the optic nerve, retinal detachment, and blindness.
- Retinal diseases. They develop due to burns, mechanical damage, and malnutrition through blood vessels. If the retina detaches, the person goes blind.
- Diseases of the optic nerve. Light streams pass through the eyes, hitting the rods and cones of the retina. From them, information in the form of nerve impulses passes through the nerve, entering the brain. The nerve is damaged due to malnutrition through blood vessels, mechanical damage, and infectious and inflammatory processes.
- Strabismus, amblyopia. If both eyes see the picture in front of them incorrectly, this leads to increased strain. As a result, not only your eyes hurt, but also your head.
There are diseases that develop not in the eyes, but in peripheral organs; with their prolonged development, complications arise from the organs of vision, this also leads to pain:
- Diabetes. A large amount of glucose accumulates in the patient’s blood, which is not distributed to the tissues, but binds to cholesterol and forms plaques. They are transported through large and small vessels, including the microcirculation of the eyes. This leads to blockage, severe pain, decreased or complete absence of vision.
- Atherosclerosis. Cholesterol accumulates in the patient’s blood, which spreads through the vessels, clogging their lumen. The mechanism of the disease is the same as for diabetes mellitus.
- Arterial hypertension. Increased pressure puts stress on the endothelium. This leads to rupture of the vessel wall and hemorrhage inside the eyeball. With chronic hypertension, the function of the visual organs decreases, and constant headaches and eye pain occur.
- Ischemic disease. A person experiences spasm of peripheral vessels. If this happens in the eyes, nutrition is disrupted. Gradually, the visual organs will stop working. Severe spasm causes severe pain.
- Vasculitis, increased fragility of blood vessels. If the endothelium is fragile, this leads to hemorrhage in any part of the body. Painful sensations appear during spasms, which causes a decrease in vision function.
- Neuropathy. The inflammatory disease can spread to the optic nerve, this is dangerous because it connects to the brain. This causes a decrease in its functionality and constant pain.
For each disease, a separate treatment is determined. Therefore, diagnostics are initially carried out, identifying the nature of pain, decreased vision function and other symptoms.
Causes
If your eyeballs hurt, the reasons can be very diverse:
- Incorrect selection of vision correction devices - glasses or lenses (when the patient takes them off, the pain either noticeably subsides or goes away completely).
- Dry eye syndrome - in most cases, moisturizing drops help get rid of it.
- Overfatigue - constant work at the computer is fraught with visual fatigue, and therefore pain in the eyes.
- Inflammatory eye diseases - they almost always cause severe pain of varying intensity.
- Inflammation of surrounding tissues - pain often occurs with sinusitis and sinusitis, since the inflamed sinuses are located directly near the orbit. In this case, you will need the help of not only an ophthalmologist, but also an ENT specialist.
- Entry of a foreign body - pain is accompanied by a feeling of sand in the eyes, pain.
- Inflammation of the optic nerve - it often becomes a complication of colds. Treatment is carried out by an ophthalmologist and (mainly) a neurologist.
Foreign body in the eye
Unpleasant sensations can be short-term, mild or long-lasting and most painful and nagging. There are many factors that cause such pain.
First aid if something gets in your eyes
If a foreign object gets into the eye, provide first aid. If there is minor damage, this can be done at home. But if blepharospasm or extensive damage occurs, contact an ophthalmologist or traumatologist.
First aid is carried out in several stages:
- Anesthesia. It is used if the patient is unable to open his eyes. Use solutions of lidocaine and novocaine. They are dripped in limited quantities, as they cause side effects with prolonged action.
- The person is placed in a dark room to reduce the strain on the visual organs. This eliminates photophobia and the patient can open the eyelids.
- Washing. It is better to use an antiseptic solution. Furacilin is suitable for this. Dissolve 1 tablet in a glass of water. Pharmacies sell ready-made solutions. The drug is instilled directly into the eyes. If this does not help, liquid is poured into the cup, and the victim lowers his open eyes into it. The fluid inside is blinked to remove the foreign body from the mucous membrane.
- If a foreign body causes a burn, you cannot do without the help of a doctor. He will remove the foreign object using ophthalmic instruments.
- Antibiotic instillation. This step is required to exclude a bacterial infection. The medicine is used for up to 7 days. They use Vigamox, Tobrex.
After completing first aid, the person is discharged home. There he must continue therapy. Ointments are used that improve the regeneration of damaged tissue, for example, Solcoseryl or Korneregel.
Anti-inflammatory drugs are used to relieve redness and swelling. For example, Visin. You can use it for no more than 4 days, after which it becomes addictive.
1 week after completing home treatment, return to see an ophthalmologist. He checks the functional condition of the eyes and assesses the degree of wound healing. If complications arise, he adjusts treatment methods.
When providing first aid, it is prohibited to try to remove a foreign object using your fingers. Cold and hot water should not be used for rinsing, as the cornea is irritated; warm solutions are used.
It is recommended to consult a doctor after removing the foreign body yourself. There are cases when the mucous membrane is damaged, so a bacterial infection penetrates into it.
Treatment
Treatment for eye pain depends on its causes. The most common treatments include the following:
Home care
The best therapy for many diseases that cause pain and tearing is rest. Staring at a computer screen or TV for too long can cause fatigue. Therefore, doctors recommend taking a break from the monitor at least once an hour with your eyes closed. You should also take breaks while reading.
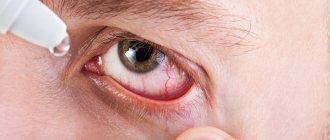
Use special eye drops that can be purchased without a prescription. To remove clogs, apply a warm, damp cloth to or massage your eyelids.
Video: Tearfulness of the eyes - causes and treatment, drops and traditional methods
Treatment by a doctor
Complex treatment and approach to therapy depend on the severity of the pathology and its etiology. In mild cases, to begin with, you can not take therapeutic actions in order to track the dynamics of the process. Depending on the etiological factors of lacrimation and pain, treatment methods will differ:
- Irritation. When the pain and watery eyes are caused by infectious conjunctivitis, your doctor may suggest not using antibiotics right away. Microbes appear on the third to seventh day, so you can get by with other medications.
- Trichiasis. If the eye is bothered by an eyelash that grows inward or a foreign object gets in, the doctor will remove them.
- Ectropion. When the eyelid is turned outward and does not lie as it should, such a defect is corrected surgically. During the operation, the ligament is tightened, which should give a normal position to the eyelid.
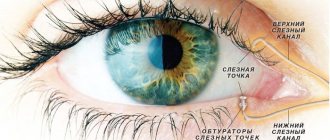
- Blocked tear ducts. A drainage system can be surgically created to connect the eye to the nose. In this case, the liquid will flow through the new channel, bypassing the part with the blockage. This surgical intervention is called dacryocystorhinostomy. It is not always necessary to make an additional nasolacrimal duct. It happens that there are no irreparable blocks on the path, but the duct is simply very narrowed. During surgery, the doctor uses a probe to expand the lumen.
Glasses
If you often wear contact lenses, alternate them with glasses. Give your eyes time to rest so that your mucous membranes can rest.
Warm compress
Doctors recommend that patients with blepharitis or stye apply warm, damp towels to their eyelids. This will help clear out a clogged sebaceous gland or hair follicle.
Washing
If a foreign body or chemical gets into your eyes, flush with cold running water or saline to remove the irritant.
Antibiotics
Antibacterial drops and oral antibiotics can be used to treat eye infections that cause stinging and tearing.
Conjunctivitis or corneal abrasions may require antibiotics, in particular Levomycetin, a broad-spectrum antibiotic, can be used
Antihistamines
Eye drops, as well as oral antihistamines, can help relieve pain associated with the allergic component.
Drops
People with glaucoma can use medicated eye drops to reduce the build-up of intraocular pressure.
Corticosteroids
For more serious infections, such as optic neuritis or anterior uveitis, your doctor may prescribe corticosteroids.
Painkillers
If the pain and tearing are severe and interfere with your normal daily activities, your doctor may prescribe pain medication. It relieves pain until the underlying condition is cured.
Surgical intervention
Sometimes surgery is required to repair damage caused by a foreign body or burn. However, this is very rare. People with glaucoma may need laser treatment to improve drainage in the eyes.
In what cases should you consult a doctor?
A doctor is always consulted if the patient uses treatment for 1 week, but the discomfort does not go away. This may mean the presence of a disease that the person does not know about.
There are symptoms for which you should not self-medicate:
- severe swelling of the eyelids, which completely covers the cornea;
- lack of pupillary reflex to bright light;
- different pupil sizes;
- hemorrhage in the cornea, visible visually;
- severe pain in which the patient cannot open the eyelids;
- extensive suppuration, in which the antibiotic does not help; perhaps the microorganisms are resistant to the active substance;
- a sharp deterioration in health (rise in body temperature, weakness, fatigue, lethargy);
- immediate decrease in vision;
- burn, mechanical damage.
Providing first aid at home with further failure to see a doctor will lead to a deterioration in health, decreased visual acuity, and complications.
Learn more about migraine symptoms
- Vomiting, dizziness, nausea.
— Heightened perception of smells, sounds and light. In this state, everything that surrounds the patient seems too bright to him.
— Visual disturbances are also possible, as a result of which luminous objects appear in the field of vision.
— With a severe migraine, speech disturbances, tingling and even numbness of the limbs may be observed.
These signs are called aura. Migraine itself is a rather painful condition that is very debilitating. For this reason, after the pain disappears, weakness and a desire to sleep appear.
Try to be outdoors as much as possible, observe the world around you, and experience more positive emotions. You should not overuse analgesics, otherwise it will negatively affect other internal organs.
When the first signs of a headache appear, try to relax and sit in a comfortable position for a couple of minutes with your eyes closed. This will slightly reduce the inflammation of the optic nerve, and the headache will not be as intense.
The next migraine attack will be less painful if you drink 100 ml of aloe infusion with chicory juice during meals. Also, steam baths will be effective for relieving migraine attacks. Pour water and vinegar in equal proportions into a container and bring to a boil. As soon as steam begins to form, you need to tilt your head over the container and take at least 70 deep breaths.
If the headache is caused by overstrain or eye fatigue, touch your forehead to the cool glass of the window. This will help neutralize the electrostatic charge that accumulates on the skin and leads to painful sensations.
If the main cause of the described disorders is hypertension, then, in addition to headaches and watery eyes, a person may be bothered by: nausea, memory impairment and tinnitus. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, the condition can lead to a decrease in a person’s memory and intellectual abilities.
When affected by migraine, pain is localized in the temple area: on the right or left side. A person suffers from severe and throbbing pain, which can occur either regularly or periodically. During movement, turning and tilting the head, the sensations intensify. Along with this, symptoms may appear in the form of nausea and vomiting, and numbness of the fingers occurs.
Colds come in different forms. Most often it entails a cough, runny nose, and fever. If we know how to treat this unpleasant trinity, then what to do with such symptoms as tears and eye pain?
What bad habits are associated with eye pain?
Bad habits that lead to impaired vision include smoking, alcoholism, and drug addiction. All toxic substances negatively affect blood vessels and nerve tissue.
Smoking reduces the flow of oxygen through the lungs into the blood. This causes hypoxia of organs, including the eyes. Smoking reduces the elasticity of the vascular endothelium. It becomes brittle, so in addition to hypoxia, the risk of hemorrhage increases.
With daily alcohol intake, ethanol accumulates in the blood and various tissues. It is toxic and leads to dysfunction of the nervous tissue (optic nerve, visual center of the brain).
Drugs destroy all tissues with which they interact. If they are used for a long time, they accumulate in the brain and optic nerve. This reduces visual acuity. Drugs disrupt the conduction of nerve impulses from cones and rods through the optic nerve to the brain. Lack of pupillary reflex is common.
Bad habits include prolonged use of electronic gadgets. They create a strain on the eyes, as the gaze concentrates only on nearby objects.
This results in a missing, curved lens. The condition is called spasm of accommodation. It causes myopia, that is, decreased visual acuity for distant objects.
Diagnostic methods
It is difficult to make a diagnosis based only on an external examination, since most ophthalmological pathologies have a similar clinical picture; the true cause of discomfort can be identified after a thorough examination.
Main types of research:
- visometry – testing visual acuity;
- checking visual fields, peripheral vision;
- ophthalmoscopy – examination of the fundus, retina, optic nerves and blood vessels;
- measurement of intraocular pressure;
- pachymetry – assessment of corneal thickness;
- Ultrasound of the organs of vision;
- examination of the cornea using special staining solutions;
- keratotopography – allows you to evaluate the curvature and refraction of the cornea;
- determining the amount of tears produced;
- neuroradiography;
- studying the condition of the retina - medications are first instilled to dilate the pupil.
When diagnosing eye problems, a visual acuity test is required.
If eye diseases develop against the background of other pathologies, a clinical blood test, studies of the vascular, nervous system, and MRI of the brain are prescribed.
Eye diagnostics do not cause much discomfort, but when measuring intraocular pressure in children, if the patient has blepharospasm and photophobia, local anesthesia is used.
Why do my eyes hurt in the morning and before bed?
Many people experience eye pain in the morning. Normally, such a symptom should not exist. It is associated with the penetration of viruses and bacteria that disrupt the microflora of the mucous membrane.
In the morning, suppuration sticks the eyelashes together, so the person is unable to open his eyes. Pain may occur due to chronic lack of sleep.
If painful sensations appear in the evening, this may be due to the following reasons:
- prolonged wearing of contact lenses, especially if they are used incorrectly or have expired;
- eye strain during the day with prolonged use of a computer, TV, phone, tablet;
- daily presence in a cramped room where the eyes do not relax, since a person looks at nearby objects and not into the distance (this leads to a spasm of accommodation, increased load on the lens);
- development of various diseases of the eyeball and surrounding soft tissues;
- high blood pressure, hypertension;
- use of glasses and lenses with incorrectly selected diopters.
Some causes can lead to complications if they are not addressed in a timely manner. For example, when choosing the wrong diopters for an optical device, vision gradually decreases, causing increased stress on the lens, retina and optic nerve.
What to do if your head also hurts
What to do if your eyes hurt as if they are pressing? If you feel unpleasant pressure in the organ of vision, first of all, you need to identify the cause, which only a qualified doctor can do, who will conduct a comprehensive examination and make a diagnosis.
To rule out dangerous diseases, the specialist will measure intraocular pressure. If necessary, biomicroscopy will be performed.
This non-contact diagnostic method allows you to study the anterior and posterior parts of the eyeball. Biomicroscopy is painless and is performed using an ophthalmological microscope.
If the doctor identifies infectious diseases of the eyeballs, he will prescribe appropriate treatment with local medications.
Antibacterial drops and ointments will help cope with the problem and relieve unpleasant symptoms. If glaucoma is confirmed, serious intervention may be needed.
But there are also drops that can lower intraocular pressure:
- Azopt has many side effects, so only a doctor prescribes the dosage.
- Trusopt relieves symptoms of glaucoma and normalizes the production of intraocular moisture.
- Travatan is also used for preventive purposes.
- Timolol increases the outflow of eye fluid.
- Betoptik reduces intraocular pressure and lasts for 24 hours.
If the ophthalmologist does not find the cause of the unpleasant symptoms, he will refer you to other specialists for examination. Identified vegetative-vascular dystonia, diabetes mellitus, osteochondrosis and other pathologies require appropriate treatment with special medications and vitamin-mineral complexes.
If pressing pain is observed against the background of a flu-like state, then most likely it is associated with it. In this case, you need to focus all your efforts on recovery: drink hot drinks and rest, take medications prescribed by your doctor, and be sure to complete your treatment.